When constructing housing, various materials are used for insulation. These include insulation with foil; what its varieties are called and in what cases they are used is described below. Read on and you will get acquainted with the features of different types of foil insulation and learn about their areas of application. A close acquaintance with the installation features will help reduce construction costs.
Ceiling insulation Source samstroy.com
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Insulation with foil has a number of features and a minimum of negative aspects. Advantages:
- Foil reflects heat. Thus, the heat remains in the house, on the other hand, it does not allow heat to enter the house in the summer.
- Increased wear resistance.
- Partially applicable as a waterproofing material.
- Easy installation, light weight, simple dismantling.
- The insulation does not allow cold wind to pass through. Maximum insulates from external influences. Resistant to deformation due to sudden temperature changes.
- Keeps out noise from the street.
- Does not rot or mold.
- This material is thinner than others, but is 20-30% more effective.
- The insulation does not emit substances harmful to health and prevents the smallest irritants and allergens from getting inside.
- There is no rigidity, so the top cannot be covered with plaster or wallpaper.
- Special adhesives are required for fixation.
- Sometimes insulation with foil is not enough to insulate a room.
Despite the disadvantages, foil material is widely used for various purposes.
Where is the foil insulation method used?
Foil insulation reflects infrared rays, which are essentially thermal rays. But there is no need to use the material everywhere. In some places it will not work properly.
It is mainly installed near thermal energy sources:
- heating devices - batteries, air heaters. The insulation is mounted on the wall with foil in the room;
- boiler, fireplace stove.
It is also used when installing “warm floors”. The reflective layer will direct the heat in the desired direction.
Small spaces where every centimeter plays a role. Here, thin insulation would be appropriate on the walls and ceiling.
In the attic. Here the insulation is installed on the roof. Apply 2 layers to combat heat and cold.
In baths and saunas. The heating of the room is not constant; foil material is suitable for such purposes.
Garages, hangars, outbuildings - an installed radiator or potbelly stove.
They also insulate heating pipes, air ducts, wells and wells.
Features of using foil thermal insulation
According to the recommendations of the current standard for thermal protection of buildings (SP 23-101-2004), external placement of a thermal insulation layer in two-layer walls is recommended. But this does not apply to foil insulation, since the relative position of the layers should prevent the structure from getting wet and not interfere with normal moisture transfer. And if there is a vapor barrier (foil) outside, drying of the main facade material will be blocked.
At the same time, the standard allows for internal insulation if a layer of continuous and durable vapor barrier is installed on the side of the room. And this exception is completely suitable for foil insulation. They also use internal insulation of the walls of hangars, warehouses and other buildings that are made of corrugated sheets.
The use of reflective thermal insulation is advisable in the following cases:
- When arranging the walls of frame houses. In this case, the wall is considered as a single-layer structure with thin-walled shells, which combines load-bearing and thermal insulation functions. And here, instead of the usual film vapor barrier, an additional layer of foil insulation is used.
- When insulating balconies. The design of the balcony fencing is similar to the wall of a frame house.
- When insulating a loggia.
- When insulating the roof of a used attic or attic.
- When insulating attic walls. In this case, their design completely coincides with the structure of frame walls.
- When insulating a bath or sauna. Internal insulation with foil materials significantly reduces the time it takes to warm up the room and saves energy resources during operation.
Foil insulation design
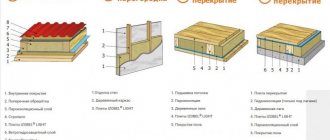
Thermal insulation with foil is produced in:
They differ in size, thickness and the foil-covered base layer used.
Base layer types:
- polyethylene foam;
- basalt wool;
- expanded polystyrene.
The foil is glued to the base layer or applied by spraying.
Some have layers of foil on both sides. Or with a layer of applied glue - self-adhesive, which allows for easy installation. Self-adhesive is used in corners and on uneven surfaces. The joints of the insulation are taped with foil tape.
When purchasing insulation with a reflector, you need to pay attention to:
- base layer;
- foil thickness;
- taped with a reflector on one side or both.
