SHARE ON SOCIAL NETWORKS
FacebookTwitterOkGoogle+PinterestVk
The concept of an electric heater has several meanings. First of all, it depends on the purpose of the device. It is used to heat air in heating systems, ventilation and air conditioning devices. In this case, different substances are used as a heating element. What types of air heaters there are will be discussed in this article.
Air heaters are used to heat indoor air
Heater: this is a device for heating air in different systems
Before you start choosing a device, you need to understand the very concept of what a heater is, as well as what types there are and what are the typical and functional features of each of them.
Air heaters are capable of heating both small and fairly spacious rooms
Air heaters are used to heat air in various systems:
- heating;
- air conditioning;
- ventilation.
Heating in thermal equipment is carried out due to the reaction between chemically aggressive substances in the middle. That is why the classification of air heaters is based on the type of heat exchanger. The device can be water, steam, freon and electric. A water heater for heating is used as a heat exchanger with an intermediate coolant. A steam heater is used to heat air in heating systems.
If we classify air heaters according to thermal and aerodynamic characteristics, then the types of air heaters are divided into three-row and four-row. Based on the number of connecting sizes, heaters of individual models are divided into 7 numbers.
Steel pipes, which have a ribbed surface on the outside, serve as a coolant transporter in the middle of the heater. Due to this design, the area increases and, as a result, such piping of the heater increases the efficiency of heat transfer. In the middle of the tubes with fins, a heating or cooling element in the form of water, steam or freon is transported. Air currents flow outside, which heat or cool during contact with the pipes.
Volcano air heater structure: 1 — movable adjustable blades, 2 — built-in diffuser with fan, 3 — heating elements, 4 — warm air supply
The general scheme is based on the following operating principle: the coolant has a high heat transfer coefficient when interacting with air flows. The rib trim on the device is metal plates that are simply mounted on tubes or wound like ribbons or wire.
Design errors
At the project creation stage, errors and shortcomings are often encountered.
This may be excessive background noise, reverse or insufficient draft, blowing (upper floors of multi-storey residential buildings) and other problems. Some of them can be solved after installation is completed, using additional installations. A striking example of low-skilled calculation is insufficient exhaust draft from a production facility without particularly harmful emissions. Let's say the ventilation duct ends in a round shaft, rising 2,000 - 2,500 mm above the roof. Raising it higher is not always possible or advisable, and in such cases the principle of flare emission is used. A tip with a smaller diameter of the working hole is installed in the upper part of the round ventilation shaft. An artificial narrowing of the cross-section is created, which affects the rate of gas release into the atmosphere - it increases many times over.
Sample Project
Water heater: operating principle and purpose
Water heaters are used to heat air in various rooms where there is no central heating. They are also intended for ventilation or air conditioning systems. This type of air heaters is climate control equipment that serves as a heat exchanger filled with an intermediate coolant. The coolant in this equipment is heated or hot water.
Important! If the heater is used in a climate with an ambient air temperature below 0°C, the device must be equipped with special frost protection. Otherwise, frozen water in the pipes may simply rupture them.
A steam heater differs from a water heater in that dry saturated steam serves as the coolant in the device. These are more advanced models of heaters, so the price of a heater of this class is much higher.
Operating principle of a heating coil: blue arrows - cold air, red arrows - warm air
Water air heater: features of the design and operation of the device
The water heater has a very high level of performance. This is possible thanks to the wide temperature range, ranging from 70 to 110°C. The temperature difference is created by the heater itself. The design of the device is a tubular metal body covered with rib plates.
The most common type of air heater is a water heater with perpendicular flow. It is used in various ventilation devices. In this case, the water moves opposite to the air flow, in a rectangular direction. As a result, water rises through the channels from bottom to top, air bubbles enter the top of the device, and are removed from there through special air vents.
In any water heater, a piping unit must be installed, which is a special component of the device responsible for supplying hot water to the heat exchanger.
The design of a water heater includes the following required parts:
- coolant circulation pump;
- three-way valve;
- structural reinforcement;
- Control block;
- a piping unit that controls the performance of the heater and prevents it from freezing.
