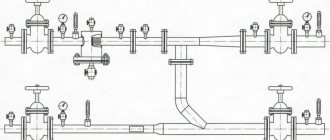
Since competition in the domestic market is growing every day, manufacturers are forced to pay attention to all cost items. If you look at this list, the cost of heating various industrial premises will be far from the last position. Since the cost of energy resources has increased, their percentage of cost has also increased.
Air heating of production premises
If earlier such a question as choosing the most economical option was not yet so pressing, now it is positioned in the category of the most relevant. Air heating of a production facility in such a situation is often considered as the most effective and at the same time the most economical option.
Infrared heating
If it is not possible to install liquid or air heating, or in the case when these types of systems do not suit the owners of industrial buildings, infrared heaters come to the rescue.
The principle of operation is described quite simply: an IR emitter generates thermal energy directed at a specific area, as a result of which this energy is transferred to objects located in this area. In general, such installations allow you to create a mini-sun in the work area. Infrared heaters are good because they heat only the area they are directed at and do not allow the heat to dissipate throughout the entire room.
When classifying IR heaters, the method of installation is first considered:
Infrared heaters also differ in the type of waves emitted:
- shortwave;
- medium wave;
- light (such models have a high operating temperature, so they glow during operation;
- long wave;
- dark.
IR heaters can be divided into types according to the energy resources used:
- electrical;
- gas;
- diesel
IR systems running on gas or diesel have much greater efficiency, making them much cheaper. But such devices negatively affect indoor air humidity and burn oxygen.
There is a classification according to the type of work item:
- halogen: heating is carried out by a fragile vacuum tube, which is very easy to damage;
- carbon: the heating element is carbon fiber hidden in a glass tube, which is also not very durable. Carbon heaters consume approximately 2-3 times less energy;
- Tenovye;
- ceramic: heating is carried out by ceramic tiles, which are combined into one system.
Infrared heaters are well suited for use in all types of buildings, from private homes to bulky industrial buildings. The convenience of using such heating lies in the fact that these structures are able to heat individual zones or areas, which makes them incredibly comfortable.
IR heaters affect any objects, but do not affect the air and do not affect the movement of air masses, which eliminates the possibility of drafts and other negative factors that can affect the health of personnel.
In terms of warming up speed, infrared emitters can be called leaders: they must be started while at the workplace, and there is almost no need to wait for heat. Such devices are very economical and have very high efficiency, which allows them to be used as the main heating of production workshops. IR heaters are reliable, capable of operating for a long period of time, take up virtually no usable space, are lightweight and require no effort during installation. In the photo you can see different types of infrared emitters.
This article discussed the main types of heating for industrial buildings. Before installing any selected system, it is necessary to calculate the heating of industrial premises. Making the choice always falls on the owner of the building, and knowledge of the above tips and recommendations for calculating room heating will allow you to choose a truly suitable heating system option.
Air circulation methods
The operating principle of the equipment depends on the organization of air exchange. The main methods of air circulation are natural and forced. Let's talk about each of them in more detail.
Natural
Air circulation can be carried out naturally or using fans. With the natural method, air masses, due to their lighter weight, rise upward and enter the room through air ducts located under the ceiling. The air speed is low: the room is heated slowly.
Forced
Forced circulation is much more effective. Fans accelerate the movement of air through the channels. The heating speed is controlled by the rotation speed of the fan blades.
Central water heating
In the case of a central heating system, heat production will be provided by a local boiler house or a single system that will be installed in the building. The design of this system includes a boiler, heating devices and piping.
The operating principle of such a system is as follows: the liquid is heated in the boiler, after which it is distributed through pipes to all heating devices. Liquid heating can be single-pipe or double-pipe. In the first case, temperature control is not carried out, but in the case of two-pipe heating, the temperature regime can be adjusted using thermostats and radiators installed in parallel.
The boiler is the central element of a water heating system. It can run on gas, liquid fuel, solid fuel, electricity or a combination of these types of energy resources. When choosing a boiler, you must first take into account the availability of one or another type of fuel. For example, the ability to use mains gas allows you to immediately connect to this system
At the same time, you need to take into account the cost of the energy resource: gas reserves are not unlimited, so its price will increase every year. In addition, gas pipelines are very susceptible to accidents that will negatively affect the production process
Using a liquid fuel boiler also has its pitfalls: to store liquid fuel, you need to have a separate tank and constantly replenish the reserves in it - and this is an additional expense of time, effort and finance. Solid fuel boilers are generally not recommended for heating industrial buildings, except in cases where the building area is small.
