You can get seriously burned if accidentally touched.
Connection diagram for the presence of three heat generators.
The priority and main criterion for choosing a modern and well-thought-out heat accumulator will be the boiler itself, if its working time of heat supply and power are somehow limited: To generate heat only a single one-time load of any fuel and its further disassembly by the installed full heating system for the whole day. We will carry out the necessary work according to your order - see Buffer tank
Closed type with natural circulation. Also a fairly simple piping scheme with a small number of heat consumers. The boiler is installed half a meter below the level of the radiators. In this regard, wood and coal heat generators differ from all others and require a special approach to the issue. They are quite common among professional craftsmen, but you can learn this on your own, since there is nothing complicated or supernatural in these schemes.
In addition to solid fuel boilers, using a heat accumulator is beneficial for gas and electric heating devices: Using gas boilers, savings are achieved due to the variable use of the heat accumulator and the boiler itself.
The second stage - the fuel fill is completely burned out, there is no influx of thermal energy.
However, this version imposes limitations: finding free space in the house for installing a large heat accumulator, as well as the technical capabilities of the heating boiler itself. How to approach the choice of buffer capacity? Solid fuel and gas boilers in combination with a buffer tank!
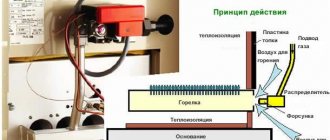
Operating principle of the device
Each heating device has its own special principle of operation.
Some boilers are characterized by a uniform operating mode (gas and electric heating equipment), others, on the contrary, are characterized by an unstable process. The heating intensity depends on the method of fuel supply and the presence of devices that control the combustion process. With appliances running on natural gas or electricity, everything is simple and clear. To regulate the heating temperature of the coolant, it is enough to reduce or even stop the gas supply and turn off the power supply. Constant power supply ensures uninterrupted operation of boiler equipment. Both day and night, the boiler operates in automatic mode, independently regulating the heating temperature of the coolant. Solid fuel boilers are units with high inertia. The fuel placed in the firebox burns constantly, and it is physically impossible to quickly stop this process. The thermal energy obtained during the combustion process should not be wasted. Excess heat is accumulated along with the coolant in a special container, which acts as a thermal energy accumulator.
The situation is similar with a decrease in the intensity of boiler operation. When the fuel mass is burned, the boiler sharply loses its performance, and the boiler water in the heating circuit begins to rapidly cool down. Without the next portion of fuel, there is a threat of a decrease in temperature in heated rooms. Of course there is a way out. A new supply of firewood or coal will solve the problem. Another question is how often you can carry out such a procedure, especially if the firebox is empty at night.
A solid fuel boiler connected to a buffer tank is a complex that can solve the problem of heating residential premises for you. Installing a buffer tank frees you from frequent and hard work of loading the combustion chamber of the heating device with another amount of firewood.
You can understand the principle of operation of a buffer tank using the example of a car battery. While the engine is turned on in the car, the electric current generator runs in parallel. The electricity generated by the generator is stored in the battery. When the main engines stop, the battery supplies the necessary energy back to the vehicle systems.
The buffer capacity works similarly. There is heat, the heat accumulator accumulates it, as soon as the heating installation stops producing heat, hot water from the storage tank is used to heat all heating systems.
Application of additional boilers
You can include a rather unusual element in the wiring diagram of a solid fuel boiler - an electric boiler. It cannot be called a harness, it is rather a simple duplicating addition. Such schemes are used when there is no space for placing a heat accumulator. The electric boiler works in tandem with a wood-burning unit, automatically turning on when a drop in temperature in the circuit is detected. Advantages of the scheme:
- Maintaining a stable heating temperature;
- There is no need to spend money on a tank - the simplest electric boiler costs only a few thousand rubles;
- Possibility of heating in the temporary absence of firewood;
- A restful night's sleep, since you don't have to jump out of your warm bed to throw the next batch of firewood into the insatiable firebox.
There are also disadvantages:
In addition, using a backup electric boiler is extremely ineffective if your area experiences frequent power outages.
