New developments aimed at saving home heating costs are increasingly attracting attention. New products also include vacuum heating radiators. These are ordinary batteries in appearance, but completely different in operating principle.
They are suitable for both centralized heating systems and autonomous ones. In this material we will talk in detail about the operating principles of vacuum radiators, their varieties, and also dwell on the nuances that you need to keep in mind when choosing heating radiators for your home.
What is a vacuum battery?
The radiator was called a vacuum radiator because the air was completely pumped out of the internal cavity of this steel sectional structure. This was done in order to reduce blood pressure.
A liquid substance is placed in hermetically sealed sections, which tends to evaporate easily at low temperatures. This is usually either ethanol or lithium bromide liquid.
In fact, the operation of a vacuum battery is based on the principle of operation of a sealed two-phase thermosyphon. At the same time, it has good heat transfer properties.
A system with such devices is low-inertia. It quickly reaches operating mode and reacts almost instantly to changes in heat loss.
| Radiator | Coolant flow g/sec. | Coolant temperature °C | Heating surface of the device in % for 2 minutes. | Heating surface of the device in % for 4 minutes. |
| Cast iron | 50 | 75 | 25 | 40 |
| Aluminum | 50 | 75 | 45 | 85 |
| Vacuum | 50 | 75 | 70 | 100 |
The table shows the heating efficiency of different radiators. From the surface of the vacuum heating unit, heat transfer into the room begins much faster.
The vacuum battery has an optimal ratio between thermal radiation and convection in the total heat transfer. The first indicator is 80%, the second - 20%.
Results
In what cases is it recommended to install a vacuum system for heating a home? With the exception of positive reviews about vacuum heating radiators, the installation of a solar system or expansion tank of the described type are auxiliary mechanisms for improving or optimizing the operation of the heating system.
A powerful vacuum pump for heating will improve water circulation, but will directly affect the thermal regime. The coolant simply does not have time to cool down sufficiently, which is unacceptable for a water heated floor - mixing flows will not lower the temperature to the required level.
When selecting and installing other elements of vacuum heating, their features should be taken into account.
Vacuum radiators
Installed electric vacuum radiator
In addition to the thermal power, the rules for installing vacuum heating radiators in a private home are observed.
The minimum distance from the heating surface to the window sill should be 8 cm. Moreover, the level from the floor to the bottom of the radiator also cannot be less than 4 cm. To improve heat transfer, it is recommended to install heat-reflecting materials on the wall behind the radiator.
Solar collectors
In some models, instead of a special liquid, you can use plain water. However, the efficiency of such installations is an order of magnitude lower than that of those described above. This point must be clarified with the seller.
Vacuum expansion tanks
Before making structures yourself, you need to choose the right material. It is best to use stainless or galvanized steel. But it should be taken into account that to weld it you need to use a special apparatus operating in a certain mode. The best way out of this situation is to purchase a suitable factory-made container and slightly modernize it by installing the necessary pipes for connection to the heating pipeline.
The video material clearly shows the operating principle of vacuum heating radiators:
Types of vacuum radiators
The line of vacuum devices includes products designed for electric heating, vacuum registers, and panel radiators. You can also find exclusive designer products on sale.
The vacuum electric radiator model deserves special attention, although they are more expensive. This is a good solution for owners of rarely visited suburban real estate.
Designer vacuum radiator in the form of a firewood stand. You can not only stack logs on it, but also dry them
Instead of a horizontal channel with a coolant, this device has a cartridge-type tubular heating element with a power of more than 50 W per section.
This heater transfers heat to the filler - oil or water, thereby heating the lithium bromide liquid. When installing such models, grounding is required.
Infrared heating of a private home: types of heaters and their application
There are several models of infrared heaters on sale with different technical characteristics. For example, short-wave devices are equipped with an open heating element, which heats up to 600 - 700 degrees, so they are unlikely to be suitable for small rooms; they are rather intended for large open spaces - balconies and terraces. The interior of the house is ideally heated by long-wave heaters with closed heating elements, the temperature of which reaches 200 - 250 degrees and their body almost does not heat up.