True, there are automated versions of boilers that are capable of independently taking fuel, and in this case the temperature is adjusted automatically, but maintenance of such systems cannot be called simple. For different models of solid fuel boilers, different types of raw materials are used: pellets, sawdust or firewood. A positive quality of such structures is the low cost of installation and resources.
Electric heating systems are also poorly suited for heating industrial buildings: despite their high efficiency, these systems use too much energy, which will greatly affect the economic side of the issue. Of course, for heating buildings up to 70 sq.m. Electrical systems are fine, but you need to understand that electricity also tends to go out regularly.
But what you can really pay attention to is combined heating systems. Such designs can have good performance and high reliability.
A significant advantage over other types of heating in this case is the possibility of uninterrupted heating of an industrial building. Of course, the cost of such devices is usually high, but in return you can get a reliable system that will provide the building with heat in any situation.
Combined heating systems usually have several types of burners built in, which allow the use of different types of raw materials.
It is by the type and purpose of the burners that the following designs are classified:
- gas-wood boilers: equipped with two burners, they allow you not to worry about rising fuel prices and problems with the gas supply line;
- gas-diesel boilers: demonstrate high efficiency and work very well with large areas;
- gas-diesel-wood boilers: extremely reliable and can be used in any situation, but power and efficiency leave much to be desired;
- gas-diesel-electricity: a very reliable option with good power;
- gas-diesel-wood-electricity: combines all types of energy resources, allows you to control fuel consumption in the system, has a wide range of settings and adjustments, is suitable in any situation, requires a large area.
The boiler, although it is the main element of the heating system, cannot independently provide heating to the building. Can a water heating system provide the necessary heating for a building? The heat capacity of water is much higher when compared with the heat capacity of air.
This suggests that the pipeline can be much smaller than in the case of air heating, which indicates better efficiency. In addition, a water system makes it possible to control the temperature in the system: for example, setting the heating at night at 10 degrees Celsius can significantly save resources. More accurate figures can be obtained by calculating the heating of industrial premises.
Requirements for heating industrial premises
At low temperatures, heating of production premises, as required by labor protection, should be carried out in cases where the time workers spend there exceeds 2 hours. The only exceptions are premises in which permanent presence of people is not necessary (for example, rarely visited warehouses). Also, structures are not heated, being inside of which is equivalent to carrying out work outside the building. However, even here it is necessary to provide for the presence of special devices for heating workers.
Occupational safety imposes a number of sanitary and hygienic requirements for heating industrial premises:
- heating indoor air to a comfortable temperature;
- the ability to regulate the temperature due to the amount of heat generated;
- inadmissibility of air pollution with harmful gases and unpleasant odors (especially for stove heating of industrial premises);
- the desirability of combining the heating process with ventilation;
- ensuring fire and explosion safety;
- reliability of the heating system during operation and ease of repair.
During non-working hours, the temperature in heated rooms may be reduced, but not below +5 °C. At the same time, industrial heating must have sufficient power to restore normal temperature conditions by the start of the work shift.
Types of air heating
There are two fundamentally different schemes for this type of heating
Air heating combined with ventilation
Heated air is transferred using elements of supply and exhaust ventilation. In this case, the operating parameter is not only the room temperature, but also the specified air exchange rate.
Heat is generated using boilers or gas heat generators. A system of air ducts is connected to them, through which warm air is distributed throughout all areas of the heated premises. The system can be supplemented with filtration, a humidifier, and a recuperator.
Air heating by heat generators
3.1. Principle of operation
Heat generators are located inside or outside the room. The required power is determined based on the total heat loss of the building, which must be balanced by the supply of hot air.
Air masses are heated by the combustion of liquid fuel or natural gas. Combustion products that have a high temperature pass through the heat exchanger and give off heat to it, which heats the air sent into the room. Warm air flow is distributed through air ducts.
3.2. Areas of application
Heat generators provide warm air in volumes of up to several thousand cubic meters per hour. Therefore, their use is most effective and economically justified for heating large areas or several rooms at once.