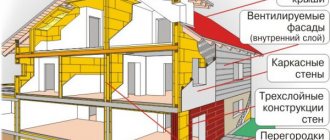
Diagram of the structure of an electric heater
Water heater for supply ventilation: operating principle and scope of use
An electric heater for fresh air ventilation is used to heat or, conversely, to cool air that comes from the street. Such devices are installed in the middle of the ventilation duct. The unit creates a beneficial microclimate, regardless of the time of year. Duct heaters are used in rooms of different sizes. The operation of a heater for supply ventilation will be especially effective in spacious workshops, greenhouses, and warehouses that are equipped with an appropriate ventilation system.
An air supply unit with a water heater is considered the most effective way of heating or cooling in large areas. Their operation is most relevant in winter, when the air that enters through the ventilation supply system requires heating.
Helpful advice! Duct-type water air heaters should be selected depending on the type of ventilation system. It is determined based on the supply ventilation scheme, which has a square, round or rectangular cross-section.
The units are installed in the middle of the ventilation duct, which has a round or rectangular cross-section. Air coming from the street is passed through the filtration system and enters the air heater for supply ventilation, where it is heated due to the heat given off by the water heating system supplied to the heat exchanger through the air heater duct.
Installation diagram of air heaters in supply ventilation
Air supply units with an electric heater also ensure that fresh, clean, cool air enters the room. At the same time, waste materials exit through the ventilation system. Both in industry and in everyday life, air supply units with an electric heater operating from the network are more in demand.
Do I need to rely on SNiP?
In all calculations that we carried out, the recommendations of SNiP and MGSN were used. This regulatory documentation allows you to determine the minimum permissible ventilation performance that ensures a comfortable stay for people in the room. In other words, SNiP requirements are aimed primarily at minimizing the cost of the ventilation system and the costs of its operation, which is important when designing ventilation systems for administrative and public buildings.
In apartments and cottages the situation is different, because you are designing ventilation for yourself, and not for the average resident, and no one forces you to adhere to the recommendations of SNiP. For this reason, system performance can be either higher than the design value (for greater comfort) or lower (to reduce energy consumption and system cost). In addition, everyone’s subjective feeling of comfort is different: for some, 30–40 m³/h per person is enough, but for others, 60 m³/h will not be enough.
However, if you do not know what air exchange you need to feel comfortable, it is better to follow the recommendations of SNiP. Since modern air handling units allow you to adjust the performance from the control panel, you can find a compromise between comfort and savings already during the operation of the ventilation system.
Water heaters with a fan: characteristics and manufacturers
A water heater with a fan is one of the most economical and efficient devices used for heating air in hangars, warehouses, gyms, shopping, exhibition and concert halls, car service centers, and workshops. It is also used to heat greenhouses, farms and other spacious objects with a large area.
Such units also come in different designs depending on the intended placement. That is, there can be wall or ceiling heaters that can be easily installed in any room.
The main advantages of water heating coils are their energy efficiency and performance, which is manifested in the ability to both increase and cool the temperature in the room. At the same time, fan heaters are generally low-cost, since they consume little electricity and allow you to save on heating.
Electric fan heater with Flowair control panel
Both foreign and domestic brands specialize in the production of such air heaters, including Teplomash, Greers, Flowair and Volcano. A water heating coil with a fan is an excellent solution in most cases for heating large objects.
KSK air heaters are considered popular in the domestic market. Devices of this brand are compact and economical. The units are widely used in industry, as they do an excellent job of quickly heating air in large areas, while using a minimum of electricity. The devices are also used as a heat exchanger. They are a component in various units, heating, air conditioning and ventilation systems. The coolant in the KSK heater is hot water with a temperature of over 190°C.
Heating coils with fans: design and operation features
Heating coils with fans are available in six standard sizes. These are very popular heating products, therefore they have a wide range of models from many manufacturers. There are two-row and three-row models. Heater power from 10 to 60 kW allows you to select equipment for rooms of different sizes.
Interesting to know! Modern fan heaters are characterized by a low noise level, which at a five-meter distance from the unit when operating at full power does not exceed 55 dB. When the fan speed is reduced, the noise level is reduced to 30 dB.
The power of heaters varies between 10-60 kW
Such heaters are also called fan heaters or duct heaters; they are compact and lightweight. They are mounted on the ceiling or wall using special brackets.
For wear resistance, the unit body is made of polypropylene or galvanized steel, and the top is coated with enamel. Polypropylene is characterized by a high degree of resistance to mechanical damage and resistance to various gases and vapors. Therefore, the housing can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to corrosion and damage of various types.