Infrared heaters must be equipped with thermostats that are designed to maintain a comfortable temperature in the room. Thermostats should be installed at a height of about one and a half meters from the floor and at some distance from the window.
Device and principle of operation
The difference between vacuum radiators and bimetallic and aluminum analogues can be seen during their external inspection. The former have a larger distance between sections. This heating device consists of a body, a horizontal channel and vertical sections.
Simplified diagram of a vacuum radiator. Its main elements are the collector (1) and vertical sections (2) in which the secondary coolant is located
The first of these elements includes two sections made of 1.5 mm steel. The horizontal channel is the primary circuit, located at the bottom and connected to the heat source. A coolant passes through it, transferring heat to the liquid located in sections that are located perpendicular to this channel.
The vertical sections are filled with a secondary coolant - a heat transformer. They are completely isolated from the primary circuit. Their number is directly proportional to the degree of heating of the room. The rate of heating of the liquid affects the pressure inside the cavities. The higher it is, the lower the pressure.
The secondary coolant is a liquid based on bromine and lithium. In the circuit it is in a small volume and tends to boil and quickly evaporate at a low temperature, about 35 °C.
The circuits are well insulated relative to each other and the environment.
The process that occurs in vacuum batteries looks like this:
- Antifreeze or water heats the horizontal channel.
- Heat from the horizontal channel is sent to the vertical sections.
- The heat transformer boils, causing the entire secondary circuit to be filled with steam.
- The walls of the secondary circuit heat up and release heat into the room.
To ensure effective transfer of heat rays from the lithium bromide liquid to the walls of the radiator, the state of the working substance must be brought as close as possible to the fog stage. Then the heat will be transported by drops of warm liquid.
To achieve this, the basic condition must be met - the pipe inlets must have a temperature of at least 40 and maximum 60 °C.
Vacuum devices provide room temperatures 2-3 degrees lower than traditional batteries. But home heating costs are reduced by an average of 17%
In the case of an autonomous system, it is difficult to achieve such indicators. In areas of the heating system remote from the source, the coolant will cool very quickly. The yield in the use of pyrolysis boilers with an optimal temperature range is from 45 to 60 °C or from 50 to 70 °C.
The problem is solved differently by installing one mixing unit in front of a group of vacuum radiators. In this case, the low-temperature level will ensure the connection of heated water with cooled water from the return. The operating cycle in the vacuum radiator is repeated after the condensate is lowered down the internal walls.
Design features
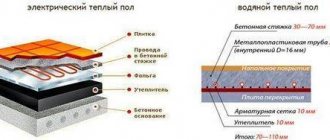
In appearance, these radiators are no different from ordinary ones. But inside there are big differences. Firstly, there is a pipeline that is laid at the bottom of the radiator. Hot water moves through it, which is heated in a conventional boiler. Secondly, the entire remaining volume is filled with a special boron-lithium mixture, which is there under vacuum. Hence the name.
Why such difficulties?
The boron-lithium mixture (refrigerant) begins to boil at a temperature of +35C. That is, hot water passing through the lower pipe heats this mixture, which boils and heats the metal body of the radiator. Hot vapors of the mixture rise upward, where they cool and condense, falling down. In this case, the temperature of the coolant may not be as high as in the case of conventional heating batteries. In them it is usually +75C. Accordingly, lowering the coolant temperature makes it possible to reduce fuel consumption costs. This is where the savings lie.
Experts note that the heat transfer of such models is lower than, say, aluminum batteries. Everything is true, but, firstly, the difference is not so significant as to make a choice between the first and second. Secondly, decent savings outweigh all other indicators. To achieve increased heat transfer, you can simply purchase a device with more sections or install another one. For private houses with a large number of rooms and a large area, these radiators are the optimal solution when it comes to the funds allocated to cover heating costs.
