Each granary must ensure the following operations with grain: reception, processing (cleaning and drying), storage, internal movements, release. All elevators, regardless of their types and purposes, operate according to the following principle:
Each granary must ensure the following operations with grain: reception, processing (cleaning and drying), storage, internal movements, release. All elevators, regardless of their types and purposes, operate according to the following principle:
1 - receiving belt conveyor; 2 - receiving hoppers: 3 - release device; 4 - elevator; 5 — overhead bunker; 6 — scales (bucket or portion); 7 - distribution pipes; 8 - over-silo conveyor; 9 — above-separator bunker; 10 - separator; 11 — silos for grain storage; 12 — silo conveyor; 13 - sub-separator bunker.
Grain and its processed products are one of the foundations of human nutrition, therefore this storage option is the most relevant among all possible grain storage facilities. The grain elevator is considered the most reliable, and therefore entire networks of such grain receivers are installed near producing areas. This makes it possible to level out grain losses during remote transportation from harvest sites.
Grain and its processed products are one of the foundations of human nutrition, therefore this storage option is the most relevant among all possible grain storage facilities. The grain elevator is considered the most reliable, and therefore entire networks of such grain receivers are installed near producing areas. This makes it possible to level out grain losses during remote transportation from harvest sites.
An elevator is understood as a special structure designed for storing large quantities of grain, taking into account bringing the grain to a condition. In addition to the storage facilities themselves, such a warehouse is equipped with a complex of special devices that weigh, receive, clean, dry and ship grain.
Alternatively, such a complex can be implemented in a mechanized silo-type device, which significantly saves space and ensures complete mechanization of the process. The first elevators appeared in Russia at the end of the 19th century; currently they are highly mechanized, efficient storage systems for grain crops.
Grain and products made from it are the basis of people's lives. The issue of their safety until transportation is very important. Grain elevators simplify it.
Grain and products made from it are the basis of people's lives. The issue of their safety until transportation is very important. Grain elevators simplify it.
The grain elevator is designed to store grain in large quantities and bring it to condition. The elevator inside includes mechanisms for loading and unloading grain and dryers. Work buildings, etc. Usually, organizations build entire turnkey elevator complexes.
In the grain harvesting and processing industry, a structure such as an elevator is often used. In other words, this structure is high-tech equipment for storing grain in special conditions and through such storage the grain is brought to a certain, required stage of condition.
Types and scope of application of grain elevators
A grain elevator is usually classified into one of the categories based on its purpose and storage volume. Types of elevators depending on the amount of grain:
- procurement - designed for 15 - 100 thousand tons of grain material, focused on work on receiving from farms and cleaning, short- and medium-term storage with subsequent shipment to larger facilities;
- long-term storage - an elevator for storing grain in large volumes (from 150 thousand tons) with maintaining condition and periodic shipment for processing;
- production - elevators for 10 - 15 thousand tons of grain, designed for prompt release into production and maintaining a supply of working material;
- transshipment or port - complexes for receiving and transshipping grain with different storage periods and the possibility of shipment to wagons, ships, and road transport.
Different types of elevators are designed and equipped depending on the specifics of storage and supporting operations. This is determined at the stage of preparing the design assignment and depends on local conditions and requirements for a particular facility.
Video description
In this video you will see how to disassemble and install a nozzle in an elevator:
Now you need to determine the size (diameter) of the nozzle (dc) using the formula below:
dс = 10d / √[0.78 / Gpr2 * (1 + u)2 * d4 + 0.6(1 + u)2 – 0.4u2],
where u is the dimensionless injection or mixing coefficient.
Next, to calculate u, you need to calculate u` using the formula:
u` = (t1 – tcm) / (tcm – tob),
where t1 is the temperature of the coolant at the entrance to the elevator (in °C).
To calculate u, you need to substitute the value of the coefficient u` into the formula:
u = u` * 1.15.
After the calculation, all that remains is to select the desired nozzle. They are available in several sizes and are marked with numbers from 0 to 7. You need to choose the one that is closer in size to the calculated value (see table No. 1).
