Engineering systems › Heating › What kind of facility do you have?
EuroHolod provides heating for production premises with turnkey installation. For questions related to heating, call +7(495) 745-01-41.
To receive a commercial offer
, write a request to e-mail [email protected] or send a quick request
During the cold season, autonomous heating of the production premises provides the company's employees with comfortable working conditions. Normalization of temperature conditions also has a beneficial effect on the safety of buildings, machines and equipment. Heating systems, although they have the same task, have technological differences. Some use hot water boilers to heat industrial premises, while others use compact heaters. Let's consider the specifics of industrial heating and the effectiveness of using various systems.
Requirements for heating industrial premises
At low temperatures, heating of production premises, as required by labor protection, should be carried out in cases where the time workers spend there exceeds 2 hours. The only exceptions are premises in which permanent presence of people is not necessary (for example, rarely visited warehouses). Also, structures are not heated, being inside of which is equivalent to carrying out work outside the building. However, even here it is necessary to provide for the presence of special devices for heating workers.
Occupational safety imposes a number of sanitary and hygienic requirements for heating industrial premises:
- heating indoor air to a comfortable temperature;
- the ability to regulate the temperature due to the amount of heat generated;
- inadmissibility of air pollution with harmful gases and unpleasant odors (especially for stove heating of industrial premises);
- the desirability of combining the heating process with ventilation;
- ensuring fire and explosion safety;
- reliability of the heating system during operation and ease of repair.
Types of IR emitters
The principle of operation of infrared rays
There is a fairly wide selection of infrared heating devices from different manufacturers on the market. Three main groups of this type of heating devices can be distinguished according to the method of arrangement of the heating elements. Namely:
- floor;
- wall;
- ceiling
Which type of emitters to use is chosen based not only on needs, but also on financial considerations. After all, equipment for infrared heating of an apartment or house is quite expensive and requires significant initial investment. Let's take a closer look at the features of these three types.
Floor emitters for infrared heating at home
Warm floor system
Infrared heating in a private house can be installed at any time. And if the “warm floor” system is usually installed at the stage of construction or major renovation, then the installation of infrared floor heating does not require any extraordinary efforts. Film flooring is a modular roll material with flat heating elements inside, which can be easily installed under a decorative covering. Moreover, it can be located under almost any type of floor: ceramic, wood, laminate, linoleum, carpet. A shielding material is placed on the prepared surface, which will prevent heat from escaping outward. Then the film emitter itself is cut into pieces of the required length and laid on top of the screen. In this case, you need to ensure that there is a distance of 10-15 cm from the walls and between the strips, and especially avoid overlapping. You should also ensure that the laying material does not end up under heavy furniture.
Wall-mounted IR heating devices
You can heat a cottage or dacha using infrared panels. There is a wide variety of choices, both in size and design. Therefore, choosing the right model will most likely not be difficult. An important issue is the method of fastening. Infrared emitters of any type must be located either above or below the level of a person’s head. It is also advisable to avoid direct exposure to radiation in areas where residents of the house may spend a long time (for example, a bed or sofa).
Another type of wall-mounted radiators is baseboard infrared home heating systems. They are installed, as the name implies, instead of ordinary skirting boards around the perimeter of the premises.
In addition, film emitters are sometimes mounted on walls. This is usually justified in cases where it is necessary to organize zone heating. Let's say, create a certain microclimate in a relaxation corner or arrange a loggia.
Ceiling heating devices
Universal film IR coatings can also be placed on the ceiling. For this ceiling, as in the case of the floor, it is first screened, and then strips of the required size are installed. However, compared to underfloor heating systems, there is a wider choice here. Ceiling infrared heating in a private house can also be organized using directional emitters. The coverage area is specified in the product passport and is one of the main characteristics. Therefore, calculating the required number of devices for heating an area is not difficult. Ceiling panels are also currently being produced that can be built into modules in Armstrong suspended ceilings.
Heating calculation
To carry out a thermal calculation, before planning any industrial heating, you need to use the standard method.
