Wet grass underfoot, foggy windows, droplets on the walls of a damp basement - all this is the result of condensation of water vapor from the atmospheric air. Everyone has encountered this, but not everyone was interested in how to determine the dew point. Most often, this task has to be solved by architects, builders and designers, and people far from this area are hardly familiar with this concept.
How to determine dew point
The nature of the appearance of dew
Water condensation on various surfaces occurs as follows.
Atmospheric air is always more or less saturated with water vapor. As the temperature drops, water changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state. This occurs when the surrounding air comes into contact with cooler surfaces and heat loss occurs. This leads to the formation of water droplets. Morning dew is easily explained by the laws of physics
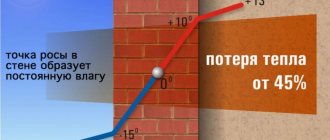
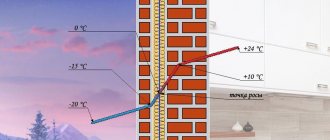
The temperature at which water vapor from the air changes its state of aggregation to liquid is called the dew point.
The higher the content of water vapor in the air (or other gas mixture), the higher the condensation temperature of water, or dew point. For example, at 100% relative humidity, the dew point is exactly the same as the air temperature. Conversely, the lower the relative humidity, the lower the dew point. This means that for condensation to form, the air must be cooled more.
Table for determining dew point
A more accessible method is to use a household psychrometer. This is a device that combines two alcohol thermometers. One of them has special moisture, the other is regular, dry.
As the moisture evaporates, the humidified thermometer cools. Lower humidity means lower temperatures. A humidity reading of 100% means that the readings of both thermometers are equal.
Knowing the humidity and temperature shown on the display, you can calculate the dew point from the table. They are used for quick calculations. The ambient temperature, humidity and the corresponding dew point value are indicated.
Do you know what the water temperature should be for bathing newborns? Study this article, there is nothing more valuable than the health of our children!
You can read everything about water aerobics and its benefits for weight loss right here, the most important, relevant and useful information!
Read all about treatment with living and dead water in the article: https://pro8odu.ru/vidy-vody/zhivaya-voda/zhivaya-i-mertvaya-voda-lechenie.html, take care of your health!
What is dew point
The dew point is the temperature at which condensation begins to form.
This term refers to the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor to the limit. When cooled below the critical point, drops or fog form on objects.
This phenomenon is based on the fact that the maximum steam production of a cubic meter of air varies depending on its temperature.
Examples (data given in grams):
- -5°C – 3.25.
- 0°C – 4.85.
- +10°C – 9.41.
- +22°С – 19.44.
- +28°С – 27.26.
The relative humidity value shows what the current set amount of water vapor is in relation to the maximum possible amount. For example, if this parameter is 34.5% at a temperature of +28°C, then the water vapor content in the air will be 27.26*0.345=9.4047 g/m3. From the above statement it follows that when the air is cooled to +10°C, the relative humidity will reach approximately 100%, i.e. this temperature is the dew point under given conditions. If the air cools further, too much water vapor is produced, some of which condenses.
Comfortable dew point values for humans
| Dew point, °C | Human perception | Relative humidity (at 32°С), % |
| more than 26 | extremely high perception, deadly for asthma patients | 65 and above |
| 24-26 | extremely uncomfortable condition | 62 |
| 21-23 | very humid and uncomfortable | 52-60 |
| 18-20 | unpleasant for most people | 44-52 |
| 16-17 | comfortable for most, but feels at the upper limit of humidity | 37-46 |
| 13-15 | comfortable | 38-41 |
| 10-12 | very comfortable | 31-37 |
| less than 10 | a little dry for some | 30 |
Scope of application of the concept
The transition of moisture into a liquid state significantly changes the living and working conditions of people and affects the functioning of structures and mechanisms. Therefore, in many areas, special attention must be paid to the location of vapor deposition.
Construction
The shell of most buildings is vapor permeable. The exception is metal workshops and garages. The relative humidity indoors is higher than outdoors, and water vapor penetrates the walls under partial pressure.
Buildings have vapor permeability, which depends on the type of building material.
If there are areas in their thickness with a saturation temperature or lower, condensation occurs, causing these effects:
- Reduced thermal resistance of the structure.
- Reducing the service life of building materials. When it gets colder, the water turns to ice and expands, causing internal damage.
- Development of mold and fungal colonies (when the surface is wet).
Building materials have different vapor permeability. The lowest is in heavy reinforced concrete (buildings with floors) - 0.03 mg/m*h*Pa, the highest in aerated concrete blocks - 0.23 (at a density of 400 kg/cubic m).
Agriculture
When the air temperature drops, moisture condenses on the shoots and leaves of plants. If repeated frequently, this leads to disease. Thus, knowledge of the condensation point allows you to plan preventive and therapeutic measures.
Moisture condenses on the leaves of plants.
On the other hand, in arid regions, condensation of atmospheric moisture can partially replace the irrigation system. Breeders are working to develop varieties that can absorb water in this way. Knowing the critical point will then help determine the required irrigation capacity if the weather forecast does not predict rain in the near future.
Conservation measures for some plants, such as grapes, are also planned taking this parameter into account. If it is high, it means there is a lot of moisture in the air and frost damage, including radiation damage, will be moderate.
If the dew point is low, cover the shoots or water the area.