Heating using heat generators is suitable for:
- office premises;
- construction sites;
- warehouse and production facilities;
- auto repair shops;
- agricultural objects.
The range of thermal powers of heat generators is wide - from 10 to 1000 kW. Thanks to various designs, the installations can be placed on internal walls, under the ceiling, on the floor, as well as outside - on the roof of a building or next to a heated room.
3.3. Safety
To ensure safe operation, installation of heat generators and their connection is carried out by specialists of our company in strict accordance with the requirements of SP 60.13330.2012.
To use gas installations, it is necessary to obtain a permit and develop a design for connecting to a common input into the main pipeline with distribution throughout the building in compliance with technical conditions and current standards. When using liquid fuel heat generators, fire safety regulations must be observed.
Why do you need heating?
It takes a lot of time and effort to create a heating circuit for a specific industrial building. After all, each of these places is individual. It has its own purpose and dimensions. High ceilings, various machines, shelving and electronics can complicate pipe installation
And yet, why is it so important:
- If your heating system is well thought out and designed to create the most comfortable working environment possible, employee uptime and productivity will increase.
- The equipment will also be operated in favorable conditions, which will protect against breakdowns. Due to hypothermia, mechanical and electrical devices fail.
- Heating will ensure the safety of products. Products suffer from hypothermia no less than people or electronics.
Entrepreneurs are stopped by the high cost of heating installation and maintenance. But if you choose a simple, reliable heating scheme designed for your industrial area, the costs will be low, and the benefits of use will more than cover them.
Advantages and disadvantages
The air heating method has undeniable advantages:
- The efficiency reaches 93%. When organizing heating, the installation of intermediate heating devices is not required.
- Heating systems of this type can be fully integrated with ventilation systems. This allows you to constantly maintain an optimal microclimate inside production complexes.
- Very low level of inertia. Immediately after activating the equipment, the air temperature in the room begins to rise.
- High efficiency has a positive effect on the economic performance of production and reduction in production costs.
Along with this, air heating also has obvious disadvantages:
- Constant technical maintenance of the active elements of the system is required. It is quite difficult to modernize already operating installations.
- To avoid interruptions in heat supply, a backup power source is required.
Water heating of industrial facilities
Water heating is appropriate if you have your own boiler room nearby or if there is a central water supply. The main component in this case will be an industrial heating boiler, which can run on gas, electricity or solid fuel.
Water will be supplied under high pressure and temperature. Usually, it cannot be used to efficiently heat large workshops, which is why the method is called “on-duty”. But there are a number of advantages:
- air circulates calmly throughout the room;
- heat spreads evenly;
- a person can work actively in conditions with water heating, it is absolutely safe.
The heated air enters the room, where it mixes with the environment and the temperature is balanced. Sometimes you need to reduce energy costs. To do this, using filters, the air is purified and reused for heating industrial buildings.
Air heating systems
Such heating can be done either local or centralized; and it is distinguished by the following features:
- air masses are constantly in motion;
- the air is regularly changed and cleaned;
- the temperature is more evenly distributed throughout the rooms;
- harmless to humans.
The heated air enters the workshop through air ducts, where it is mixed with the existing air. Moreover, most of it then passes through special filters, is heated again and used. Thus, energy losses are minimized. In addition, such a system provides air supply from outside, which already meets sanitary standards. However, if during the production process some harmful substances are released into the atmosphere, then such a recycling system is unlikely to be effective and safe. In this case, you will have to completely remove all the air coming out.
Note that when using local air heating, the heat source is located in the center of the building. The latter is usually taken as VOA, heat guns and the like. However, only the air inside can be processed in this way, and fresh air masses will not be supplied.
Airborne solar collector
Local heating scheme
When the area of the heating system extends to just one room in which the heat center itself is located, the scheme is called a local air heating scheme for industrial premises. The calculation and selection of the scheme are made depending on the specifics of the production facility and taking into account a number of operational requirements.
Central heating circuit
Another name for this scheme is channel. Its meaning is that the air is heated to the required temperature in the thermal center, and then supplied to the premises through air ducts. The thermal installation can be placed both inside the building and outside.
Heating systems built according to the central type, in turn, can be recirculation, direct-flow, or partially recirculation.
