Lightweight polymer insulation materials, unpretentious to use and resistant to the external environment, are widely used in construction today. These include extruded polystyrene foam - an affordable material that will protect the foundation, reduce heat loss and prevent premature destruction of the structure.
Insulation of the foundation with polystyrene foam Source stroy-dom-pravilno.ru
History of the material
Foundation insulation with extruded polystyrene foam has been used since the middle of the last century. Obtained in the USA in 1941, the material had the necessary properties - low thermal conductivity, biological inertness, resistance to water, inorganic acids and alkalis. Thanks to this, the polymer became widespread as a heat insulator, first abroad, then in Russia.
In 1998, domestic companies mastered the production of thermal insulation materials based on extruded polystyrene foam. Studies have confirmed a reduction in energy costs for heating by up to 20%. The practice of using slab insulators in our country is short-lived - only 20 years. But all indicators, as well as the experience of American and European countries, confirm the high efficiency of using insulation to increase the energy efficiency of industrial and civil buildings.
Extruded polystyrene foam Source obustroeno.com
Bridge of Cold
A cold thermal bridge is a structural element of a building with low thermal resistance.
Masonry elements and monolithic structures are conductors of cold into the building, as they contain concrete, mortar and metal in their composition. These materials cool much faster than others, and along them, like bridges, heat leaves the building. The more such bridges are in direct contact with the external environment, the lower the thermal protection efficiency of the building.
The lower the energy efficiency of the structure, the greater the energy consumption will be. Heating costs will increase. At the same time, cold bridges contribute to the formation and accumulation of water condensate. This affects the appearance of mold and various fungi. Condensation also gradually leads to corrosion and destruction of building elements.
Why insulate the foundation
The underground part of the structure operates in difficult conditions. It absorbs loads from the building, soil pressure, including lateral pressure. Deep and surface waters moisten the base and walls of the foundation. Alkaline or acidic environments have an adverse effect on cement stone and reinforcement.
Seasonal freezing is the scourge of clay soils. The forces of frost heaving, resulting from the transformation of water into ice, lift even massive foundations. In the spring, after thawing, they fall again. Such movements have a destructive effect on the foundations of buildings, causing cracks, deformations, and chips. This inevitably entails a decrease in the load-bearing capacity of underground structures and, as a consequence, damage to the above-ground parts of buildings.
Freezing is one of the reasons for the formation of cracks Source svarog-dom.ru
Before the advent of expanded polystyrene, foundations were insulated by backfilling with expanded clay. To combat heaving, the sole was buried below the freezing mark of the soil. These measures led to higher construction costs, especially for small buildings without a basement. 30% of the entire budget allocated for the facility was simply buried in the ground in the form of heavy reinforced concrete blocks or a monolith.
Today, thanks to the use of lightweight, inexpensive insulation materials, it is possible to build houses up to 2-3 floors high on shallow strip or columnar foundations and slabs. The laying in these cases does not exceed 30-50 cm.
Insulation of foundations is carried out for the purpose of:
- protect structures from external influences;
- prevent premature destruction of reinforced concrete;
- reduce heat loss through the base and plinth;
- reduce the cost of constructing a massive foundation for low-rise buildings.
Foundation insulated with expanded polystyrene Source plastprom.ru
Expanded polystyrene, like many other polymers, is an unpretentious material. But without knowledge of its properties, features and application technology, you may not achieve the desired effect.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in repairing and designing foundations and insulating houses.
Let's sum it up
Insulation of foundations using polystyrene foam boards is a universal means of solving problems of soil heaving and energy saving. The lightness and good workability of the slabs allows you to carry out most of the work yourself. The exceptional weather resistance of these materials makes it possible to insulate in several stages without fear of loss of properties under the influence of temperature, moisture and solar radiation.
A large number of foundation insulation schemes using EPS and polystyrene foam indicate the variety of issues being solved for a wide variety of building designs. We recommend that developers and homeowners study all popular technologies for using polystyrene insulation.
Production of extruded polystyrene foam
The insulation is produced in the form of slabs 10-500 mm thick, 500-2000 mm long and 500-6000 mm wide. Enterprises agree on the dimensions and shape with the consumer and can change them.
Standard dimensions of expanded polystyrene for foundation insulation are 1200x600 mm and thickness 20-150 mm. A quarter is selected in the edges for ease of installation.
A heat insulator is made from granulated polystyrene, which is melted and treated under pressure with a mixture of freon and carbonic acid. The resulting thick foamy mass is squeezed out through an extrusion unit. After the polymerization reaction and gas evaporation, the workpieces are cut into sheets. The material acquires a finely porous structure with a cell diameter of 0.1-0.2 mm. The cavities have a closed shape, as a result of which there is no connection with the atmosphere. This determines the low thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam in combination with low density.
