NAVIGATION
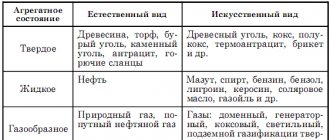
1. Gas. 2. Solid fuel. 2.1. Firewood 2.2. Euro firewood (briquettes) 2.3. Fuel granules (pellets) 2.4. Sawdust and wood chips 2.5. Coal 2.6. Peat 3. Liquid fuel 3.1. Diesel fuel (diesel fuel) 3.2. Fuel oil 3.3. Biofuel 3.4. Waste oil 4. Electricity
Due to the nature of the production of the following types of fuels, their combustion rate and the amount of heat generated (i.e. calorific value or specific heat of combustion) can vary greatly from each other. For example, differences in the calorific value of birch and spruce firewood can be more than 30%.
Therefore, the “pros and cons” given below in the text are presented solely as a comparative example and cannot reliably reflect the effectiveness of a particular type of fuel. We ask you to pay special attention to this and before making a final decision, study this or that type of fuel more carefully yourself.
We would also like to note that calculations of the cost of heating costs are provided for informational purposes only. In all modern boilers, the technical documentation indicates the features and fuel consumption, which are close to the most reliable and it is on them that you should rely when making the final decision.
So, let's start, as a rule, in practice it is customary to use the following types of fuels:
GAS
Natural gas is a mixture of gases that are formed underground during the decomposition of organic matter, which is why it is a mineral.
At 101.325 kPa and 20 °C, natural gas acquires a gaseous state, which is why, as a rule, natural gas underground is in a gaseous state, i.e. in the form of separate accumulations, gas deposits. But it is also found in the form of gas caps in oil and gas fields or in a dissolved state, for example, in oil or water. 92-98% of natural gas is methane (CH4), while its composition may also include heavier hydrocarbons, such as ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10) and other non-hydrocarbon substances such as hydrogen (H2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), helium (He).
It is worth mentioning that natural gas, in its pure form, has no odor or color, which increases the risk of poisoning if it leaks. In order to determine the source of the gas leak, experts began adding special substances to it - odorants, for example, ethyl mercaptan, which has a strong unpleasant odor of rotten cabbage, rotten hay and rotten eggs.
ADVANTAGES
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low cost
Compared to other types of fuel, gas is the cheapest type of fuel, taking into account the costs of transportation, storage and associated labor costs.
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If you have a gas main, when gas pipes are already connected to your house from the street, you just have to connect them to the boiler and no longer worry about replenishing fuel. But in the absence of a gas main, you will be forced to purchase gas using gas cylinders (gas holders) of 50 liters, which in turn will need to be changed every 1-2 days.
Labor costs
If there is a gas main, labor costs are minimal. If there is no gas line, you will have to take care of transportation, storage and replacement of gas cylinders.
Warehouse space
If there is no gas main, you will have to allocate premises for storing gas cylinders. To create an autonomous heating system, reduce labor costs and eliminate a separate storage room, large-volume gas tanks should be installed underground and filled before the start of the heating season.
Chimney
If the boiler has an open combustion chamber, then the installation of a full-fledged chimney system will be required to remove the exhaust gases, and if the combustion chamber is closed, then a coaxial chimney will be sufficient.
Danger to others
If gas boilers have an open combustion chamber, then a certain amount of exhaust gases can enter the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. In contrast to gas boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimal.
Energy independence
All gas boilers with a closed combustion chamber require constant power supply, unlike gas boilers with an open combustion chamber.
Cons
Explosion hazard
High probability of explosion if safety precautions, operation, installation and maintenance are violated.
Difficulty of installation
Due to the high risk of explosion, the installation of a heating system requires appropriate permits and qualified personnel.
Separate space
The room in which the gas boiler will be located increases the level of fire and explosion hazard, which imposes certain restrictions on the design of the house.
Noise
Compared to electric boilers, gas boilers create noise when operating.
Installation cost
High installation cost for creating an autonomous heating system in the absence of a gas main.
Electricity
Heat is produced by converting electrical energy into heat using heating elements of boilers, convectors, heaters, and radiators.
Advantages of electricity for heating a home:
- highest possible efficiency;
- maximum possibility of automation of the heating process;
- long service life of heat sources;
- low cost of equipment and its installation;
- absence of combustion products, which means no chimneys and the possibility of widespread installation;
- silent operation;
Disadvantages of an electric heating system:
- the most expensive type of fuel;
- mandatory registration in electrical networks, installation of electrical networks with separate metering at an increased tariff;
- 100% - I am dependent on the power grid.
CALCULATION OF THE COST OF GAS COSTS
To calculate gas consumption for heating, you must use the following formula:
V = Q / (n/100 x q)
- Q is the heat load for heating (kW/h), for example, let’s take 24 kW/h.
