When designing a heating system, the main goals are comfort and reliability. The house should be warm and cozy, and for this, hot coolant should always flow into the radiators without delays or temperature surges.
This is difficult to achieve with a solid fuel boiler, because it is not always possible to fill a new portion of firewood or coal on time, and the combustion process itself is uneven. A heat accumulator for heating boilers will help correct the situation.
With a simple design and operating principle, it can eliminate a number of inconveniences and disadvantages of the classical heating scheme.
Battery buffer tank volume
Let's figure out what volume the heat accumulator should be. There are differing opinions that are based on calculations based on:
- room area;
- boiler power.
Let's look at each of them. Based on the area of the room, there can be no exact recommendations. Since there are many factors that influence the battery life of a system without a boiler, the main one is the heat loss of the room. The better the house is insulated, the longer the buffer tank will be able to provide the home with heat.
Of course, the larger the tank, the better, but to heat a larger amount of coolant you will need more heater power. Calculation of boiler power is done based on the heated area. One kilowatt warms up ten meters. You can install a five-ton tank, but if the boiler cannot handle such volumes, there will be no point in installing such a large heat accumulator. This means that adjustments need to be made to the calculation of the power of the boiler itself.
It turns out that it may be more correct to make the calculation based on the power of the boiler. Let’s take for example the same house of 200 sq. m. An approximate calculation of the volume of the buffer tank is as follows: one kilowatt of energy heats 25 liters of coolant. That is, if there is a 20 W heater, then the volume of the heater should be about 500 liters, which is clearly not enough for such housing.
Based on the results of the calculations, we can conclude that if you are planning to install a heat accumulator, then you need to take this into account when selecting the boiler power and take not one, but two kilowatts per ten meters of heated area. Only then will the system be balanced. The volume of TA also affects the calculation of the capacity of the expanzomat. An expansion tank is an expansion tank that compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant. To calculate its volume, you need to take the total volume of coolant in the circuit, including the capacity of the buffer tank, and divide by ten.
Selection of heat accumulator
The remaining criteria for choosing a container are not so important and mainly relate to different options. One of them is a built-in coil that heats water for household needs. It may be useful if there are no other means of heating, but for high costs in the DHW network this method is definitely not suitable. In addition, the heat exchanger will take away part of the “charge” of the heat accumulator, reducing the autonomous operation time of the heating.
A useful option is a heating element built into the top of the tank, capable of maintaining the temperature of the coolant at a certain level. Thanks to electric heating, the system will not defrost in the event of an accident and will even be able to heat the house for some time after the battery has been “discharged” and the boiler has not yet been started.
The second coil for connecting the solar system is useful only in the southern regions, where solar activity will allow the heat accumulator to be loaded. But what you should pay attention to when selecting is the operating pressure of the tank. It should be taken into account that most solid fuel boilers are designed for pressure in the jacket up to 3 Bar, which means that the buffer tank should easily withstand the same amount.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating with a heat accumulator
The advantages of such systems are:
- Reduced energy costs.
- Increasing the efficiency of the heating system.
- No overheating.
- Reducing the amount (frequency) of loading solid fuel into the boiler.
- Fine-tuning the temperature in the rooms.
- Possibility of modernization (combination with a hot water supply system, use of alternative energy sources instead of fuel).
With all the advantages, heating equipment of this type also has disadvantages:
- The power of the installed boiler allows you to heat an area twice as large as required (power reserve).
- The system takes a long time to start from a cold state before entering normal operating mode.
- Due to the bulkiness of the equipment and the large number of components, transportation, placement and installation are complicated.
- There remains a need for a fuel warehouse in close proximity to the boiler room.
- The cost of equipment and the lack of quick payback, especially when replacing the boiler.
The last drawback can be successfully solved by installing the heat accumulator with your own hands.
Types of heating systems with heat storage and different numbers of coils
The coil plays the role of a heat exchanger, that is, liquids of different systems do not mix with each other, and heat transfer occurs through the walls of this spiral. Made from copper or stainless steel. Sometimes ferrous metal is used to reduce the cost of the structure.
There are four main types of systems:
Without coil. Instead, an additional tank of smaller diameter can be installed, connected to a small circuit. Heat transfer occurs due to the physical properties in which it rises up and the cold coolant falls to the bottom of the container. This system is the simplest and works with only one consumer, for example a heating system and one source. This can be either a solid fuel boiler or a solar collector. Features: minimal cost, ease of installation.
