A constant supply of hot water to a multi-apartment high-rise building can be carried out using two methods using different operating principles:
- In the first case, the hot water supply of an apartment building takes water from the cold water supply (cold water supply) pipeline, then the water is heated by an autonomous heat generator: an apartment boiler, a gas water heater or boiler, a heat exchanger that uses the heat of a local firehouse or thermal power plant;
- In the second case, the hot water supply scheme of an apartment building takes hot water directly from the heating main, and this principle is used in the residential sector much more often - in 90% of cases of organizing hot water supply in a residential building.
Important: the advantage of the second option of a water supply system for a residential building is better water quality, which is regulated by GOST R 51232-98. Also, when hot water is taken from a centralized heating main, the temperature and pressure of the liquid are quite stable and do not deviate from the specified parameters: the pressure in the pipeline of the hot water supply system is maintained at the level of the cold water supply, and the temperature is stabilized in the common heat generator.
Let us consider the water supply of an apartment building according to the second option in more detail, since this is the scheme that is most often used both in urban areas and in country houses, including country houses or garden houses.
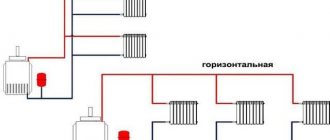
DHW and heat supply diagram
A hot water supply system (DHW) is a set of devices that provide heating of cold water and its distribution to water distribution devices.
There are two domestic hot water and heat supply systems for residential buildings:
An open hot water system means that hot water is drawn from the heating system. Accordingly, for this, the coolant must be of good quality, suitable for domestic use and comply with sanitary standards. In terms of design, such a scheme is much simpler and its production requires much less material, but the volume of liquid must be constantly monitored to prevent airing of the heating system.
Thus, the main advantage of an open scheme is its lower cost compared to a closed one. The main disadvantage is the need to constantly monitor the volume of coolant.
In a closed system, the coolant and consumed water do not mix with each other. It delivers to consumers not the coolant, but its heat. The latter is transferred in a heat exchanger.
This is precisely the scheme that is preferred in modern housing construction, both private and multi-apartment. The disadvantage of such a system is its cost. Installation requires expensive equipment - a boiler, boiler, etc. The undeniable advantage of a closed hot water supply system is the complete independence of the consumer from central heating networks and the ability to individually adjust the water temperature.
Open and closed hot water supply systems are systems with different operating principles.
- Closed - designed so that cold drinking water taken from the main water supply is heated in the heat exchanger by the network coolant, and then supplied to the consumer.
- Open is a system in which heated water is taken from the supply and return heat pipelines into a mixer, where it is brought to a temperature of 65ºC, and then supplied to hot water taps for domestic use.
This is what the hot water supply system of an apartment building looks like, diagrams.
Natural and forced circulation - what's the difference?
Natural is built on the physical process of heated water rising upward. The density of hot water is less than that of cold water, so warm layers are displaced by less heated layers. This phenomenon occurs without human participation, you just need to create the conditions to start the process.
However, natural circulation is unstable, without the necessary pressure. The speed of movement of layers of water is low; it cannot push the flow through the pipeline. In addition, it is almost impossible to regulate the natural process, just start or stop it.
Forced is the movement of water using special pumping equipment. The process occurs evenly, it can be adjusted, flow parameters changed or stopped as needed. The pump creates pressure that allows water to move through a branched, extended system.
The natural process is used where slow, ineffective mixing of layers of water at different temperatures is sufficient. As a rule, it is used in small water supply systems of a private home, when only a small exchange of layers is needed.
For apartment buildings, only forced circulation is suitable, allowing the water flow to be raised to the upper floors and effectively replacing cooled water.
Elements
A water metering unit is a piping unit of a water supply network consisting of shut-off valves, measuring instruments and fittings. The elevator unit is an element of the heating system that allows you to reduce the temperature of the coolant supplied from the thermal power plant to the set level.
The heating elevator mixes high-temperature coolant from the thermal power plant and cooled coolant from the return heating line of an apartment building.
Bottlings
Water supply bottlings are horizontal pipes that run through the basement and connect the risers to the elevator and water meter units. The filling diameter, depending on the material and volume of water consumers, ranges from 32 to 100 mm.
A water supply project for an apartment building must take into account not only the current condition of the pipelines, but also their inevitable overgrowth with sediment and rust after 20-25 years of operation. There are two dispensers in the hot water circulation system.
