The availability and high insulating qualities of modern foamed polymer materials give rise to the idea of using them for insulating interior spaces. For example, insulate the floor with penofol. The material is inexpensive, with good mechanical characteristics and low thermal conductivity. In addition, the process of laying penofol on the floor is simplified by the format of the material, usually it is a sheet rolled into a roll, which can easily be cut and laid in accordance with the configuration of the room.
When adjusting, the foam floor can be temporarily secured with ordinary tape
Features of floor insulation work with Penofol
Penofol is a combined material made of foamed polyethylene and aluminum foil with a thickness of 4-10 mm. It prevents heat loss in three directions - through convection, conduction and in the infrared spectrum.
Most other insulators have only one of these properties. This means that a thin sample can replace insulation materials of much greater thickness. There are several modifications of polyethylene foam, which differ in the placement of aluminum foil on one or both sides and the presence of an adhesive layer.
The scope of use of the material is quite wide. It does not have pores and does not allow air to pass through, so it is often used to insulate the floors of saunas and baths. The product copes with the insulation of concrete and wooden flooring. Penofol is also present in the structure of heated floors.
Installation of insulation is always carried out on the sheathing. It is necessary to create a gap above the foil. The air passing through it will remove accumulated moisture.
In most cases, Penofol is used with other insulation materials. It interacts well with polystyrene foam, penoplex, mineral wool and other products. It is also used as an independent heat insulator.
Manufacturers and prices
To insulate floors, not only Penofol is used, but also other types of insulation, so we will present the most popular products from famous brands.
| Manufacturer | Features of the heat insulator | Price, in rubles |
| Rockwool | Basalt wool with foil, supplied in packs of 8 sheets, which can cover 4.8 m2 | 700 |
| Izolon | Foamed polyethylene, supplied in rolls. Price per meter of material, 3 mm thick | 200 |
| Penofol | -//- | 100 |
| Ecofol | -//- | 70 |
| Porilex | -//- | 50 |
| Xotpipe | Basalt wool, supplied in rolls. Cost per 1 meter. | 100 |
Thermal insulation with foil has become very popular; owners of private houses have already appreciated its high performance characteristics. It has proven itself to be a good thermal insulation material that does not allow cold air and dampness to pass through, and also protects the home from heat loss by reflecting infrared rays into the room.
Penofol floor insulation technology
The insulator can be used to insulate surfaces made of any material. Before laying Penofol on the floor, stock up on glue to fix it to the base and reinforced tape to seal the joints. They will improve the quality of the heat-insulating layer.
Selection of materials for floor insulation
Along with the canvas, they always buy a means for securing it to the base and a tape that prevents the formation of cold bridges at the joints of the material. The correct choice of components will reduce heat loss in the apartment.
Penofol for flooring is available in various designs. For insulation, rolls with special letter designations are used:
Adhesive tape is a metallized (aluminum) reinforced tape designed to seal and insulate surfaces. The main indicators that it should have:
Laying Penofol on a concrete base
Let's look at some ways to insulate a cold base. As a rule, to insulate a concrete floor, the product is used together with another type of heat insulator.
Features of the work:
Installation of Penofol on a wooden surface
Thermal insulation of wooden floors is usually performed in private homes. Let's consider two options for installation work - with removing the old covering and by placing the product on top of the existing flooring.
In the first case, the canvas is spread under the boards. The sequence of operations when insulating a floor with Penofol is as follows:
Use of Penofol in the "warm floor" system
The use of this material in heated floors allows increasing the heat transfer of the system by 15-20%.
The technique for arranging such a heating system in a room looks like this:
How to insulate a floor with Penofol - watch the video:
Source
Is it possible to insulate a floor using penofol as the only insulation?
Due to its high thermal insulation qualities, this material is well compatible with any type of screed. If you do not have the opportunity to use other types of materials for floor insulation, you can use penofol without the risk of getting low-quality thermal insulation.
