Why does air appear in the heating system?
There can be many reasons, here are just the main ones:
- The coolant contains dissolved air, which is released when heated. To a greater extent, this applies to systems where ordinary tap water, containing a large amount of dissolved oxygen, is used as a coolant. When the coolant is heated, oxygen separates, forming many small bubbles, which create an air lock;
- The heating circuit was filled with coolant too quickly, as a result of which it was not possible to bleed off all the air. The heating system should be filled slowly (on average 1 floor - 1 hour), especially if it is an extended system with a large number of components;
- The required pipe slopes were not observed;
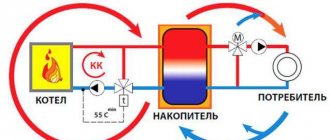
Automatic air vent in the mine.
- Air locks always form after repair work. Repair or replacement of radiators, replacement of fittings, etc. — all this leads to airing of the heating system;
- Low pressure in the system can lead to an increase in the amount of compressed air, which will also create air locks;
- The air vent is out of order or faulty;
- A leak in the heating system can also cause blockages;
- Oxygen permeability of heating pipes. To a greater extent, this applies to polymer pipes (except those with anti-diffusion coating), the walls of which allow oxygen into the system.
- Sometimes air accumulates in the corners of the pipeline. This indicates an installation error: individual sections of pipes were not installed level. In such a situation, it is best to cut a tee into the problem area to install an air vent;
- Some low-quality aluminum batteries react with water, as a result of which air pockets will constantly form. In such a situation, we can recommend one thing: to use only high-quality heating devices, and not to choose something cheaper. It is recommended to replace a cheap device with a new one of better quality.
Air vent with Danfoss ball valve on the technical floor of the hotel.
Note! In multi-storey buildings, air locks most often form in apartments on the top floors, because air always “strives” to the upper sections of the heating system.
When airing occurs in the system
First of all, you should find out the reason why airing occurs. And in general, it will be useful to know what it is and how it arises in general. Airing the heating system is nothing more than air getting into the pipeline or radiators. For this reason, plugs occur in the heating batteries, which prevent the circulation of the coolant. The result is a decrease in the quality of heating the room, but at the same time, the boiler equipment still worked and still works.
Important! When an air lock forms, nothing prevents the circulation of the coolant, as before it moves through all elements of the system, it’s just that the liquid does not enter the place where oxygen has accumulated, but flows on.
Most often the system will be ventilated:
- when changing radiators, when the crimping was not done well enough;
- poor connection of pipes and the battery itself can allow oxygen to pass through;
- a rotten pipeline will release air;
- Violation of the integrity of the battery also provokes airiness in the heating system.
That is why it is very important to periodically carry out sealing checks in order to avoid future troubles that appear at the most inopportune times. Agree, it will be unpleasant if, some time after startup, the radiators stop heating your home.
Tip : It is best to check the integrity of the entire heating system twice a year to protect yourself from unnecessary problems.
Twice a year is not that much, just a couple of hours spent on checking will save the time required to bleed air from the heating system to de-air it.
How to prevent air from entering the system
Here it is necessary to consider several situations - when filling the system with coolant and during its operation. Its design must include air vents and Mayevsky taps, allowing for de-airing of the heating system. The recommendations given apply to a closed system with forced circulation.
Installation of air vents
They are placed in critical places, such as pipeline bends or their highest points. In many cases, when the heating system is constantly airing, they help cope with this problem. There are manual and automatic.
- Manual air vents. These include, first of all, the Mayevsky crane, named after the inventor. Installed at the end of the battery, thanks to it you don’t have to think about what to do if the heating system is airy. With its help, you can independently release the accumulated air.
- Automatic air vents. They allow you to solve the problem of how to ventilate the heating system without additional participation and expense.
| Manual air vent |
Filling the system with water
It is carried out from the bottom up with cold water. In this case, all taps must be open, except those that drain water. Thanks to this filling, the heating system will not be aired; as the water rises, it will squeeze the air out of it. Filling is carried out smoothly; with a sharp rise in water, the formation of closed volumes and the formation of air bubbles is possible.