Table No. 1. Nozzle diameter.
| Nozzle size | Water consumption, t/hour | Nozzle weight, kg | Nozzle neck diameter, cm |
| 0 | 0,1-0,4 | 6,4 | 1 |
| 1 | 0,5-1 | 8,1 | 1,5 |
| 2 | 1-2 | 8,1 | 2 |
| 3 | 1-3 | 12,5 | 2,5 |
| 4 | 3-5 | 12,5 | 3 |
| 5 | 5-10 | 13 | 3,5 |
| 6 | 10-15 | 18 | 4,7 |
| 7 | 15-25 | 18,5 | 5,9 |
Functions and principle of operation of elevators
An elevator is an industrial grain storage facility, the design and arrangement of which takes into account all technological processes that ensure the reception, preparation, storage and release of grain. The principle of the elevator is the sequential execution of technological processes.
- Reception of grain. Can be organized with any type of transport. In procurement elevators for farms, a vehicle unloading point into pits and bunkers is mainly designed. At transshipment elevators, berths and railway tracks can be organized.
- Processing and preparation. The elevator design allows for grain heap cleaning, drying in grain dryers, and sorting by size (calibration). Depending on the sources of grain supply, ZAV and KZS complexes, mine grain dryers, and aspiration units can be used.
- Storage. The main function is that the elevator grain storage is designed on the basis of metal silos with internal and external support systems.
- Loading of grain. An elevator is a logistics hub equipped with a set of means for dispensing material on any scale using conveyors, pneumatic hoses, and bunkers. The composition of the equipment is determined by the volume of grain storage and transport capabilities for release.
Elevators are needed to solve complex problems of grain storage; their functions may differ depending on the characteristics of logistics, grain material, location on the ground and connection to other objects.
Features of grain elevator storage
Elevator-type warehouses are necessary for long-term and compact storage of grain - the grain is located in vertical containers that look like silo towers. This storage option allows you to preserve the taste and technological properties of grain for a long time - this is the storage option that is considered optimal.
In addition to grains, elevator storage is also applicable for fodder and oilseeds. In this case, the initial moisture content of the product can be anything, which allows you to optimally preserve the crop regardless of weather conditions. The design of the grain dryer and technological features make it possible to ensure uniform drying of grain, which is not achieved by any other type of storage. At the same time, the physical costs of drying and storing the crop are minimal. Elevator warehouses are safe and demonstrate excellent value for money, which has led to their popularity both in Russia and abroad.
Elevator structure according to functional systems
The elevator structure is a complex of silos, transport and preparation systems, control equipment and internal logistics. A grain elevator is an industrial facility in which the composition of the equipment and the design of all systems are standardized and are aimed at fulfilling the main task - to ensure the safety of grain within the conditions established as the storage standard. Most elevators include a functionally necessary set of equipment.
Reception systems and equipment
Pits, bunkers, hydraulic lifts for cars, pneumatic hoses for unloading cars and ships are used to unload grain into temporary containers. The composition is determined depending on logistics; in small farms it is enough to equip the elevator with devices for unloading cars.
Equipment for cleaning and preparing grain
The elevator's technological chain may include KZS and ZAV complexes as modular ready-made solutions. It is possible to install cleaning, aspiration, and other equipment in separate lines. The grain elevator can receive material after primary cleaning or work with ready-made grain.
Internal technological transport of the elevator
This is a set of equipment and machines for moving grain mass. It usually includes:
- pneumatic transport system;
- horizontal and inclined scraper conveyors;
- bucket elevators for lifting grain;
- conveyors and bag loading devices for feeding grain into silos;
- screw conveyors for feeding grain to equipment and unloading silos;
- gravity flow system with plugs, dampers and other devices for controlling grain flows.
Suction equipment
Depending on the specific elevator unit, aspiration systems with cyclones and cyclone batteries are used, which can separate dust and small inclusions from the air.
The main equipment of the elevator is silos
A modern grain elevator is a complex of metal containers - silos, into which grain prepared for storage is loaded. The height and diameter of the silo are selected according to the standard elevator design, based on capacity, space availability, wind and seismic activity.
