Many modern solutions for water heating of houses require the use of a pump group. The design and installation of a heating system with forced circulation must be carried out taking into account technical issues that arise due to the rapid movement of the coolant.
The high pressure in the heating circuit allows for the implementation of many wiring schemes. Agree, this is an important advantage of a heating system with forced circulation. However, the arrangement of such a scheme requires competent design.
We will tell you by what characteristics the main operating components of the system are selected, and we will also describe in detail the possible options for wiring the main line and methods of organizing the heating circuit.
Features of the operation of the forced heating system
The heating circuit, in which fuel circulates naturally, is as simple as possible. In such a chain, the coolant is heated in the boiler and, in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics, rushes up the riser. Having reached the radiators, the carrier gives up part of the thermal energy, its temperature decreases. Under the pressure of newly arriving doses of heat, the cooled fuel is lowered back into the boiler to repeat the cycle.
Such an elementary scheme has significant disadvantages, especially in combination with the single-pipe type of wiring:
- Heat is distributed unevenly: in rooms located next to the heat source (boiler), the temperature is higher than in those located at a greater distance from it.
- A system with natural circulation consumes a significant amount of heating material, which is not in favor of its rationality. These problems can be partially neutralized by installing a two-pipe distribution system.
The efficiency of a heating circuit with forced circulation is due to the inclusion of a pump in it. Its function is to impart greater speed to the movement of fuel along the heating main. The value of this indicator is directly dependent on the temperature of the heated premises.
The presence of a circulation pump in the heating system gives it undeniable advantages:
- efficiency. Associated with both the rational use of heat resources and reasonable financial costs for the purchase of small-diameter pipes;
- ergonomics. The uncluttered design allows you to hide its elements in the walls, under the floor, etc.;
- the ability to operate in heating projects of any complexity with various combinations of heating equipment. The heating circuit may contain radiators, thermal curtains, and heated floors. The main concern when designing a forced circulation heating system is the uninterrupted supply of electricity, since it is electricity that is used to drive the pump. Therefore, it is a good idea to take care of a backup power supply.
Where is the best place to locate the boiler room?
A heating boiler, even if all required safety rules are observed, is a source of increased fire hazard. Therefore, you should approach the choice of the place where it will be installed very responsibly and seriously. It is necessary to consider not only the cost of placement and operational safety, but also ease of use. Based on this, there are three main ways to locate a boiler room.
The first is out-of-home placement. It should be said right away that this method is as expensive as it is safe.
But keep in mind that you will have to develop a separate drawing, pour an additional foundation, think about installing external utility networks and their thermal insulation.
You will have to spend a lot of money and time. And the ease of use is significantly reduced. Secondly, if the designs of houses with a boiler room were initially developed taking into account the installation of the necessary equipment, then the heating boiler can be located on the ground floor or even in the basement. Most people prefer to place it in the basement. Then you won’t have to allocate 15-16 square meters of usable space on the ground floor, which means that the freed up space can be used to greater advantage.
To install a diesel boiler or solid fuel boiler, it is necessary to provide a separate room: when coal, wood, peat or diesel fuel is burned, a large amount of smoke is released, which can cause certain problems for the inhabitants of the house. Well, even the most economical owner can allocate 15 square meters when building luxurious two-story houses with a boiler room.
two-story house
If you prefer an electric heating boiler or a not too powerful (no more than 30 kW) gas boiler, then you can install the equipment in the kitchen. Modern equipment is small in size, so it is not noticeable and does not take up extra space. If desired, you can even choose special wall-mounted boilers that take up virtually no useful space in the room.
Of course, the kitchen must have high-quality ventilation, and simply monitoring the condition of the equipment will never be superfluous.
And finally, an option that allows you to combine the advantages of the two described above and at the same time, partially get rid of their disadvantages. When designing wooden houses with a boiler room, you need to provide a small extension in advance.
wooden house
A foundation is also poured under it, which is part of the main foundation. In most cases, extensions are made from lightweight materials (frame construction), which allows you to save a considerable amount during construction. This simplifies the organization of high-quality ventilation. As a result, you get a boiler room, which is located in close proximity to the house. Thanks to this, you will not have to spend extra money on laying the pipeline.