Publications
- In Ukraine, the week will bring warm days
Natalya Didenko ForecasterWeather in Ukraine for tomorrow February 14 21:30
- Igor Kibalchich Forecaster
Overview of weather conditions in Ukraine for the week: February 14 – 20, 2022
Weather in Ukraine for tomorrow 13 February 13:25
- Igor Kibalchich Forecaster
Weather forecast in Ukraine for the weekend: February 12 – 13, 2022
Weather in Ukraine for tomorrow 11 February 14:24
- Igor Kibalchich Forecaster
How do cloud streets appear and where can they be observed?
Interesting facts about the weather February 10 18:44
- Igor Kibalchich Forecaster
Snow pellets. Its features and structure
Interesting facts about the weather February 8 10:16
Where should the dew point be?
The ideal location for the dew point in a wall is the insulation on the outside of the wall. The thickness of the insulation on the wall should be such that during the coldest period of time, condensation does not flow into the wall itself, and if it does flow, it does not remain there for a long time.
Dew point isolated
The destructive effect of dew point in the body of a load-bearing wall can be seen in the following article.
Walls based on porous materials, such as foam blocks and sandwich blocks, brick and similar materials, require a higher layer of thermal insulation, since they absorb and accumulate moisture. Therefore, even a short-term (a few days) dew point in a porous wall can have a detrimental effect on the internal integrity. Thus, so-called warm masonry materials can only be effective in certain regions where winters are less frosty.
However, if it is predicted that the dew point will periodically move deeper into the wall of the house, or if this is likely, this fact should be taken into account when choosing masonry materials. In such cases, high-density masonry materials that can withstand several freeze-thaw cycles without damage are well suited. With a high frost resistance coefficient. Such frost-resistant materials include brick and foam concrete.
Frost resistance indices of the most commonly used wall materials
Vapor permeability of building materials
We present in the table below the vapor permeability coefficients of building materials
To ensure that the microclimate in the house is normal, when constructing wall “pies”, both the thickness of each layer and its water absorption and vapor permeability properties are taken into account. The layers of the cake should be arranged in such a way and have such thicknesses that vapor permeability increases from the inside to the outside. This “rule of vapor permeability” is best observed. Otherwise, there are two options:
- Poor ventilation and high humidity in the house means that you can get the dew point in the wrong place, and as a result, dampness and mold and fungus on the walls, and possible destruction of the walls.
- There is little humidity inside the house, and ventilation is organized - there will be no harmful consequences for the microclimate from violating the rule, except for the harmful effect of moisture on the wall material.
All this is true, the dew point must be taken into account, since it is a risk factor. But the degree of this risk depends on the real, actual amount of water condensed in the wall and on the properties of the wall material. The less water absorption a wall material has, that is, the less moisture it absorbs, the less it is at risk of destruction when this moisture freezes and expands in the pores. Brick Khrushchev buildings have been standing for more than 60 years, but they don’t even think about collapsing, although according to thermal engineering calculations they have condensation in the walls. Ceramic brick has good frost resistance characteristics; the frost ends and the brick releases moisture into the air. But we must remember that the walls of the Khrushchev buildings are half a meter thick.
How to calculate the dew point in a wall with insulation
It is impossible to accurately calculate one place in the wall where condensation will form. Because the dew point depends on several parameters and is a variable value. You can only calculate a certain distance in the thickness of the wall where liquid will form under different temperature changes outside the house.
For example, if the indoor temperature is stable and the temperature outside becomes colder, the dew point will move along the thickness of the wall, closer to the room.
This formula can be used to calculate the dew point as accurately as possible for both homogeneous and multi-layer walls.
Calculating the dew point for any multi-layer wall is quite simple; the following data is required:
- Dew point at relative humidity in your area (table below)
- External temperature
- individual thickness of each wall layer
- internal temperature
- Thermal conductivity coefficient of the material from which the walls of the house are made
To determine in which part of the designed wall the dew point and condensation will be located, you need to know two values.
- The dew point temperature in our region, as well as the humidity and temperature inside the building of interest to us. We can see this in the table above. Let's call this indicator Tp (dew point).2
- The air temperature that will occur at the boundary of two layers of the wall at the values of interest to us. Let's call this number Tc (the point between the layers).
If the difference between the above values is positive, the dew point is inside the insulation, if the value is negative, the dew point will accumulate liquid inside the wall or house.
In other words, if the temperature at the interface between the insulation and the wall is higher with a positive sign than the dew point temperature from the table, condensation will form in the insulation.
Let's take the following conditions as an example:
The dew point temperature in a region with 60% humidity and a room temperature of 21ᵒC according to the table will be 12.9ᵒC. The air temperature at the interface between the thermal insulation and the wall is 15 ᵒC.
The difference between these values is 15 ᵒC – 12.9 ᵒC = +2.1
If the difference between the above values is positive, as in our case, the dew point is in the insulation, if the value is negative, the dew point will collect liquid inside the wall or house.
In our case, the temperature of liquid vapor release occurs before the saturated air reaches the main wall. And condensation will settle in the insulation, and not in the load-bearing wall of the house or inside the house.
This raises the question: if we take the dew point temperature at a given humidity level from a given table, how do we calculate the temperature between the layers of the wall?
The temperature at the boundary between two wall layers is relatively easy to calculate using the following formula:
Tc (temperature between wall layers) = (t2 – t1)x (S1x0.01/k) / (S1x0.01/k), where:
t2 – internal air temperature
t1 – external temperature
S1 – wall material thickness
k – thermal coefficient of the wall material
Simple example:
Let's take as an example a region where the dew point is 12.9 ᵒC in a region with 60% humidity, the indoor temperature is 21 ᵒC, and the outdoor temperature is 12 ᵒC below zero.