Production of expanded polystyrene Source pinterest.es
Preparatory stage
Expanded polystyrene PSB-S
First you need to calculate how many insulation boards will be needed for the foundation. The dimensions of a standard polystyrene foam board are 600x1200 mm, thickness from 20 to 100 mm. For the foundation of a residential building, slabs 50 mm thick are usually used, laid in two layers. To find out how many slabs will be needed, the total length of the foundation is multiplied by its height and divided by 0.72 - the area of one sheet of polystyrene foam.
For example, if a 2 m high foundation is insulated in a 10x8 m house, the thermal insulation area is equal to 72 square meters. Dividing it by 0.72, we get the number of sheets - 100 pieces. Since the insulation will be carried out in two layers, it is necessary to buy 200 slabs 50 mm thick.
This, however, is a very average calculation, based on the fact that the insulation thickness will be exactly 100 mm. But this value can be greater - it all depends on the climatic conditions of the region, the foundation material, and the type of insulation.
There is a special system for calculating thickness, which requires knowing the R index - this is a constant value of the required heat transfer resistance established by SNiP for each region. You can check it with your local architecture department, or take it from the table below:
| City (region) | R - required heat transfer resistance m2×°K/W |
| Moscow | 3.28 |
| Krasnodar | 2.44 |
| Sochi | 1.79 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 2.75 |
| Saint Petersburg | 3.23 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 4.84 |
| Voronezh | 3.12 |
| Yakutsk | 5.28 |
| Irkutsk | 4.05 |
| Volgograd | 2.91 |
| Astrakhan | 2.76 |
| Ekaterinburg | 3.65 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 3.36 |
| Vladivostok | 3.25 |
| Magadan | 4.33 |
| Chelyabinsk | 3.64 |
| Tver | 3.31 |
| Novosibirsk | 3.93 |
| Samara | 3.33 |
| Permian | 3.64 |
| Ufa | 3.48 |
| Kazan | 3.45 |
| Omsk | 3.82 |
Calculator for calculating the thickness of foundation insulation
In order not to bother the reader with calculation formulas, below is a special calculator that will allow you to quickly and accurately find the required thermal insulation thickness. The result obtained is rounded up, leading to the standard thickness of the panels of the selected insulation:
In addition to polystyrene foam you will need:
- mastic or roofing felt;
- gravel;
- glue;
- mushroom dowels;
- putty or polyurethane foam;
- level;
- notched spatula;
- cement mortar;
- sand;
- reinforcing mesh;
- roller
When all the materials have been prepared, a trench is dug along the perimeter of the foundation. You need to dig to the freezing level, that is, to a depth of 1.5-2 m. To make it convenient to work in the trench, its width should be 0.8-1 m. Of course, soil excavation is carried out exclusively by hand, since equipment can damage the foundation. The walls of the base must be thoroughly cleaned of soil, unevenness and cracks must be repaired with mortar.
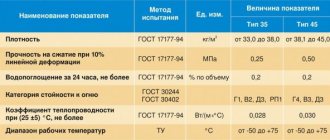
Properties
The physical and mechanical properties and technical characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam are regulated by GOST 15588-2014. In accordance with it, slabs are marked as PPS 10...45 depending on the maximum density.
Main properties of insulation:
- Density 10-45 kg/m?. The material is very light due to the high air content in the smallest bubbles.
- Thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.031-0.041 W/m°C. This is the lowest characteristic among building thermal insulators. Due to the finely porous structure of the material, heat transfer occurs primarily by convection, so energy moves through the layer very slowly.
- Water absorption on the first day is within 0.2%, over the next month - up to 0.6% by volume. The low value is due to the closed nature of the pores. Moisture penetrates only into the surface layer of the material destroyed during cutting.
- The compressive strength of expanded polystyrene is determined at a linear deformation not exceeding 10%. To insulate the underground parts of buildings, a material with a characteristic of at least 100 kPa is used. The required strength grade is determined by calculation, taking into account the design of the base. For example, a foundation slab creates a significant load. To withstand it without destruction, use PPS grades of at least 40...45.
- Low vapor permeability. The passage of water vapor is prevented by a dense layer of bubbles; the polystyrene foam board is practically airtight.
- Heat resistance in the range -50°C ... +75°C while maintaining the physical properties of the material.
- The service life of expanded polystyrene boards reaches 50 years. This is difficult to verify yet due to the relative novelty of the material, but the NIISF Institute has conducted research. They confirmed the durability of the polymer when used under conditions close to real ones. European and American builders testify to the same thing.
- Environmental Safety. It is known that polystyrene, when heated to high temperatures, releases poisonous suffocating gas. During the operation of the foundation, such a situation is unlikely to arise; the structure in the thickness of the earth is not at risk of fire. With the correct insulation technology, there is no possibility of overheating.