With one coil. The spiral is located inside the main tank; coolant from the source circulates through it. The energy is transferred to a storage tank from where it is circulated further to the consumer. The peculiarity of such a system is that there is no mixing of different coolants
This may be important if they have different chemical compositions
The system can also work in the reverse order; the heating system or hot water supply can flow through the coil.
With two coils. An additional small heat exchanger circuit is fed into a system connected to an alternative energy source. This system allows the use of a wider range of equipment for heating the coolant.
With three spirals. It is assumed that a single heating complex includes a solid fuel boiler and two alternative sources, for example, solar and geothermal batteries. Maximum solid fuel savings. The boiler can be used as an additional (backup) boiler.
With additional tank. There are systems in which another circuit with a heat exchanger is turned on so that hot water appears in the tap immediately after starting the boiler, without waiting for the optimal heating mode to reach. However, in such systems, the supply of hot water is limited; after its expiration, further heating will proceed more slowly than through the coil.
Application of different types of systems
Heating systems, which include only solid fuel boilers, are used, as a rule, for heating private houses. The need to build a coal (wood) warehouse is inconvenient, but this configuration is sufficient for heating in the most severe frosts.
Heating systems that include solar collectors can save up to 30% on energy costs, but cannot replace a solid fuel boiler. Therefore, it is used as an auxiliary one, especially since the sun does not always shine. But to always have water at home, the power is enough (replaces 50-90%).
Combined configurations involve the use of gas and solid fuel boilers. This is convenient when starting the system in a frozen building. If the gas unit is connected to a hot water supply system, then there will always be water. In this case, there is no need to add firewood; just press the start button of the gas burner. and the main task of heating the water will be taken on by a solid fuel boiler.
What is a heat accumulator and what function does it perform?
When the combustion is strong, the system overheats; when it is weak, it cools down. The amplitude can be reduced and the period of oscillations can be increased by using a large tank with a heat accumulator. The latter is a heat exchanger with a large container filled with heat transfer fluid. One part of the system takes excess energy from the boiler, the second gradually releases heat into the heating system, preventing the temperature from dropping sharply. This entire process occurs automatically through coils controlled by three-way valves.
In other words. TA will allow you to load a full firebox of wood and not worry that the water in the boiler will boil. After the fuel burns out, the heating system will still be able to operate for some time due to the heat accumulated in the tank.
Operating principle
A heat accumulator is a container within which a hot coolant fluid circulates. The temperature is maintained in the desired range thanks to the dosing of energy transferred to the circuit. The heated tank releases heat into the rooms gradually. As a result, there is no need to constantly maintain combustion in the boiler furnace.
Video review of such a system
How to calculate the volume of TA
In order for a heat accumulator for heating to perform its functions, its volume must be selected correctly. There are several methods:
- by heated area;
- by boiler power;
- according to the time available.
Most of the methods are based on experience. For this reason, there is a “fork” in the recommendations. For example, from 35 to 50 liters per square meter of heated area
How exactly to determine the number? It is worth taking into account the region of residence and the degree of insulation of the house. If you live in a region with not the most severe winters or the house is well insulated, it is better to take the lower limit or so
Otherwise - on the top.
It is possible to power not only radiators, but also heated floors from the TA, and you can also install a heat exchanger for hot water
When choosing the volume of a heat accumulator for heating, two points must also be taken into account. First, a large amount of water will allow you to heat it much less often.
Due to the stored heat, the temperature can be maintained for a long time. But, on the other hand, the time it takes to “accelerate” this volume to the required temperature greatly increases (heating to 85-88°C is considered normal). In this case, the system becomes very inertial. You can, of course, take a more powerful boiler, but paired with a buffer tank, this will cost a considerable amount. Therefore, you have to maneuver, finding the optimal solution.
By heated area
You can select the volume of the heat accumulator for the heating system according to the area of the room. It is believed that 35 to 50 liters are needed per ten square meters. The selected value is multiplied by the quadrature divided by ten to obtain the desired volume.
For example, in the heating system of a house with an area of 120 m² with average insulation, it is better to install a heat accumulator for heating 120 m² / 10 * 45 l = 12 * 45 = 540 liters. This will not be enough for the Middle Zone, so you should look at containers with a volume of approximately 800 liters.
The greater the system performance, the larger the TA should be
In general, to make it easier to navigate, for a house with an area of 160-200 square meters, located in the middle zone, with average insulation, the optimal tank volume is 1000-1200 liters. Yes, with such a volume, you will have to heat it more often in cold weather. But this will not undermine your budget too much, and will allow you to live quite comfortably almost all winter.