At any time you can enter the extension both from the side of the house and from the street: in most cases, extensions are equipped with two doors. If a gas leak (carbon monoxide or explosive) occurs, the risk of serious damage to the main building is minimized. Therefore, an extension to the house dedicated to the boiler room can be called the optimal solution.
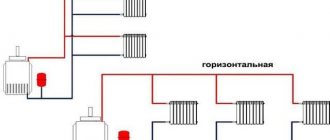
Forced schemes
Conventionally, all forced schemes can be divided into one-pipe and two-pipe. The most popular today are two-pipe ones. But let's look at the differences
Single-pipe connection diagram
It involves the operation of one pipe for supplying coolant from the boiler and for its return outflow. This option does not require large pipe footage, the number of shut-off valves, fittings and other elements, therefore, installation work is reduced to a minimum. Minus: sequential heating of heating devices gradually reduces the temperature of the supplied fuel in the equipment chain. The heating system can operate in a natural or forced way.
Information that will be useful to craftsmen
Before starting installation work, you should discuss all the nuances with the selected specialist, and also tell about your vision of the heating system.
The master should provide:
- Complete information about the materials from which the roof of the house, window structures, and wall coverings are made.
- House plan.
- Drawings showing the locations of plumbing units.
The period of operation of the heat supply system will be influenced not only by the quality of design and correct installation, but also by the selected materials, boiler equipment and the correct use of heating elements.
Two-pipe connection diagram
In this heating model, two pipes work: the first supplies fuel to the heater, the second removes the cooled medium to the boiler.
This is the main difference from the first option, with the ensuing consequences: an increase in the metal consumption of the structure due to larger pipe measurements, shut-off and connecting elements in the circuit. Installation is more complicated. A positive point, as a reward for the financial and labor costs incurred: each heater in the system is supplied with coolant of the same temperature. Depending on the direction of flow of hot and cooled fuel, there are:
- a parallel connection diagram, where the coolant supply and its removal move in the same direction, allowing all devices in the chain to heat up at the same speed;
- dead-end, which involves faster heating of devices located closer to the boiler.
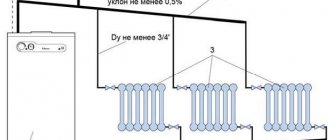
Beam wiring
A very similar modification to a two-pipe forced circulation heating circuit. The difference is the point of distribution of hot fuel and the collection of cooled fuel, which is not the main riser, but distribution manifolds. Each heating device has a separate coolant supply and drainage line. Of course, such a scheme assumes a balanced heat distribution in temperature and pressure. The overhead of such a heating arrangement is obvious: significant costs for materials, high cost and labor-intensive installation work. In addition, it is very difficult to make adjustments to the circuit with distribution nodes (for example, adding heating equipment).
Finally, about the advantages and disadvantages
First, let's reveal the main disadvantages of this heating:
- significant investments during construction - the homeowner bears the costs of purchasing materials, equipment and installation;
- during operation, it is necessary to monitor the operation of the thermal power plant, diesel and wood-burning boilers must be loaded with fuel on time;
- there is a possibility of leakage or defrosting of heating network elements.
The listed shortcomings cannot be called critical. The investment gradually pays off; if there is a lack of funds, installation is carried out independently. The likelihood of leaks is reduced to zero due to high-quality assembly and filling of non-freezing coolant (antifreeze), if the heating is turned on periodically.
The list of advantages looks much more impressive:
- Versatility. To heat the working fluid, you can use equipment that uses various energy sources and fuels. If necessary, 2-4 different water heating units are installed.
- Wide selection of components. The developer can select a design and materials to suit his personal budget - use inexpensive polypropylene pipes, install panel radiators and an electric boiler.
- Flexibility. Any closed type scheme can be easily adapted to the homeowner’s requirements; pipelines can be laid in a closed or open way. An exception is gravity (gravity) wiring, installed according to strict rules.
- The surface temperature of the devices does not exceed 80 degrees, soft infrared heat is released, and the air does not dry out.
- In parallel with heating, it is not difficult to organize hot water supply - install and connect an indirect heating storage boiler to the heat generator.
- It is possible to fully automate and control the heating remotely - via GSM connection or the Internet.