Recirculation system. Requires relatively low initial costs, operating costs are also low.
Partial recirculation system. It is a more flexible system, implemented due to mechanical impulses of air movement. It is capable of operating in different modes: with partial or complete air replacement. Can work in combination with ventilation units.
Direct flow system. The use of such a system is relevant for rooms in which explosive, toxic or fire hazardous substances are released - in cases where the penetration of these substances into other rooms is unacceptable.
Features of industrial heating
- Firstly, most often we are talking about work on energy-intensive Objects of a fairly large area, and there is a requirement for heating systems (as well as for all other auxiliary) systems to achieve the maximum possible energy savings. It is this factor that is put at the forefront
- In addition, often in heated rooms there are non-standard conditions in terms of temperature, humidity, and dust. Therefore, the thermal equipment and materials used must be resistant to such adverse effects.
- A number of Facilities may use flammable and explosive substances, and, based on this, the installed system must meet strict explosion and fire safety requirements
- Another important difference between the systems under consideration is, as a rule, their large total power. It can reach hundreds of megawatts. Therefore, boilers used to heat homes are often not suitable for the scale considered. The use of cascades from domestic boilers is simply becoming economically infeasible
- In addition, heating of industrial buildings is often designed and installed in a single complex with climate control systems. This makes it possible to heat industrial premises with large areas and at the same time save resources and the space occupied by highways. First of all, this method is used when organizing air heating
- The next feature that industrial heating of a building has is its “unconventionality”. There are certain standard solutions on the basis of which heating of a country house is carried out. These solutions can be applied with minor nuances almost everywhere and always. Technical solutions for large-scale Objects are much more diverse. The art of engineering in this segment lies in selecting the optimal technical solution. Before the start of the design stage, the most important step will be the competent preparation of the Technical Specifications. And when heating installations for industrial facilities take place, the Technical Specifications drawn up by qualified designers and engineers will help optimize the installation process. Designers carry out various engineering calculations. Based on an individually selected engineering solution, the most effective method of heating the Object in question is determined
- Often, when it comes to production, technological equipment is located at the Facility - machines, conveyors, production lines. Also, perhaps, the people working on it. This needs to be taken into account
- As a rule, uniform distribution of heat is necessary unless the project involves the creation of zones with a special temperature regime. By the way, the presence of such zones is also a feature that must be taken into account when organizing heating of industrial buildings
- As already mentioned, the traditional method for heating housing (in particular, cottages) using a household boiler and radiators is, as a rule, ineffective under the conditions under consideration. For this reason, industrial heating systems are built according to different principles. Recently, these are most often autonomous systems of the scale of the Object, and sometimes of its individual parts. Autonomous heating is easier to control than centralized heating (through CHP) due to the ability to control and regulate the consumption of fuel resources
- There are also some peculiarities at the operational stage. In the residential sector, the level of service of the heating system is often not professional enough. If heating is installed in a building for industrial purposes, then, as a rule, you can be sure that technical service will be carried out by a qualified team (most often, this is the service of the chief power engineer or a staff department of the enterprise with similar functions). On the one hand, this somewhat eases the responsibility of the installation organization. Most likely, after the facility is put into operation, no one will deal with “little things.” On the other hand, the requirements for the composition and level of writing of executive documentation are increasing. Operations service employees, being professionals, know well what exactly it should include and how to compile it. All necessary licenses, certificates, permits, equipment passports, and work completion certificates must be provided. Only after this the system will be put into operation
Use of automation in the heating system of workshops
Most companies strive to automate work and system management. However, certain problems arise along the way, since the heating network is quite large and has a complex structure.
Which functions can be set to automatic mode:
- Notification of accidents and other emergencies
- Maintaining the same temperature according to the set value
- During an emergency, the system will automatically switch on a new operating mode
- If this is not possible, a complete power outage will occur.
Of course, the main priority at the enterprise is the precise and efficient operation of the automatic heating system. There is no need to skimp on equipment and materials. In addition, when choosing a contractor and other project participants, it is necessary to carefully check their experience and qualifications. Otherwise, the consequences may be unpredictable and very sad.
Radiant or convective heating
In traditional heating systems, it is considered normal when the air temperature near the ceiling is significantly higher than near the floor. This is due to objective physical laws - the density of heated air is less, which is why it rises. As a result of these processes, an uneven temperature distribution along the height is formed. And the most unpleasant thing is that the warm layers remain inaccessible to humans.