Now we need to calculate for these conditions what the temperature will be between a standard 38 cm thick one-and-a-half brick wall and a 10 cm thick external foam insulation. Subtract the dew point temperature from the table.
To do this, we will use the formula given above.
Tc (temperature between wall layers) = (t2 – t1)x (S1x0.01/k1) / (S2x0.01/k2)
According to the convention:
t2 = +21ᵒC (indoor air temperature)
t1 = -13 ᵒC (outside air temperature)
S1 = 38 cm (wall thickness)
K1 = 0.6 (thermal resistance coefficient of brick)
S2 = 10 cm (foam insulation thickness)
K2 = 0.04 (foam thermal resistance coefficient)
Calculation of the temperature between the brick wall and the foam insulation, under the climatic conditions we have chosen, will look like this:
( +21 – (-13ᵒC))x(38×0.01/0.6) / (10×0.01/0.04) = 9.52
According to our calculations, the temperature between a 10 cm thick foam core and a 38 cm thick brick wall, when the outside temperature is -13 degrees Celsius and the temperature inside the house is +21 degrees Celsius, is 9.52 degrees Celsius.
Therefore, if we subtract 12.9 degrees Celsius from the temperature between the insulation and the wall, which is 9.52 degrees Celsius, we get 9.52-12.9 = -3.38.
The calculated dew point is in the wall.
As you can see, the dew point is negative, i.e. the brick wall will reach a state of condensation and moisture will accumulate in it.
The above dew point calculation is more accurate with an error of up to 0.5 degrees Celsius, unlike some online calculators and other devices that do not take into account different material structures.
Education mechanism
So what happens when the temperature drops at night or early in the morning? That is, what is the dew point according to physics, and what processes occur when it is reached? Extremely interesting.
A thin layer of gas of the same temperature forms near the surface of the coldest objects. Its thickness may be tiny, but it is in it that condensation forms and falls onto the surface of the object. On the street, this can primarily be stones, metal structures, or grass. This happens if the air temperature is above the dew point. In winter, everything happens a little differently. This phenomenon can be observed when breathing in the cold, when steam comes out of the mouth. Instantly cooling, water in a gaseous state turns into tiny droplets. Something similar happens high in the atmosphere when clouds form.
Dew point calculation online calculator
There are many programs on the Internet that can be used to calculate the approximate position of the dew point on the wall. The program calculates the dew point based on a number of criteria that must be entered manually. It includes information about the material from which the wall will be built, the number and thickness of layers of the wall, air temperature inside and outside the building and humidity. The online calculator is easy to use for calculations. Along with digital calculations, you can see charts and graphs of dew point movement depending on changes in air temperature. However, the calculation results of many calculators vary, and the accuracy of the calculations is unknown.
Online dew point calculator
Dew point temperature calculation
It is possible and necessary to calculate the dew point; for this it is not necessary to study the science of heating engineering. It can be considered from calculators from the Internet, quite decent, working on the basis of thermal formulas and a database of material characteristics. It is better, of course, to entrust the final calculation to professionals.
Here is a table with the ability to calculate the dew point temperature.
Breathing walls
Regarding the issue of wall breathing. Perhaps this question relates not so much to construction physics as to ideology? There were once slit windows, they had wonderful vapor permeability, and the walls breathed with might and main. At the same time, you didn’t have to pay a good part of your salary for heating. Today the situation is different, and has been for a long time - the issue of energy saving for a private home is acute. Well-established phraseological units of the type - energy-saving house, energy-efficient building material - already speak volumes. Perhaps the walls of the house should keep the heat in, and breathing should be ensured by well-organized ventilation? After all, marketers know how to tell fairy tales, and about the breathing of houses that have grown gills thanks to innovative building materials... too.
If you don't take into account the dew point
In the construction industry, ignoring the rules can lead to undesirable consequences. Metal, brick, concrete, wood and other materials will have a shorter lifespan. The formation of condensation in the area of polymer-density materials when installed as thermal insulation is unacceptable and leads to the following problems
- Structures fail prematurely, leading to premature failure.
- The surface of the material swells;
- Condensation is necessary on surfaces with temperatures below the dew point;
- Large areas of finishing material peel off;
- Harmful fungi and mold develop on walls, causing illness;
The importance of determining dew point
If you do not take into account the position of the dew point in the wall, a series of negative events will follow.
The insulation material quickly becomes unusable, and the service life of the wall material itself is reduced. Due to regular wetting, the finish will not hold up: the wallpaper gradually peels off, the plaster crumbles, and the paint peels off. Due to excess humidity in the room, mold, mildew and other pathogenic microorganisms develop in a short period of time on walls, ventilation systems, ceilings and other surfaces.
Ignoring the physical nature of condensation can lead to unsanitary conditions in the room
How to move the dew point in a wall
If, after performing all the calculations, you are not satisfied with the position of the dew point, you should consider moving it. This can be done as follows:
- improve the microclimate in the room - install forced ventilation, additionally heat the air.
- increase the insulation layer on the outside;
- remove the thermal insulation layer from the inside and move it to the outside;
- Use a material with high water vapor permeability;
The appropriate option should be chosen depending on the climatic conditions of the area, the design features of the house, financial capabilities and the building materials used.
Ignoring such a phenomenon as condensation in a wall “oven” can be very expensive. The minimum is an unpleasant smell in the room and constant dampness. The maximum is large colonies of mold, damaging the interior decoration of the walls, destroying the insulation and the health of the residents. Therefore, calculating the dew point is very important if you want to build reliable and dry walls in your home.
Why do windows cry?