The thickness of the insulation itself depends on the base material used.
Insulation technology
It's time to tell how reflective thermal insulation is installed on the ceiling in a private house. To install insulation on a self-adhesive base, you do not need to construct a sheathing on the base. The base needs to be well prepared - cleaned of old finishes, putty on defects and uneven surfaces. The insulation is glued to the primed surface. To do this, remove the protective film from the adhesive layer.
The heat insulator without an adhesive base is mounted between two battens. Moreover, the insulation is laid in two layers - the first is fixed directly to the main ceiling, after which the sheathing is mounted with other heat-insulating material embedded in its cells, and then another layer of penofol or isolon is attached to the sheathing from below. Next comes another lathing to create an air gap between the insulation and the finish. This ventilation gap will prevent condensation from accumulating.
Tools and materials
To insulate the ceiling with isolon from the inside, you will need the following tools and materials:
- perforator;
- drill;
- wooden slats for sheathing;
- wood hacksaw;
- self-tapping screws and dowels for fastening the sheathing;
- laser level;
- roulette;
- ruler;
- pencil;
- ladder;
- foil insulator (taking into account two-layer laying);
- primer;
- reinforced tape;
- putty;
- rollers and spatulas;
- solution container;
- cutter or scissors;
- stapler and staples for it.
Installation of foil insulator on the ceiling
Installation of penofol on the ceiling is carried out in the following order:
- We remove the old finish from the base ceiling, eliminate all defects with putty, and level the surface with mortar. After the putty mixture has dried, the surface is primed twice.
- We install the first layer of reflective insulator on the ceiling. For initial fixation, we use double-sided tape (if there is no self-adhesive base), then we press the covering with the lathing slats. We install the slats in increments of 500 mm. We tape all the joints of the reflective insulation with tape.
- If necessary, we place another heat-insulating material (mineral wool, foam plastic) between the slats, but you can do without it. Next, we attach strips of foil insulation to the slats. We lay the material end to end and shoot it with staplers. All joints are sealed with reinforced tape.
- We install another sheathing of wooden slats 2 cm high.
- After this, we attach the selected finishing material (plasterboard, plywood, MDF, PVC panels, lining, etc.) to the installed sheathing.
Types of foil penofol
There are 3 types of penofol with foil on sale. Each is marked with Latin letters, which indicate the packaging.
Folgoizolon for external and internal work
TYPE A – heat insulator made of polymer, foil layer on one side. Produced in different thicknesses. Suitable for complex insulation of buildings inside. Glass wool is used together with this insulation. They also produce foil insulation with perforation. It is installed in log houses to allow the wood to “breathe.”
What is better - foil penofol or basalt insulation?
The building materials market is full of types of insulation. They have their own characteristics, positive and negative sides.
General thermal insulation parameters:
- Weight. The insulation should not weigh much, because when installing it on the structure there should be no weight.
- Thickness. The thinner the material, the more space remains in the room.
- Low thermal conductivity.
- Moisture permeability. The material should absorb moisture as little as possible.
- Noise insulation. Does not allow sounds from the street to pass through.
- Environmentally friendly material. Should not emit harmful substances.
- Easy to install.
When comparing basalt insulation and foil penofol, you need to compare their characteristics.
Basalt wool
Made from rock of volcanic origin. It does not burn, has good sound insulation properties, and does not lose its qualities over time. It is completely safe for health.
Penofol - application
Made from polyethylene foam with a porous structure. A layer of foil is glued on top as a heat reflector. This thermal insulation material is several times thinner than basalt wool. In addition, it reflects heat and practically does not absorb it.
Which insulation to choose depends on the budget for insulation, as well as personal preferences.
The most popular type of insulation with foil for interior finishing is aluform
Bestizol or alufom is a bubble base consisting of aluminum foil (outer layer) and polyethylene (inner layer) on one side. The foil acts as a reflector of solar and heat rays. The polyethylene layer has a cellular structure and neutralizes sound waves and shocks. The advantage of this material is low thermal conductivity.