Qt (kW/hour) =V*∆T *K/860
Where:
- Qt – heat load on the heated space;
- V – internal area of the room requiring heating (W*D*H);
- ∆ T – the value of the difference between the external and desired internal temperature;
- K – heat loss coefficient;
- 860 – recalculation per kW/hour.
The heat loss coefficient, which is included in the calculation of the heating system for industrial premises, varies depending on the type of building and the level of its thermal insulation. The less thermal insulation, the higher the coefficient value.
Similar documents
Development of master plans for enterprises and industrial areas. Constructing a wind rose. Construction of an industrial building. Heat consumption for heating the building. Calculation of water heating, supply ventilation, water supply and sewer networks.
course work, added 12/24/2009
Features of installing a heating system when building a modern house. Promising developments in this area. Classification of heating systems, assessment of their efficiency. Description and technical characteristics of various types of two-pipe heating systems.
course work, added 11/17/2009
General characteristics of the building. Design of heating and hot water supply systems. The operating principle of water heating systems with natural circulation. Pipeline accessories. Carrying out welding work. Hydraulic testing of heating systems.
thesis, added 11/02/2009
Types of heating systems and their mode of operation. Advantages and disadvantages of heating systems depending on the type of coolant. Standard thermal conditions for various premises. Correct placement of heating devices and increasing their efficiency.
thesis, added 06/20/2014
Calculation of heat transfer of the outer wall, floor and ceiling of the building, thermal power of the heating system, heat loss and heat release. Selection and calculation of heating devices of the heating system, heating point equipment. Hydraulic calculation methods.
course work, added 03/08/2011
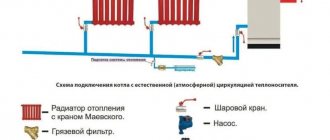
Convective or radiant heating of premises, carried out by a special technical installation. Schematic diagrams of water heating with natural circulation. Heat pipelines of central systems. Comparison of the main coolants for heating.
abstract, added 02/20/2014
Thermal engineering calculation of enclosing structures. Development of a heating system, determination of thermal loads. Hydraulic calculation of water heating. Selection of heating point equipment. Design of ventilation systems, calculation of air exchanges.
course work, added 12/01/2010
Climatic characteristics of the construction area. Thermal engineering calculation of external building envelopes. Determination of the thermal power of the heating system. Design and calculation of heating and ventilation systems. Calculation of air exchange.
course work, added 12/24/2010
Thermal engineering calculation of the first floor floor, external walls and insulated attic floor. Description of the designed heating system. Calculation of heat loss through external fences. Hydraulic calculation of heating and ventilation systems.
course work, added 02/20/2015
Studying the activities and procedures for completing construction projects. Study of types of heating systems for a two-story cottage. Installation of radiators. Installation of risers and connections from them to devices. System testing.
practice report, added 12/08/2013
Posted on https://www.allbest.ru/
Specialty: 270116 “Installation, adjustment and operation of electrical equipment of industrial enterprises and civil buildings”
The course project involves designing a heating and ventilation system for an industrial building.
The building is a one-story repair shop.
Building dimensions:
L = 105 m
B = 24 m
H = 8 m
The walls are made of brickwork, the side walls have double glazing. The roof is a roofless roof made of reinforced concrete slabs with a cement screed with a layer of insulation and waterproofing.
There are double-leaf wooden gates on the front wall. The floor is covered with asphalt concrete (on the ground).
The windows are double sash with double glazing (distance between panes 30÷60 mm).
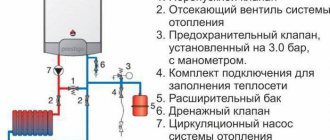
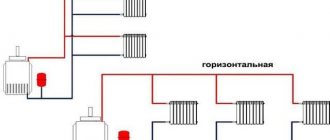
The heating system used in the building is a two-pipe system with bottom wiring, connected to the heating network through a control unit located along the facade wall. The heating source is water from a thermal station.
Coolant parameters: external heating network temperature – 70 ÷ 150 ºС
The water temperature in the local network is 70 ÷ 95 ºС.