When creating the same environmental conditions, the heat saving coefficient of grade B penofol, having a thickness of 4 mm, will be comparable to:
- masonry of clay bricks 2.5 bricks thick;
- silicate brick masonry 3.5 bricks thick;
- 38.4 centimeters of aerated concrete;
- 49 centimeters of expanded clay concrete;
- 6.7 centimeters of stone wool;
- 4.6 centimeters of polystyrene foam.
Does it work or not?
The foil underfloor heating is the most controversial. There are two opposing opinions. One is for using this material. Its supporters claim that there will be significant savings on losses “to the floor” due to the reflection of heat back.
Second opinion - you need thermal insulation, put 50 mm EPS. Foil or 2 mm backing with a shiny floor will not help with this. And reflection in a solid body does not work, so it makes no sense to talk about reflected heat in the thickness of concrete. Let's take a closer look at both points of view, and then look at the test results.
How can foil in a screed help?
As you know, radiation can be reflected from shiny surfaces. The heat in the screed is also partially transferred by radiation. By turning back at least some of the downward rays, you can reduce heat loss. This is what the foil underlay for heated floors is designed for. It is placed on the base, and on top are pipes with coolant. That part of the thermal radiation that is directed downward will be reflected and returned to the room. In theory, losses should decrease.
This is exactly what sellers of foil materials say. Many people decide that the costs are not too high, and a possible reduction in the payment for coolants warms the soul. Moreover, the screeds (the preparation and the actual screed with the heated floor) still need to be “untied.” So you can use not just plastic film, but foamed polyethylene with lavsan coating or foil.
When installing a film heater, a substrate must be laid underneath it. As a backing, you can use foil material or any other type of thin elastic material (technical cork, pine backing, etc.). Film heated floors are most often made under laminate, and it has a drum effect. The main task of the substrate is to level out micro-irregularities in the base and reduce the drumming effect. Foamed polyethylene copes with this task well. And the foil film helps retain heat. These are again the sellers' arguments. Sounds tempting.
Arguments of opponents
Let's discuss the second opinion, which is that foil, foil backing or any other shiny material in a screed cannot work. For now we are talking about the possibilities of reflecting radiant heat. Yes, shiny surfaces reflect radiation (light and heat, in particular). But for this, in front of the reflective layer there must be a layer of material transparent to this radiation. So, when insulating walls/ceilings, an air gap of several centimeters is left between the foil layer and the finishing. In this case, no questions arise about its effectiveness. There is no mention of a gap in the screed. Or rather, not quite like that.
Theoretically, such a gap exists if a layer of foil or other protective material is filled with a transparent polymer. This was done to protect the foil from destruction in the concrete layer. Simply, the gap size must be no less than the length of the reflected wave. And it is a fraction of a millimeter. So, in theory, the protective layer of polymer is sufficient to meet the reflective conditions. But is it possible to say that reflected rays can significantly affect the overall heat loss...
In the thickness of concrete, heat exchange by radiation constitutes a very small proportion. There is no specific data, but this is not even 1%, but less. However, we will assume that one percent of the heat is transferred by radiation. Let half be directed downwards (in reality less). This is 0.5%. Not everything that is directed downward will be reflected either. Let it be half too. Total, this is 0.25%. That is, no more than 0.25% of heat can be returned. With underfloor heating costs of 5,000 thousand, the savings will be 12.5 rubles per month. Not funny.
Plus, the most popular (because the cheapest) material in this category is polyethylene foam with a shiny coating. It is suitable for insulating walls and ceilings. And in a screed or under a laminate, under load it wrinkles. There is no trace left of the “foaming”. All that remains is a thin layer of polyethylene and a film on top. So it cannot work as insulation in a screed. In general, it is difficult to say whether reflective insulation works in a heated floor design.
What do experiments show?
All disputes and statements are just theories and attempts to apply existing knowledge to an unexplored area. No one has yet carried out a “pure” experiment that would clearly prove whether foil works or not in a heated floor design. There are a couple of experiments carried out by “ordinary users” who wanted to find out for themselves the feasibility of using a foil backing for a heated floor.