There are specific recommendations for the microclimate in a residential area. This is humidity -40-50% and temperature +18-23C . Maintaining these parameters minimizes the possibility of condensation forming on the glass surface.
Its appearance is also associated with human life (it also releases moisture!). That is, there should be as many people in the room as sanitary standards allow.
High humidity can also be associated with improper air exchange. Here, too, there are standards: at least 3 “cubes” per “square” of area in one hour.
For kitchens, these requirements are even stricter: from 6 to 9 “cubes” per hour, depending on the type of stove ( 9 cubic m/hour for a gas stove ). Therefore, everything depends on the quality of ventilation.
There is a contradictory situation; The house was completely renovated, the old windows were replaced with double-glazed windows, and mold began to appear in the rooms. What is this connected with?
The fact is that during a complete reconstruction, the heating is changed, modern boilers are installed instead of old gas water heaters, and the windows are insulated. By and large, there are fewer opportunities for natural ventilation.
If previously moisture from the room could escape through loose window slits, through the hood of an old gas water heater, now there is no such possibility.
The operational characteristics of a double-glazed window (the “K” coefficient, in particular) are important, but secondary.
About the dew point in plastic windows
When it comes to the dew point for plastic windows, many people imagine a certain, secret place. In reality, as we have already seen, it is impossible to see the dew point. Let's repeat: the dew point is the temperature at which water vapor in the air becomes saturated and condenses after cooling to it. There are special tables that allow you to calculate the dew point for a certain relative humidity and a certain temperature. One such table is shown below.
Dew point for relative humidity
Note. Let's assume that the air humidity is 50% and the temperature is +21 degrees. Under these conditions, the dew point is +10.2. What does it mean? If the surface temperature in the apartment drops to +10.2 degrees, condensation will form on it. As a rule, the coldest surfaces in an apartment are plastic windows, so this is where excess moisture most often gets in.
People often encounter condensation on double-glazed windows. Based on what was said above, condensation can be dealt with in two ways - increasing the temperature of the windows and reducing the humidity in the apartment. A comfortable level of humidity can be achieved by ensuring normal air exchange. Any excess moisture - from laundry, a boiling pan, etc. – Any excess moisture – from washing, pots, etc. – must go away and not accumulate in the room. First of all, the apartment should be regularly ventilated. The frequency of ventilation is determined individually, but we recommend doing this for at least 10 minutes twice a day. Also, do not forget to use special ventilation valves.
Examples
Another simple example can be considered when something is brought into a warm room from the cold. The air above it cools, becomes saturated with water vapor, and water droplets condense on things.
Subsequently, the item warms up to the room temperature and the condensation evaporates. By the way, this phenomenon determines the recommendation not to immediately plug in household electrical appliances brought in from the cold.
Another, no less familiar example is fogging of glass in the house. Many people have windows that “cry” in winter; condensation falls on them. It is necessary to understand that this phenomenon is largely influenced by two factors - humidity and temperature.
Therefore, if you have a normal double-glazed window and proper insulation, but there is condensation, it means that not everything is in order with humidity; Possibly poor ventilation or exhaust.
One of the most interesting physical phenomena is a change in the state of aggregation of water, in particular the boiling of water. Read more detailed information in the article The boiling point of water is really very interesting. We are sure that you will find a lot of new things for yourself here.
You can read everything about breaststroke swimming in this article; it’s time to take care of your health right now!
Harmless dew point location
There are exceptions that, when a dew point occurs, do not harm walls, windows and other materials at all. If, for example, condensation forms on the outside of a wall on thermal insulation, this will not affect the internal structure and microclimate.
This is the most favorable position for the dew point, since in cold weather drops of moisture will not penetrate the wall. The dew point can also be located on the inside of the wall itself if it is close to the outside surface to keep the interior of the structure dry.
In all other cases, side effects may occur. To avoid such consequences, under no circumstances should you insulate walls from the inside. Such isolation will lead to the following consequences:
- Rotting walls from the inside. In very bad cases and at very high dew points, internal wall rot can occur. This leads to the destruction of the building material itself. As a result, the wall may simply collapse.
- Moisture will begin to accumulate at the boundary between the wall insulation and its covering. As a result, mold grows right inside the wall and cannot be eliminated.
- Drops of moisture will gradually move towards the thermal insulation. If condensation previously appeared only in the center, then it will gradually move towards the thermal insulation, forming fungal compounds.
To avoid this condition, you must check this value regularly. If dangerous values occur, immediate action must be taken. However, you should know from the very beginning that thermal insulation has no place on the interior walls of the house.
Calculation of dew index
Correct calculation of the dew point in a specific area is important not only for determining the state of human health. It is necessary when carrying out construction and installation work, since the strength of materials, structures, and their ability to withstand corrosive destructive processes depends on the conditions for the formation of condensate.
Calculating the dew point is of great importance when choosing finishing materials for premises. The material can successfully withstand external moisture in the form of precipitation or simply exposure to water, but the formation of condensation inside it can have a quickly destructive effect.
Correct determination of dew point is important in aviation. Condensation formed at a certain flight altitude can lead to icing of the aircraft body with multiple negative consequences. Icing can especially hinder a successful flight during takeoff and landing, so treating the hull with anti-icing agents is an important part of preparing for a flight.
In forestry, the dew point is calculated when carrying out fire prevention measures. In agricultural work, determining the seasonal dew point is especially necessary during sowing. Through breeding methods, crop varieties are developed that are capable of forming condensate even in the absence of precipitation for a long time.