For internal hot water pipelines, SNiP 2.04.01-85 recommends the use of plastic pipes and fittings. Fittings are used from:
- polyethylene,
- polypropylene,
- polyvinyl chloride,
- metal-polymer,
- fiberglass,
- other plastic materials for water supply networks.
To avoid corrosion, the systems are made of galvanized pipes.
For all internal water supply networks of an apartment building, you can use:
- copper pipes,
- shaped parts,
- bronze pipes,
- with protective coating against rust,
- brass pipes.
With pipe diameters of more than 150 mm in open heat supply systems, black pipes can be used. Thermal insulation of these elements is mandatory for hidden wiring and in unheated rooms. You can use foamed polyethylene, it will make a so-called “fur coat”.
Radiators for heating systems of high-rise buildings
Cast iron radiators, which have previously been used for decades, are familiar to many residents of multi-storey buildings. If it is necessary to replace such a heating battery, it is dismantled and a similar one is installed, which is required by the heating system in an apartment building. Such radiators for centralized heating systems are considered the best solution, since they can withstand fairly high pressure without problems. The passport for a cast iron battery indicates two numbers: the first of them indicates the operating pressure, and the second indicates the test (pressure) load. Typically these values are 6/15 or 8/15. The higher the residential building, the greater the operating pressure. In nine-story buildings it reaches 6 atmospheres, so cast iron radiators are suitable for them. But when it is a 22-story building, then for the working functioning of centralized heating systems, 15 atmospheres will be required. In this case, steel or bimetallic heating devices are needed.
Experts do not recommend using aluminum radiators for central heating - they are not able to withstand the operating condition of the water circuit. Also, professionals advise property owners, when carrying out major renovations in apartments and replacing batteries, to change the coolant distribution pipes to ½ or ¾ inches. Usually they are in poor condition and it is advisable to install ecoplast products instead.
Some types of radiators (steel and bimetallic) have narrower water flows than cast iron products, so they become clogged and subsequently lose power. Therefore, at the point where the coolant is supplied to the battery, a filter should be installed, which is usually mounted in front of the water meter.
Risers and liners
Risers are responsible for the vertical distribution of water in apartments located one above the other. The connections perform the function of distributing liquid through taps and other plumbing fixtures inside the apartment.
In apartments, serial (tee) wiring is traditionally used. The collector type is more material-intensive and requires hidden installation of connections, which greatly complicates their further maintenance.
DHW systems are divided into two types:
- centralized,
- local (decentralized).
In centralized systems, a heating installation in a central heating point (centralized heating point) can serve one or more buildings within a microdistrict or village. Centralized circuits are designed and installed with circulation pipelines for uninterrupted supply of hot water. Without them, in the absence of water supply in the supply pipelines, the water cools down, and the consumer is forced to drain it, which leads to excessive water consumption on the meter. In addition, heated towel rails are installed, which cannot work in the absence of circulation.
Decentralized (local) hot water supply is used in cases where the construction of a centralized scheme is not economically profitable: with a low density of heat loads in rural settlements, etc.
DHW schemes are:
- With a dead-end pipeline, where, with low consumption or no water withdrawal, the water quickly cools down. This scheme is used in low-rise residential buildings with a short network, bath and laundry plants.
- With circulation risers. Similar schemes are used in multi-storey residential buildings and hotel complexes.
Dependence of the system on the heat source
The system can be classified according to a variety of criteria. If we consider them on a large scale, we can distinguish several options:
- Centralized are associated with the installation of a boiler room. It heats the medium, which is supplied to several multi-storey buildings at the same time.
- Locals are required to service only one structure. They are characterized by low power, since they are designed to heat a small volume of medium.
In industrial buildings, a system can often be installed that involves the use of secondary steam to heat the premises. This option reduces costs because thermal energy is reused.
Methods of obtaining and types of hot water supply
According to the method of production, DHW systems are divided into two types:
Hot water supply for an apartment building comes in two versions:
- with single-pipe risers,
- with two-pipe risers.
The two-pipe system consists of two risers:
The heated water flows through the supply riser to the apartments, and through the circulation riser into the central main. Both pipelines are nearby. Heated towel rails are placed on the circulation riser in bathrooms - curved pipes that not only heat the rooms, but also compensate for temperature changes in the length of the pipe. The water in them will no longer be disassembled by consumers, but will be returned through the central pipeline back to the boiler room.
In a single-pipe scheme, each consumer has one riser - supply, and all circulation pipes are combined into one “idler”. It has no consumers, and the water through it returns to the main line.