First experiment
The first testing was carried out with a heating film on which the laminate was laid. One part uses Folgoizol 2 mm thick with foil and a protective coating, the other uses foamed polyethylene of similar thickness, but without lamination. Readings were taken using a pyrometer. As usual, in such devices the temperature is displayed in color. The darker the orange, the warmer it is. This model also had the ability to display results in the form of a table. Data in the photo.
According to these data, it turns out that there is a difference in the temperature of the floor with the same insulation with and without foil. It is 1.5°C. Not much, but quite noticeable. Just like with our hand, we feel the difference between the forehead of a healthy person (36.6) and a sick person (38). Approximately the same difference will be felt by the legs.
Checking the work in the screed
The second experiment was carried out by simulating a water heated floor. Three pieces of screed 35 mm thick were poured onto a concrete hollow slab. One area was without insulation, the second was using Folgoizol. This is 2 mm polyethylene foam with a foil coating. The third is with foamed polyethylene 5 mm thick. A coolant pipe is passed through all three ties. To level out the temperature difference, the speed of movement was chosen to be high, which minimized the difference.
If you look at the graphs, it turns out that the temperature of the screed with foil is 1.5 degrees higher than without it. That is, this experiment shows approximately the same difference as the previous one, but under different conditions.
conclusions
Based on these two different experiments, it turns out that practice shows: foil underfloor heating works. It’s not clear why, but the reflective layer makes a difference of about 1.5°C, which is pretty good.
To be fair, it must be said that the experiments are not entirely “clean”; there are flaws in the organization. But there are no similar refutations. Believe them or not is your business. Whether to use a foil underlay for a heated floor or not is also your choice. There are no final conclusions either in favor or in denial. So you make the decision yourself.
The only thing that is known for sure is that aluminum foil is not poured into the screed. It turns into dust in a couple of months. But foil or its spraying is more effective than lavsan spraying (also shiny). And to prevent the foil from corroding, it is protected with a layer of polymer. So if you decide to use a foil underlay for a heated floor, choose one with foil and a protective film on top of it.
So what to do?
Heat loss when heating the floor can be reduced by using insulation of appropriate thickness (50-70 mm optimal). And two millimeters of foil insulation (even if the reflection works) will not affect the picture too much. Even if you take a centimeter foil insulation. Under the weight of the screed, it is compressed into a couple of millimeters of hard polymer with fairly good thermal conductivity. So it will not be able to significantly reduce heat loss.
Don't want to warm the planet or your neighbors below? Place full-fledged normal insulation under the screed with heated floors. EPPS performs best. It needs 50-70 mm. Does the idea of reflected heat and savings due to this warm you up? Attach foil to the EPS and cover with film. The effect will be the same.
Do you need a foil backing for a film heated floor? According to the technology, it is necessary to lay a substrate under the heating film that will compensate for micro-irregularities. Ideally, a technical cork, but foamed polyethylene will also work. If you don't really need to reduce heat loss, it's not bad.
Penoplex and foam plastic
If foam plastic is used when insulating a wooden floor from below in a private house, you must take into account several rules for working with it:
- Foam absorbs water, so waterproofing is required. Many experts do not take this property into account during installation, which leads to a decrease in thermal insulation characteristics.
- It is recommended to cut the sheets not exactly to the size of the gap between the joists, but 1–2 cm smaller. This will allow you to fill the gaps between the sheet and the joist with polyurethane foam, which will increase the thermal insulation properties. The joints between the sheets also need to be foamed.
Sheets can be fastened using slats, spacer wedges or special adhesives.
Floor insulation with foam plastic in a wooden houseSource sk-amigo.ru
The principle of working with penoplex is no different. But due to the smaller thickness of the material, it can be laid with overlapping sheet joints to avoid the formation of cold islands (similar to mineral wool).
But this method significantly increases material consumption, which means additional financial costs.
Penofol
Due to its property of not allowing moisture to pass through, penofol does not require additional installation of vapor and waterproofing. But to prevent the water vapor that forms in the room from settling on the insulation layer, an air gap is needed between it and the flooring for air circulation.
Laying is done with the foil side up only. This will allow heat to be reflected, which will increase the temperature in the house. Penofol can be used as waterproofing when laying mineral wool or polystyrene foam. This can increase thermal insulation several times, but this method is quite expensive.