Copper tubes are used to produce the heat exchanger, and aluminum plates are used for fins. They are mounted on the rear panel of the device, which greatly simplifies the installation of the device and improves its design.
The device is equipped with a silent axial fan with blades made of a special profile and bearings of the highest class that do not require lubrication. This device provides high performance with low power consumption. In addition, the air flow is adjustable within the operating range. Water from the central heating system serves as the coolant.
The units are produced in ceiling and wall versions. Due to the lightness of the mounting console, the unit can be rotated 180 degrees during operation.
Ceiling heating fan heater
An example of calculating heat loss at home
The house in question is located in the city of Kostroma, where the temperature outside during the coldest five-day period reaches -31 degrees, the ground temperature is +5°C. The desired room temperature is +22°C.
We will consider a house with the following dimensions:
- width - 6.78 m;
- length - 8.04 m;
- height - 2.8 m.
The values will be used to calculate the area of the enclosing elements.
For calculations, it is most convenient to draw a house plan on paper, indicating on it the width, length, height of the building, the location of windows and doors, their dimensions
The walls of the building consist of:
- aerated concrete with thickness B=0.21 m, thermal conductivity coefficient k=2.87;
- foam plastic B=0.05 m, k=1.678;
- facing brick B=0.09 m, k=2.26.
When determining k, you should use information from tables, or better yet, information from a technical data sheet, since the composition of materials from different manufacturers may differ and, therefore, have different characteristics.
Reinforced concrete has the highest thermal conductivity, mineral wool slabs have the lowest, so they are most effectively used in the construction of warm houses
The floor of the house consists of the following layers:
- sand, B=0.10 m, k=0.58;
- crushed stone, B=0.10 m, k=0.13;
- concrete, B=0.20 m, k=1.1;
- ecowool insulation, B=0.20 m, k=0.043;
- reinforced screed, B=0.30 m k=0.93.
In the above house plan, the floor has the same structure throughout the entire area; there is no basement.
The ceiling consists of:
- mineral wool, B=0.10 m, k=0.05;
- plasterboard, B=0.025 m, k= 0.21;
- pine panels, B=0.05 m, k=0.35.
The ceiling has no access to the attic.
There are only 8 windows in the house, all of them are double-chamber with K-glass, argon, D = 0.6. Six windows have dimensions of 1.2x1.5 m, one - 1.2x2 m, one - 0.3x0.5 m. The doors have dimensions of 1x2.2 m, the D value according to the passport is 0.36.
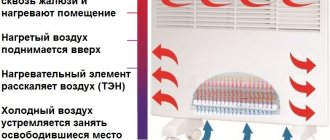
Electric heater: operating features
Electric heaters are now successfully used to heat various premises, both residential and commercial and industrial. Considering that the source of energy is electricity, there are certain safety measures when using them. First of all, the presence of vapors from explosive objects, as well as conductive dust, should be excluded.
Electric heaters are mainly installed in spacious warehouses, workshops, halls, garages and drying chambers. They are available for vertical and horizontal installation. An important condition for safe operation is access to the system reboot panel in manual mode. Air heaters are especially popular and are successfully used on construction sites.
Electric heaters significantly speed up the drying process of various building materials, in particular plaster and paint. They are often used to form a thermal curtain at gates or door structures.
The wide temperature operating range allows its use in the temperature range from -30 to 50°C. To avoid overheating of the unit, care should be taken to ensure sufficient air flow, so it is necessary to first carry out the appropriate calculation. If used correctly and carefully, the heater can last quite a long time.
The heater can be used in the temperature range from -30 to 50°C
Helpful advice! When choosing an electric industrial heater, you must be extremely careful and take into account the size of the serviced area. It is also necessary to take into account that wall-mounted units are most often used, therefore, for safety reasons, care must be taken to securely fix them using special brackets.
Fourth method (see Figure 14).
The use of cellular humidifiers makes it possible to solve the issue of air humidification in the most optimal way from the point of view of energy consumption. By setting the frontal speed of movement Vf = 2.3 m/sec of the supply air in the cellular humidifier, you can achieve the relative humidity of the supply air:
- with a honeycomb nozzle depth of 100mm - φ = 45%;
- with a honeycomb nozzle depth of 200mm - φ = 65%;
- with a honeycomb nozzle depth of 300mm - φ = 90%.
Construction of air treatment processes on the Jd diagram.