Filling the heating system with water
As soon as water flows through the open tap, it is closed, and so they gradually rise higher until the entire system is filled. After this, it is quite possible to start the pump; if everything is done correctly, then circulation will occur, and there is no need to rack your brains about how to bleed the heating system.
How is airing dangerous for the system?
Okay, now you know the reasons for the creation of air locks, now you need to figure out how this will affect radiators and other elements. Deterioration in heat transfer from batteries is only one of the obvious manifestations that the heating system is airy. The following problems will appear later:
- The occurrence of corrosion - as is known, steel batteries, as well as aluminum analogues, do not tolerate air. The first ones begin to rust from the inside, their capacity decreases, and therefore heat transfer is lost forever. The latter simply oxidize, which entails a reduction in the service life of the metal product.
- Increased fuel consumption - it should be recalled that if an air lock has formed in the system, its performance decreases, but consumption does not.
- The possibility of a radiator or pipeline breaking - if there is a place through which oxygen enters the pipes or radiator, this very place will be the “Achilles heel” of home heating. Firstly, corrosion or oxidation processes will begin here, and secondly, sooner or later liquid will flow from here.
Advice : If you want your system to cost you the most economically, do not be lazy in performing maintenance. Remember that it is much cheaper than repairs and de-aeration.
Once again, it should be recalled that all these problems can be avoided and significant time can be saved, you just need to check your own system for integrity.
Reasons for the formation of air jams
The finished closed-type heating system is sealed, but this does not guarantee the absence of air bubbles. Where does the gas in pipes and radiators come from?
Air appears in the heating system for the following reasons:
:
- The coolant is tap water that has not undergone special preparation - when heated, air dissolved in the water begins to release, and plugs form from small bubbles.
- The tightness of the system is broken, and air is gradually sucked in through loose connections.
- During the repair work, part of the circuit was disconnected by shut-off valves, some elements were replaced or cleaned, and then the coolant was again supplied to the repaired circuit.
- The pipeline was laid in violation of standards - the small angle of inclination of the pipes and improper installation of kinks prevent gas bubbles from entering special devices - air vents. As a result, gas accumulates in problem areas and interferes with the normal circulation of the coolant.
- If the heating system of a private home fills up very quickly (or when the coolant supply is not at the lowest point), the liquid is not able to completely displace air from complexly configured places in the pipeline and radiators.
- Air vents are missing or incorrectly positioned. Also, the reason for the incorrect operation of the air bleed device is its contamination by mechanical inclusions in the unfiltered coolant.
Mayevsky's manual tap on the radiator
Separately, it is worth considering gas formation in aluminum radiators. When metal comes into contact with a slightly alkaline coolant, hydrogen is released, which accumulates at the highest point of the heating device. If the radiator is not equipped with an air vent, over time the gas lock will not allow the coolant to pass freely through the internal channels of the heating device.
How to deal with airiness
The issue outlined in this section worries many residents of private houses and owners of apartments on the upper floors. Fortunately, today this is no longer a problem. Scientific and technological progress has provided many ways, or rather devices, with which air can be bleed from the heating system. This can be done manually or automatically. The most important question is “how?” Therefore, we will consider each device separately.
Mayevsky crane
This is a small device that is installed at the end of the heating device. It has a special fitting installed, unscrewing which gives access to the heating battery itself. And since air usually accumulates in the upper part of the radiator, the Mayevsky valve was installed in the upper pipe instead of one of the casings.
Mayevsky crane
Some may ask why an air vent is needed if the heating of city apartments is a system with forced circulation of coolant. It will still break through. No one doubts it, but the air will create interference, hence poor-quality circulation, and, therefore, ineffective operation of the system as a whole. Therefore, whether you want it or not, you still have to bleed the air. Let us add that air accumulates at the very top of any system, and the upper end of the radiator is the highest point if we are talking about heating in a multi-story building. Therefore, the Mayevsky crane is usually installed in the apartment on the top floor.
The most important thing is that with the help of this simple device, residents began to relieve the airlock themselves, without calling plumbers. Instructions on how to do this are available today on many websites, including ours. So it makes sense to familiarize yourself and apply knowledge in practice.