Vacuum battery
Positive and negative qualities of devices
The following arguments are usually given in favor of using radiators that do not contain gases in the cavity:
- guaranteed absence of such a phenomenon as airing of the system;
- low hydraulic resistance;
- complete absence or minimal corrosion;
- stable heat transfer, because Dirt does not settle on the inner surface of the case;
- a minimum number of threaded connections, which makes leaks unlikely;
- wide choice of coolant: antifreeze, water, steam, etc.
If we compare these products and the usual water ones, then in apartments heated centrally, the air will not be heated equally. In the second case, the water entering the system heats the entire body of the radiator directly. In a vacuum, water from the central line heats only the lower part.
The use of vacuum radiators saves coolant up to 80%. In addition, when the battery is disconnected, the heated gas particles slow down, so it takes a long time to cool down
The remaining sections of the battery receive heat from the evaporated liquid. Due to the fact that the heat transformer has both a temperature and thermal conductivity lower than that of water, the walls of the vertical sections of the radiator will heat up less.
To ensure the same temperature conditions as with water batteries, the vacuum radiator must have a larger area.
Manufacturers claim that sections of the product warm up instantly. With a small volume of water of 0.5 liters, one fragment has a heat transfer of 300 W. It should be noted here that each section of the now classic cast iron radiator contains 4 liters of liquid.
The savings are especially noticeable when using antifreeze. The costs of its acquisition will decrease significantly. A small amount of coolant and no need for expensive equipment are the main advantages of using vacuum radiators.
The advantage of these devices is the fact that the room warms up more smoothly vertically. According to measurements, for every meter of height the difference is about 0.5 °C. In a room with a ceiling height of 2.5 m between the appliance and the floor this will be approximately 1.25 °C.
The effectiveness of vacuum radiators is manifested when using alternative energy sources, such as a heat pump, solar panels.
While cast iron batteries can heat the room when the coolant reaches a temperature of at least 65 °C, for vacuum devices 35 °C is sufficient
You should know that if a section depressurizes due to some circumstances, the vacuum radiator will not work. The reason is that the pressure inside and outside the housing will be equal.
Such a breakdown poses a threat to the well-being and health of the people living in the house, since the liquid inside is poisonous.
How does this equipment work?
Vacuum radiators appeared on the domestic market relatively recently, but have already gained considerable popularity among consumers. Visually, these heating devices are not much different from the sectional batteries we are used to. They are made from carbon steel and have a traditionally white or decorated surface.
But vacuum radiators are designed radically differently. The heating fluid (water, antifreeze) in the vacuum radiator circulates only through a straight pipe located in its lower part. Sections of the device, instead of water, contain a small amount of lithium bromide liquid, which boils under vacuum conditions already at 35 degrees. Contact of the primary coolant (water) with the secondary (special liquid) occurs exclusively through the metal surface of the pipe.
The operating principle of a vacuum radiator is as follows:
- Water from the heating system enters the lower part of the radiator.
- Heat is transferred to the secondary coolant.
- The working fluid turns into a vapor state.
- Powerful evaporation quickly and evenly heats the metal body of the device and the radiator releases heat to the surrounding air.
- The condensate falls down along the inner walls of the sections, and then, boiling, turns into steam again.
One section of the vacuum radiator contains only 50 ml of coolant (for comparison: in aluminum - 350 ml). A smaller volume of coolant is easier and faster to heat - because this requires much less heat. Considering that lithium-bromide liquid begins to “work” at a very low temperature, it is obvious that the energy costs for heating water in the system when installing vacuum heating radiators will be small. This is the main “trump card” of the equipment compared to other water heating units (cast iron, aluminum, bimetallic).