Heated towel rails with this design:
- placed on the supply pipe,
- electric ones are installed,
- connect to the heating bed.
In the latter case, heated towel rails only operate during the heating season.
With any wiring scheme, the hot water supply system of an apartment building must be able to drain periodically occurring air pockets. With the top wiring, automatic relief valves are installed for such purposes; with the bottom, air can be removed through the top water intake valve.
Private sector
What hot water supply schemes with circulation are used in cottages?
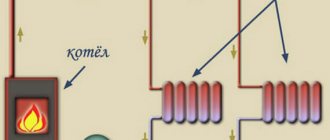
Actually, there are only two basic diagrams: with circulation through the water heater (for this it must be equipped with an additional pipe for connecting the DHW return) and with a thermal mixer. The water is driven by a small-sized pump with a wet rotor.
Closed circuit with circulation pump and boiler with three outlets
Pump for heating and hot water needs with a wet rotor
A three-way thermostatic valve allows you to implement recirculation even if in your home an electric boiler or an indirect boiler with two pipes (DHW and make-up) is responsible for heating the water.
Scheme with a conventional boiler and a three-way thermal mixer
Wiring in the apartment
There are two main schemes for distributing water supply in an apartment:
- tee (sequential),
- collector
Both schemes have their advantages and disadvantages. Sometimes it makes sense to use a combination of these schemes.
The sequential scheme is the traditional way of designing and installing water supply in an apartment. This circuit consists of one common pipe to which all devices are connected in series. Tees are used to connect plumbing fixtures, which is why this scheme is called a tee. The main pipe must be larger in diameter than the others, as it takes on the functions of a collector.
One of its significant advantages is the smaller number of pipes compared to the collector circuit. Therefore, the costs of its installation will be minimal.
The collector wiring diagram is the optimal choice for large apartments, as well as in places where the installation of a large number of plumbing fixtures is required. Water from the common riser enters the collector and is then sent to consumers, that is, to appliances.
Each consumer is connected separately. One of the main advantages of the collector circuit is the uniform distribution of water. This means that the number of connected devices and the length of water pipes do not reduce the pressure for any of the consumers.
The video demonstrates the cold and hot water input unit in an apartment in a multi-storey building.
Do housing and communal services have the right to come up with names for their services?
The state seeks to standardize the procedure for paying for housing and communal services, since it is carried out every month throughout the country. Therefore, a list of services has been compiled that have their own names. The organization does not have the right to come up with names, as this may lead to problems for residents of the house with calculations and confirmation of expenses.
The information above indicates that there are several different water supply and heating systems. When developing, the layout, area of the structure, climatic conditions and other points must be taken into account. Therefore, professional companies are involved in drawing up the project. If the proper amount of hot water is not getting into the house or the towel dryer is constantly cold, then there is a possibility that the design developed does not meet the established standards.
Malfunctions
Main malfunctions of the water supply system valve:
- when closed, it allows water to pass through,
- liquid flows through the rod,
- presence of leakage through threaded connections.
The causes of malfunctions are wear of the rubber valve gasket, seat shell, worn rod threads, worn out stuffing box, weak seal of threaded connections.
If a mixer with a ceramic axle box begins to make noise, then the cause is a sagging silicone washer. It is best to replace the ceramic valve axle with the same new one or an analogue.
Lever mixers make virtually no noise, but if this does happen, the only solution is to normalize the pressure in the system. To do this, reducers are installed in front of the mixer, which limit the pressure, then the noise stops. A similar approach can be used to eliminate noise in a hygienic shower mixer.
The video shows how to correctly calculate the cost of hot water.
DHW system of a private house
Household water heating devices are:
- electrical,
- gas,
- on solid fuel,
- indirect heating.
Based on the method of heating the liquid, water heaters are divided into two types:
- Flow-through, in which heating occurs as water moves past heat-transmitting elements.
- Cumulative, where heating is carried out in special containers of the device using heat transfer elements.
In a private house, as a rule, a collector water supply system is designed and installed.
The choice of design and installation of apartment building systems, as a rule, depends on the conditions for implementing SNiP 2.04.01-85 and the capabilities of the customer.
Installation of central water supply in a multi-storey building
The source of water supply in a multi-storey building, as a rule, is the city water distribution network. A central supply pipe is introduced into the house, which usually has a large cross-section to ensure sufficient fluid flow. A valve is installed at its end, after which a water metering unit is installed for centralized recording of the volume of water consumed by the house as a whole.