Table of expanded polystyrene sizes Source it.decorexpro.com
A separate topic is the resistance of expanded polystyrene to chemical attack. Acids, alkalis, salts, alcohols and components of cement-based building mixtures do not react with the polymer. Danger comes from organic substances - hydrocarbons, solvents, polyesters and ethers, oil paints, ketone compounds, tar. When interacting with them, the polymer is destroyed.
Pros and cons of EPS
Expanded polystyrene insulation at the lower level of the building confidently competes with the more familiar mineral wool. The latter loses its effectiveness when wet, so it is not advisable to use it underground. Expanded polystyrene will absorb less than 1% of its total volume during a whole month of direct contact with water (for example, with groundwater that becomes active in the spring). In addition, this material does not rot, is not susceptible to chemical influences and can withstand up to a thousand freezes without deforming or losing its properties.
The main positive quality of extruded polystyrene foam, which is extremely important for thermal insulation of foundations - low thermal conductivity - is explained by its unique closed-porous structure. Expanded polystyrene is, in fact, a cluster of closed cells filled with gas. Together they form a kind of air cushion that does not release heat from the inside and does not let in cold from the outside. That is, EPS ideally meets the requirements that high-quality insulation must meet.
The density of expanded polystyrene significantly exceeds the “ceiling” required to insulate the basement and basement (up to 35 kilograms per cubic meter).
Finally, the clear benefits for consumers are:
- light weight of the material;
- ease of cutting;
- ease of installation, ensured by connecting tenons and grooves along the edges of the slabs;
- resulting from the previous point, the ideal joining of the plates, so that the cold will not penetrate between them.
Expanded polystyrene also has its negative sides. The main one is the flammability of the material. Treatment with a protective compound will help solve this problem.
Insulation of strip foundations
It is optimal to insulate the foundation from the outside. In this case, the structure does not freeze or become wet. This method is used for thermal insulation during the construction stage.
If access to the outer part of the base is difficult, the foundation is insulated from the inside with expanded polystyrene. This will not protect structures from cold and moisture, but will reduce heat loss.
Drainage and waterproofing
The preparatory stage for vertical thermal insulation of a strip foundation is the installation of drainage and waterproofing of the outer surface. These measures protect structures from moisture, which has a positive effect on their performance. The absence of moisture suction additionally prevents freezing of reinforced concrete.
Waterproofing strip foundation Source readmehouse.ru
Thermal insulation of the blind area
Insulation of the soil around the building is used to protect it (the soil) from heaving and reduce the depth at which the foundation is laid. Expanded polystyrene prevents deformation. This increases the reliability and durability of the base.
How to properly insulate a blind area
Optimal design of blind area insulation
Thermal insulation of the surface begins with vertical laying, after which the sand is poured back 15 cm below the ground level. The formwork is carried out at a distance of about a meter from the wall, the bottom is leveled and compacted. After this, the slabs and waterproofing film are laid and the concrete is poured. It needs to be leveled so that there is a slight slope towards the outside. If the concrete has hardened, the formwork is removed and the blind area is finished with stone or paving slabs.
Insulation of the blind area
Video description
The process of insulating the foundation with extruded polystyrene foam is shown in this video:
Final works
After insulation, carefully fill the sinuses with non-heaving materials - sand, crushed stone. A horizontal layer of roofing material 0.7-1 m wide and expanded polystyrene slabs are laid along the perimeter. Cover with waterproofing, concrete the blind area using a reinforcing mesh.
When installing a shallow foundation, the insulation is also installed under the sole. For floors on the ground, polystyrene foam is laid over the entire area of the first floor, then the screed is poured.
The base is finished with plaster, decorative panels, and tiles. A fine mesh net is used to keep rodents out.
Finishing with decorative panels on top of PPS Source seloidacha.ru
Fastening technology
To insulate a shallow strip base, the insulation sheets are fastened with special glue. It should not contain organic solvents. The layer of bitumen mastic applied for waterproofing must cool before installing polystyrene foam. The adhesive composition is applied pointwise to the slab; 7-8 strokes will be required in the corners and in the middle. Pressing the material against the wall with your own hands, you need to hold it for a while to fix the glue.
Laying insulation outside starts from the corner of the house. To avoid distortions, the correct installation is checked with a building level. Each next row of slabs is fixed with an offset of half a sheet. The ease of installation is facilitated by the tongue-and-groove material locking system. The remaining gaps between the plates are filled with foam. Even if the thermal insulation technology does not require laying EPS in two layers, it is better to provide double protection at the corners, extending 1 meter in each direction.