As you understand, the publication is for informational purposes and will be useful to homeowners who have not decided on the method of heating their home. You will find more detailed instructions on choosing thermal power equipment, pipes and fittings used on other pages of our resource (transitions are highlighted in blue in the text of the article).
Installation of heated floors
A truly complex scheme with forced circulation of heating, which is also expensive, but also the most comfortable. In small rooms, simple combinations of pipe laying are used with one inlet for the heated coolant and an outlet for the cooled one. Larger areas will require more complex designs using distribution node connections. Often, installing a heated floor involves installing a separate circulation pump in sections of the system.
Local automatic temperature stabilization
Single-pipe adjustable radiator unit with a straight-through (a) or three-way (b) thermostatic valve on the top supply.
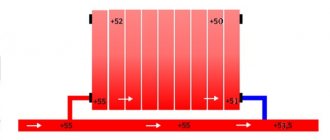
An adjustable radiator unit for vertical single-pipe heating can be made with a straight-through (Fig. a) or three-way (Fig. b) thermostatic valve (thermostat). The piping unit branches the coolant into two flows: through the device and through the bypass. The diameters of the thermostat valve plunger and the opening for the passage of liquid are made to the maximum. The thermostat does not clog when the coolant is contaminated and ensures its free flow (when fully open). Unauthorized replacement of the radiator, accompanied by removal of the thermostat, does not lead to imbalance of the entire heating system, as in the two-pipe version.
If the room air temperature exceeds the set one, the valve will close (go to minimum mode), directing the liquid through the bypass past the radiator. Closing (minimum opening) the valves of all thermostats of a given riser increases the proportion of coolant passing through the bypasses from 80% to 90%, while simultaneously reducing the flow through the radiators, i.e. without changing the total flow rate.
Open and closed heating circuit using a pump
The coolant moving in the pipes gains volume during the heating process. The resulting excessive amount flows into a specially equipped container. An open heating system provides for the installation of a maximum height expansion tank in the current, in which the atmospheric environment and the coolant are directly connected.
Conceptual diagram of the operation of the circuit: an increase in temperature provokes an increase in the coolant in volume and, as a consequence, its level in the expansion tank. A certain amount of air from the tank is removed through the pipe. As the temperature drops, the fuel level in the tank decreases, and its place is taken by external air coming from the nozzle.
A closed heating system with forced circulation uses a pressurized expansion tank. It is presented in the form of a high-strength metal container, consisting of a pair of rolled parts. The tank contains a rubber heat-resistant membrane and contains a small amount of gas (nitrogen pumped in by the manufacturer or air accumulated in the system). The membrane divides the tank into two halves: one receives excess coolant that appears during heating, the other is intended for air or nitrogen that does not interact with the fuel. The system operates as follows: the coolant is supplied to the expansion tank when heated, and enters the membrane. During the cooling process, the gas on the other side of the membrane pushes the coolant back into the system.
Selecting a circulation pump
A high-quality pump for a forced circulation heating system must meet the following criteria:
- energy saving;
- simplicity and reliability in operation.
Power characteristics are determined by the dimensions of the living space that needs to be heated. For example, to heat an area of 250 sq.m, a circulation pump with a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure of 0.4 atm is required. In addition, the choice of equipment is influenced by calculations from the heating system design. These include:
- material of pipes intended for installation and their diameter;
- total footage of the scheme;
- number of heating devices;
- type of coolant.
Selecting a pump yourself can cause a number of difficulties, so it is best to get advice from a competent specialist on this issue.
The need to maintain pipe slope
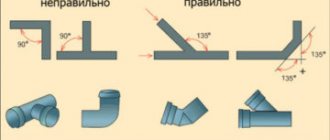
When installing a heating system with forced circulation of coolant, compliance with the requirements for pipe slope is not necessary. Heating mains are installed straight or with a slight slope in relation to the drain. This will make it easier to drain the coolant before carrying out repair work or if a situation arises when the system faces a long downtime.
Additional requirements for the boiler room
Regardless of where you decide to install the heating boiler - in the house, in an extension or a separate building, the room must meet certain requirements.
Moreover, the requirements are also different for different types of boilers. For example, if you are building a frame house with a gas boiler room, then the area of the boiler room must be at least 15 meters with a height of 2.2 meters. However, this only applies to heating boilers with a power of no more than 30 kW. If you are using a boiler with a power of 30 to 150 kW, then the ceiling height should be at least 2.5 meters.