Bestizol can be used in both cold and hot weather. Due to its small thickness (1 cm), the material is used for hard-to-reach places:
- for winding ventilation pipes;
- air duct coverings;
- insulation of pipelines and other outlet communications.
Installation of rolled foam foam inside and outside: how to stick it?
Basic installation rules:
- The material is mounted straightened, uncompressed, without folds. Fix to the lathing or directly to a clean surface.
- Penofol is secured with foil towards the heat to reflect it. This is an obstacle to the release of thermal energy to the street.
- The material is glued end to end. The borders are taped to seal.
- To glue the insulation, special types of glue or a self-adhesive type are used.
Installation is quick and easy, both inside and outside. The work is identical in sequence and principle inside and outside. It is easy to cut and quickly installed.
Before gluing penofol, you do not need to pay attention to its weight. The material is lightweight and can be supported by universal glue. But, for strength, they purchase adhesive compositions intended for this purpose.
The adhesive must correspond to the characteristics of the thermal insulation material:
- temperature range +100/-600C;
- indoor use, not outdoor use;
- non-toxic;
- good adhesion.
The adhesive composition should not emit harmful substances. Penofol is able to absorb 3% of heat, which means the glue on the back side can also warm up.
How to glue insulation with foil to the wall near the radiator and door
For gluing the surface and penofol, craftsmen recommend purchasing the following brands:
- Weicon Easy-Mix PE-PP 45. Two-component adhesive designed for gluing concrete (brick) surfaces with polyethylene, polypropylene.
- Moment - has many positive aspects, including good adhesion. The glue will quickly and permanently bond the insulation to the surface behind the radiator or near the door.
- Liquid nails are capable of fixing heat-insulating material for a long time.
Other brands: Titan, Tilit, Atlas Stopter K-20 kley, Ceresit (ST83).
How to lay it correctly
The presence of foil on the insulation dictates a slightly different installation technology. Therefore, we will consider some features of performing thermal insulation work with unusual insulation.
Which side should the insulation be placed on the structure to be insulated?
The answer is short: foil insulation indoors can only be placed with the foil facing out. When installed on the contrary, there is no reflection of heat waves back into the room. On the façade also, outwards. The metallized layer in this case is primarily a wind and vapor barrier, and only secondly helps the base of the insulation to retain cold air.
Floor insulation
Floor insulation is carried out using two technologies:
- "floating screed";
- “floating floor” - used mainly when installing “warm floors”.
"Floating screed"
Before laying the insulation on the concrete base of the floor, the following preparatory work is carried out:
- the concrete floor is freed from the old screed;
- repair work is being carried out to restore the surface of the concrete slab;
- the base of the floor is primed;
- waterproofing work is being carried out, etc. Detailed instructions for preparing the floor for pouring screed are given in the article “Preparing the floor for pouring screed”.
When using insulation without a self-adhesive side, the concrete base and insulation are lubricated with glue for the selected type of base. The edges of the slabs are also treated with adhesive. If the glue is contact (for Penofol), a pause is made for about 30-40 seconds, during which polymerization of the open surface of the glue occurs. After the specified time, the mats are fixed.
For better adhesion, the surface is carefully smoothed with smooth movements with little effort. Thin (2-3 mm) “Penofol” is placed on the walls to a height of 5-7 cm, and overlapped in the middle of the room. Thick slabs (5-10 mm) are mounted tightly to each other, without gaps. The joints are taped with aluminum tape (insulating aluminum tape). A fiberglass reinforcing mesh is attached to the laid insulation layer, after which the screed is poured.
Under "warm floor"
When installing a “warm floor” with heating elements placed inside a cement screed, the work is performed in the same sequence as when insulating a floor under a “floating screed”.
Under the infrared film, 3 mm thick insulation is attached to the base of the floor. A heating element is placed on it, and logs or sheets of plywood or OSB are attached on top of it. For this option, experts recommend buying ALP type insulation.
If possible, you should ground the foil through a Euro socket - if the infrared heater film breaks down, the aluminum foil will be energized. Cases of electric shock have not been written about on the forums, but such a possibility exists. Therefore, it is better to play it safe.