By boiler power
Since the boiler will have to work on heating the water in the tank, it makes sense to calculate the volume based on its capabilities. In this case, 50 liters of capacity are taken per 1 kW of power.
You can make it even simpler - use the table (the values that are optimal in terms of cost and performance are shaded in yellow)
The calculation is simple. For a 20 kW boiler, a TA of 1000 liters is suitable. With such a volume of heat storage for heating, you will have to heat it twice a day.
According to the desired duration of downtime and heat loss
This method is more accurate, as it allows you to select dimensions specifically for the parameters of your home (heat loss) and your wishes (duration of downtime).
Let's calculate the volume of a heat accumulator for a house with a heat loss of 10 kW/hour and an idle time of 8 hours. We will heat the water to 88 °C, and it will cool down to 40 °C. The calculation is as follows:
- To maintain normal temperature, the container must accumulate 80 kW of heat (10 kW * 8 hours).
- Temperature delta: 88°C - 40°C = 48°C.
- Next, we calculate using the formula for determining the heat capacity of water.
- Substituting the values we get: 80000 W / 1.163 W/kg°C * 48°C = 80000 / 55.824 = 1433 liters.
For these conditions, the required capacity of the heat accumulator for heating is 1500 liters. This is because heat loss of 10 kW/hour is too much. This is a house with virtually no heating.
What is important to consider when buying a heat accumulator
Before purchasing a heat accumulator, you should consider the following points:
- Installation dimensions. This is the most important point, since you will have to drag the heat accumulator into the house and then install it. Therefore, it must be sized to fit through doorways and also fit comfortably into the boiler room.
- Permissible coolant pressure in the storage tank. Before purchasing, it is important to clarify information about the pressure under which your heating system operates.
- Optimal and maximum water temperature in the heat accumulator circuit. It is especially important to clarify the information if special antifreeze circulates in your system. Then a regular water battery will not suit you, since a higher temperature can cause it to leak or malfunction.
- Material of manufacture. This is an equally important nuance, since the quality of functioning, efficiency and service life depend on the material. Stainless steel models are considered the best, but they usually cost more than units in the mid-price segment.
It is also important to pay attention to whether additional equipment can be connected to the container.
Do not focus too much on price, as in this case you can choose a cheap and low-quality heat accumulator. The price of a heat accumulator for heating starts from 10-15 thousand rubles. It’s simply not worth taking a cheaper one, since most likely there will be difficulties with this tank in the future during operation.
We hope that our article was useful and informative for you, now you know what a heat accumulator for heating boilers is and how it is installed. All the best!
How to make it yourself
The easiest way to make a heat accumulator for heating with your own hands involves having a ready-made steel barrel.
Barrel for heat accumulator
If the required container is not available, then it must be welded from steel sheets, the thickness of which should be 2 mm. If the heat accumulator is connected as a hydraulic separator, then two fittings must be inserted from below and two from above; the length of these devices must be identical to the thickness of the insulation. Tees with thermometers must be connected to the lower pipes. Next, the barrel needs to be wrapped in foil, and then with insulation.
As insulation, it is important to use a material that, when in contact with hot surfaces, does not emit toxic fumes. The last stage: the container, previously lined with a heat insulator, is covered from the outside with a casing made of thin sheet steel or tin
If the heat accumulator is used in parallel to heat hot water, then it is necessary to make another coil. The material is a copper pipe with a diameter of 20 mm.
Another method that ordinary people prefer is to make a heat accumulator from a Eurocube with a capacity of 1000 liters. It is recommended to use Eurocubes, the high quality of which is confirmed by an international quality certificate.
Before you start making a thermal accumulator from a Eurocube, you should remember that the temperature of the liquid that will be in such a tank should not exceed 72°C, therefore standard Eurocubes are not suitable for heating systems with high temperatures.
In order to independently build a heat accumulator from a Eurocube, you need the following materials:
- Eurocube made from food materials;
- heating element 3000 W, 3 pieces;
- foot with gaskets G2″ to G1″1/4, 5 pieces;
- coupling D32 - G1 1/4″, 2 pieces;
- adapter adapter G1″1/4, 2 pieces;
- lock nut G1″1/4, 5 pieces;
- bend G1″1/4 30 cm, 2 pieces;
- plumbing flax or special paste;
- sealant;
- cardan key.