1. We select the internal air parameters from the zone of optimal parameters:
- temperature – maximum tB = 22°C;
- relative humidity – minimum φВ = 30%.
2. Using two known parameters of internal air, we find a point on the Jd diagram - (•) B.
3. The supply air temperature is taken to be 5°C less than the internal air temperature
tP = tB - 5, °C.
On the Jd diagram we draw the supply air isotherm - tP.
4. Through the point with the parameters of the internal air - (•) B we draw a process ray with a numerical value of the heat-humidity ratio
ε = 5,800 kJ/kg H2O
until it intersects with the supply air isotherm - tП.
We get a point with the parameters of the supply air - (•) P.
5. From the point with the parameters of the outside air - (•) H we draw a line of constant moisture content - dH = const.
6. From the point with the parameters of the supply air - (•) P, draw a line of constant heat content - JP = const until it intersects with the lines:
relative humidity φ = 65%.
We get a point with the parameters of humidified and cooled supply air - (•) O.
constant moisture content of outside air - dН = const.
We get a point with the parameters of the supply air heated in the heater - (•) K.
7. We pass part of the heated supply air through the cellular humidifier, and pass the remaining part of the air through the bypass, bypassing the cellular humidifier.
8. Mix humidified and cooled air with parameters at point - (•) O with air passing through the bypass, with parameters at point - (•) K in such proportions that the mixture point - (•) C is aligned with the supply air point - (•) P:
- line KO - total amount of supply air - GP;
- line KS - the amount of humidified and cooled air - GO;
- CO line - the amount of air passing through the bypass - GP - GO.
9. External air processing processes on the Jd diagram will be depicted by the following lines:
- line NK - the process of heating the supply air in the air heater;
- line KS - the process of humidifying and cooling part of the heated air in a cellular humidifier;
- CO line - bypassing heated air, bypassing the cellular humidifier;
- line KO - mixing of humidified and cooled air with heated air.
10. Treated external supply air with parameters at point - (•) P enters the room and assimilates excess heat and moisture along the process path - the PV line. Due to the increase in air temperature along the height of the room - grad t. Air parameters change. The process of changing parameters occurs along the process beam to the point of outgoing air - (•) U.
11. The amount of air passing through the irrigation chamber can be determined by the ratio of the segments
12. The required amount of moisture to humidify the supply air in the irrigation chamber
Schematic diagram of supply air treatment during the cold season - HP, for the 4th method, see Figure 15.
Household electric heater: features and types
There are special autonomous heating electric heaters for the home. Such devices are used mainly as a source of temporary heat during periods when there are interruptions in centralized heating, or in conditions of early or prolonged cold weather. Modern manufacturers offer a wide range of different heaters.
Related article:
Heating collectors: guarantee of efficient operation of the heating system
Features of the technological unit. Principle of operation. Varieties of design. Material of manufacture. Selecting a collector comb. Manufacturers.
To choose the right option, it is necessary to take into account a number of features, in particular, pay attention to the power of the heating element compared to the area of the heated room. You should pay attention to the functionality of the heater and how quickly and efficiently it warms up the room. Energy saving is also a very important issue in the process of choosing a heater.
The modern heater market offers the following types of electric household heaters:
- oil radiator;
- electric convector;
- heat fan;
- infrared heater.
Dimensions of various fan heaters from the manufacturer Volcano
When giving preference to one or another type of heater for domestic needs, the expected operating conditions should be taken into account. The power of the heating element plays an important role. This concept refers to the amount of thermal energy that is produced over a certain period of time.
For standard apartments, where the ceiling height does not exceed 2.5 m, the heater is selected based on the following conditions: 1 kW of power is required for 10 square meters. If the heater serves as an additional source of heat, then a device with a power of 1-1.5 kW is sufficient for a room of 25 square meters. In an unheated room, the device is selected based on the requirements: 1 kW per 25 meters of area.
Oil heater: advantages and operating features
The safest in the list of electric heaters for the home is an oil heater. Outwardly, it is a radiator familiar to the eye, but it is made in such a way that it is impossible to get a burn when touched. The main difference from other types of heaters is the coolant - oil is used as it, which expands when heated, filling all the containers. The heating element in such a device is an ordinary heating element.
The positive qualities of this equipment are that one such unit is quite enough to heat one room with an average area. It may be sufficient even in an unheated room, provided that the temperature outside is not freezing. The installed thermostat on modern heaters allows you to control the temperature of the heater - it is triggered when the desired value is reached and, based on its signal, the heater turns off.