And we also note that many experts advise first reinforcing the insulation, and then attaching a reinforcing mesh over the heating elements. This is exactly the case when “you can’t spoil porridge with butter.”
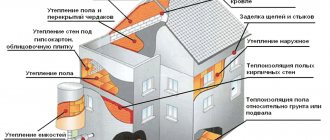
Wall insulation
Foil insulation for walls can be based on fiberglass or polyethylene foam. It is attached to the surface using glue (in this case, only vertical slats are stuffed for fastening sheets of gypsum plasterboard, plywood or OSB) or placed in the cells of the sheathing.
The connecting seams are taped with metallized tape (adhesive tape). The gaps between the slats and the insulation are foamed with polyurethane foam, but it is better to avoid them. Vapor barrier work is not carried out - foil serves as a barrier to vapor molecules. From above, everything is covered with a protective screen made of plasterboard, plywood or OSB.
Ceiling insulation
Thermal insulation of the ceiling is carried out mainly by Isolon, 2-5 mm thick, type B (foil on 2 sides) or C (self-adhesive).
In the first case, the lathing is placed directly on the ceiling, in the second - on top of the heat-insulating layer. In both cases, the insulation is fixed with glue. In addition, you can use special self-tapping dowels with a large plastic head. When installing a stretch ceiling, no other types of work are performed. If the ceiling is to be painted or wallpapered, then plasterboard is attached to the sheathing.
Bath insulation
Rolled glass wool of medium thickness is ideal for insulating the ceiling and walls of a bathhouse. Insulation work starts from the ceiling and ends on the walls. Quite often they play it safe and attach parchment paper to the ceiling - it serves as an additional barrier to the penetration of steam into the insulation.
The insulation scheme includes:
- lathing device;
- laying insulation in the cells of the frame;
- gluing the joints with special tape (metalized);
- A counter-lattice is attached on top of the frame. The goal is to create a ventilation gap and a base for attaching the finishing trim.
Roof insulation
For thermal insulation of the attic space, foil mats made of mineral fiber are best suited. The order of work is as follows (enlarged):
- on the roof, all detected cracks are sealed with tow and foam;
- a counter-lattice is placed on the boards;
- a class B vapor barrier film (with the smooth side facing the room) or glassine is attached to the created frame with glue or a construction stapler;
- At the bottom of the rafter system, strips are placed behind which the thermal insulation will be laid;
- foiled mineral wool mats or expanded polystyrene slabs are laid;
- connecting joints are glued with metallized tape.
Insulation from outside
To insulate the facade you will need:
- foil mineral wool of medium thickness;
- reinforcing fiberglass mesh;
- wooden planks for lathing;
- glue;
- dowels with self-tapping screws.
According to the instructions, technological operations are performed in the following sequence:
- wooden slats are attached vertically to the wall using dowels in increments equal to the width of the insulation. Experts advise reducing this distance by a few mm so that the insulation fits tightly between the studs;
- sheets are glued to the wall;
- a reinforcing mesh is attached on top of the thermal insulation layer;
- The finishing work on the facade is carried out using the grid: siding is installed or decorative plaster is applied.
Life time
Since foil insulation appeared relatively recently, it is not yet possible to determine the exact expiration date. However, after conducting experiments, we can say that the material does not lose its properties for 200 years.
The service life of the installed insulation depends on the adhesive used. If the adhesive composition has passed its expiration date, then you can re-install it with the same heat insulator.
There are a lot of insulation materials on the construction market. The choice is so wide that the question arises, which is better. To answer, you need to compare the characteristics of the thermal insulation material and the scope of application - street, living room, garage or agricultural building.
Recommendations for choosing material
When arranging the inside of any room, you should not limit yourself to choosing one type of insulating agent. It would be more correct to combine several types and use all the advantages of each.
There is no single recipe; what is important here is the approach and analysis of all influencing factors for each decision:
- Material of floors and walls,
- Presence of other types of insulation;
- Room humidity.