Heat accumulator made of Eurocube 1000 l
Assembly is carried out in the following way:
- Using a drill in the container body, you need to make an insert for the heating elements, then insert the fittings into the holes using gaskets and silicone glue-sealant, secure the fittings from the inside with locknuts and install the heating elements.
- Then it is necessary to ensure the supply of water to the heat exchanger, this is done using a standard drain neck through adapters.
- The next stage: the “return” is cut into the upper part of the Eurocube and connected, after which you need to mark the place for the cut-in and installation of the heat exchanger, as well as cut in the fittings and screw the fittings into them.
- On the inside of the ejectors, you need to screw the couplings to connect the corrugation, then secure it and distribute it evenly throughout the volume of the heat accumulator for heating.
- When connecting a heat accumulator, you need to install an EPS sheet at the installation site of the device, the thickness of which should be 10 cm, and also lay a 15 cm thick PSB along the rear wall.
The heat accumulator is insulated using a 10-centimeter sheet of polystyrene foam. It needs to be glued to the body of the Eurocube.
In addition to solid fuel boilers, using a heat accumulator is beneficial for gas and electric heating devices:
- Using gas boilers, savings are achieved due to the variable use of the heat accumulator and the boiler itself. In this case, gas is consumed in smaller quantities, since the gas burner is turned on much less often.
- For electric boilers, it is enough to turn on the heat accumulator at full power only at night, since electricity tariffs are much lower at this time. During the daytime, when the boiler is turned off, heating is carried out using the heat that has accumulated during the night.
The heat accumulator has no moving mechanical elements and its operation is static. This means that this device is reliable and long-lasting in use.
Features of internal and external devices
The heat accumulator is a vertical cylinder-shaped tank made of high-strength black or stainless steel sheet.
There is a layer of bakelite varnish on the inner surface of the device. It protects the buffer tank from the aggressive influence of industrial hot water, weak salt solutions and concentrated acids. Powder paint is applied to the outside of the unit, resistant to high thermal loads.
The tank volume varies from 100 to several thousand liters. The most capacious models have large linear dimensions, making it difficult to place equipment in the limited space of a home boiler room
External thermal insulation is made of recycled polyurethane foam. The thickness of the protective layer is about 10 cm. The material has a specific complex weave and an internal polyvinyl chloride coating.
This configuration prevents particles of dirt and small debris from accumulating between the fibers, provides a high level of water resistance and increases the overall wear resistance of the heat insulator.
The heat insulator is not always included in the heat accumulator kit. Sometimes you have to buy it separately and then install it on the unit yourself
The surface of the protective layer is covered with a cover made of good quality leatherette. Thanks to these conditions, the water in the buffer tank cools much more slowly, and the level of overall heat loss of the entire system is significantly reduced.
Making a solid fuel boiler with your own hands
A solid fuel boiler for a private home can theoretically be made independently. To do this, you need to take a large 300 mm pipe, from which a meter-long piece is cut. You need to cut the bottom from a steel sheet according to the diameter of the pipe and weld the elements. The legs of the boiler can be 10-centimeter channels.
When making a solid fuel boiler for a private home, you will need to make an air distributor in the form of a circle from a sheet of steel. Its diameter should be 20 mm smaller than the pipe. An impeller from a corner must be welded into the lower part of the circle. The size of its shelf should be 50 mm. A channel with the same dimensions is also suitable for this. A 60 mm pipe should be welded into the central upper part of the distributor, which should be located above the boiler. A hole is made in the middle of the distributor disk through the pipe to form a through tunnel. It is necessary for air supply.
A damper is attached to the top of the pipe, which will regulate the air supply. If you are faced with the question of how to make a solid fuel boiler, then you should familiarize yourself with the technology. The next stage indicates the need to complete the lower part of the equipment, where the door to the ash pit will be located. Holes are cut at the top. At this point a 100 mm pipe is welded. At first it will go at a certain angle to the side. Then up 40 cm, and then strictly vertically. The chimney passage through the ceiling must be protected according to fire safety rules.
Completion of the boiler is accompanied by work on the top cover. In its central part there should be a hole for the distributor pipe. The fit to the wall of the equipment must be tight. Air ingress is excluded here.
Having made a long-burning solid fuel boiler using wood, you will have to light it for the first time. To do this, remove the lid, lift the regulator, and fill the equipment to the top. Fuel is doused with flammable liquid. A burning splinter is thrown inside through the regulator pipe. As soon as the fuel ignites, the air flow will need to be reduced to a minimum so that the wood begins to smolder. As soon as the gas ignites, the boiler will start.