Very often, in multi-storey buildings, Mayevsky cranes are installed specifically on technical floors, which are located at the very top of the building. To do this, a riser is brought to this floor and a relief valve is installed into it using a pipe with internal thread. This is done so as not to disturb the residents of the house, that is, the process of bleeding air occurs outside the apartment.
Air separator
This is a very unique device. If the Mayevsky valve removes the air lock, then the air separator removes the air dissolved in the coolant. Do you feel the difference? It is this technology that allows the device to be installed anywhere in the heating circuit.
The process of removing the air mass is carried out by converting it into bubbles, collecting them and removing them outside. In fact, this device is part of a separator unit, which is installed in the basement of the house. Manufacturers are currently offering an improved design of this device. Most likely, this is a double separator, one part of which is responsible for collecting debris and sludge, the second for collecting air. So to speak, two in one. At the same time, both compartments work efficiently, plus there was a saving in materials for their manufacture, which was reflected in the price of the device, and saving on installation space.
The only thing I would like to note is that air separators are usually installed in buildings where a central heating network is used. It is unprofitable to use them in autonomous heating.
Automatic air vent
From the name itself it already becomes clear that this mechanism does everything itself without direct human participation. How does he work.
- The coolant passes through the internal cavities of the air vent, where a special plastic float is installed.
- This float is connected by means of a flag to a rod, on which a spring presses from the reverse side.
- When the inside of the housing is filled with water, the float presses on the rod, which blocks the access of air inside the system.
- If there is no coolant inside, the rod opens the passage.
Automatic air vent
I would like to note that all modern air vents operate on this operating principle. Let us add that this device has a fairly long service life if it is installed and operated correctly. True, it also has breakdowns.
- Most often, they all occur due to low quality coolant. For example, a salt deposit forms on the rod needle, which does not allow the passage to be completely blocked. Hence the leaks and improper operation of the entire mechanism. It is not difficult to repair this defect. You just need to remove the cover of the device, get to the needle and clean it.
- The junction of the cover and the body begins to leak. Defect - the gasket is leaking. It just needs to be replaced with a new one.
How to prevent air from forming in the heating system
Even at the design stage of the heating system, it is necessary to install all the elements in such a way as to ensure the free, unhindered “circulation” of the air that is formed when the coolant is heated.
All closed systems must be equipped with air vents.
Air and sludge separator Honeywell HF49.
In closed heating systems, air separators can be used, which allow you to completely clean the coolant, both from dissolved air and from air in the form of small and large bubbles. The design of the separator allows you to retain and remove air particles.
Filling the system correctly
The easiest way is to pump water or antifreeze into pipelines connected to an open expansion tank. To do this, you need to open all the valves (except for the drain) and, by connecting the hose to the make-up fitting, fill the lines and radiators with coolant
In this matter, it is important to take your time and allow the air to leave the system on its own through the expansion tank
Advice. After filling, turn on the circulation pump and boiler, and then warm up all heating devices. Then release the remaining air from them through the Mayevsky taps. Do not forget to bleed the pump before starting, as described above.
Now about how to bleed air from the radiators and pipelines of a closed heating system in a private house. The proposed technique is constantly practiced by our expert, plumber Vitaly Dashko. performed in the following order:
- Open all shut-off valves of the main circuits (except for the drain).
- Close all radiator valves, excluding the very last batteries at the ends of the loops, so that circulation occurs through them.
- Get an assistant to do the work. Its task is to be in the boiler room and maintain the pressure in the network at a level of 1 bar using a pressure test pump or through a feed branch from the water supply.
- After opening the water supply, fill the main lines, expansion tank and boiler tank. Air must be released through the safety group valve and air vent at the highest point (if equipped).
- Go to the first radiator from the boiler and open both taps at the same time (slowly). Bleed the air through the Mayevsky valve and close the valves again. The assistant at this time does not allow the pressure to drop below 1 bar.
- Repeat the operation on all batteries, then turn on the circulation pump and start the heat generator. When the lines begin to warm up, open all the radiator valves one by one and remove any remaining air from them again.
Important point. Before squeezing air plugs out of radiators, be sure to bleed the air from the circulation pump and turn it on for 5-10 minutes to bleed the pipelines.