Penofol joints are sealed with adhesive tapeSource build.4-u.info
The material is sold in rolls and can be easily cut into pieces of the desired size. Fastening is carried out with a construction stapler on staples or with thin slats that are nailed. To improve the result, it is recommended to lay penofol in several layers.
One of the main problems of wooden houses is cold floors, which interfere with a comfortable life and increase heating costs. Proper insulation will solve this problem. Regardless of the material that is chosen for insulating the finished floor in a wooden house from below, it is necessary to strictly follow the general technology and procedure for insulation, as well as take into account the features of a particular insulation. The cost of installing insulation pays off within one season.
Types of thermal insulation with foil coating
Foamed polyethylene with a shiny coating is traditionally used as a foil backing for heated floors. It's just the most advertised. And there are much more foil thermal insulation materials. Here's what you can find on the market:
There is also construction foil, foiled craft paper, based on fiberglass mesh and fiberglass. So the choice is really wide. To create a reflective barrier on the surface of the EPS (if you want), foil paper or fiberglass (mesh) may be suitable. It makes no sense to lay thin polyethylene just because of the presence of foil. The same craft paper will be cheaper.
Insulation of walls from the inside
Insulating walls with this insulation is easy to do with your own hands. To do this you will need:
- penofol;
- thin pieces of wood for the frame;
- additional insulation for electrical wiring (if necessary);
- nails or screws, respectively, a hammer or screwdriver;
- sheathing
Step-by-step description of the process:
- At the initial stage, a frame is constructed from thin wooden blocks. In this case, a distance of 2 cm from the penofol to the surfaces should be maintained. The air layer will enhance the effect of the insulation.
- Then, using a special glue, the material is glued to the frame. Rarely, not in all cases, you can use a construction stapler for fastening. This method is possible when insulating a balcony.
- Provide additional insulation for wiring if required. And this is required in the case when the electrical wiring is laid behind the insulation, because penofol with a layer of foil conducts current well and can lead to unpleasant consequences.
- Then you need to assemble another frame, which will be about 2 cm thick. And the necessary sheathing is attached to the second frame.
Rules for laying foil backing
Foil underfloor heating can be in rolls, mats or slabs. When laying, this coating must be joined both in length and width. In order for the connections to have the same properties, the fragments are glued together with special metallized (foil) tape. You must glue carefully, avoiding gaps, try to make the fit as precise as possible, without gaps.
When laying thin rolled foil material in a screed, the strips may overlap one another. The size of this “overlap” is at least 10 cm. This joint is glued twice on one side and on the other. We make cross connections according to the same rules.
When laying mats or slabs, they are joined close to one another, then glued with the same shiny tape. Some manufacturers make a lock along the edges of the slabs, which reduces the possibility of heat leakage through the joints. Despite this, we also glue the locking joints with tape. This makes it much more reliable.
Source
Instructions for forming hydro- and vapor barriers
Waterproofing
- Mount the rough base. Carefully place a moisture barrier film on top of it.
- Lay the material in exact accordance with the contours of the insulated structure. As a result, there will be enough free space between the lags for laying insulation.
- When laying the canvas, make sure that the resulting overlap is at least 12 cm.
- Also check that the waterproofing material on the wall side reaches a height of approximately 20 cm.
- Protect the joints with reinforced tape, connecting them on both sides.
Vapor barrier
This task is performed after laying the thermal insulation layer
If mineral wool is used, it is important that there are no gaps in the cells. When laying expanded polystyrene and polystyrene foam, no reserve is left; the slabs are cut exactly to the size of the cells
After installation is completed, to increase the reliability of the insulation, the seams are filled with polyurethane foam.
Vapor barrier is performed in this way:
- install a protective membrane on top of the heat-insulating layer;
- securely attach the film along the joists and perimeter using staples;
- Attach counter slats (elements in the form of bars) along the wooden logs, which will become the basis for the floor covering;
- Attach sheet material, such as plywood, across the surface of the slats. As a finishing coating, you can use any material taking into account your own preferences, for example, linoleum, laminated flooring or parquet.