Types of accumulating models
Drives function the same way, but differ in their design, so the following types of storage devices are distinguished:
- hollow (does not have an internal heat exchanger);
- with 1 or 2 heat exchangers (ensures correct operation of the unit);
- with a built-in small diameter boiler.
Hollow heat accumulators are the simplest and have the lowest cost. They can be connected to one or more units. You can also install an additional heating element that runs on electricity. The heat accumulator guarantees good heating of the living space, reduces the likelihood of overheating of the coolant and ensures the safe operation of the system. A heat accumulator with one or two coils is an advanced type of device with a wide range of uses. The heat exchanger, which is located at the top, removes thermal energy. The one at the bottom intensively heats up the buffer tank.
A thermal buffer unit costs significantly more than a hollow unit, but this is completely justified. The device significantly increases the functionality and efficiency of the system. A storage tank with a built-in tank accumulates the heat generated in excess of the norm and supplies hot water.
Connecting (piping) the heat accumulator to the heating system
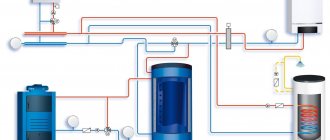
As a general rule, the buffer tank is connected to the heating system in parallel to the heating boiler, therefore this circuit is also called a boiler piping circuit.
Let us present the usual diagram for connecting a heating unit to a heating system with a solid fuel heating boiler (to simplify the diagram, shut-off valves, automation and control devices and other equipment are not indicated on it).
Simplified wiring diagram for a heat accumulator
This diagram identifies the following elements:
- Heating boiler.
- Thermal accumulator.
- Heating devices (radiators).
- Circulation pump in the return line between the boiler and the heat exchanger.
- Circulation pump in the return line of the system between heating devices and heating equipment.
- Heat exchanger (coil) for hot water supply.
- Heat exchanger connected to an additional heat source.
One of the upper pipes of the tank (item 2) is connected to the boiler outlet (item 1), and the second is connected directly to the supply line of the heating system.
One of the lower pipes of the heat pump is connected to the boiler inlet, and a pump (item 4) is installed in the pipeline between them, ensuring the circulation of the working fluid in a circle from the boiler to the heat pump and vice versa.
The second lower pipe of the TA is connected to the return line of the heating system, in which a pump is also installed (item 5), which ensures the supply of heated coolant to the heating devices.
To ensure the functioning of the heating system in the event of a sudden power outage or circulation pumps failure, they are usually connected in parallel to the main line.
In systems with natural circulation of coolant, there are no circulation pumps (items 4 and 5). This significantly increases the inertia of the system, and at the same time makes it completely energy independent.
The heat exchanger for DHW (item 6) is located in the upper part of the heat exchanger.
The location of the additional heating heat exchanger (item 7) depends on the type of incoming heat source:
- for high-temperature sources (heating elements, gas or electric boiler) it is placed in the upper part of the buffer tank;
- for low-temperature ones (solar collector, heat pump) - in the lower part.
The heat exchangers indicated in the diagram are optional (items 6 and 7).
Connection diagrams
Complete TA connection diagram for the heating system
The simplest connection diagram assumes the presence of a boiler heating circuit ring. This will make it possible to reduce the heating time of the main circuit. The thermostat will not allow cold coolant (water or glycol) to pass through the heat accumulator until the temperature is established at the required level.
As soon as this happens, the coolant is distributed in two directions:
- Warming up the TA.
- Warming up the main tank.
In the latter case, it is assumed to be mixed with the coolant and redirected to the tank. This increases efficiency and reduces the warm-up time of the main circuit. This connection allows the system to operate autonomously (with the pump turned off).
A separate circuit communicates with the TA and radiators. To eliminate the need to control the operation of the heating system, two bypasses are introduced into its structure:
- Contains a ball valve that closes when the pump is off. The check valve is activated.
- If the pump is stopped and the ball valve is out of order, the coolant is pumped through the second (backup) bypass.
The circuit can be simplified by eliminating the check valve. This is done on the basis that it is characterized by high flow resistance. When taking this step, you need to remember that in the event of a power outage, you will have to manually open the ball valve.
A more complex system using an alternative energy source and a hot water circuit
If outages are possible, an alternative power source or uninterruptible power supply is included in the system. This will require additional costs. The feasibility of purchasing this equipment appears after calculating the cost of pipes, fittings, pumps and valves, which may become unusable. As a result, purchasing a UPS (uninterruptible power supply) does not seem too expensive.