In addition, unused thermal energy is lost through the ceiling structures. That is why when designing air, steam or water heating, the height of the premises must be taken into account. Depending on this value, the power of the heating equipment is selected. The higher the ceilings, the higher the capacity you need to buy a boiler.
Radiant heating systems in industrial buildings with high ceilings look much more preferable. IR rays are directed to the lower zones and transfer thermal energy to the surface rather than to the air. Thanks to this, there is no need to purchase expensive powerful equipment. Heat losses are also reduced, since heated air does not accumulate near the ceiling.
The air temperature in the building itself is slightly lower than generally accepted, but the working staff do not experience any discomfort. The high temperature of working surfaces (table, machine, tool, etc.), even in relatively cold rooms, has a beneficial effect on the productivity of enterprise employees. Radiant heat generators do not require a coolant and transfer the generated energy directly to the object.
Design
There are many different ways to heat a production facility, with different heat sources and methods of supply. The main sources are hot water boilers, but heat can be generated in many other ways, such as using ground heat. There are also many solutions for supplying heat to a room; in principle, heat transfer is carried out in three ways: convection, radiation and thermal conductivity; all heating devices transfer heat in all three ways. The main difference is the percentage of heat transfer in one way or another, for example, radiators heat the room mainly by radiation, but there is also heat transfer from the surface of the radiator to the air and convective currents around the heated surface.
Design of water radiator heating in the workshop
The most traditional and often found in the workshop is water heating based on radiators or registers made of smooth pipes. In workshops with high humidity, in workshops with the release of various oils, in paint shops and other rooms with active release of pollutants, even if there is exhaust ventilation in the workshop, registers are still designed from smooth pipes. In relatively clean workshops, warehouses, and hangars, conventional radiators can be used. The advantages of this scheme are simplicity and reliability, the system is simple, access to all elements of the system is simple and cleaning or repair does not cause any difficulties. Among the disadvantages, it can be noted that in workshops with high ceilings the system is not very effective, since all the heat rises upward.
Design of air heating in the workshop
Air heating is most often used to heat the workshop using fan heaters, less often using an air-conditioning unit or roof top. The advantage of air heating based on a fan heater is a more uniform temperature distribution, since the fan has a high flow rate, thanks to which it actively mixes all the air in the room. Another advantage is lower capital costs, because the fan heater has a fairly high performance and, accordingly, fewer of them are needed to supply the required heat. Since the quantity is smaller, the hydraulic circuit is simpler and not so highly branched.
Designing an infrared heating system in a workshop
Infrared heating systems are often designed in workshops where there is no need to heat the entire volume of the room, but there are personnel working in certain permanent places. Specialists from our design institute for climate systems recommend installing infrared panels above workplaces, the coolant of which can be gas, water or electricity. The main feature is that the panel does not heat the air, but the surface over which it is installed, while the workplace is heated and the staff can work calmly. In this way, the entire workshop can be heated; in each specific case, it is necessary to calculate operating and capital costs.
Air heating installation
Heating of production workshops
Having a clear plan for the location of components and assemblies of the system, it is very easy to carry out installation work by the company’s employees. However, if you wish, you can contact specialized companies
When installing it yourself, first of all, you need to pay attention to the completeness of the delivery. Manufacturers supply air ducts, dampers, inserts and other standard elements to order
In addition, you can additionally purchase the following materials:
- flexible lines
- aluminum tape
- insulation and mounting tape
Insulating some areas is very important because it helps prevent condensation. For this purpose, a layer of foil insulation on a self-adhesive base is laid on top of the pipeline walls.
Its thickness may vary. The most in demand are materials with a thickness of 3-5 millimeters.
Depending on the geometry of the premises and the design solution, rigid or flexible lines are installed. Individual sections are connected to each other using reinforced tape, plastic or metal clamps. All installation work boils down to performing the following set of actions:
- installation of warm air supply lines
- installation of distribution sockets
- installation of a heat generating unit
- laying a thermal insulation layer
- installation of additional equipment
Air heating in warehouses. production and utility rooms is a complete heat supply system. It is characterized by efficiency and high efficiency.