Foil insulation for floors: properties, types and how to properly insulate the floor
Floor insulation is necessary to reduce heat loss both after laying a heated floor system and during installation of the finishing coating. Now there are many types of this useful material on the market, but foil floor insulation is recognized as the leader among them. How to choose the right foil insulation? What are the nuances during installation? We will answer these questions in our article.
Foil insulation for floors
Foil insulation for floors
The variety of products in construction stores is very large and it is extremely difficult not to get confused among the entire assortment and choose a truly high-quality, effective material, the use of which will not force you to soon redo all the repairs, but, on the contrary, will give you the joy of the fact that it was carried out using high-quality materials .
What is reflective insulation
Foil insulation is a relatively new material on the market. Previously, the category of insulation for floors, walls, and roofs was represented by one single type - mineral wool, which had a lot of disadvantages. This material gets wet, and when in contact with water it loses most of its properties. At the same time, working with it was difficult due to unpleasant tactile sensations, and sometimes dangerous.
Foil insulation is a two-layer material, most often supplied in rolls, but is sometimes also found in the form of slabs. Layers are represented:
On a note! Foil insulation has special properties precisely due to the presence of a foil layer. It has the ability to reflect thermal energy and direct it inside the room, preventing it from escaping outside, strictly limiting the area of heat distribution.
Foil floor insulation consists of two layers
Also, material covered with foil does not get wet, which means it also has certain water-repellent properties, although it cannot be used as a waterproofing coating.
Depending on the type of material from which this type of insulation is made, it can be thick or thin, retain heat worse or better, have pores of different sizes, which contain air in one quantity or another.
Materials for thermal insulation work
The quality of the created thermal insulation layer depends on the technical parameters of the insulation material.
Familiarize yourself with the features of suitable materials for insulation and decide what is better to insulate the floor from below in a wooden house in your case, so that it is most profitable and effective.
Now the market offers a wide selection of thermal insulation materials, but it is recommended to choose from the best and most popular options, such as penoplex, mineral wool, penofol, expanded polystyrene.
Mineral wool
Manufacturers of building materials offer several types of mineral wool:
The advantages include a high level of heat and sound insulation, non-flammability, biological resistance, and resistance to aggressive substances.
- insufficiently high resistance to mechanical stress, this is due to the strength of the material;
- low vapor permeability;
- lack of absolute safety for human health;
- loss of thermal insulation properties due to gradual absorption of moisture.
Mineral wool can be purchased in the form of flexible mats and rigid slabs.
Attention!
When installing the slabs, one important feature should be taken into account: they must be placed with the hard side facing outwards, which is easy to identify - it is marked with a blue stripe.
Buyers mainly prefer Rockwool and Izovol, which are based on mineral wool. The first option of insulation can withstand loads, does not deform and retains heat well. In a wooden house, floor insulation with Izolon is also more preferable than with mineral wool, since this material has low thermal conductivity, it is not flammable and is more moisture resistant.
Expanded polystyrene
Are you deciding what is the best way to insulate the floor in your dacha? Consider another insulation option - expanded polystyrene, which is known to many as polystyrene foam. It’s not for nothing that it still remains popular, because there are many advantages, but the number of disadvantages is insignificant.
Properties of foil thermal insulator
Good insulation with a layer of foil has not only heat-insulating properties. It is distinguished by high levels of sound insulation, is not afraid of temperature changes, protects the room from moisture penetration, and has vapor barrier properties.
Foil insulation, especially from the category of materials made from penofol or expanded polystyrene, is resistant to mechanical stress - even heavy furniture can be placed on the floor under which such material is laid. The insulation will not lose its properties even in this case.
It is especially important to use foil insulation when installing heated floors. It will minimize heat loss, making the room warmer, and the cost of paying utility bills will be significantly reduced. The working insulating layer itself prevents cold air from outside from penetrating into the apartment, and the foil will ensure that heat is retained inside it.