Detailed video review of the system
Advantages of thermal accumulators
The mechanism of operation of the thermal accumulator
The heat accumulator can fully replace the hot water boiler. Moreover, both devices are comparable in cost.
However, the heat accumulator will not only provide hot water supply, but will also solve a whole range of additional problems. By using a solid fuel boiler with a heat accumulator, you can get many advantages:
- the service life of heating equipment increases several times;
- the boiler will never operate at maximum loads or idle;
- the temperature of the heating supply to the house is equalized. If the water in the boiler does not have time to heat up, hot coolant is automatically supplied from the reserve tank. Conversely, excess temperature of the carrier will be selected and accumulated;
- a correctly selected container continues to take heat from the boiler even with complete combustion of the fuel;
- resource savings reach 30%.
The advantages of batteries have been appreciated by many manufacturers of solid fuel boilers.
And now they provide their equipment warranties only if additional tanks are installed. Date: September 25, 2022
Advantages and disadvantages
You can install a heat accumulator, which has boiler functions.
Advantages of using a heat accumulator:
- Retains thermal energy for hours and days.
- Overheating of the boiler is avoided.
- Thermal energy is not wasted, but is accumulated to be used in the future, thanks to this the efficiency of the boiler and the heating system as a whole increases.
- Allows you to save money.
- The air temperature in the rooms is easily maintained at the optimal level, sudden temperature changes are excluded.
- There is no need for frequent fuel loading.
- In addition to a solid fuel boiler, you can install a solar system, which is a free source of thermal energy.
- Some models of thermal accumulators for heating can combine the functions of a boiler.
Disadvantages of the system:
- Long heating - optimal installation in houses intended for permanent residence. In country cottages that are visited on weekends in winter, such a device will not be of any use.
- High cost - they cost about the same as the boiler, and sometimes more.
- Significant dimensions and weight - because of this, certain difficulties arise during transportation and installation. In addition, a heat accumulator intended for heating is installed in close proximity to the boiler; additional equipment must also be located there, so it is often necessary to allocate a special room for installing devices and prepare it in a special way: to equip a support platform capable of supporting the weight of the accumulator. When filled, the tank can weigh 3-4.
- A high-power boiler is required - the purchase of a storage tank is justified if the boiler’s power is not fully used; there is at least a double power reserve, otherwise the device will be inactive.
You can make a heat accumulator with your own hands from stainless steel and copper pipe.
By making a heat accumulator with your own hands, you can save a significant amount. The simplest design is made from a stainless steel barrel or even stainless steel sheet with a thickness of at least 3 mm. You will also need a copper tube with a diameter of 3 cm and a length of 14 m. It is bent into a spiral and placed inside the tank. A cold water supply is made from below, a hot water outlet is made from above, and shut-off valves are installed on the outlets. It is imperative to insulate a heat accumulator made by yourself for a solid fuel boiler, otherwise it will be ineffective. It is also necessary to install pressure and temperature sensors.
If you can’t weld a cylindrical container, you can make a heat accumulator for heating in the shape of a parallelepiped - it’s easier to make a tank of this shape with your own hands. The corners are further strengthened, and the structure is supplemented with stiffening ribs from the outside - they are welded at a distance of 30-35 cm from each other. The ratio of the diameter and height of the device is 1:3(4).
Calculation of heat storage volume
To calculate the volume of the buffer tank, it is necessary to determine the storage capacity of water. It is known that to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by one degree Celsius, it is necessary to expend energy of 4.187 kJ or 1.167 W•h. The mass of one liter of water is 1 kg.
For example, if the volume of a tank is 1000 liters, and the water in it is heated by 50 degrees, then this tank can supply 58 kW • hour of energy. In other words, if the owner of the house wants to receive 58 kW• hour of energy when the boiler is not working, then he should purchase a tank with a volume of 1000 liters.
Top 10: types of heat accumulators for heating, features, price
The ten most popular heat accumulators for solid fuel boilers are as follows:
- Nibe BU – 500.8
- ETS 200
- HAJDU AQ PT 500
- HAJDU AQ PT 1000 C
- S-TANK HFWT -300 SERIES
- S-Tank AT 300
- S-TANK AT AT-1000
- HAJDU AQ PT 1000
- HAJDU PT 300
- S-TANK AT PRESTIGE -500
In retail, the price can vary from 55 to 200 thousand rubles. Many models of Belarusian and German manufacturers are presented in the form of steel tanks, without thermal insulation casing. The number on the label indicates the storage capacity.