To ensure that the interior walls of a room are always dry, materials with a zero vaporization parameter or tending to it are needed. Then, when choosing, you need to pay special attention to the following:
- Fire safety - for interior spaces it is better to select materials of non-flammable class NG, but, according to the standards, it is possible to use G1;
- The absence of toxic substances in the materials that may be released during operation;
- Low thermal conductivity, the lower, the better the heat will be retained.
- Service life or durability is an indicator that indicates the stability of the properties of a material over a certain period of time.
Insulation of heating lines
Useful video
Various building materials are used to insulate residential and non-residential buildings. Penofol is also used as insulation. Let's consider what this material is, what its advantages and disadvantages are.
What it is?
Penofol is a two-layer heat-insulating building material, which can be made from one or 2 layers of foil applied to a base layer of polyethylene foam. Depending on the type of product, the density and thickness of the foam may vary. Utilitarian and inexpensive insulation is in great demand among buyers, because it has high performance characteristics.
A layer of foil, the thickness of which is 20 microns, provides penofol with excellent heat-reflecting qualities.
This insulation is used in everyday life and industry as the main insulating material or as an auxiliary thermal insulation layer.
Penofol is used as the main insulating material in cases where it is necessary to insulate a room with normal heat loss and where there is a powerful heating source (bathhouse, sauna, underfloor heating system in a wooden house). As an additional insulating building material, penofol is used to create complex heat insulation in residential and industrial premises, and such premises must be equipped with vapor barrier and waterproofing.
New thermal insulation materials are appearing on the market with increased thermal protection and unique qualities. Such a material is penofol.
The use of penofol insulation allows you to achieve serious results due to its reflective and insulating qualities.
Penofol insulation is an excellent way of thermal insulation.
Roll material laying technology
Step 1. The material produced in a roll must be laid on a surface cleared of debris. The base is swept, washed if necessary and dried.
Preparing the base
Step 2. The insulation is cut into pieces of the required length and size.
Cutting foil insulation
Step 3. The material is leveled over the surface of the room.
The insulation is leveled over the surface
Another photo of the process
Step 4. In small rooms, the insulation is attached along the walls and across with wooden blocks. Its individual sheets are glued together with tape.
The insulation is attached using bars
The process of installing bars
Step 5. If the floor covering allows it (it is quite dense), then lathing is done on top of the laid insulation. This makes it possible to create an air gap.
Creating a sheathing
Next, the floor is covered with a finishing coating or filled with concrete screed; work is also carried out on the installation of heated floors, if necessary.
Warm floors are a serious cost item during renovation, so it is important to accurately calculate how much and what materials will be needed. To ease your labor costs, we have prepared special instructions telling you how to calculate a heated floor - water or electric. Online calculators included. And in the article “ What do you need for a heated floor? » you will find a complete list of everything that may be needed during installation.
Video - Laying roll backing
Insulation with a layer of foil is a good option for high-quality thermal insulation material. It will serve for many years if you choose it correctly in accordance with operating conditions, as well as with proper installation. It’s easy to avoid mistakes; the main thing is to carefully familiarize yourself with all the nuances of using the material.
* * * * * * *
For purely practical reasons, and also as an example of the effectiveness of using foil insulation, especially when combined with other thermal insulation material, below is a calculator for calculating the insulation of a balcony. Since it makes no sense to consider the floor on a balcony or loggia separately, the calculator allows you to make calculations for the entire room, for each of the surfaces that require thermal insulation.
Brief explanations on how to use the program will be given below.
Properties and characteristics of penofol
Operating principle
The photo shows a roll of one-sided foam foam used for interior work.
Penofol is a combined material consisting of foamed polyethylene and purified foil with a high reflectivity of infrared waves.
The operating principle of the material is based on complex resistance to the processes of thermal energy propagation.
As you know, there are three ways to distribute heat:
- convection,
- direct heat transfer,
- and radiation.
Most isolators prevent any one of these methods.