The oil heater body does not heat up, which ensures its safety
Helpful advice! Heating equipment should be purchased in specialized stores that have all the necessary documents and permits for the sale of electrical appliances.
Thanks to the device being equipped with a timer, it can work continuously for several days without requiring special control. This advantage allows you to leave the oil heater on for a short time. The only drawback of such equipment is its inertness, since the coolant in the form of oil requires some time to heat it to the desired temperature.
Oil radiators have their own subtypes:
- electric wall heater;
- floor mobile heater;
- electronically controlled oil heater;
- mechanically controlled radiator.
Waste oil heater and gas heater: options for the garage
In heating garages, homemade units that run on waste oil are often used. Such a device provides double savings - it serves as a waste oil recycler, and also does not require the purchase of expensive heating equipment.
A heater is a common option for heating a garage.
With the help of such a heater, you can heat rooms with an area of over 300 cubic meters, provided that the owner also took care of insulation. If the insulation is weak, then a normal temperature for life can be maintained in a room with a volume of up to 200 cubic meters. The oil consumption is equal to 300 ml per hour.
The heater can additionally be equipped with automation and special temperature sensors to determine the presence of a flame and temperature indicator. The design must include an oil pump, as well as fans for pressurizing and blowing the heat exchanger. The heater fans themselves are also equipped with automation. This is a simple thermal relay that is activated when the device warms up and when it cools down. The oil pump, operating in automatic mode, delivers used oil drop by drop into the perolysis cup. You can select the desired level and rate of oil supply.
To heat technical rooms, gas heaters are also used, which are low-power heating devices that run on liquefied gas. The fuel can be propane-butane or pure propane. Such equipment has an advantageous combination of small build and power, so the unit can be easily moved and used in limited space.
Electric heater with fan
Fan heater: small-sized heater for home and garden
For premises that are used as temporary housing, for example, for a summer residence, it is best to choose a small and inexpensive heating option, which is a household fan heater. By design, it is an ordinary incandescent coil made of metal or ceramic, housed in a plastic casing. A fan is installed directly behind the coil, directing a flow of cold air to the heating element. Thus, the device blows already heated air around the room. This device is a prototype of an industrial heater with a fan.
Helpful advice! In order not to make a mistake in choosing a household heater, just look at the device’s passport. The document indicates the power of the device in terms of thermal energy productivity. Here you should be guided by the standard for calculating the heater: 1 kW per 10 square meters of area.
A fan heater can heat up an entire room in a short period of time. Its compactness allows for placement anywhere, directing the warm flow where it is needed. This heater has an affordable price and low energy consumption. Most models are equipped with special power regulators that regulate the intensity of the ventilation device.
Modern models are also equipped with a remote control system. In addition, in summer, the device can be used as a regular fan. To do this, just turn off the heating element. The main disadvantage of such heaters is that they do not operate for long; moreover, immediately after switching off, the temperature in the room drops sharply.
Tabletop heater for use in small spaces
Online calculator
Note! Today, the Internet allows you to use a computer to calculate the power of heating radiators, taking into account all innovative construction technologies
Calculation of heating radiators
The online calculation formula is similar to the standard one, but is slightly modified to take into account adjustment factors. They are installed:
- On plastic windows that reduce heat loss.
- For external walls - the more there are, the higher the coefficient.
- To the height of the room. If it is more than 2.5 meters, then the coefficient increases.
The basic online calculation takes as a basis the average values for each type of heating battery, the center distance of which is 500 mm. For heat transfer, the following data are accepted into the standard calculation:
- For cast iron radiators - 145 W.
- For bimetallic - 185 W.
- For aluminum - 190 W.
To carry out the calculation, you need to enter all the requested data into the computer database:
- Area and height of the room.
- Number of windows and external walls.
- Type of room and selected radiator.
- Condition and material of the walls.
- Minimum temperature outside.
After filling out the fields of the online form, you only need to click the “Run calculation” option, and after a few seconds the computer will display the result. It's very simple and convenient. An online calculator can be found on the radiator manufacturer's website.
An example of calculating apartment ventilation
The design and calculation of supply ventilation for residential premises is carried out in several stages:
- calculation of air quantity;
- selection of ventilation ducts;
- heating calculation;
- selection of sizes of grilles, valves and other elements;
- calculation of fans or control units;
- choice of automation.