The water metering unit includes a water meter, in front of which a coarse filter is installed. A check valve is installed after the meter, which prevents the return flow of the liquid when the pressure in the pipeline drops. The water metering unit is limited by two shut-off valves. In addition, bypass devices are often installed. In fact, this is a spare water meter unit through which water is directed during maintenance, repair or verification of the main water meter. The use of a bypass scheme makes it possible to carry out this work without interrupting the water supply to consumers.
At the outlet of the water metering unit, water enters the main pipeline, from which it is distributed into risers. These are vertical sections of the main water supply through which the liquid rises to the floors, from where it is distributed to apartments and to the final water intake points along horizontal distribution. So that in an emergency, for scheduled maintenance and repairs, only one riser can be closed, a shut-off device is installed on each of them - a valve or ball valve. This allows you not to turn off the entire house’s water supply when performing work on a specific riser.
Video
The process of operating a hot water supply device in a multi-storey building is demonstrated in this video.
A constant supply of hot water to a multi-apartment high-rise building can be carried out using two methods using different operating principles:
- In the first case, the hot water supply of an apartment building takes water from the cold water supply (cold water supply) pipeline, then the water is heated by an autonomous heat generator: an apartment boiler, a gas water heater or boiler, a heat exchanger that uses the heat of a local firehouse or thermal power plant;
- In the second case, the hot water supply scheme of an apartment building takes hot water directly from the heating main, and this principle is used in the residential sector much more often - in 90% of cases of organizing hot water supply in a residential building.
Important: the advantage of the second option of a water supply system for a residential building is better water quality, which is regulated by GOST R 51232-98. Also, when hot water is taken from a centralized heating main, the temperature and pressure of the liquid are quite stable and do not deviate from the specified parameters: the pressure in the pipeline of the hot water supply system is maintained at the level of the cold water supply, and the temperature is stabilized in the common heat generator.
Let us consider the water supply of an apartment building according to the second option in more detail, since this is the scheme that is most often used both in urban areas and in country houses, including country houses or garden houses.
Temperature requirements
The parameters of hot water in a residential building are regulated by the requirements of GOST 2874-82 and sanitary hygiene standards.
These requirements are provided by resource organizations. The water temperature should be between 60-75⁰ C.
Attempting to use heating water in the water supply network is punishable by law.
What elements does the water supply scheme of an apartment building include?
The water metering unit, which organizes the supply of water to the house, is responsible for several functions:
- It takes into account the consumption of cold water supply, that is, it acts as a water meter;
- It can shut off the supply of cold water to the house in emergency situations or when it is necessary to repair components and parts, as well as to eliminate leaks;
- Serves as a filter for coarse water purification: any hot water supply scheme for an apartment building should contain such a mud filter.
The device itself consists of the following components:
- A set of shut-off valves (taps, valves and valves) at the inlet and outlet of the device. Standardly these are gate valves, ball valves, valves;
- Mechanical water meter, which is installed on one of the risers;
- Mud filter (filter for coarse water purification from large solid particles). This could be a metal mesh in the housing, or a container in which solid debris settles to the bottom;
- Pressure gauge or adapter for inserting a pressure gauge into a water supply circuit;
- Bypass (bypass from a section of pipe), which serves to turn off the water meter during repairs or for data verification. The bypass is equipped with shut-off valves in the form of a ball valve or valve.
Heating point
It is also an elevator unit that performs the following functions:
- Ensures full and continuous operation of the heating system in an apartment building, and also regulates its parameters;
- It delivers hot water to the house, that is, it provides hot water supply (hot water supply). The coolant itself in the heating system enters the hot water supply system of the apartment building directly from the centralized heating main;
- The heating point can switch the hot water supply between return and supply. This may be necessary during severe frosts, since at this time the temperature of the coolant on the supply pipe can rise to 130-150 0 C, and this despite the fact that the standard supply temperature should not exceed 750 C.
The main element of a heating point is a water-jet elevator, where hot water from the working fluid supply pipeline circuit in the house is mixed in a mixing chamber with the return coolant by injection through a special nozzle. Thus, the elevator allows a larger volume of low-temperature coolant to pass through the heating circuit, and, since injection is carried out through a nozzle, the supply volume is small.
Adapters for connecting DHW can be inserted between the valves at the inlet of the route and the heating station - this is the most common connection scheme. The number of inserts is two or four (one or two each on the supply and return). Two inserts are typical for old houses; in new buildings, four adapters are practiced.