Penofol is able to create a barrier to direct heat transfer due to a layer of foamed polyethylene, which has in its structure many sealed pores filled with air or carbon dioxide. Thus, heat transfer through this layer is difficult. Most insulation materials, such as polystyrene foam, mineral wool or polyurethane foam, work on the same principle.
In addition, our insulation has a layer of reflective foil. It is applied to polyethylene by thermal welding and has a reflection coefficient of at least 97%. It should be said that ordinary foil has a reflection coefficient of 50 - 70%.
The foil used in the production of penofol has a thickness of 20 - 30 microns. Polyethylene foam can have different thicknesses, from 2 to 10 mm. Sometimes thicknesses reaching up to 40 mm are used, but this is rare.
So, we get a material that resists not only direct heat transfer, but also prevents the penetration of infrared thermal radiation outside the room, reflecting it inside. In addition, penofol has excellent soundproofing and vapor barrier properties, which is also important and saves money on additional materials.
The price of the material fluctuates in the middle and lower ranges, significantly inferior to the cost of many modern insulation materials, such as polyurethane foam. Installation work can be easily done with your own hands without the involvement of specialists, which also saves money.
Application area
The scope of application of penofol is so wide that it can be found in the most unexpected places.
Penofol is used for insulation:
- Residential buildings: light and country buildings, cottages, private houses, multi-storey buildings;
- Sauna, baths;
- Industrial and administrative buildings;
- Medical institutions, kindergartens;
- Warehouses, hangars, both heated and cold;
- Capital and temporary trade pavilions, shops, supermarkets and shopping and entertainment centers;
- Refrigeration chambers;
- Pipelines for various purposes;
- Heating, air conditioning, ventilation and water supply systems;
- Cars, railway cars, vans, refrigerators.
It is possible to process the following structures:
- External and internal walls;
- Ceilings;
- Roof insulation;
- Ceilings over cold basements;
- Floors.
Important! When using the material, it should be remembered that aluminum foil is an excellent conductor of electric current, so the insulation of electrical wiring must be checked with special care, otherwise people may suffer from electric shock.
Characteristics
Hoods treated with reflective insulation.
Popular brands and prices
Each foil insulation has its own leaders in the sales market. Here are the top three manufacturers of polyethylene foam, expanded polystyrene, glass wool and basalt wool (based on sales volumes) and the prices for these products.
Foil polyethylene foam. Many companies produce polyethylene foam insulation with a foil side. The leaders among them are:
- “Izolon” - can be bought from 78 rub./m2 with a thickness of 2 mm and from 110 rub./m2 with a thickness of 3 mm;
- “Penofol” - the price varies from 65 rub./m2 for insulation with a thickness of 3 mm to 456 rub./m2 with a thickness of 20 mm;
- "Ekofol" - sold at prices from 37 (2 mm) to 70 (10 mm) rubles/m2.
Please note: prices are average. Listed for St. Petersburg. In other regions, they may differ slightly in one direction or the other.
In addition to the above companies, Isoflex, Jermaflex and Folgoizol receive positive reviews.
Foiled polystyrene foam. Buyers are well aware of such brands of foil foam as Penoplex, Knauf, Technonikol and others. Prices depend on the thickness of the base. Therefore, for comparison, we will give in m3, although such a comparison does not make it possible to understand the huge variability of the price range: from 2.0 to 9.0 thousand rubles. for 1 cubic meter
Foil glass wool. Most often, foiled mineral wool is purchased - the price of insulation with a thickness of 50 mm is in the range of 130-140 rubles / m2. The brands “Rockwool”, “Knauf”, “PAROC” also find their buyers. However, prices here are much higher and have a wide range, and therefore it is inappropriate to list them.
Foil basalt wool. Among foiled stone wool, the leaders are “Rockwool” and “PAROC”. Prices are high and start at 4,000 rubles/m3 and end at around 14,000 rubles/m3.
Installation
Wall treatment from the inside
Wall insulation with penofol is done using self-tapping screws or a stapler.
For interior work, one-sided penofol with a thickness of 4–5 mm is used. You can also use double-sided, but its installation is different, since it is necessary to maintain an air gap on both sides. In ordinary apartments and houses, one-sided material is sufficient, but if the walls are too cold, then they should be additionally insulated with polystyrene foam or cotton wool.