- q is the calorific value of the gas (kW/m³), which depends on the brand of gas supplied. To find out exactly what brand of gas is used in your home or area, we recommend contacting your gas supply company directly.
- n – coefficient of performance (efficiency) of a gas boiler, expressed as a percentage. It is indicated in the boiler passport.
For example, let’s choose a boiler - Lemax Premium 35 V. This boiler was chosen due to its technical power indicators, its value is very close to the thermal load value for a house with 300 m3, namely 24 kW/h. It is also worth noting the high efficiency rate of 90%. To ensure that the boiler power is enough to heat the house even in the most severe frosts, it is recommended to use a reserve of 30%. For the purpose of calculation, we take G20 gas with low calorific value, namely Hi = 9.5 kWh/m.
Now we substitute all the values into the formula and calculate:
V = 24 / (90.0 / 100 × 9.5) = 2.5 m³/h.
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need 60 m3 of gas. And for the heating season, it turns out to be 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(60 m3 (daily gas consumption) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 5490 m3
SOLID FUEL
Solid fuels are combustible substances, which are predominantly composed of carbon. These include substances that have the properties of a granular body, allowing them to be extracted, stored and moved using well-known mechanical systems and transport devices.
Solid fuel can be natural, i.e. natural, for example, wood, peat, slate, etc., as well as artificial, for example, charcoal, coke, semi-coke, etc.
2.1 FIREWOOD
Firewood is one of the most affordable types of solid fuel. There are a huge number of tree species that can be used for heating purposes.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Environmental Safety
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low ash and no sulfur
Unlike other types of fuels.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Neutral:
High labor costs
Before firewood is used for heating, it must be sawed, split, and allowed to dry for a year or two in an appropriate room. An alternative option is to buy ready-made firewood, which in turn will increase their cost.
Price
Purchasing untreated firewood can significantly reduce costs, while increasing labor costs for subsequent processing.
Cons
Lack of autonomy
It is necessary to constantly manually replenish the boiler with fuel, as well as periodically service it, cleaning it from ash, etc.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
High requirements for fuel storage
If stored improperly, firewood may become wet, which will reduce its calorific value; therefore, a room protected from precipitation is required.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing firewood for the winter.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
2.2 EUROWOOD
Euro firewood (briquettes) is waste from wood processing, food industry or agriculture pressed into the form of logs or bricks, where a natural polymer, lignin, is used as an adhesive.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to other types of fuels.
Environmental Safety
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Low ash and no sulfur
Unlike other types of fuels.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Low labor costs
Unlike traditional firewood, Eurowood does not need to be sawed, split, or allowed to dry for a year or two in an appropriate room. On the contrary, the fresher the fuel, the better, because Over time, they can accumulate excess moisture, which will negatively affect the heating value.
Neutral:
Lack of autonomy
It is necessary to constantly manually replenish the boiler with fuel. An alternative option is to install an additional automatic fuel supply system to the boiler, but in this case the cost and complexity of installation will increase. Also, do not forget about the need for periodic maintenance, cleaning from ash, etc.
Cons
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
High requirements for fuel storage
If stored improperly, the fuel may become wet, which will reduce the calorific value; therefore, a room protected from exposure to precipitation is required.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
2.3 FUEL GRANULLES (PELLETS)
Fuel granules (pellets) are waste from wood processing, food industry or agriculture pressed into granules. A distinctive feature of pellets is their higher density and lower humidity compared to standard firewood and Euro firewood, while the heat transfer remains at the same level.
The pros and cons are the same as those of Euro-firewood, except for the lack of autonomy. If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
2.4 SAWDUST AND CHIPS
Sawdust and wood chips are crushed waste from wood processing, food industry or agriculture. Unlike Euro firewood and pellets, they have not undergone any processing; accordingly, they have low density and high humidity. But the lack of processing significantly reduces their cost.
The pros and cons are the same as those of edrov and fuel pellets, except for the lack of autonomy. If you wish and have the funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, where the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
2.5 COAL
Coal is a sedimentary rock of plant origin, consisting of combustible carbon and other chemical elements. The “older” the rock, the less moisture it contains and the greater its calorific value.
ADVANTAGES
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Low cost
Unlike other types of fuels.
Cons
Low calorific value
Compared to liquid fuel and gas.
Huge harm to the environment
Compared to other types of fuels.
Presence of coal dust
Polluting the room.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
Presence of sulfur
Destroying the cauldron.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, as well as the presence of coal dust, a spacious room is required to store fuel for the winter.
Danger to others.
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Lack of autonomy.
It is necessary to constantly replenish the boiler with fuel manually. Also, do not forget about the need for periodic maintenance, cleaning from ash, etc.