On the cold water supply route, a dead-end tie-in scheme with two connections is usually used: the water metering unit is connected to the bottling, and the bottling itself is connected to the risers through which pipes are routed to apartments. Water will move in such a cold water supply system only during disassembly, that is, when opening any mixers, taps, valves or valves.
Disadvantages of this connection:
- If there is no water supply to a particular riser for a long time, the water will remain cold for a long time when drained;
- Heated towel rails embedded in the DHW inlets from the boiler rooms, which simultaneously heat the bathroom or toilet, will only be hot when the DHW is drawn from a specific riser in the apartment. That is, they will almost always be cold, which will cause the appearance of moisture on the walls, mold or fungal diseases of the building materials of the room.
Read more: Library manager qualification directory
A heating station with four hot water connections in the house makes the circulation of hot water continuous, and this happens through two bottlings and risers connected to each other by jumpers.
Important: if mechanical water meters are installed on the hot water taps, then the water supply consumption will be taken into account without taking into account the water temperature, which is incorrect, since you will have to overpay for hot water that was not used.
Hot water supply can operate in three ways:
- From the supply pipe to the return pipe to the boiler room. Such a hot water system is effective only in the warm season when the heating system is turned off;
- From supply pipe to supply pipe. Such a connection will bring maximum benefits in the demi-season - autumn and spring, when the coolant temperature is low and far from maximum;
- From the return pipe to the return pipe. This DHW scheme is most efficient in extreme cold, when the temperature at the supply pipe rises to ≥ 75 0 C.
For continuous movement of water, a pressure difference is required between the starting and ending points of insertion into one circuit, and this difference is ensured by limiting the flow. This limiter is a special retaining washer - a steel pancake with a hole in the middle. Thus, the water that is transported from the inlet to the elevator encounters an obstacle in the form of a washer body, and this obstacle is regulated by a rotation that opens or closes the retaining hole.
But too much restriction of the movement of water in the pipeline route will disrupt the operation of the heat station, so the retaining washer should have a diameter 1 mm larger than the diameter of the heat station nozzle. This size is calculated by representatives of the heat supplier so that the temperature at the return heating pipe of the elevator unit lies within the standard temperature limits.
What is pipe filling and riser
These are pipes laid horizontally and carried through the basement of a residential building, which connect the risers to the heating station and water meter. Bottling of cold water supply is done in single copies, bottling of hot water supply - in duplicate.
The diameter of the DHW or cold water filling pipes can be 32-100 mm, and depends on the number of connected consumers. For any water supply scheme, ø 100 mm is too large, but this size is taken taking into account not only the actual condition of the route, but also taking into account the size of salt deposits and rust on the inner walls of metal pipes.
A vertical pipe riser distributes water to the apartments located above it. The standard layout of such wiring includes several risers - for cold and hot water supply, and sometimes separately for heated towel rails. More wiring options:
- Several groups of risers passing through one apartment and providing water to water points located at a great distance from each other;
- A group of risers in one apartment that supplies water to a neighboring apartment or several apartments;
- When organizing hot water supply, pipe jumpers can be used to connect up to seven groups of risers across apartments. The lintels are equipped with Mayevsky taps. This is called a circulation pipeline, or CTP.
The standard diameter of cold and hot water supply pipes for risers is 25-40 mm. Racks for heated towel rails and single risers are mounted from ø 20 mm pipes. Such risers provide both one-pipe and two-pipe home heating systems.
Closed hot water system
The constant circulation of water in a closed hot water supply system is based on the principle of taking cold water from the pipeline and supplying it to the heat exchanger. After heating, the water is supplied to the distribution system throughout the apartment. The working fluid in the heating system and hot water for the technical needs of consumers are separated, since the coolant may have toxic inclusions to improve its heat transfer qualities. In addition, hot water pipes rust faster. Such a scheme is called closed because the consumer uses the heat, and not the coolant itself.
Pipe liner
The main function of the connections is to distribute water to the water collection points in the apartment. The standard diameter of the supply pipes is 15 mm, the grade of pipes is DU15, the material is steel. For PVC or metal-plastic pipes, the diameter should be the same. When repairing or replacing the liner, it is not recommended to use a smaller diameter so as not to change the design pressure parameters that the hot or cold water supply circulation system must comply with.
To organize the correct wiring, tees are most often used; for more complex wiring schemes, manifolds are used. The collector supply requires hidden installation, so the collector should be installed when servicing a large number of rooms in the house. After 10-15 years, metal pipes become overgrown from the inside with salt mineral deposits and rust, so preventive work to restore the system’s functionality consists of cleaning the pipes with steel wire, or replacing old pipes with new ones.