Installation of penofol inside the house
At the same time, installation of foil insulation is very simple and it does not matter whether it is supplied in rolls or slabs. The material is easy to process - in order to cut a piece of a suitable size, you do not need to purchase any complex equipment. It is enough to have any cutting tool with you.
Attention! If no insulation was used during the installation of the floor covering or heated floor system, this is considered a gross mistake and a violation of the material laying technology.
What does a pie look like for a heated floor?
Advantages and disadvantages of penofol
The main advantages of the material:
- Low ability to conduct heat. The thermal conductivity index can vary between 0.039-0.051 W/(m*C).
- The vapor permeability level is 0.01 mg/(m*hour*Pa).
- The heat reflection rate can be over 97%.
- Excellent sound absorption performance.
- Penofol does not absorb moisture, the moisture absorption rate is less than 1%.
- At elevated temperatures, the material is not subject to melting (up to 1100 C).
- Differs in small sheet thickness.
- Durable, resistant to mechanical stress and has a long service life.
- Very easy to install.
- Has an affordable price.
The density of penofol can vary from 25 kg/m³ to 50 kg/m³. If penofol is used in combination with other types of insulation, its effectiveness increases significantly.
Disadvantages of a heat insulator:
- Insufficient level of rigidity. It is not possible to paste wallpaper or paint it on top of insulation boards.
- When fixing penofol, it is necessary to provide protection for the electrical wiring and you will need to beware of breakdowns.
- Low level of adhesion. In order to obtain reliable adhesion to the insulated surface, you will need to use a special adhesive mixture or use dowel-nail fastening.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of any insulation with a foil layer is its technical performance, which is significantly increased compared to similar materials, but without a foil layer. However, due to additional production costs and complicated technology, such a heat insulator is more expensive. In general, foil insulation has a lot of positive qualities.
Insulation with foil is significantly superior to conventional heat insulators
Pros and cons of foil insulation
The disadvantages of the material include softness, which prevents the use of foil insulation when laying some soft types of floor coverings, as well as high cost compared to ordinary thermal insulation materials.
When to do bottom insulation correctly
Above a cold basement, it is better to insulate the floor from below, while insulation above the attic is recommended to be done from above. This approach is technically competent and allows you to achieve the best results. But when implementing thermal insulation from below, some problems sometimes arise:
- limited choice of materials;
- unreliable fixation of insulation;
- due to the fact that installation work is carried out on the ceiling, the craftsmen quickly get tired;
- the difficulty of implementing the assigned tasks in low-level conditions.
How and where to use insulation with foil
Foil insulation can be used on almost all surfaces of the room, depending on its purpose. They are used for laying walls, roofs, ceilings and floors.
On a note! Foil insulation for floors is indispensable in rooms located on the first floors.
Where can foil insulation be used:
Using foil insulation in a bathhouse
In general, the type and method of using foil insulation depends on the room in which the repair work is being carried out, as well as on the purpose of this room, the properties and microclimate of the building, etc.
What to glue it with?
A correctly selected adhesive solution for foil material does not yet guarantee a successful installation. For a quality connection of materials, it is necessary that the surface to be glued be carefully prepared. All defects, irregularities, and various debris must be eliminated.
Concrete floors and walls are leveled, cracks are sealed, and metal products are treated with an anti-corrosion agent.
Adhesive for foil insulation can be either specialized or universal. You can also use liquid nails, double-sided tape, or a thin layer of foam. The choice of glue depends entirely on the purpose of the surface and its further use.
The adhesive composition must correspond to the performance indicators of the insulating material:
- permission for indoor use;
- the toxicity of the solution should be 0;
- high resistance to adhesion;
- the glue must withstand temperatures in the range of -60 to +100 degrees.
In order for penofol to be reliably glued to the surface, the glue must be applied to the side that does not have a foil layer. The adhesive solution is applied evenly, without gaps. The edges of the panel are carefully coated with glue so that the foil material does not come off during operation.
Before you start fixing the penofol, you need to wait 5-60 seconds for the glue to dry slightly. This ensures better adhesion to the products. Penofol is pressed to the surface, holding it, and smoothed out with special care.