Also note that you cannot store a gas tank (whether cylinders or another container) in the same room as the boiler, in order to avoid fire and a terrible explosion.
For boiler rooms with solid fuel boilers, the area can be reduced to 7 square meters, and you can choose the height that seems sufficient to you.
If you are using a wall-mounted boiler, make sure that the boiler room layout includes one wall built of non-combustible material (brick or concrete). When choosing a heavier floor-standing boiler, make sure that the boiler room foundation can withstand such a significant load. Of course, the floor must have a completely non-flammable coating. When creating a heating system in an extension or outdoors, it would be better to fill the floor with concrete. If you are installing the boiler indoors, it will be enough to lay a steel sheet of sufficient thickness on the floor.
You should not skimp on components. Yes, by buying high-quality smoke detectors, bypasses, shut-off valves and other equipment in a specialized store rather than on the market, you will spend several hundred or even thousands of rubles more. However, in this case, you will be sure that each part is made of high-quality materials, and not brittle alloys that cannot withstand significant pressure and frequent temperature changes.
This means you guarantee the safety of yourself, your loved ones and your property. Isn't it worth the extra thousand rubles spent? In some cases, it is necessary to connect a sewer drain to the boiler room. Condensate that, under certain circumstances, occurs in the chimney of the heating boiler will flow there.
After all, it is important not only to correctly calculate the power of the installed boiler, but also to select suitable equipment based on the size of the premises, the thickness of the walls, the area of windows, the strength and direction of the wind in a given region, and the temperature (average in winter and extremely low). Therefore, most people prefer not to even try to draw up a plan on their own, entrusting this extremely complex and responsible work to specialists
Yes, because of this, the already expensive operation of installing a heating boiler turns into the most expensive of all installation procedures for engineering systems. But you can be sure that nothing threatens your family and you personally. And that even on the coldest winter days, when a blizzard howls outside the window, you will be warm and feel really comfortable.
A properly designed heating system for a one-story house can provide high-quality and efficient heating of the premises, but to do this you need to know how to properly implement such a system in your home. One of the most popular individual heating systems is the single-pipe natural circulation water heating system.
Most often, the installation of heating pipelines is carried out with metal-plastic pipes due to their practicality and reasonable price.
As a rule, water is used as a coolant, but it is also possible to use a non-freezing liquid that will prevent the heating system from freezing during the cold season.
Pipe diameter in forced system
A heating system that includes a circulation pump does not place any special demands on the pipeline. For such a scheme, it does not matter what size and composition of the pipes will transfer heat. Thus, inexpensive models with small diameters can be used. This will save a decent amount when organizing heating. We should not forget that the parameters of the pipes are taken into account when purchasing a circulation pump.
It is important to understand that with smaller pipeline diameters in a forced circulation system, resistance also increases.
Principle of operation
To better understand the operating principle of this system, it is worth first understanding how the SO EC functions. This issue has been discussed in detail here. By integrating a circulation pump into such a system, it is possible to eliminate most of the shortcomings and achieve uniform distribution of hot coolant throughout all heating devices, thereby increasing the efficiency of the CO and reducing the fuel consumption required by the boiler to maintain the specified temperature parameters.
The main disadvantage of forced heating
Since heating a house with forced circulation works only with a circulation pump. Therefore, such a pump needs a stable and high-quality supply of electricity.
This is the only and biggest disadvantage of heating a house with forced circulation. For example, your electricity was cut off. There is no heating. Electrical network failure - no heating. The voltage in the network has dropped - the pump does not produce rated power - again there is no heating.
How to improve a forced circulation system?
It is, of course, advisable to properly insulate the pipes of heating systems in order to minimize the loss of precious heat. Then it will be economical. The main thing when choosing a forced circulation system for your home is not to make a mistake when calculating it.
It is necessary to pay close attention to the number of heating appliances, the number of heating circuits, selection of the optimal pipe diameter and pump power.
It is with the violation of these laws that the most problems arise. Either they incorrectly calculated the number of devices, or they narrowed the pipelines and there is not enough heat for the radiators, or they installed a weak pump that wears out, and so on.