The apartment taken as an example with a total area of 81 m2 consists of three residential premises. Using calculation standards from SNiP, we will draw up a table of the required air exchange for each room. Since 5 residents live in the apartment, there is less than 20 m2 of space per person. The living room and kitchen are combined (add 100 m3/h for the gas stove).
| № | The name of a room | Square | Air exchange, m3/h |
| 1 | Kitchen-dining room (living room) | 30,3 | 191 |
| 2 | Bedroom | 13,74 | 41 |
| 3 | Bathroom | 1,26 | 25 |
| 4 | Bathroom | 2,64 | 25 |
| 5 | Wardrobe | 4,4 | 3 |
| 6 | Bedroom | 14,92 | 45 |
| 7 | Hallway | 14 | |
| Amount, m3/h | 330 |
Supply is organized into the living room and bedrooms, and exhaust is carried out using wall fans and ventilation ducts from the gas stove area, bathroom and bathtub.
Apartment ventilation diagram.
Supply grilles and diffusers are located at some distance from the exhaust elements. The air is heated by electric, water heaters or heat pumps.
A note on water heating efficiency
There is a common misconception that electric water heaters have an efficiency of 100%. This is due to the fact that in theoretical calculations energy losses are often neglected due to their small magnitude. But when calculations have practical application, it is easy to notice that in reality, energy losses when heating water occur from the first seconds. Depending on the heating device, these can be the following main types of losses:
- to warm up the heating element itself (especially a lot for an electric stove),
- to heat the walls of the container (kettle, tank),
- heat transfer and thermal radiation of energy into the environment from the walls of the container and the non-submersible heating element),
- evaporation from the surface of water in open containers (pots and kettles without lids),
- losses due to vaporization during boiling (the most powerful loss channel).
Based on the directions of the main losses, it is not difficult to determine measures to increase the efficiency of the water heating process:
- use of an immersion heating element,
- using a closed container,
- thermal insulation of the container,
- using the minimum required heating temperature,
- shutdown when boiling occurs.
Additional losses include:
- losses in electrical wires and contacts (heating of the wires and plug of the electrical appliance).
- losses due to side electrochemical processes (ionic heaters, electrochemical decomposition of water, electrochemical dissolution of the anode),
- sound losses (noise produced by steam bubbles at the point of contact of the heater or hot surface with water).
From the point of view of energy losses alone, additional losses are negligible and insignificant, but from the point of view of unplanned costs and risks, these losses require special attention:
- Heating the power supply wires, at best, leads to temporary breakdown of the wires/socket/plug, and at worst, to a fire, electric shock, or burn.
- Electrochemical processes saturate the water with metal ions, corroding the tank and immersion heating element. The former makes the water undrinkable, the latter shortens the life of the water heater and can cause a flood if the tank rusts through.
- Noise when heating water is an indicator that steam formation occurs at the surface of contact between water and hot metal. This process leads to the formation of scale. Due to the fact that scale does not conduct heat well, the heating element begins to overheat, becoming unusable at an accelerated rate (the heating time also increases slightly). Failure of the heating element may result in electric shock to persons.) Also, noise itself can disturb others, causing noise pollution.
Based on the areas of additional losses, measures to avoid and reduce their negative consequences are highlighted:
- Use of a working electrical network (working grounding), periodic checking of the heating of the supply wires, timely elimination of problems.
- Heating of drinking water only with devices specially designed for this purpose.
- Timely replacement of the anode in water heaters (magnesium anode, aluminum anode).
- Disconnecting the heater from the water supply and electrical network while people are away.
- Use of active leakage protection systems (an automatic valve shuts off the water supply when the floor gets wet where the sensor is installed).
- Using an RCD (residual current device) for water heaters, and periodically checking the functionality of this device once every six months.
- Reducing the surface temperature of hot metal at the point of contact with water (to reduce the formation of scale and noise) by the following methods or combinations thereof: – reducing the heater power without reducing the contact area; – increasing the contact area of the heater with water without increasing power (for example, prefer a heater with a larger specific area, if space allows); – active regulation (limitation) of the heater temperature by a triac (transistor) control unit; – installation of additional heaters operating simultaneously, but with reduced power (sequential activation); – periodic checking for scale, timely cleaning; – increasing the speed of water flow near the heater or heating surface.