Types of foil insulation
In general terms, it is clear what properties a heat insulator with foil has, however, depending on the type of material, they may differ slightly.
Expanded polystyrene
It is a rather voluminous and thick sheet of material with a layer of foil on one of the surfaces. It is produced using complex technology, during which individual polystyrene granules are fused into a single whole. As a rule, it is installed where there is high humidity and significant mechanical impacts on the floor covering are possible. Most often - when installing a water heating system.
Polyethylene foam
Rolled material with a thin aluminum coating on one or both sides. The thickness of the heat insulator varies from 2 to 10 mm. It is usually used to insulate floors and walls, sewers or ventilation shafts. Interestingly, foamed polyethylene is also used in the shoe industry - insoles are made from it.
Foamed polyethylene foil
Foiled polyethylene foam includes penofol, ecofol, isolon and other materials.
Most often, penofol (ethylene foam) is used for installing floors. This material, depending on its qualities and characteristics, can be divided into 4 types:
Penofol can be of several types
On a note! A good insulation material is polypropylene film, which has metal inclusions, due to which heat is evenly distributed over the entire surface of the floor and is retained for a long time.
The material is self-adhesive. Peel off the film
Mineral wool
A type of insulation familiar to many. Mineral wool with foil is sold in the form of rolls or slabs and is usually used for thermal insulation of roofs, floors in bathhouses and on loggias or balconies. The foil layer is applied only to one side of the material. The thickness of mineral wool can vary from 5 to 10 cm. The base is a basalt slab or fiberglass. When installing even in non-residential premises or outside the house, it is recommended to cover it with film.
The material is far from safe for health, and it is not worth using such insulation in an apartment. It can cause the development of respiratory tract diseases, as it releases a dangerous substance – phenol – into the air.
Basalt insulation
This type of insulation belongs to the category of materials based on mineral wool. It is used in the construction of stoves and fireplaces due to its non-flammability. Used for thermal insulation of walls and roofs, floors between floors.
How to style
When faced with an unusual underlay, many buyers do not know how to put the underlay under foil laminate flooring. They also don’t have an answer to the question of which side to put the foil backing on. Foamed polyethylene is cut to size and left rolled out for a day.
Then the first sheet is laid, with the obligatory approach to the walls at the points of contact. The height of the overlap is 5-10 cm (if the substrate is visible above the floor, it is carefully cut off with a construction knife and covered with a plinth). Be sure to lay the foil side up.
Since it is strictly forbidden to walk on the foil, the laminate is installed on the laid sheet. Then the second sheet is rolled out, touching the walls at the beginning and end, and end-to-end with the first sheet. The seam is glued with a special metallized tape.
The sheet substrate is laid in the same way as brickwork is laid - the connecting seams should not coincide. Wall climbing is not allowed. The sheets are laid close to each other. The seams are sealed. Just as with polyethylene underlayment, a row of underlayment is laid down and slats are placed on top of it.
During work the following must not be allowed:
- coincidence of the seams of the substrate with the locks of the laminate;
- creasing of material when applying to the wall;
- gaps between laid canvases or substrate slabs;
- gluing metallized tape together.
In addition to laminate, such a substrate is also used for linoleum. And here many novice builders have the desire to make a sandwich: floor base-foil backing-chipboard-linoleum. They are driven by the desire to provide water and sound insulation, as well as dampen floor vibration when walking.
So how to put a backing with foil under the chipboard? No way. If the subfloor is wooden, then when attaching the chipboard to the base with self-tapping screws, the foil will be torn, and the point of laying such a substrate is lost.
On a concrete base, chipboard falls between two layers that do not allow steam to pass through: foil on the bottom, linoleum rubber on top, which is extremely undesirable. Practice shows that chipboard very often swells in such a situation.
There is another problem here: chipboard raises the floor, which does not always match the floor level in other rooms. Here it is better not to use additional layers of material at all, but to put a backing on the screed, and linoleum on top of it.
The foil backing for linoleum does not lie under the chipboard, but on the chipboard. In this case, it performs all the functions that are inherent in this type of material (details about the functions of the substrate can be found in the work “Which substrate to choose for laminate”).