Given the apparent functionality and durability of PVC or metal-plastic pipes, it is recommended to use steel products for liners - they withstand water shocks and temperature changes well. Such deviations in the DHW operating mode can often be observed when the heating system is turned on or turned off in an emergency. Pipe material should be included in the plan for the water supply scheme of a residential building at the stage of drawing up the project and estimate.
What pipe products are recommended for use in cold and hot water supply schemes with constant water circulation:
- Galvanized metal pipes - they have been used for many decades, and they have proven themselves to be the best. The zinc layer on the metal prevents corrosion from developing and does not retain salt deposits. When purchasing galvanized products, you should remember that welding work is not carried out on such a surface, since the weld seam will remain unprotected by zinc - all connections must be made on threads;
- Pipe connections on fittings for soldering copper connections last much longer than steel and even galvanized pipes. Such connections with a solder connection do not need to be maintained, and they can be laid in both open and hidden ways;
- Corrugated pipe line for cold or hot water supply made of stainless steel. Such products are simply and quickly mounted on threaded connections or compression fittings. No special equipment other than two adjustable wrenches is required for this. The guaranteed service life of stainless steel is not limited by the manufacturer. The only thing that will have to be changed over time is the silicone seals.
How to organize yourself?
The circulation diagram of a private house is usually created independently, taking into account the configuration of the premises, the number of water points, branches, and additional lines. The main task is the constant operation of the heated towel rail, which is installed in a gap in the hot water supply line.
If the water cools down, the device will stop heating the room and drying towels, and the bathroom will be damp and cold.
For medium-sized buildings, one bottling is used, but for large cottages, several boilers with their own systems are often installed. Let's look at the most common options.
Through a storage boiler
A storage boiler is a container with insulated walls where hot water is accumulated and supplied as needed.
The circulation system is not important for it, since the return line temperature will be lower than in the main tank. This will require heating or changing the water.
If you refuse circulation, the water in the dead-end lines will completely cool down and the hot water supply mode will be disrupted.
Therefore, to organize the flow movement, perform the following actions:
a direct DHW line is drawn to all consumers and returns to the storage tank;- a circulation pump is installed before entering the container;
- The make-up pipeline from the boiler is connected either with a separate input or connected to the return pipe through a three-way valve.
The tank is recharged only when the pressure in the DHW system drops or when the temperature drops significantly. For the correct operation of such a system, a control unit with a system of sensors is required, which will continuously provide information about the state of the flow.
This scheme requires the use of a separate boiler not connected to the heating system. Therefore, it is used only in the southern regions.
Through an indirect heating boiler
An indirect heating boiler is a heater where the working “body” is a coil with hot coolant. As a rule, it is built into the heating system.
The hot stream passes through the coil at a sufficient speed to ensure that enough thermal energy remains to heat the home. At the same time, the DHW line is always ready to supply water at the required temperature. Circulation is needed only to prevent the water from cooling in dead-end lines.
Assembly order:
- The boiler is connected to the heating system. To do this, it has a separate pair of pipes for supply and exit of coolant. Typically, the boiler is located next to the boiler in order to receive coolant at the maximum temperature.
- The hot water supply line is looped and connected through a circulation pump to the boiler. As a rule, the return flow is connected to the farthest point of water collection and directed to the tank along the most direct path so as not to lose thermal energy.
- Connect the cold water make-up pipeline. It supplies water when the level in the tank drops. The float valve gives the start command.
- They start circulation and adjust the heating mode by changing the speed or volume of coolant supply to the heater.
- They check the system for operability and eliminate any deficiencies found.
The circulation option through an indirect heating boiler is considered the most efficient and stable. In the summer, the heating circuit is turned off and the boiler only works to heat the tank.
Features of hot water supply and calculation of the volume of hot water
Calculation of the amount of hot water in the system depends on technical and operational factors:
- Estimated hot water temperature;
- Number of residents in an apartment building;
- The parameters that plumbing fixtures can withstand and the frequency of their operation in the overall water supply scheme;
- the number of plumbing fixtures that are connected to the hot water supply.
- A family of four uses a 140 liter bathtub. The bathtub fills in 10 minutes, the bathroom has a shower with a water consumption of 30 liters.
- Within 10 minutes, the water heating device must heat it to the design temperature of 170 liters.