How to organize production heating
If the height of the premises does not exceed 6 m, then the heating ceiling is installed immediately. Most often, such buildings have concrete floors, so wooden sheathing will be required. Also, do not forget about thermal insulation. For this purpose, you can use any construction insulation (for example, expanded polystyrene with a thickness of 100–150 mm).
The owner should also take care of the quality of the enclosing structures. The presence of numerous cracks, crevices and voids, constant drafts, etc. will lead to significant heat loss, as a result of which either the heating ceiling system will not cope with the task, or heating the production will be extremely expensive due to increased energy consumption.
What to do if the ceiling height is higher than permissible? In this case there is also a solution.
This may be equipment for a rough ceiling in the form of a suspended structure. Some of our customers lowered the ceiling from 12 to 5 meters using cable braces.
h1 - 6.9 m. h2 - 5.0 m. 1 - Ceiling slabs. 2 — Cable stretchers. 3 - Wooden sheathing. 4 - Expanded polystyrene 100 mm. 5 - Folgoizolon. 6 — High-power film electric heaters.
And a heating ceiling was installed on the resulting structure with wooden lathing.
If reducing the ceiling height is unacceptable, then you can use high-temperature infrared heaters; they work well at a height of up to 10 m.
Average energy consumption of film electric heaters
The allocated power of the electrical network is of great importance when heating production. For heating alone, about 12 kW is needed for every 100 m², so it is important to correctly calculate the energy consumption.
What is the average energy consumption in a particular production facility if a heated ceiling is installed there?
The energy consumption of any heating system, including film electric heaters, directly depends on the level of thermal insulation of the building envelope. With minimal heat loss, the system only maintains the set parameters, that is, it turns on less often and for a shorter time. Industrial buildings are most often made of concrete or brick and are not insulated in any way. With high heat losses, heating production will require 30–40 W/m² of heated area per hour. For smaller heat losses, for example heating a frame house, no more than 12–18 W/m² of heated area is required, because in it the level of insulation of enclosing structures is an order of magnitude higher than that of industrial premises.
Industrial heatingcolor
Industrial heating is a system of measures aimed at creating favorable conditions for production activities. The main task of industrial heating is to maintain a comfortable temperature in the workplace, which, as a rule, helps to increase labor productivity. Maintaining an optimal temperature is also necessary to protect equipment from sudden changes in heat, which can lead to failure of machines and equipment, which leads to unnecessary financial costs for their repair or replacement. The management, which has set the task of organizing industrial heating, faces complex issues that need to be resolved in the most optimal way. The problem immediately arises of how to achieve this goal while spending a minimum amount of money. First of all, the entrepreneur must take into account the climatic features of the area where industrial heating is required. For the regions of Moscow or St. Petersburg, these will be the same conditions with the typical climate for this area; for Tyumen or Yakutia, completely different conditions due to severe frosts and winds in winter. All these features are taken into account in the color>questionnaire for calculating heat losses in production presented on the website.
Heating systems producedcolor>
Industrial heating systems are technical means that make it possible to create acceptable climatic conditions in workplaces for production activities. The most common heating systems today are infrared, air and water. The last two belong to central systems that provide heat from heating plants. With an air-based industrial heating system in a workshop area, air ducts are installed through which warm air is supplied from a heat generator located outside the production facility. The efficiency factor (COP) of this heating method reaches about 50%. Water, unlike air, has its advantages and disadvantages. Since the heat capacity of water is significantly higher than the heat capacity of air, its consumption for heating the same room will be much less, and therefore the coolant delivery system is much less than that of air. At the same time, the water heating system has great inertia due to the fact that heating water takes much longer than air. This significantly increases the time required to warm the room to the desired temperature. The main disadvantage of these industrial heating systems for enterprises is the presence of a significant amount of additional equipment (heat generators), bulky supply systems that ensure the delivery of heat to the heated object, large heat losses along the route, and low efficiency.