For reference: if instead of chipboard you have to install plywood, then everything said for the first material also applies to it.
Nuances of fastening and installation
When laying foil insulation, you may need the following tools and materials:
When installing insulation with foil, it is important to avoid the mistake of laying the material with the shiny side down. In this case, the material will not perform its heat-reflecting functions. The foil side must “look” into the room in order to be able to return thermal energy to the room.
An example of laying lag on foil insulation
Advice! You can leave a small air gap between the insulation and the floor covering. Then the floors will be even warmer.
It is also important to remember that the insulation does not overlap. The sheets should be placed end to end and secured with tape or nails, depending on the type of base. Insulation with an adhesive layer may not be additionally fixed, but it is still recommended to secure it with fastening materials. All joints after laying the material are taped.
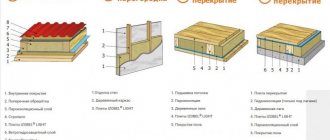
Thermal insulation for heated floors
Work on laying insulation can be dry or wet. In the second case, the material will be filled with concrete screed. In the first one, it is advisable to install an additional waterproofing layer.
Recommendations and common mistakes
The main mistake that all beginners make is when trying to tightly tie penofol and screed. Concrete will certainly shrink, as a result of which part of the foil may be damaged. Therefore, the contact surface between concrete and penofol is often additionally covered with film. In this case, even with repeated heating and cooling of the thermal insulation, the penofol does not wrinkle, and the floor remains intact.
Gas in the open pores of penofol can cause cracks.
The second serious mistake is related to the use of nails and screws. With their help it is convenient to attach logs, but you cannot pierce the foam foam sheet. Under load, the self-tapping screw can work like a knife, and over time, part of the insulation will be shredded into noodles. You just need to glue or secure with tape.
Roll material laying technology
Step 1. The material produced in a roll must be laid on a surface cleared of debris. The base is swept, washed if necessary and dried.
Step 2. The insulation is cut into pieces of the required length and size.
Cutting foil insulation
Step 3. The material is leveled over the surface of the room.
The insulation is leveled over the surface
Another photo of the process
Step 4. In small rooms, the insulation is attached along the walls and across with wooden blocks. Its individual sheets are glued together with tape.
The insulation is attached using bars
The process of installing bars
Step 5. If the floor covering allows it (it is quite dense), then lathing is done on top of the laid insulation. This makes it possible to create an air gap.
Next, the floor is covered with a finishing coating or filled with concrete screed; work is also carried out on the installation of heated floors, if necessary.
Warm floors are a serious cost item during renovation, so it is important to accurately calculate how much and what materials will be needed. To ease your labor costs, we have prepared special instructions telling you how to calculate a heated floor - water or electric. Online calculators included. And in the article “ What do you need for a heated floor? » you will find a complete list of everything that may be needed during installation.
Video - Laying roll backing
Insulation with a layer of foil is a good option for high-quality thermal insulation material. It will serve for many years if you choose it correctly in accordance with operating conditions, as well as with proper installation. It’s easy to avoid mistakes; the main thing is to carefully familiarize yourself with all the nuances of using the material.
For purely practical reasons, and also as an example of the effectiveness of using foil insulation, especially when combined with other thermal insulation material, below is a calculator for calculating the insulation of a balcony. Since it makes no sense to consider the floor on a balcony or loggia separately, the calculator allows you to make calculations for the entire room, for each of the surfaces that require thermal insulation.
Brief explanations on how to use the program will be given below.
Laying on a wooden floor
When insulating wooden floors, proceed as follows:
- Before starting work, carefully inspect all floorboards, then replace any that have been damaged by time.
- Unfold the roll and glue it with the adhesive side down. If such a layer is not found, you will have to buy suitable glue.
- Assemble and place a sheathing over the insulation, which will create a small gap between the foil layer and the covering.
- Fix the chipboard or hardboard using lag.
- Lay your chosen covering on top.
You can place insulation inside a wooden house under the boards. To do this, you must first remove the old coating.