Read more: The height of the gym should be at least
These theoretical calculations work based on average water consumption by residents.
DHW. What it is?
DHW – hot water supply to meet the needs of the population, the temperature of the supplied medium reaches +75°C. This system is an important indicator of living standards. It is represented by a combination of several different elements:
- Water heater.
- Pump.
- Pipe
- Fittings.
The abbreviation in question is often used in regulatory documents. Different DHW systems are characterized by their own characteristics that must be taken into account.
Breakdowns in the hot or cold water distribution system
You can fix the following emergency situations with your own hands:
The valve or faucet is leaking. This happens most often due to wear of the oil seal or seal. To eliminate the malfunction, it is necessary to open the valve completely and with force so that the raised oil seal stops the leak. This technique will help for a while; in the future, the valve must be rebuilt and worn parts replaced.
Noise and vibration of a valve or faucet when opening in a hot water supply system (less often cold). The cause of noise is most often wear, deformation or crushing of the gasket in the gearbox of the mechanism. Noises appear if the tap is not opened all the way. This fault can cause a series of water hammers in the pipes, so its elimination is of utmost importance. The faucet valve is capable of closing the valve seat in the faucet or valve body in a few milliseconds, if it is not a ball valve, but a screw valve. Why is the risk of water hammer higher in hot water supply systems? Because in hot water pipes the operating pressure is higher.
How to fix the problem:
- Shut off the water at the inlet;
- Unscrew the valve housing of the noisy faucet;
- Replace the gasket, but before installing, chamfer the new gasket so that the valve does not vibrate when opening under high pressure.
The heated towel rail does not heat up. The cause of the breakdown may be the presence of air in the water supply system with constant coolant circulation. Typically, air accumulates in a pipe jumper, which is installed between adjacent risers, after an emergency or scheduled drain of water. The problem is eliminated by bleeding the air plugs. To do this you need:
- Vent the air at the highest point of the system - on the top floor;
- Shut off the hot water supply riser located in the apartment (the riser is closed in the basement of the house);
- Open all hot water taps in the apartment;
- After bleeding air through taps and mixers, you need to close them. And open the shut-off valve on the riser.
Hidden faults
At the end of the heating season, the pressure difference between the heating main pipes may not be maintained, and because of this, heated towel rails connected directly to the hot water supply will be cold. This is not a cause for concern - you need to bleed off the air, which equalizes the pressure, and the heating will be restored.
Perhaps everyone knows that the huge boiler-cooling towers and striped chimneys emitting smoke, which are visible from anywhere in the city, belong to the thermal power plant. Moreover, many people know that these colossuses provide our homes with light, heating and hot water. But what exactly is the process of heat generation and how cooling tower columns are involved in it is a rather confusing question.
Background
Dead-end cold and hot water supply systems are typical for buildings built by Stalin and Khrushchev. In a dead-end system, the bottling flows into risers, and each riser ends with a water supply on the top floor with a cistern and mixers connected to it. Water in such a system begins to move only at the moment when one of the residents opens the taps.
Black pipes - tie-ins of a dead-end hot water system into the supply and return of the heating network
For cold water this is quite acceptable, but in hot water it has a couple of unpleasant consequences:
- If in your part of the house (along a riser or in a group of risers) no one has used hot water for a long time, it cools down in the pipes. Yes, yes, despite the thermal insulation of the bottlings: insulation slows down cooling, but does not stop it completely.
As a result, in order for hot water to come out of the tap, you are forced to drain cold water for several minutes: its volume with a DHW filling diameter of 80-100 mm can amount to tens of liters;
Do you want to wash your face? Drain the cooled water in the pipes!
Please note: this situation is especially bad for the owners of water meters installed in the apartment. They drain cold water and pay for hot water: there are no temperature sensors on mechanical metering devices.
A mechanical device takes into account water flow without recording its temperature
- Heated towel rails were installed everywhere in Khrushchev-era bathrooms. They are connected to the gap in the hot water supply, between the riser and the taps, and heat up only when water is consumed in that particular apartment.
Khrushchev: the dismantled heated towel rail was installed between the water supply and the riser
Since hot water is rarely used for more than an hour a day, these appliances sit cold most of the day and night. Hence the musty smell of towels, cold and dampness in the bathroom, and often fungus on the walls.
Mold is one of the consequences of cold in the bathroom
A revolution in the design of domestic hot water systems took place on January 1, 1977, when SNiP II-34-76 was released. Paragraph 2.8 directly stated that hot water supply must now be designed with continuous circulation of water through ring jumpers and risers.