Types of silos for grain storage:
- flat-bottomed - large-capacity storage facilities designed for long-term storage of material with active cross-ventilation of the mass;
- with a conical (conical) bottom - elevator silos in which operational stock is stored, grain for shipment or that has not undergone a full cycle of preparation for long-term storage.
The fundamental difference between the two types of elevator silos is not only in volume. More capacious flat-bottomed grain storage facilities in the elevator have ventilation ducts in the bottom and are installed on a more durable solid foundation. To unload them, capacious pits with high-capacity conveyors are required. The last layer of grain from the bottom is unloaded by a radial screw conveyor.
Silos with a conical bottom are installed on durable metal structures and are practically suspended to create conditions for unloading grain through the outlet hatch by gravity. When calculating these silos, the deformation load that occurs when a mass of material exits from below must be taken into account.
Completed projects
Construction of elevators, grain complexes. Production of elevator equipment.
Grain elevator logistics
A grain elevator constantly handles large flows of material, which requires active movement of grain between processes. The idea of organizing storage in a battery of silos makes it possible to optimize internal logistics and thus obtain a number of effects important for the industrial organization of production:
- reduce the time required to complete transport operations;
- shorten grain movement paths;
- reduce the number of transshipments - changes in the type of transportation when moving;
- use all the capabilities of gravity systems as they are the least energy-consuming.
An elevator silo for grain storage is a kind of logistics basis for a complex system of transports that are concentrated around it and form short radial connections for supplying and selecting material. Flat storage does not provide an opportunity to provide efficient and low-cost internal transportation of grain material.
System for maintaining grain condition in elevator silos
A modern grain elevator is equipped with silos with complex internal systems. The ventilation system is of particular importance - thanks to the constant supply of air, the grain does not become moist during storage. Elevator silos for grain storage use horizontal and vertical ventilation, directing air flows through the entire mass in layers. This takes into account the effect of decreasing and increasing temperature due to pressure drop.
An equally important set of devices and units is the silo aspiration system. It must constantly capture and remove dust from the air, which creates the danger of grain contamination and the likelihood of cotton under the roof of the silo. Special equipment is provided for this, including several hatches to maintain normal pressure in the upper part of the silo. In grain storage elevators, the silo aspiration system is built on the basis of general industrial units, filters and air ducts.
Elevators are designed and built using standard design products and certified equipment. Manufacturers of equipment and silos operate in Russia, providing a full range of services from elevator design to its installation and turnkey launch. What types of elevators there are for storing grain and seed material can be seen in the photo in the section of our website.
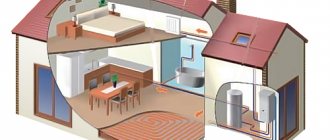
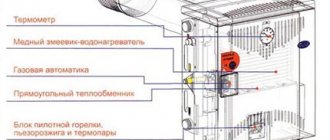
Node calculation
Elevator units of the heating system are the central elements of heating systems that heat residential or non-residential premises without unnecessary heat consumption. Since these systems may differ in the number of objects served, it is necessary to calculate the elevator so that the installed device works correctly. The essence of such calculation of the parameters of the future elevator is that it is necessary to find out two numbers: the size of the chamber for mixing liquids (d) and the nozzle (dс).
The size (diameter) of the internal chamber mixing water of different temperatures is calculated by the formula:
d = 0.874 * √Gpr,
where Gpr is the amount of mixed water (given), indicated in tons per hour.
To calculate the amount of water, you need to substitute the values into the following formula:
Gpr = Gс / √h = Q / [(tcm – tob) * √h * 1000],
where Gс is the estimated water consumption (t/h);
h – reverse effect from the heating system (resistance; measured in meters of water column);
Q – amount of heat consumed (in kilocalories per hour);
tcm, tob - denotes t of the water mixture that goes for heating, and, accordingly, the cooled water that goes back, that is, through the return (expressed in degrees Celsius).