Methods for determining dew point
You can easily measure the dew point yourself. There are several methods for calculating it. It is important to choose the one that is most convenient and practical. The main thing is to understand that after calculation you can only get an approximate value, since it is impossible to determine exact data for some indicators. Let's look at each method separately.
According to a special formula
This formula is one of the most accurate ways to determine dew point. The problem, however, is that you need to know the other values in order to use them to calculate the final value. The formula looks like this:
A, b – constants (17.27; 237.7);
T – air temperature;
Rh – relative air humidity.
The error of this calculation is one of the smallest - it is only 0.5 degrees Celsius. However, it is necessary to know the temperature and relative humidity, which is not always possible.
Using special calculators
Currently, there are various online services with which you can easily calculate the dew point. In these special mini-programs, all fixed data and approximate values are already entered, which are also necessary for more accurate calculations. All you have to do is enter the required values and see the result.
The information entered usually includes the material from which the value is calculated and its thickness. However, this information must be entered for both internal and external parties. The program will then output a table with the following data:
- Minimum or maximum dew point.
- Moisture content in kg per cubic meter;
Based on this data, it will be easy to understand what condition the walls of the room are in and what needs to be applied. However, there is no guarantee that such calculators will provide accurate results, so caution should be used.
In addition, in some cases the following data is required:
- Average air temperature. The approximate outdoor and indoor temperatures should be indicated. These indicators also affect the final result of the calculation.
- Type of number. The humidity level, for example, in the bathroom should be very high, while in the living room it should not exceed 70%.
- Geographical position. The climate in different regions of the country is very different. Based on this, we can conclude that the normal dew point for the subjects is not the same. It should be borne in mind that somewhere outside the humidity level will be even higher.
- Layers of material. This line indicates what is behind the main supporting material. This is important because if there is no other room behind the wall, the dew point values will be very different.
Advanced programs can even be downloaded onto devices. They have a much higher priority than traditional online calculators because they already use much more data to produce a result, which means the dew point will be determined more accurately. In addition, immediately after the final calculation, a special graph will appear on the screen, which is a schematic representation of the dew point in the wall.
The influence of dew point on human condition and comfort
Now let's briefly look at how the dew point value affects a person's degree of comfort. When the air temperature is high, the human body uses the evaporation of sweat to cool itself. This feature is very effective, but not in all cases. The rate at which sweat evaporates depends on how much moisture is in the air and how much moisture it can hold at a given pressure. If the air is already saturated with moisture (at 100% relative humidity), sweat will no longer evaporate. The body's thermoregulation will cause sweating to maintain normal body temperature, even if the rate at which sweat is produced exceeds the rate of evaporation, so on humid, hot days it is possible to become covered in sweat even without doing any physical activity. In this case, the dew point will be as close as possible to the actual temperature and usually if it is above +16...+18 °C, then the person feels stuffiness, difficulty with physical activity, sometimes headaches and other feelings of discomfort. The maximum recorded dew point on the planet under natural conditions was +35 °C. This value was recorded on July 8, 2003 in the city of Dhahran, Saudi Arabia. The actual air temperature that day was +42.2 °C. Taking into account a weak wind of 1 m/s, the effective temperature (the virtual temperature that a person dressed for the season would feel) reached +115 °C!
Low dew point values (mostly below -5 °C) also cause discomfort, as this means extremely low air humidity. Dry air can cause cracking of the skin and drying out of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and respiratory tract. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain the room temperature within +19...+24 °C and relative humidity 20 - 60%, which is equivalent to a dew point of approximately +4.0 to +16 °C). Interestingly, people living in humid tropical and subtropical climates acclimatize to higher dew points. For example, a resident of Singapore or Miami may have a higher threshold for discomfort than a resident of a city in a temperate climate (Kyiv or Warsaw). People accustomed to temperate climates often begin to feel uncomfortable when the dew point exceeds 15 °C, while others may find dew points as comfortable as 18 °C. Thermal comfort depends not only on the physical characteristics of the environment, but also on psychological factors.
How to use the obtained result?
As you already understand, good thermal insulation is such thermal insulation (now we are talking about external thermal insulation of the facade) in which the dew point is in the middle of the thermal insulation. This parameter depends on many factors, for example, the thermal insulation properties of the insulating material decrease with increasing water content, i.e. A material with low water absorption should be used as an insulator.
How to calculate the required insulation thickness so that the dew point is inside the insulation? The properties of the insulation and walls are important here: the thicker the insulation, the faster the cold passes. From this we can conclude that a porous material will have better thermal insulation properties, and a wall made of dense concrete will require more insulation than a wall made of cinder blocks.
Relationship between dew point and construction
The dew point value directly depends on the relative humidity and temperature outside and inside the building. For example, if the temperature outside is 8˚C, the temperature inside the house is 22˚C, and the relative humidity is 45%, condensation will form on the outside wall.
There are other factors that influence dew point, such as regional climate conditions, insulation of the entire building envelope, quality and type of heating system, length of occupancy (permanent or temporary, as in a house or garage), and ventilation.
It is very important for builders to know the dew point in order to accurately calculate the location of condensation on the walls and determine the required insulation thickness. Knowing this, you can minimize heat loss during the cold season.
The location of the dew point may vary depending on the thickness of the wall. It depends on the thickness and type of materials of the wall itself and insulation, the temperature and humidity of the air inside and outside the building.
Each material used for the construction and decoration of walls, with the exception of metal, has its own degree of water vapor permeability. From a physical point of view, this is an indicator of the amount of water vapor that a material can pass through itself in a certain time.