Infrared heating systemscolor> are devoid of all the disadvantages inherent in the above methods. There is an opportunity to significantly free up the workspace from unnecessary bulky heat management of production areas that take up a lot of space and to deploy on it the production of additional products manufactured by the enterprise. At the same time, the efficiency of this heating system is about 70 - 90%, depending on the method of using infrared heating, which also provides serious savings in money and ultimately allows you to reduce the cost of the final product. The absence of expensive supply systems and heat losses along the route also reduces operating costs for industrial heating, which in turn makes it possible to additionally provide heat to new jobs. The customer, as a rule, chooses which industrial heating system to use at a given enterprise. But at the same time, it is necessary to take into account all the features inherent in one or another method of coolant delivery and its efficiency, depending on the current conditions and prices on the market.
Heating options for spacious non-residential buildings
To heat large areas, three main types of systems are usually used:
- water;
- air;
- radiant.
Water heating refers to systems using radiators. They are beneficial due to the wide selection of heating devices. But at the same time, many premises owners are not satisfied with the irrational use of space, high costs and energy consumption, and high thermal inertia. The systems are not suitable for many retail outlets and warehouses, because... radiators take up space near the walls, where it is convenient to place shelving. Air and radiant heating are more popular, so we will consider their arrangement in detail.
Heating with infrared heaterscolor
Heating with infrared heaters
- one of the many heating options that uses infrared radiation as a heat generator.color>
The properties of infrared radiation to transfer heat over long distances make it possible to develop and use economical heating systems used to maintain comfortable heat in work areas. Infrared heating electriccolor> allows you to heat people in the workplace using infrared heat supplied in the form of a stream of radiant energy. At the same time, in contrast to convection heating, bodies and objects located in the path of propagation of the infrared ray that accumulate heat are first heated; the air is heated secondarily from the heated bodies. This eliminates excess transfer coolant (air), which provides additional savings. A worker who is at work in a local heating zone of infrared radiation receives heat both from the heater itself and from the partially reflected radiation of the rest of the heated surface (floor, equipment, etc.). Infrared heat has a positive effect on humans, it allows you to feel great at fairly low temperatures in the air around you. The thermal sensations of a person located in the operating zone of an infrared heater are 1 - 2 degrees higher than with conventional heating, which allows the temperature in the local area to be reduced to +15 ° C and the worker will feel comfortable. Reducing the temperature by one degree allows you to save up to 5% of the electricity used for heating production. Since people (equipment) receive heat primarily, and the air secondary, the gradient of the temperature difference between the working area and the ceiling (12 meters) will be about 3 - 4 degrees, that is, at the level of the ceiling space the air temperature will be about 19 - 20 ° C , which will significantly reduce heat losses due to the thermal conductivity of the room. Using infrared heaters for heating production, it is possible to organize local heating of workplaces, which is impossible to do with conventional heating. In this case, only the space where the person is is heated and a comfortable temperature for him will be maintained, the rest of the room is heated to a temperature 3 - 5 ° C lower due to convection of heated air and secondary radiation from walls and equipment. During an employee’s absence from the workplace, infrared heating can be completely or partially turned off, which will reduce the temperature in the production room to 5 - 10 ° C, resulting in additional savings in electricity supplied for heating production. Due to the fact that this type of heater enters operating mode within five minutes, a comfortable temperature will be achieved in 30 - 60 minutes, that is, heating can be turned on at full power an hour before the start of the work shift. The costs of introducing industrial heating with infrared heaters are significantly lower than when laying expensive heating mains or gas pipelines, this is due to the fact that the workshop usually has excess electricity capacity and redistributing electrical networks will not be difficult.
Implementation of heat exchange
The transfer of thermal energy from one medium to another occurs in a heat exchanger. There is no mixing of air media. Combustion products are discharged outside the building through an air duct.
Supply
In this case, the heating process is implemented as follows:
- The coolant is prepared in a heat generator.
- The heated liquid is transported to the heat exchanger.
- Electric fans distribute warm air throughout the room.
- Contaminated air masses are removed through the exhaust system.
The volume of supply air is calculated based on the cubic capacity of the room and air exchange cycles.
Recirculating
A significant amount of heat is recovered from an already heated room. The used air is not completely removed outside the building, but is returned to the heat source, where it is combined with fresh outside air and reheated. This process is called heat recirculation. Energy-efficient technology saves significant amounts of energy and reduces heating bills.
Combined
In this case, 2 circuits are installed in the heating system. The heating source may be electrical. In some cases, diesel fuel is used. An electric fan is responsible for air distribution. The combined system is often used for heating domestic buildings and industries.