Fixation of extruded polystyrene foam requires only an adhesive composition. Driving plastic dowels into the underground part is strictly prohibited, as it will break the tightness of the waterproofing coating. When insulating the basement floor, disc dowels are driven in 5 pieces per slab. To install the fastening, holes are drilled in the slabs and the wall of the house into which plastic dowels are driven. Work begins 3 days after gluing, when the composition has dried. The final finishing of the base is done with facing material.
Insulation of slab foundations
This type of base is called an insulated Swedish plate. The foundation is a complex structure consisting of layers of thermal and waterproofing, reinforcement, stiffeners, concrete and a built-in heating system. Expanded polystyrene slabs are laid on a compacted bedding made of drainage materials. Insulate the outer surfaces of the base and blind area.
Insulated Swedish stove Source mosarmprof.com
The resulting “bowl” is an energy-saving base on which the house is subsequently mounted. This design simultaneously serves as the floor of the first floor, part of the heating system and a heat accumulator. Saving fuel resources compared to other types of foundations reaches 30%.
How to choose
When buying EPS, you must definitely ask for a quality certificate. The sheets themselves also need to be inspected. They can be of different colors, but the color must be uniform. It is advisable to break a piece of the sheet; a characteristic crack should be heard. Then look at the structure; regular polyhedra will be visible on the fault lines. When you press on the sheet with your finger, it should spring back, but a small dent may remain.
All insulation sheets must be the same thickness
When choosing EPS for foundation insulation, you need to pay attention to the density. For these works, the density of polystyrene foam must be at least 35 kg/cubic meter. m.
A very important point: how thick should the EPS sheet be? The answer to this question can be found in SP 50.13330.2012, which provides indicators and requirements for thermal protection of buildings.
A key indicator of the thermal protection of a structure is heat transfer resistance. For ease of use, the Rules provide the values of the reduced resistance to heat transfer of enclosing structures, broken down by degree-day of the heating period. For each construction area, the normalized heat transfer resistance is calculated, adjusted by a coefficient that takes into account the conditions of the region.
The heat transfer resistance of the enclosing structure consists of the sum of the thermal resistances of each material (layer) of the structure, taking into account the heat transfer coefficients of the internal and external surfaces of the structure. Thermal resistance is the ratio of the thickness of the structure to the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material of the structure (sq. m*ºС/W), i.e. the structure is homogeneous.
Returning to the question of choosing the thickness of the EPS for the base, you need to use the formula:
δth – thickness of the insulation layer (m);
R0 – reduced heat transfer resistance of the building envelope of the construction area, according to the table taking into account GSOP (sq. m*ºС/W);
δ – foundation thickness (m);
λ – thermal conductivity coefficient of the foundation material (W/m*ºС);
λth is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation (W/m*ºС).
Preparation and waterproofing
The preparatory process has its own nuances for each type of foundation. A “tape” of standard depth should be manually dug into a trench up to one meter wide and to the freezing depth. No technique is used in this case, so as not to accidentally “injure” the foundation. The surface is cleaned and leveled - the protrusions are chipped off and cracks are sealed with cement.
Waterproofing
Then a waterproofing layer is applied: bitumen mastic using a roller or liquid rubber from a spray bottle. It is important that the waterproofing material is applied in a continuous layer and does not contain organic solvents that have a destructive effect on EPS.
Even more effective protection for strip foundations will be provided by a combination of bitumen and rolled material. Ruberoid, fiberglass, etc. are applied to the mastic in a heated state with an overlap of up to 150 mm, the joints are coated with bitumen. In the same way, a slab foundation can be insulated from moisture.
If the foundation is on stilts
With a pile foundation, a combination of a waterproofing compound and a drainage system is required to protect against groundwater. The drainage is installed in the following sequence:
- a shallow trench is dug;
- the bottom of the trench is covered with crushed stone;
- geotextiles are laid on top of the crushed stone;
- pipes for drainage of water are laid at an angle from the house;
- on top of the pipes there is another layer of geotextile;
- a top layer of crushed stone is laid.
Horizontal installation method
Slab foundation insulation scheme
Horizontal insulation is used for slab and strip foundations, for which polystyrene foam up to 10 cm thick is used.
Step 1. First, the site is cleared of soil, leveling the bottom, the last few centimeters are removed manually.
Step 2. The base is covered with sand, which needs to be compacted.
Step 3. Temporary formwork is performed, which is filled with a layer of concrete without reinforcement.
Step 4. Then, when it hardens, laying the slabs begins.
Step 5. A thick film is placed on top as waterproofing, which is glued with tape.
Step 6. Formwork is made, then reinforcement is made and the foundation is poured.
Step 7. When the formwork hardens, it is removed and additional thermal insulation of the side walls is performed.
Installed insulation