Vapor permeability is one of the decisive factors when choosing thermal insulation materials, and is also important when analyzing the condition of external walls.
During periods of low temperatures, water vapor under pressure in the room will tend to escape through all layers of the outer walls. The lower the vapor permeability coefficient of the insulation, the smaller the layer that needs to be laid. Its coefficient should increase from the inside to the outside, as does thermal conductivity.
If all calculations are performed correctly, the dew point will be in the thermal insulation layer of the wall, closer to the outer surface. In this case, the water vapor will turn into condensation and will only dampen the wall. This is how water vapor accumulates in winter, and in summer it is necessary to create conditions for the evaporation of accumulated moisture.
The main condition for good insulation is the creation of conditions for the evaporation of accumulated moisture. To do this, it is necessary to make special calculations and select finishing materials.
Less suitable is the location of the dew point in the load-bearing wall of the house. This occurs if the wrong type and thickness of insulation is selected.
In the worst case, condensation is on the inside of the wall. This situation is possible if the wall is not insulated at all or if the insulation is located indoors. In the latter case, mold may form under the insulation, and the wet insulation will not retain heat at all.
Damage to dew point for house walls
We figured out that the dew point can be located in three different parts of the wall:
- in external wall insulation
- in the wall, closer to the outside
- in the wall, closer to the inside
In each of the listed places, the dew point will manifest itself differently. If in one place it is harmless, then inside the house or in the wall it will have certain destructive consequences on the integrity of the wall. Below, we will analyze the behavior of the dew point in each of the listed places.
Dew point in external insulation
This is the most harmless dew point for your home. In this case:
- When the dew point occurs, condensation forms directly in the insulation itself.
- The insulation is not hygroscopic, therefore moisture is not retained in the wall structure and evaporates when the air temperature changes.
- Due to the vapor barrier properties of the insulation, the moisture that is formed when condensation evaporates goes outside and does not interact with the wall of the house.
- The walls of the house are dry throughout the year, both from the outside and from the inside
- The walls retain their strength and integrity for many decades
insulation on the outside
Dew point in the wall of the house, closer to the outside
- The behavior of a wall largely depends on the material from which it is made. Walls made of dense and heavy building materials such as brick, expanded clay concrete, stone, and wood can withstand dew point better. Because they are less susceptible to destruction and have a higher frost resistance coefficient.
- The walls of houses built from porous materials that absorb moisture well and allow steam to pass through. Such as foam blocks, gas blocks and similar materials, the effect of the dew point should be minimally short.
destruction of a wall due to moisture
- When condensation occurs inside the wall, the wall material becomes saturated with liquid. When the air temperature subsequently drops below zero, the accumulated liquid freezes and increases in volume. An increase in the volume of liquid destroys any wall material from the inside. This leads to the formation of both small and large cracks in the wall structure. The walls crumble and finally lose their strength.
- If the wall, in which the dew point is inside and is insulated from the outside, then the insulation will not prevent the accumulated moisture from escaping outside. Therefore, all the liquid will accumulate on the surface, between the insulation and the wall. This entails the formation of mold and mildew, with all the ensuing consequences that are harmful both to the building and to human health.
- If the wall of the house is not insulated from the outside, then the liquid will come out as the air temperature rises, but this will not protect the wall from internal destruction after the water freezes. We can observe similar evaporation of liquid from a damp wall in the form of a white coating on brick walls.
release of moisture from a brick wall in the form of a white coating
Dew point in the wall of the house, closer to the inner surface
It occurs when steam passes through the middle of the wall thickness and condensation begins to form closer to the surface of the wall, which is located inside the house.
Consequences of dew point for the interior decoration of the house:
- The masonry, saturated with moisture, begins to release liquid in the form of water droplets on the inner wall and into the house.
- A wet wall surface destroys the interior decoration of the room: putty, wallpaper and other finishing materials.
- Mold and mildew form on the walls and in the corners, which will be very difficult to get rid of.
- An unpleasant, shabby smell of decomposition appears in the house, which is harmful to health.
- The overall heat temperature in the house decreases.
mold on the wall inside the house
The most destructive and harmful consequences for the house is when the dew point is closer to the inner surface of the wall.
Dew point is an important parameter that should be taken into account when designing and constructing walls, roofs and the construction of the entire house. Failure to comply with it can lead to irreversible and critical consequences for the entire building.
Consequences of incorrect calculations
When choosing insulation materials, it is important to remember that one of the most effective ways to protect external walls from dampness is to properly install layers of insulation.
High-quality thermal insulation will help significantly reduce heat loss and make your home more comfortable, as well as extend the life of your walls.
A thick layer that does not allow water vapor to pass through and a porous layer that allows moisture to pass out should be located on the inside of the load-bearing wall.
It is also necessary to create conditions for ventilation in the condensation zone. This way, the condensate will evaporate freely.
A properly insulated exterior wall will help reduce heat loss during the heating season from 45 to 95% and create comfort in the house.
If the thermal insulation is chosen incorrectly, moisture will gradually accumulate in it, reducing the thermal resistance of the wall. Therefore, in the second or maximum in the fifth heating season, heating costs will increase, if we are talking about a private house, the apartment will simply be much colder in winter.
Professional insulation is a long and expensive process. Today there are many insulating materials. Do not try to save on them, as cheap materials will become unusable after just a few heating seasons.
There are several consequences of incorrect calculations, but some of them can have a negative impact on your quality of life. The main consequences are constantly damp walls, mildew, mold, mildew and germs on the walls, which lead to many chronic diseases.