After the heating devices have completely warmed up, the pressure in the system should be in the range of 1.3-1.6 Bar. At this point the procedure is considered complete. If the system contains heated floors, then they should be filled last, using the same algorithm (on cold floors!). That is, having pumped up the pressure in the main line, you need to alternately open and close the floor circuits, bleeding air through the manifold valves, and then warm up and adjust the coolant flow.
Note regarding the installation of automatic air release valves. Such a device should always be in the boiler safety group, and the second, third, and so on - only when the lines pass above the radiators. With lower wiring in a one-story house, air accumulates in the radiators, since they are located above the pipelines, and it is not necessary to install valves on them.
Filling the heating circuit with coolant
In order for the heating system to work correctly, it must be flushed and then refilled with water. It is often at this stage that air leaks into the circuit. This occurs due to incorrect actions while filling the contour. In particular, air can be trapped by too fast a flow of water, as mentioned earlier.
The diagram of the expansion tank of an open heating circuit allows you to get an idea of the procedure for filling such a system with coolant after flushing
In addition, correct filling of the circuit also facilitates faster removal of that part of the air masses that are dissolved in the coolant. To begin with, it makes sense to consider an example of filling an open heating system, at the highest point of which the expansion tank is located.
Such a circuit should be filled with coolant starting from its very bottom. For these purposes, a shut-off valve is installed at the bottom of the system, through which tap water is supplied to the system.
A properly designed expansion tank has a special pipe that protects it from overflow.
A hose of such length should be attached to this pipe that its other end is brought out into the area and is located outside the house. Before you start filling the system, you should take care of the heating boiler. It is recommended to disconnect it from the system at this time so that the protective modules of this unit do not work.
Once these preparatory steps have been completed, you can begin filling the contour. The tap at the bottom of the circuit through which tap water flows is opened so that water fills the pipes very slowly.
The recommended filling flow rate should be approximately three times less than the maximum possible. This means that the tap should not be turned off completely, but only to one third of the pipe lumen
Slow filling is continued until water flows through the overflow hose leading outside. After this, the water tap should be closed. Now you should go through the entire system and open the Mayevsky valve on each radiator to bleed air.
Then you can reconnect the boiler to the heating system. It is also recommended to open these taps very slowly. While the boiler is filling with coolant, you can hear a hissing sound produced by the air release safety valve.
This is normal. After this, you need to add water to the system again at the same slow pace. The expansion tank should be approximately 60-70% full.
After this, it is necessary to check the operation of the heating system. The boiler is turned on and the heating system is warmed up. Radiators and pipes are then examined to identify areas where heating is missing or insufficient.
Insufficient heating indicates the presence of air in the heating radiators; it must be bled again through the Mayevsky taps. If the procedure for filling the heating circuit with coolant was successful, do not relax.
For at least another week, the operation of the system should be closely monitored, the water level in the expansion tank should be monitored, and the condition of pipes and radiators should be checked. This will allow problems to be quickly resolved.
In a similar way, closed-type systems are filled with coolant. Water should also be supplied to the system at low speed through a special tap.
You can fill a closed-type heating system with working fluid (coolant) on your own. It is important to arm yourself with a pressure gauge for this.
But in such systems, pressure control is an important point. When it reaches a level of two bars, you should turn off the water and bleed air from all radiators through the Mayevsky taps. At the same time, the pressure in the system will begin to decrease. It is necessary to gradually add coolant to the circuit to maintain the pressure at two bar.
It is difficult to perform both of these operations alone. Therefore, it is recommended to complete the filling of a closed contour together with an assistant. While one person bleeds air from the radiators, his partner monitors the pressure level in the system and immediately corrects it. Collaborative work will improve the quality of this type of work and reduce its time.
Causes and consequences
The reasons for the occurrence of air jams are the following factors:
- Errors were made during installation, including incorrectly placed bends or incorrectly calculated slope and direction of pipes.
- Filling the system with coolant too quickly.
- Incorrect installation of air vent valves or their absence.
- Insufficient amount of coolant in the network.
- Loose connections between pipes and radiators and other parts, which allows air from outside to enter the system.