Ventilation – supply and exhaust with natural and mechanical impulse.
The heating system of buildings, regardless of their type of purpose (residential, industrial, industrial, administrative, high-rise, etc.), is a system that combines air and water heating. This system can be built on the basis of both central and autonomous heating. They will differ only in the presence or absence of the energy source itself - a boiler or heat generator.
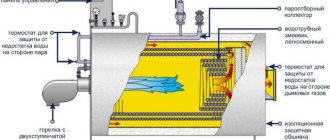
Steam heating of industrial buildings
Heating the production premises using steam allows you to maintain a high temperature of the environment (up to 100 degrees). When organizing the heating process, you do not need to take into account the number of floors. You can bring the temperature to the required value in a short time. This applies to both heating and cooling. All equipment, including communications, does not take up much space.
The steam heating method is optimal if the production premises need to be heated or reduced in temperature periodically. The method is more effective than the water method.
The following disadvantages are identified:
- there is a lot of noise during operation;
- it is difficult to regulate steam flow;
- The steam method is not recommended for use in rooms with aerosols, flammable gases, or heavy dust.
Water heating of industrial facilities
Water heating is appropriate if you have your own boiler room nearby or if there is a central water supply. The main component in this case will be an industrial heating boiler, which can run on gas, electricity or solid fuel.
Water will be supplied under high pressure and temperature. Usually, it cannot be used to efficiently heat large workshops, which is why the method is called “on-duty”. But there are a number of advantages:
- air circulates calmly throughout the room;
- heat spreads evenly;
- a person can work actively in conditions with water heating, it is absolutely safe.
The heated air enters the room, where it mixes with the environment and the temperature is balanced. Sometimes you need to reduce energy costs. To do this, using filters, the air is purified and reused for heating industrial buildings.
Air heating
Most enterprises during the existence of the Soviet Union used a convection heating system for industrial buildings. The difficulty in using this method is that warm air, according to the laws of physics, rises, while the part of the room located near the floor remains less heated.
Today, more efficient heating is provided by an air heating system for industrial premises.
Operating principle
Hot air, which is preheated in the heat generator through air ducts, is transferred to the heated part of the building. Distribution heads are used to distribute thermal energy throughout the space. In some cases, fans are installed, which can be replaced by portable equipment, including a heat gun.
Advantages
It is worth noting that such heating can be combined with various supply ventilation and air conditioning systems. This is what makes it possible to heat huge complexes, something that could not be achieved before.
This method is widely used in heating warehouse complexes, as well as indoor sports facilities. In addition, this method in most cases is the only possible one, since it has the highest level of fire safety.
Flaws
Naturally, there were some negative properties. For example, installing air heating will cost the owners of an enterprise a pretty penny.
Not only do the fans necessary for normal operation cost quite a lot, but they also consume huge amounts of electricity, since their productivity reaches about several thousand cubic meters per hour.
Infrared heating
Not every company is ready to spend a lot of money on an air heating system, so many prefer to use another method. Infrared industrial heating is becoming increasingly popular every day.
Principle of operation
An infrared burner operates on the principle of flameless combustion of air located on the porous part of the ceramic surface. The ceramic surface is distinguished by the fact that it is capable of emitting a whole spectrum of waves that are concentrated in the infrared region.
The peculiarity of these waves is their high degree of permeability, that is, they can freely pass through air currents in order to transfer their energy to a certain place. The stream of infrared radiation is directed to a predetermined area through various reflectors.
Therefore, heating industrial premises using such a burner allows for maximum comfort. In addition, this heating method makes it possible to heat both individual work areas and entire buildings.
Main advantages
At the moment, the use of infrared heaters is considered the most modern and progressive method of heating industrial buildings due to the following positive characteristics:
- quick heating of the room;
- low energy intensity;
- high efficiency;
- compact equipment and easy installation.
By performing the correct calculation, you can install a powerful, economical and independent heating system for your enterprise that does not require constant maintenance.