Constantly damp walls become a breeding ground for fungi and mold, and their spores are transmitted by airborne droplets and cause diseases.
Because wet rooms are difficult to heat, their comfort levels are reduced. High humidity in such walls can cause respiratory diseases.
Another unpleasant consequence of a miscalculation is the destruction of finishing materials - tiles crumble, bricks on the outer wall crumble, and the surface of the inner wall begins to swell.
Undried condensation is the main reason that the outer wall is susceptible to weathering and peeling of finishing materials.
To remedy this situation, the condition of the walls and insulation must be analyzed by a professional. With the correct calculations, you can correct all mistakes and create a comfortable and warm environment in your home.
The principles and formulas of thermal engineering calculations for the correct design of a house will be discussed in the next article, which we strongly recommend that you read.
Thermal insulation material
To protect buildings from heat loss, high humidity and point shifts, it is insulated with thermal insulation materials. In winter, insulation helps reduce heating costs, and in summer it keeps the room cool. Each product has its own areas of application and properties. Eco-friendly and easy-to-install materials are used in construction. The required type of insulation is selected for certain conditions.
With proper insulation from the outside, the dew point will be located inside the insulation
According to their form, materials are divided into:
- roll;
- leafy;
- bulk;
- single.
By structure:
- fiber;
- cells;
- grainy.
Raw materials can be organic, inorganic and mixed.
Main characteristics of insulating materials:
- thermal conductivity;
- moisture absorption;
- porosity;
- humidity;
- density;
- vapor permeability;
- specific heat;
- strength, etc.
Penoplex
Penoplex is also called expanded polystyrene. Unlike foam polystyrene, the material has a higher density and is less subject to mechanical damage. It almost does not conduct steam due to its low vapor permeability coefficient. However, it belongs to group IV of flammability (it ignites quickly).
Penoplex is recommended for external wall insulation
Penoplex of the “comfort” category is produced for insulating walls, terraces, loggias, and balconies. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 9 times less than that of mineral wool. The material requires little time to heat the room after cooling due to its low heat capacity. The operating temperature range is -70…+70℃. Penoplex of this type does not have the best sound insulation, has the lowest density and lower tensile strength compared to other materials.
Penoplex for walls is suitable only if an effective ventilation system is installed in the room to maintain comfortable humidity.
A 2 cm wide layer of polystyrene foam retains heat almost as well as 40 cm of mineral wool or 37 cm of brickwork.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam is a material characterized by lightness and buoyancy. It is resistant to fire, but when exposed to fire it begins to melt. The material is easy to process and is not subject to infection by fungi and mold.
Polystyrene foam is obtained from foamed polymer raw materials: polystyrene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane. It consists of small identical balls that are fastened together. High-density rigid foam is used for insulation. The panels are easy to connect using rubber or epoxy adhesive.
The temperature range is not important for polystyrene foam, but the material is subject to mechanical damage.
Slabs 5 and 10 cm thick are used as thermal insulation. But, despite the structure, the material is sound-permeable.
Polystyrene foam is one of the most common materials for home insulation.
Mineral wool
Thermal insulation material consists of compressed fibers. Glass, basalt and slag are used as raw materials. The starting material is melted and spun into fibers. Their length is 2-60 mm. The air pores of the mats fill approximately 95% of the total volume. The product is easy to produce and has a low cost.
Mineral wool has many qualities suitable for home insulation.
Due to its porosity, cotton wool allows air and steam to pass through, maintaining air exchange. At the same time, it does not burn and is resistant to moisture, has good sound insulation. But the material has 2 drawbacks:
- contains phenol;
- Flying pieces of cotton wool, falling on human skin, cause itching.
How to change the location of a point
If errors in calculations are made during the construction of a new house, this can lead to the permanent formation of mold on cold surfaces and further damage to the entire structure.
A problem in a house that has been in use for a long time can be solved by changing the main influencing factors. The following measures are provided for this:
- Organize a reliable ventilation system. If a finished building (guest house, bathhouse or cottage) is used temporarily, for example in the summer, you may notice an increase in humidity levels in all rooms. The best solution is to organize a ventilation system that provides good air exchange at any time of the year.
- Additional heating. If condensation persists on the ceiling, it means that the heating of the room is not sufficient to reduce the humidity level. The best solution is to additionally use portable heaters or household dehumidifiers.
- Make the building thermally insulated. You can move the point towards the street using façade insulation. Why is it useful to insulate walls outside? In this case, the condensation point will be between the insulator and the wall, so that even in the event of significant changes in climatic conditions, surface moisture can be prevented.
When determining the location of a point in the wall, many factors must be taken into account: climatic conditions, wind strength, sun angle, temperature, humidity conditions inside the building, floor thickness and materials.
The minimum level of humidity is specific to each type of material; the main thing is not to allow it to increase significantly. In addition, each homeowner can determine the temperature of the condensation on the surface. If thermal insulation technology is used, you can be sure of reliable protection and durability of the walls.
Condensation on windows
Very often, manufacturers of modern windows have to accept complaints that their customers' windows are fogging up. The formation of condensation on windows is not only aesthetically unsightly, but also threatens the wooden structures with waterlogging and, as a result, the formation of mold. Let's look at the possible causes of condensation on windows.
Condensation is a liquid that has passed the dew point and fallen in the form of droplets on the window.
Well, if this happened on windows, then only the windows and their manufacturers are to blame. Logically this is correct, but if there is no water in the window itself and it cannot release it, where does the condensation come from?