We advise you to study - Ecowool - disadvantages and advantages of insulation
Many are skeptical about the advantages of vacuum radiators, but practice shows that the operating principle of the units is very effective
Thermal imaging confirms the uniform heating of the vacuum radiator and its higher operating efficiency compared to a cast iron battery
Vacuum radiators “combine” perfectly with many heat sources - stoves, electric and gas boilers, solar collectors. They are a worthy choice for both autonomous and centralized heating systems. Efficiently heating residential and industrial buildings, vacuum-type radiators are increasingly becoming a confident choice for practical consumers.
When is a vacuum radiator beneficial?
Based on the features of the vacuum radiator, we can conclude that its use in a centralized heating system will not bring much benefit.
The use of the device is justified when choosing an autonomous heating system. If it is not water that circulates in it, but a non-freezing liquid, then the cost of the coolant will decrease significantly.
A heating system with vacuum radiators is very effective in tandem with a solar collector. For a cottage this is the best modern technology
Installing vacuum batteries is a rational solution to the problem if a low-power boiler is purchased. Such a source will not be able to heat the coolant to the high temperature required for the operation of traditional appliances. In the case of a vacuum unit, this is not required. The reaction inside it will start at 35 °C.
Country cottages, which the owners do not use for permanent residence, take a long time to warm up in cold weather. A vacuum radiator will speed up the process. The heating process with its participation occurs quickly, and the heat is distributed evenly.
Solar heating systems
Solar heating element
The use of solar energy is one of the promising areas in the development of heating systems. In addition to the well-known solar panels, collectors that use the thermal energy of the sun have become widespread. Structurally, they represent a network of pipelines forming a single field. Inside them there is a coolant with a low boiling point. Just like in vacuum radiators, it is enclosed in low pressure tubes. This structure is located on the sunny side of the site or the roof of the house. As it heats up, the coolant begins to circulate and enters the heat exchange tank of the vacuum solar collector for heating the house. There, its energy is transferred to water, which can be used both for heating and for hot water supply.
The main element of a vacuum solar collector for heating a house is a frame with vacuum tubes. Depending on its area, the total power of the entire system changes. The operating features of collectors of this kind are as follows.
- Possibility of use as an auxiliary source of thermal energy. Unlike the operating principle of vacuum heating radiators, the operation of which is not affected by weather factors, solar collectors require constant exposure to UV radiation from the sun. Therefore, it is not practical to use such a system in winter;
- Energy saving. In summer, solar collectors successfully cope with the task of hot water supply and heating of small rooms in early autumn. In this case, energy costs are minimal and can be associated with the operation of the pump to ensure fluid circulation;
- Relatively high cost. The average price of a vacuum manifold with a frame is 45 thousand rubles. If you plan to purchase a full-fledged water supply system for 300 liters, then it will cost from 150 thousand rubles. Autonomous vacuum solar collectors designed for home heating and hot water supply will cost at least 310 thousand rubles.
But, despite the high cost, such systems are becoming increasingly popular. The emergence of new, cheaper and more efficient manufacturing materials provides the prerequisites for a reduction in prices.
Product selection rules
With the growing popularity of this high-tech equipment, there are more and more low-quality counterfeits on the market.
When purchasing, you should check whether the appropriate certificates and other technical documentation are included with the device. It should be remembered that the basic rule for effective operation of the unit is complete tightness.
Another important parameter for the radiator is the amount of coolant in the vertical sections - the lithium-bromide mixture. A large volume may result in liquid overflow.
To assess the compliance of the volume, you need to focus on the sound that occurs when the unit rocks. It should resemble a soft rustling sound. If the sound of flowing liquid is clearly distinguishable, the radiator, with a high degree of probability, may turn out to be a handicraft fake.
European manufacturers provide a guarantee of up to 5 years for most of their models. Their prices are directly proportional to the number of sections and they are higher than for water analogues
On products manufactured using factory technology, the welding seams do not have any flaws, unlike units of unknown origin.
Manufacturers with a good reputation cover product bodies with high-quality powder paint. Therefore, the integrity of the paint layer is difficult to damage even when in contact with a solvent. You should not miss such a moment as the tightness of the filling valve.