2.6 PEAT
Peat is a natural material that forms in swampy areas. Therefore, it contains quite a high percentage of water and needs to be dried. After drying, dry peat crumbles extremely easily, making it inconvenient to use. Therefore, it is mixed with sawdust and pressed into various shapes.
ADVANTAGES
Environmental safety
Low emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion
Low cost
Unlike other types of fuels.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Energy independence
No power connection required.
Cons
Lack of autonomy
It is necessary to constantly manually replenish the boiler with fuel. Also, do not forget about the need for periodic maintenance, cleaning from ash, etc.
Low calorific value
Compared to liquid fuel and gas.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
High requirements for fuel storage
Fuel may catch fire if not stored properly.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
Complete smoke exhaust system
Chimney installation required.
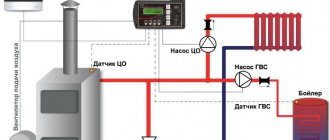
Firewood for water heaters
This type of fuel is used quite rarely to ensure the operation of boilers. But still, sometimes in private homes or even in enterprises you can see heating equipment that runs on wood. The advantage of this type of fuel is, first of all, its relative cheapness. However, using a boiler when using firewood is usually very inconvenient. The boiler room operator should add solid fuel of this type into the firebox 2-3 times a day. The same feature applies to the operation of a wood-fired water heater in a private home.
Of course, there are no special requirements for logs when using them for boilers. The only thing is that this type of fuel for boiler houses must be quite dry. Firewood should be stored under a shed or in a special small separate room - a wood shed. Traditionally, hardwood logs are used for boilers, as well as for stoves. When burned, conifers leave a lot of ash and soot due to the resin. Birch firewood is best suited for a solid fuel boiler.
CALCULATION OF THE COST OF EXPENSES FOR SOLID FUEL
As an example of calculating costs for solid fuel, let’s take firewood from wood, whose calorific value is 2716. The calculation will be carried out using a simplified formula:
V = 24 * Q / (q * 0.01efficiency)
- 24 – number of hours per day;
- V – amount of fuel per day;
- Q – heat load (kilowatt-hour) required for heating 300 m2;
- q is the calorific value of 1 cubic meter of wood (kW/m3), in our case 2716;
- Efficiency is the efficiency factor (%) of the boiler; for example, let’s take 80%.
V = 24*24/(2716*0.8) = 0.26 m3
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need 0.26 m3 of wood. For the heating season, which is 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(0.26 m3 (daily gas consumption) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 24 m3.
LIQUID FUEL
Liquid fuel is a mixture of various hydrocarbons, the molecules of which are connected in very long chains; thanks to this connection, the fuel acquires a liquid state of aggregation. To achieve maximum combustion efficiency, it is recommended to spray liquid fuel in the form of tiny particles in the combustion chamber and only then mix it with air. The main disadvantage of liquid fuel is the threat of low temperatures; it must be stored at a positive temperature.
3.1 DIESEL FUEL
Diesel fuel (diesel fuel) is a petroleum product consisting of a mixture of hydrocarbons that are obtained by distillation and selection of certain fractions from them. Nowadays diesel fuel is widely used as fuel for internal combustion engines of agricultural and construction vehicles, diesel locomotives, ships, and passenger cars.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
Environmental harm
High amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
High requirements for fuel storage
Fuel may catch fire if not stored properly.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
High price
Compared to other types of fuels.
Presence of odor and operating noise
Compared to other types of fuels.
3.2 MAZUT
Fuel oil is a relatively inexpensive type of fuel, which is obtained from the products of oil refining and gas condensate raw materials, or as a result of secondary processes of their processing. Fuel oil consists of hydrocarbons (with a molecular weight of 400 to 1000 g/mol), petroleum resins (with a molecular weight of 500–3000 or more g/mol), asphaltenes, carbenes, carboids and organic compounds containing metals (V, Ni, Fe , Mg, Na, Ca).
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
Low ash content
Around 0.3-0.5%.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
Unstable composition of fuel oil
From close to oil to highly viscous cracking residues, which leads to coking and prolongation of the combustion process.
Environmental harm
High amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
High price
Compared to other types of fuels.
Presence of odor and operating noise
Compared to other types of fuels.
High sulfur content
Around 3.5%.
High pour point
Around +(25-30 °C).
3.3 FUEL
Biofuel is a combustible mixture created from plant or animal raw materials, such as soybean seeds, sugar cane, and various organic wastes. Biofuels include bioethanol, biomethanol, biobutanol, demethyl ether, and biodiesel.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
Environmental Safety
Low amount of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere during combustion.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
High cost
Compared to other types of fuels.
High fuel storage requirements
If stored improperly, the stove may catch fire.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
3.4 USED OIL
Waste oil is hydraulic, transmission, transformer oil, as well as vegetable oil, used for its intended purpose.