Our instructions will help you understand how to insulate a wall with penofol from the inside:
- We roll out the roll of insulation and cut off a strip equal in length to the length of the wall;
Cut the strip to the required length.
- Starting from the ceiling, we nail the strip to the wall with a stapler;
Carefully attach the insulation strip.
- If the wall is wooden, you can also use a screwdriver. We put large washers on the screws, like on umbrella-type dowels;
We put washers on the screws.
- If the wall is concrete and it is impossible to nail the material to it with staples or screws, use glue;
- We cover the entire wall with penofol end-to-end, without making any overlaps;
We cover all walls without overlaps.
- We glue the joints with aluminum adhesive tape;
We glue the joints with aluminum tape.
- On top of the insulation we place a lathing made of slats or plywood with a thickness of at least 1.5 - 2 cm;
We fill the crate on top.
We stuff the casing on top.
Important! On the side of the foil coating, be sure to leave an air gap 1.5–2 cm thick, otherwise condensation will accumulate on the surface. If the material is double-sided, the gap must be maintained on both sides.
Ceiling and floor
Insulating the ceiling with penofol significantly increases the energy efficiency of the room.
Installation of material on the ceiling is not fundamentally different from similar work on walls.
First, the material is cut, the desired strip is taken and attached along the wall, starting from the middle:
We mount the strip from the middle along the wall into the corner.
We reach one corner, nailing the side closest to the wall:
We fasten one side.
Then from the middle we move in the opposite direction, attaching the strip further:
One side of the strip is nailed.
Next, from the middle point we move perpendicular to the foam sheet and shoot at the line indicated in the photo in green:
We nail the middle line.
Next, we move from the middle to the corners, smoothing and shooting the material towards the ceiling:
We finally fasten the strip.
Similarly, you can insulate the floor with penofol or insulate the loggia. The main thing to remember is the basic rule: leave a gap between the casing and the foil!
Advice! In the case of a loggia, penofol should be used together with expanded polystyrene, since the balcony structures are too thin for serious thermal insulation.
During floor insulation work, the material is placed with the foil facing up. We glue the insulation to the screed or floor slab with any glue suitable for such substances. Then we lay logs on the carpet, on which we mount floorboards or plywood.
When using double-sided material, it is usually placed in the joist space so that there is an air gap on both sides. To do this, you can nail the carpet to the joists in the middle of the distance from the floor to the upper plane, then throw the material over the slats, and fasten it on the other side as well.
Then the insulation is stretched in the middle of the space, between the floor and the boards.
In addition, do not forget to attach the strips end-to-end, and treat the joints with aluminum tape. The material is soft and pliable, making it easy to cover curved and curved areas of walls. The low weight of the coating does not create any noticeable additional load on the structure.
Weaknesses and strengths of foil thermal insulators
The ability of materials to retain thermal energy is largely determined by their structure, the presence of air layers and thickness. This is the so-called passive thermal efficiency. The addition of a reflective surface forces insulation to take a more active role in retaining heat.
Foil heat insulators work on the principle of a thermos. The heat flow is reflected from the mirror surface, returning back into the room. Thanks to this ability, combined insulation materials have acquired additional qualities:
- in winter the building retains heat better, and in summer it retains coolness;
- reducing costs for heating fluids;
- protection from moisture – you don’t have to install additional waterproofing;
- providing additional thermal insulation;
- environmental safety of the foil shell;
- due to the increased thermal insulation qualities, it is possible to use insulation materials of smaller thickness;
- versatility - suitable for solving various problems;
- variety of designs - rolls, slabs, pipes.
Installation of reflective heat insulators is no different in labor intensity from the use of conventional insulation. The weaknesses of the material are:
- aluminum is susceptible to corrosion processes - they are sluggish, but over time the reflective characteristics weaken somewhat;
- heating the metal layer - a small gap is required between the finishing and thermal insulation;
- price - foil insulation is more expensive than their single-component counterparts.