Factors influencing heat loss
Thermal processes correlate well with electrical processes: temperature difference acts as voltage, heat flow can be thought of as current - there is no need to create a special term for resistance. The concept of least resistance, called thermal bridges in heating engineering, is also completely correct.
If you consider any material in cross section, it is quite easy to determine the path of heat flow at both the micro and macro levels. As the first model, we will take a concrete wall in which, due to technological necessity, the through fastenings are made with steel rods of arbitrary cross-section. Steel conducts heat slightly better than concrete, so three main heat flows can be distinguished
- From steel bars to concrete
- Through the thickness of concrete
- Through the steel bars
Heat loss through thermal bridges in concrete
The most interesting model is the final heat flow. Because the steel core heats up faster, the temperature difference between the two materials will occur closer to the outside of the wall. Thus, the steel not only “pumps” heat out itself, but also increases the thermal conductivity of the adjacent concrete masses.
Thermal processes in porous media proceed according to a similar pattern. Almost all building materials consist of an extensive network of solid materials, between which there is a space filled with air. Therefore, a solid, dense material is the main conductor of heat, but due to its complex structure, the path along which heat moves is larger than its cross-sectional area. Therefore, the second factor determining thermal resistance is the heterogeneity of each layer and the entire building envelope.
Reducing heat loss and shifting the dew point in the thermal insulation of external walls
When is internal insulation possible?
Table for determining dew point depending on air temperature and humidity.
It is not always possible to carry out insulation from the inside, since if done incorrectly, dew will constantly fall out from the inside, rendering all building materials completely unusable, creating an uncomfortable microclimate inside. Let's consider when it is not recommended to insulate from the inside, and what it depends on.
Is it possible or not to insulate from the inside? The solution to this issue largely depends on what will happen to the structure after the work is completed. If the wall remains dry all year round, then work on its thermal insulation from the inside of the room can be carried out, and in many cases it is even necessary. But if it constantly gets wet every winter, then it is absolutely impossible to carry out thermal insulation. Insulation is allowed only if the structure is dry and it gets wet extremely rarely, for example, once every ten years. But even in this case, work must be carried out very carefully, since otherwise such a phenomenon as the dew point will be observed constantly.
Let's consider what determines the occurrence of the dew point, how to find out whether or not it is possible to insulate the walls of a house from the inside.
As already said, the dew point arises due to factors such as:
- humidity;
- indoor temperature.
Article on the topic: Wallpaper for painting: photos in the interior, which is better, pros and cons, how to paint it yourself, reviews, smooth stencils, structural, fiberglass, video
The humidity in the room depends on the presence of ventilation (hood, supply ventilation, air conditioners, etc.) and on the mode of residence, temporary or permanent. The temperature inside is affected by how well the insulation was installed and the level of thermal insulation of all other structures of the house, including windows, doors, and roof.
From this we can conclude that the consequences for internal insulation depend on:
- temperature of condensation moisture, that is, from the dew point;
- from the position of this point to the thermal insulation and after it.
How to determine where the dew point is? This value depends on many parameters, among which it is necessary to highlight:
- thickness, wall material;
- average indoor temperature;
- average outside temperature (influenced by climate zone, average weather conditions throughout the year);
- indoor humidity;
- the level of humidity outside, which depends not only on the climate, but also on the operating conditions of the house.
Let's put all the factors together
Graph of thermal resistance and dew point shift when using insulation.
Now we can collect all the factors that influence where the dew point will be located:
- mode of residence and operation of the house;
- availability of ventilation and its type;
- quality of the heating system;
- quality of work when insulating with foam plastic or other material all structures of the house, including the roof, doors, windows;
- thickness of individual layers of the wall;
- temperature indoors, outdoors;
- humidity indoors, outdoors;
- climate zone;
- operating mode, i.e. what is outside: street, garden, other room, attached garage, greenhouse.
Insulation from the inside is possible, based on all the above factors, in the following cases:
- when permanently residing in the house;
- when installing ventilation in accordance with all standards for a particular room;
- during normal operation of the heating system;
- with insulation, which is laid for all structures of the house that require thermal insulation;
- if the wall is dry, it has the required thickness. According to the standards, when insulating with polystyrene foam, mineral wool and other materials, the thickness of such a layer should not be more than 50 mm.
Related article: What spider web tulle looks like on windows
In other cases, insulation cannot be performed from the inside. As practice shows, in 90% of cases the walls of a house can only be thermally insulated from the outside, since it is quite difficult to provide all the conditions, and often not entirely feasible.
Useful tips
Ventilation must be ensured in such a way that the relative humidity in the home does not exceed normal values (40%-60%). This requires an air flow from outside. In houses and apartments with natural ventilation, it should enter through the cracks in the windows.
But when you replace windows with sealed vinyl windows, there is no air flow. Ventilation does not work, even if the exhaust ducts are equipped with fans. This problem can be solved by installing window or wall valves.
Also make sure there is a gap under the inner door.
Ways to eliminate condensation on entrance doors
The way to get rid of condensation is to ensure the influx of dry fresh air from outside and the outflow of vapors from the enclosed space. It is possible to install a “warm curtain”, which will heat the door with heated air. The surface temperature of the door leaf will increase and the dew point will shift. Insulating the door leaf will not eradicate condensation problems. Condensing moisture settles due to the large temperature difference between the outside and the room. In this case, it is recommended to install an unheated vestibule at the entrance. It would not be amiss to equip a canopy over the entrance to protect the door from direct exposure to the sun's rays and precipitation. It is recommended to open the metal sheet of the front door with special powder polymers. It is better to fill all hollow elements in a metal door with foam in order to eliminate the appearance of cold bridges.