- The first start-up and excessive heating of the coolant, from which oxygen is more actively removed under the influence of high temperature.
Air can cause the greatest harm to systems with forced circulation. During normal operation, the bearings of the circulation pump are constantly in water. When air passes through them, they are deprived of lubrication, which leads to damage to the sliding rings due to friction and heat or completely damages the shaft.
Water contains oxygen, carbon dioxide, magnesium and calcium in a dissolved state, which, when the temperature rises, begin to disintegrate and settle on the walls of the pipes in the form of limescale. Places of pipes and radiators filled with air are more susceptible to corrosion than others.
Signs by which you can determine whether there are air pockets in pipes and radiators
Due to air in the heating system, the radiators heat up unevenly. When checked by touch, their upper part, compared to the lower part, has a noticeably lower temperature. The voids do not allow them to warm up properly, so the room is less heated. Due to the presence of air in the heating system, when the water is very heated, a noise appears in the pipes and radiators, similar to clicks and water flowing.
You can determine the place where the air is located by ordinary tapping. Where there is no coolant, the sound will be louder.
Note! Before removing air from the network, you should find the cause of its appearance and eliminate it. The network is especially carefully checked for leaks.
When the heating is running, it is extremely difficult to identify leaky connections, since water quickly evaporates on a hot surface
Check the network especially carefully for leaks. When the heating is running, it is extremely difficult to identify leaky connections, since water quickly evaporates on a hot surface.
Main stages
Particular attention is paid to this during setup. Fixing the problem takes more than one day. Removing air bubbles that create blockages in pipes is not so easy. The logical answer to the question: how to properly ventilate a heating system would be to check the radiators installed at high points in the system. After all, air, as you know, goes up. Ideally, each radiator should have its own valve through which air is released.
Valves are manual and automatic. The automatic valve should close after the radiator has been bled out of air and filled with water. When using a manual valve, the device is opened using a special “key”. You need to remember this in order to know how to eliminate air from the heating system.
They stop bleeding air when the coolant flows from the valve in a steady stream.
Every radiator is checked. During the bleeding process, the pressure in the system usually decreases.
You definitely need to keep an eye on its size. Normal pressure indicators at a certain coolant temperature are:
- 20˚С – 1.2–1.3 bar;
- 70˚С – 1.9–2.0 bar.
How to remove an air lock from an engine cooling system
So, let's start with simple cars (old foreign cars, domestic auto industry). On such cars, air is removed from the cooling system as follows:
- All you have to do is drive the car onto the overpass. This must be done in such a way that the front part is slightly raised.
- Next, you need to unscrew a special cap on the radiator, after which the engine can be started.
- After several minutes of operation at idle, the air is bled from the engine cooling system.
However, this method will not help solve the problem on more modern cars. On such vehicles, the cooling system is of a completely closed type, that is, to de-air the air must be “expelled”. To do this, you can go in two ways.
The first method involves unscrewing the cap of the expansion tank, then the engine with the cap open runs at idle for some time, then you need to get into the car and accelerate intensively, raising the speed to 3-3.5 thousand rpm. Next, you need to tighten the cover and check the operation of the system.
If this method does not help, then the upper pipe that comes from the stove is weakened. You need to be prepared for the fact that the antifreeze itself will begin to leak. Next, the engine starts, and you need to monitor when air bubbles disappear from the leaking coolant. Their disappearance will indicate that the air lock has been successfully removed from the system. Let's look at this method in more detail using the VAZ Kalina model as an example.
Before starting work, you should prepare the keys for dismantling the plastic protective elements. You will also need a screwdriver to loosen and then tighten the clamps.
So, the first step is to remove the plastic protection. This protection on the specified vehicle model is attached to the body using studs that have rubber seals. Next, you need to remove the clamp from the upper or lower pipe. Now you need to unscrew the cap of the expansion tank
If the engine is hot, be careful as hot coolant may splash out of the reservoir! Then cover the neck of the tank with a clean rag. Next, pull a suitable rubber tube onto the neck
After this, you need to supply some air to the tank by blowing into the tube. It is advisable to do this using a compressor.