ADVANTAGES
High calorific value
High calorific value compared to solid fuel.
Independence from main communications
Unlike gas.
No explosion hazard
Unlike gas.
Cheap and easy installation of a heating system
No permitting documents are required, unlike gas, and qualified employees.
Neutral:
Autonomy
If desired and available funds, it is possible to install an autonomous heating system, when the fuel will flow into the boiler automatically as it burns.
Danger to others
For boilers with an open combustion chamber, there is a risk of exhaust gases entering the room in which the boiler is located, which can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning in surrounding people. Unlike boilers with a closed chamber, where the likelihood of exhaust gases entering is minimized.
Cons
Additional costs
For filtration before use and for converting the boiler to waste oil
High fuel storage requirements
If stored improperly, the stove may catch fire.
Warehouse space
Depending on the needs and volumes of heating, there may be a need for a spacious room for storing fuel for the winter.
High fuel cost
Compared to other types of fuels.
Pricing policy for long-burning boilers
The price is determined based on many indicators and values, the main ones fit into three fundamental factors:
- Brand, country of origin;
- Characteristics of thermal power;
- Multifunctional design and ability to process various types of fuel.
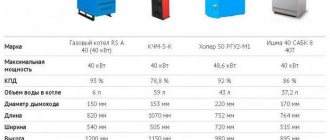
By the way, long-burning wood-burning boilers from Stropuva with a power of 20 kW are in the price range of 1400-1900 euros. At the same time, similar power, but on a universal model, will cost 2000-2400 euros.
The classic is represented on the market by the Buderus long-burning boiler from a German concern. Operation is allowed on wood, coal, anthracite and pellets. The cost of the Buderus boiler is determined by the thermal output and ranges from 1400-1900 euros.
Let's add another EU manufacturer from Germany - the company's long-burning solid fuel boiler (Junkers) shows excellent performance. The Junkers boiler with a power of 32 kW with a price per unit of 1600 euros stands out from the range for the better.
The Viessmann company asks for the highest price for its long-burning pyrolysis boiler; for the Vitoligno model, the concern wants to receive from 2300 to 5900 euros for a boiler with a maximum industrial power of 80 kW.
It's time to turn to a domestic manufacturer. Available options start from 35 thousand rubles, so a Russian-made Cooper solid fuel boiler can be purchased for 40 thousand rubles.
Also on the Internet there is a huge amount of advice on how to make a long-burning solid fuel boiler with your own hands. If you have the material and skillful hands, you can create your own cauldron!
conclusions
In conclusion, we would like to say that you should not give in to the impulse to buy a long-burning solid fuel boiler, calculate all the options, and once again compare the calculations of the operating savings of an electric boiler. Try to clarify the necessary and sufficient power of the heat-generating equipment. Most likely, the issue price will be in the same range.
It is possible that an electric boiler, in combination with, say, a heated floor of a film type of infrared radiation, will be equally costly from a financial point of view in comparison with a long-burning boiler, but less troublesome to use. Well, if you decide that you can’t do without a long-burning boiler, don’t skimp and buy a device with automatic coal supply, it will greatly improve your life.
CALCULATION OF LIQUID FUEL COSTS
As an example of calculating heating costs, let’s take diesel fuel (diesel fuel). The approximate consumption of diesel fuel per hour of boiler operation can be found by multiplying 0.1 by the boiler power according to the passport. For example, if we chose a 25 kW boiler to heat 300 m3, then it will consume 0.1 * 25 = 2.5 liters of diesel fuel per hour.
Thus, to heat 300 m3 per day you will need:
2.5 liters (consumption per hour) * 24 (hours in a day) = 60 liters of diesel fuel.
For the heating season, which is 183 days (from October 15 to April 15), taking into account temperature fluctuations, you will need:
(60 liters (daily consumption of diesel fuel) x 183 days (heating season)) / 2 (taking into account temperature fluctuations) = 5490 liters.
Fuel briquettes, pellets
Developed countries have long switched to environmentally friendly raw materials for heating boilers. Recently, the countries of the former CIS have begun to use briquettes and pellets more often. High quality raw materials, suitable for humidity, weight, volume, ash content.
Thanks to proper preparation of the material - pressing, granulation, raw materials can be stored for a long time without fear of a decrease in the density of the material or rotting. Easier to transport than logs of firewood.
You can make the boiler ignition process automated. Purchase a pellet tank with which raw materials are supplied to the firebox automatically. Owners do not need to throw briquettes for uninterrupted heat supply.
Briquettes and pellets differ in production technology. Pellets are more often used for boilers; briquettes are used for open fires.
Firewood for heating the boiler
It is better to find a production of raw materials near your home. It is more profitable to order from the manufacturer than from mark-up stores.