Recommendations for use
The equipment in question has proven to be an economical and very effective way to heat summer cottages used seasonally and large private houses intended for year-round use. The heating system is activated within a few minutes and does not require pre-bleeding.
Experts advise, even at the installation stage, to take care of creating certain conditions that will facilitate the rationalization of the use of vacuum equipment:
- a building or an apartment must be insulated as much as possible in order to reduce the level of heat loss. A reasonable solution would be to install modern types of double-glazed windows on the windows, seal the cracks, and provide the roof and floor with high-quality thermal insulation. In this case, the devices will function more efficiently;
- the number of sections, respectively, and their overall performance must match the parameters of the sections being serviced. Even at the stage of selecting devices, you need to take into account the height of the ceilings and the size of the rooms;
- The heat transfer of equipment is always determined by the temperature of the working environment; optimal conditions are when the water is heated to at least 60°C.
In the core market, there is a systematic increase in demand for batteries using a lithium-bromide mixture, due to which manufacturers have significantly expanded the possibilities of their use. In addition to heating cottages and private houses, vacuum systems are in demand at production and warehouse facilities, when arranging garages and public buildings, greenhouses and farms.
DIY installation subtleties
Installing a vacuum radiator is not difficult, but in order to avoid any alterations, you need to learn a few rules. It is necessary to follow the recommendations regarding the placement of the unit relative to the wall, floor, and window sill.
At the same time, the distance between the radiator and the wall is at least 50 mm, between the device and the floor - from 20 to 50 mm, the optimal distance to the back of the window sill is 50-100 mm.
The photo shows options for connecting radiators. You should be aware that the inclusion of other heating devices in the heating circuit, along with vacuum ones, reduces its efficiency
The installation itself is not much different from inserting other types of radiators into the system. The only difference is that the entrance and exit are at the bottom.
Installation of a vacuum unit involves a chain of actions following each other:
- Drain the coolant and dismantle the old heating device.
- Mark the installation sites.
- Attach the brackets. They are tested for stability and strength.
- Ball valves are installed. Through them the device is connected to the main line. The joints must be sealed using tow or sealant.
- Check the system for leaks.
To improve heat transfer, you can place a sheet of foil on the wall behind the radiator. If you have previously completed thermal insulation, you will have to increase the length of the brackets by an amount equal to the thickness of the thermal insulation layer. If the house is insulated, the efficiency of the heating system will increase.
Economic criterion
Let us add that each section contains only 0.05 liters of coolant. This is seven times less than in aluminum devices. It will be very easy to heat such a volume, the costs for it will be negligible. In addition, air jams never form in vacuum radiators; there is no need to install additional devices, for example, Mayevsky taps. Saving again.
They are installed in any heating systems with various heating devices. These can be ordinary stoves, boilers operating on any type of fuel. The degree of savings varies, it all depends on the type of fuel:
- When using electric boilers, the savings are 40%.
- Use of coolant from central heating networks – 50%.
- On gas boilers, savings are 40-50%.
There is minimal resistance to the movement of coolant, so in such systems there is no need to install a circulation pump. Vacuum radiators and metal corrosion are nonsense. Therefore, they have a very long service life. Most often, the pipe through which hot water flows fails. But if you never drain the coolant from it, then it will serve for centuries.
You can install a vacuum radiator yourself; there are no complicated connections. To do this, you will need standard tools and a little skill in working with them. Installation diagram:
- The exact installation location is determined.
- Brackets are attached to the wall.
- The radiator is hung.
- A connection is made to the pipeline through which the coolant moves. Mandatory installation of shut-off valves or ball valves.
Variety of sizes
The best manufacturers of vacuum radiators
Vacuum heating devices do not yet have a wide range of heating devices on the market. EnergyEco products enjoy special authority among consumers . This Russian manufacturer uses 1.5 mm steel to make batteries. Users note high-quality performance, good heat dissipation - about 170 kW per element.