Scope of application
It is worth noting that such equipment is used, among other things, for heating poultry houses, greenhouses, cafe terraces, auditoriums, shopping and sports halls, as well as various bitumen coatings for technological purposes.
The full effect of using an infrared burner can be felt in those rooms that have large volumes of cold air. The compactness and mobility of such equipment makes it possible to maintain the temperature at a certain level depending on the technological need and time of day.
Safety
Many people are concerned about the issue of safety, since they associate the word “radiation” with radiation and harmful effects on human health. In fact, the operation of infrared heaters is completely safe for both humans and equipment located in the room.
IR gas heaters
It is worth noting right away that this type of fuel for IR heaters has a lot of advantages, which are precisely what many potential buyers appreciate. The very first and most important of them is the cost-effectiveness of the device to use.
Types of gas heaters
To begin with, we will definitely separate the heaters into two groups. Infrared ceiling heaters intended for production sites will be divided into:
- Light emitters. These devices are designed specifically to heat factories where ceilings are more than 4 meters high. At the moment, these are one of the most popular devices in industrial production. According to calculations, approximately for every 20 - 25 meters, you will need 1 installation with a power of 1 kW. If it is necessary to warm up about 100 cubic meters, then use mounted heaters with a power of 5 kW. During their operation, the gas outlet channel will eliminate combustion products, which are extremely harmful to health.
- Dark type of emitters. In this type of system, gas begins to be absorbed only at a temperature of no more than 400 degrees. Due to this, the metal tube will not glow red-hot during operation, which is where the name of the emitters actually came from. Before you start installing such heaters, it is worth considering that they are quite small, unlike light emitters. But factories and other industrial facilities purchase both types of emitters. The choice is up to the buyer.
Advantages of gas-type emitters
For the industrial type of gas emitter, a number of specific advantages can be identified, which are clearly appealing to many buyers:
- there is an opportunity for the enterprise to heat the premises locally;
- fairly low heat costs;
- the device will pay for itself in literally 2–3 years;
- no need to spend money on staff to serve;
- can be turned on at any convenient time of the year;
- extremely fast heating of a large cold zone.
The only caveat is that this type of heater is not particularly suitable for home use. That's why it's called industrial. In order to use it, ceilings of at least 3–4 meters are required. If the height is below 3 meters, then using the emitter is dangerous.
SNiP standards for heating industrial premises
Before you start designing a particular system, and think about which industrial heating boiler to choose, you need to study the following rules and follow them. It is imperative to take into account heat loss, because not only the air in the room heats up, but also equipment and objects. The maximum temperature of the coolant (water, steam) is 90 degrees, and the pressure is 1 MPa.
When drawing up a heating project, staircases are not taken into account. The use of boilers and other gas-powered equipment is permitted only if oxidation products are removed closed and there is no danger of an explosion or fire in the workplace.
Each of the listed heating methods has its own disadvantages and advantages. It is necessary to choose the optimal method based on the technological processes that are carried out in a particular workshop. Workers cannot be indoors if the air temperature there is below 10 degrees. Warehouses usually store finished products. To maintain its quality, you need to maintain an optimal microclimate.
We are a professional engineering design and installation company. On our website you can receive a commercial offer and find the necessary information.
EuroHolod provides heating for production premises with turnkey installation. For questions related to heating, call +7(495) 745-01-41.
To receive a commercial offer
, write a request to e-mail [email protected] or send a quick request
See below
- Heating systems. Heat supply for buildings
- What is your object?
Advantages and disadvantages
The air heating method has undeniable advantages:
- The efficiency reaches 93%. When organizing heating, the installation of intermediate heating devices is not required.
- Heating systems of this type can be fully integrated with ventilation systems. This allows you to constantly maintain an optimal microclimate inside production complexes.
- Very low level of inertia. Immediately after activating the equipment, the air temperature in the room begins to rise.
- High efficiency has a positive effect on the economic performance of production and reduction in production costs.
Along with this, air heating also has obvious disadvantages:
- Constant technical maintenance of the active elements of the system is required. It is quite difficult to modernize already operating installations.
- To avoid interruptions in heat supply, a backup power source is required.