The document has now been canceled, but there are current reissues of it.
What the circulation of water in the water supply system does is quite obvious: from now on, the water in the hot water supply and in the risers has become hot around the clock. To heat the water flowing from the tap, it is enough to drain the few liters of water that are in the water supply.
Heated towel rails migrated from the supply to the riser and began to heat constantly - as long as circulation was maintained in the risers. As we will find out later, it is possible that this circulation may stop.
In new houses, dryers are connected not to the inlets, but to the risers
Steam production
The huge steam boiler in the turbine hall - the height of a 9-story building is not the limit - can be called the heart of the thermal power plant. It is powered by prepared fuel, releasing a huge amount of energy. Under its force, the water in the boiler turns into steam with an outlet temperature of almost 600 degrees. Under the pressure of this steam, the generator blades rotate, resulting in the creation of electricity.
The thermal power plant also produces thermal energy intended for heating and hot water supply to the region and city. For this purpose, there are selections on the turbine that remove part of the heated steam before it reaches the condenser. The exhausted steam is transferred to a network heater, which acts as a heat exchanger.
Water heating equipment
A standard water heater can be used for domestic hot water or heating. In case of equipment breakdown, housing and communal services tariffs will not be reduced. Repair work will also fall on the shoulders of consumers, who are obliged to monitor its good condition.
Thermal energy component
It is responsible for heating cold water. Moreover, counters are not installed on the component. Before calculating the thermal energy for DHW, the following parameters must be taken into account:
- tariff for hot water supply;
- system operating costs;
- costs for coolant transfer;
- calculation of heat loss.
Also taken into account is the fee for regular water supply, calculated on the basis of consumption (RUB/cubic meter).
Heating network
Once in the tubes of network heaters, the water is heated and transferred through underground pipelines further into the heating network due to pumps driving the water through the pipes. Heating networks, as a rule, carry water at 70-150 degrees - it all depends on the temperature outside: the lower the degree outside, the hotter the coolant.
The central heating point (CHS) becomes the transfer point for the coolant. It serves an entire system of buildings, an enterprise or a microdistrict at once. This is a kind of intermediary between the object that creates heat and the direct consumer. If water in a boiler room is heated due to fuel combustion, then the central heating station works with an already heated coolant.
Payment
Finally, we will answer several questions, one way or another related to the growing tariffs for heat and hot water every year.
How are payments for heating and hot water supply calculated?
The key parameter in charging for heating is the amount of heat spent to maintain a comfortable temperature in the apartment or to heat water. The cost of thermal energy for 2017 is 1000 - 1800 rubles per gigacalorie, depending on the region.
Utility tariffs for 2022 for the city of Berdsk
However, not all apartments have heat meters, so the following appear on receipts much more often:
- Fixed payment for heating a square meter (it is calculated as the product of the heat consumption standard for a given region and the price of a unit of thermal energy);
Simplified diagram: heating costs are calculated based on the square footage of the heated area
- The cost of a cubic meter of hot water, including the meter (90-170 rubles per cubic meter).
How can you save on heating?
To reduce costs you need to:
- Install heat metering devices on each radiator;
- Install chokes or thermal heads on the connections to limit the flow of coolant through the heating device.
The photo shows a sectional radiator with a heat meter and a throttling thermostatic head
Is it possible to use hot water supply to heat an apartment?
Technically yes. To do this, it is enough to form a closed heating circuit (for example, the simplest one-pipe Leningrad) and connect it to the gap in the hot water riser. Since there are no metering devices on the riser, the heat obtained in this way will be absolutely free for you.
The simplest heating system - Leningradka
However:
- Any change in the configuration of public utility networks requires approval from the housing organization and, in the case of hot water supply and heating, from the relevant service providers. It is clear that none of the organizations will give permission for such a change in the heat supply scheme;
- Uncoordinated redevelopment of communications is an administrative offense and is punishable by a fine with an order to restore the original configuration at your own expense;
The Housing Code regards uncoordinated redevelopment of communications as an administrative offense
- Finally, the main thing: you can disconnect from the central heating system only at your entrance or home, providing a plan for an alternative heating scheme and agreeing with electricity or gas suppliers (alternative heat sources). Without an official termination of the heating service, you will continue to receive bills that you want to get rid of.
To stop paying for central heating services, you need to cut off the heating devices from the heating risers and draw up a disconnection certificate with representatives of the housing residents