The working pressure for the radiator is from 0.6 to 1.3 MPa. Even at 2 MPa the device can work, but 5 MPa is too much for it - it begins to collapse. The cost of a radiator from EnergyEko is considerable, but the demand for it does not fall.
The manufacturer Forvacuum produces wall-mounted and baseboard-type vacuum devices. The heat output of a register 1 m long at a coolant temperature of 50 °C is 239 W.
The thermosiphon register has a low metal consumption, since its thin-walled body is not designed for high internal pressure. At 50 °C and using ethanol it is only 0.027 MPa
You can also find Chinese-made radiators on the market. They will have a lower price, but sometimes of dubious quality. When purchasing, you should carefully inspect them and check the documentation.
Safety comes first!
Typically, consumers of all kinds of heating devices pay attention to the appearance of the devices. Another important criterion is heat transfer. Next comes the service life. After all, for some reason many people still believe that metal devices last a very long time.
A very important aspect of purchasing a heating device is its safety. Unfortunately, very few consumers are interested in this particular criterion when purchasing.
Very much in vain. Of course, such cases do not occur so often when, due to the rather low quality of heating radiators, all plugs, seals and fittings cannot withstand the pressure of the system or the aggressiveness of the coolant.
Operating principle of the heating device
And if this happens, then the financial costs of restoration will be measured in tens of thousands of rubles. Unfortunately, only those consumers who have already been taught by life think about security issues seriously.
A vacuum heating radiator is a safe device from this point of view. This is achieved through several aspects of the work:
Water heating radiators
- Minimum connections. The devices simply do not have nipples, plugs, gaskets, Mayevsky taps and other elements. The design of the device is a monolithic body that has two threaded connections to connect the heating system. It is very difficult to depressurize such a device.
- There is very little traditional coolant in a vacuum radiator. Even if there is mechanical damage, there will simply be no place for a flood in the room to come from.
- Hydraulic pressure in vacuum heating radiators is only at the bottom. This is where the through pipe passes for the coolant to flow. The pressure inside the battery in the area of the secondary coolant is very low. If it is 70 degrees on the convection surface, then it will only be no more than 0.78 atmospheres.
So, if the system suddenly depressurizes, the only trouble will be that the heating device itself will fail.
Advantages of the system
The heat output of vacuum radiators is very high . After all, such a battery can be powered by a boiler, boiler, stove, or even a solar collector. To heat large rooms, boilers with lower power can be used. In this case, you will not need to heat a lot of water (coolant). But you should also not expect that the volume of energy will be reduced several times. Of course, the savings will be noticeable, but this is not a panacea for bills.
Reviews of vacuum heating radiators show that these are effective innovative devices, which are therefore becoming increasingly widespread nowadays.
And several significant advantages of vacuum batteries should be noted:
- The volume of coolant required is reduced by 80%.
- The amount of heat consumed from centralized systems will be greatly reduced. Sometimes this figure can reach up to 50%! Of course, the benefits are obvious if all the heat is taken into account by meters.
- Electrical energy consumption will be reduced by 30-40 percent.
- Installing a vacuum radiator is very simple - installation is no different from conventional heating radiators.
Externally, vacuum radiators do not differ from conventional radiators
- Sections of the vacuum battery are not subject to corrosion processes. Also here you will not have problems with airing areas of the heating system.
- The circulation of a small amount of coolant will be facilitated due to the fact that the resistance of the liquid mass is reduced.
- High heat transfer is due to the boiling boron-lithium mixture.
Useful tips
Vacuum batteries have proven themselves best in private homes or seasonally used premises: in the country or in a country house. When choosing a device, you should take into account the footage of the rooms and the height of the ceilings.
Manufacturers recommend installing vacuum radiators in a centralized heating system only if there are heat meters. This makes it possible to somehow regulate the temperature of the primary working fluid. The ideal range is 40-60 °C. At higher temperatures (and in the central system they are always much higher), the liquid will completely evaporate, turn into steam and will not be able to circulate.