Remember, coolant is a strong poison! Only as a last resort, blow out the reservoir with your mouth, but do not allow the coolant to get inside, into your eyes or onto your skin, and do not inhale the vapors!
- After air is supplied to the tank, antifreeze should begin to flow out of the pipe from which the clamp was previously removed. After this, you need to make sure that there are no air bubbles in the leaking coolant, then quickly put the pipe over the fitting, put the clamp in place and tighten it. At this stage, the deaeration process can be considered complete.
- Next, you will need to bring the coolant level to normal (usually “on cold” it is poured 4-5 mm higher than o, since after warming up the internal combustion engine, the liquid will increase in volume and rise to o).
- After this, the engine can be started and warmed up. In some cases, this procedure requires slightly screwing on the expansion tank cap without tightening it. Then you should let the power plant idle, periodically raising the speed. This method will allow you to remove excess air that could have formed when adding liquid.
- If everything is in order, you can tighten the cap more tightly, but do not try to tighten it too much.
What are the risks of air jams?
The presence of air in the lines will not allow the radiators to be supplied with the required amount of coolant, which means that the heating devices will not produce the required heat and the room temperature will be lower than desired. The noise inherent in overcoming an air obstacle in the system will not cause irritation during the day, but at night it will prevent you from falling asleep. In places where traffic jams form, the internal environment becomes aggressive, which contributes to the active formation of rust.
The most unpleasant thing is overheating. The presence of air in the heat exchanger or heat “supply” pipeline will impede the movement of the coolant, and an increase in temperature can damage the coil or pump.
The ability to bleed air from a boiler or individual areas will allow owners of private houses with autonomous heating to get rid of traffic jams on their own, preventing harmful consequences, without resorting to the help of service providers.
Determining the location of the plug and removing it
How can you tell if there is air in the radiator? Usually, the presence of air is indicated by extraneous sounds, such as gurgling or water flowing. To ensure complete circulation of the coolant, it is necessary to remove this air. When the system is completely aired, you must first determine where the plugs are forming by tapping the heating devices with a hammer. Where there is an air lock, the sound will be louder and stronger. Air is collected, as a rule, in radiators installed on the upper floors.
Having realized that there is air in the heating device, you should take a screwdriver or wrench and prepare a container for water. Having opened the thermostat to the maximum level, you need to open the valve of the Mayevsky tap and substitute the container. A slight hiss will indicate that air is escaping. The valve is kept open until water flows and only then closed.
Eliminating an air lock in a heating battery using a Mayevsky tap installed on it: the valve is opened with a special key or manually and kept open until water appears
It happens that after this procedure the battery does not heat up for long or not well enough. Then it needs to be blown out and washed, since the accumulation of debris and rust in it can also cause air to appear.
If, after bleeding the air, the battery still does not heat up well, try draining about 200 g of coolant to make sure that the air lock is completely removed. If this doesn’t help, you need to blow out and flush the radiator to remove any accumulated dirt.
If there is no improvement after this, you need to check the filling level of the heating system. Air locks can also form at pipeline bends.
Therefore, it is important during the installation process to observe the direction and magnitude of the slopes of the distribution pipelines. In places where the slope for any reason differs from the design, additional air vents are installed
In aluminum radiators, air pockets form more intensively due to the poor quality of the material. As a result of the reaction of aluminum with the coolant, gases are formed, so they must be regularly removed from the system. In such situations, it is recommended to replace aluminum radiators with devices made of higher quality materials with anti-corrosion coating and install air vents. In order for the heating of the rooms to be normal, before filling the heating system with water, it is necessary to promptly remove air from it, which impedes the normal movement of the coolant, and then in winter your home will be warm and cozy.
Top supply in an apartment building - how to release air
Buildings with a top spill have the following characteristics:
- The supply bottling is located on the technical floor, and the return bottling is in the basement;
- each riser is a jumper between them, disconnection is possible both from below and from above;
- the feeding bottling is done with a slight slope;
- at the very top there is an expansion device with a discharge outlet, while the discharge is often discharged through all floors to the elevator unit in the basement or at most close to it.
The function of the air vents is assigned to the vent on the expansion device. Thanks to the discharge to the basement, the start of heat supply in the fall is simplified.