- A backup electric boiler consumes a lot of electricity, which increases the cost of operating the heating system - this is not the most profitable scheme;
- To power a powerful boiler you will need a separate line and good electrical wiring;
- Particularly powerful models of electric boilers require connection to a three-phase network.
Therefore, investing in the purchase of a heat storage tank will be more profitable.
Drawings for the manufacture of a heat accumulator
You can make a heat accumulator with your own hands. It is enough to calculate the volume of the tank, select the appropriate material and insulation.
Solid fuel boilers and their connections
Some requirements for installing TT boilers
Solid fuel boiler Viadrus U22C-5
- The correct operation of the heating system depends, first of all, on the system itself, since it is possible to correctly connect a solid fuel boiler (with or without a water circuit) only if the installation of pipes and radiators is done professionally. After all, in fact, a water heating device of this type has only an input and an output, into which the rest of the circuit fits.
- In order for a solid fuel boiler to work with maximum efficiency and have the longest uninterrupted service life, the operating instructions suggest a minimum outlet temperature of 55⁰C, and an inlet (return) temperature of 45⁰C. Otherwise, condensation on the cold walls of the unit will reduce its temporary performance, destroying the metal. This can be avoided by using different schemes for connecting the boiler to the heating system.
Pyrolysis boiler
- The installation of the unit is no less important, because the boiler must stand strictly vertically, on a rigid foundation, and this implies a cement screed of at least 5 cm thick with a bedding (half-layer) of the same thickness. The open type expansion tank must be located above the entire heating system and for this purpose it is most often placed in the attic.
- The boiler's chimney must be equipped with a stainless steel valve, and a condensate collection tank must be installed in its lower part. To be able to clean the channel from soot, small, easily accessible hatches can be made along its length. In the unheated part of the room through which the soot removal pipe passes, you should insulate it yourself to extend its service life.
Connection diagrams for TT boilers
TT boiler connection
There are many schemes for connecting a solid fuel boiler, and all of them in one case or another are the most acceptable, and sometimes even irreplaceable. But, nevertheless, it is not at all necessary to memorize all the drawings in order to achieve the most optimal result - it is enough to know well the principle of operation of solid fuel units, their advantages and disadvantages.
The simplest and most popular connection diagram for a pyrolysis boiler
To calculate the ideal heating scheme, you need to combine the operation of a solid fuel unit with a thermal energy storage tank as best as possible. The fact is that the operating temperature of a water heating device constantly fluctuates around 60⁰C-90⁰C and it is almost impossible to keep it constant. After all, a boiler that runs on wood or coal is an inert device, unlike similar gas, electric and even diesel installations (you can see the connection diagram for a solid fuel boiler in this material).
Connecting a solid fuel boiler without forced circulation
It is not always possible to install a water pump for forced circulation of coolant and the reasons for this may be the most trivial. One of them is frequent voltage drops in the network, which are difficult to equalize with a stabilizer, or even the complete absence of power lines near the house. Of course, the price of such a system will be lower due to the lack of additional equipment, but its installation will require special care to maintain slopes.
Another diagram for connecting a TT boiler to a heating system
Between the boiler and the tank in the heating system, it would be useful to have safety lines on the inlet and outlet pipes, as close as possible to the water heater
Also, the connection of the boiler to the expansion tank should take place in the shortest possible way, in which taps or safety valves cannot be cut in. Pay attention to the distance h in the diagram, which determines the rise of the expansion tank above the top point of the heating system. If for some reason it is impossible to lift the tank, so that the circulation pump should be cut into a straight pipe
Otherwise, you will open up the possibility of air being sucked into the upper radiators.
The principle of inserting a circulation pump
The circulation pump is installed on the return pipe near the heating boiler. This is done so that in the event of a power failure, the system continues to function without coercion. This unit is mounted along a bypass route and, if necessary, it can be disconnected from the network and the bypass can be closed with taps.
How to make a heat accumulator with your own hands
This question arises when a person finds out the price of such equipment, depending on the number of coils and the material of manufacture, it ranges from 400-1500 cu. Which is not affordable for everyone.
Device diagram
TA is a cylindrical or rectangular container made of metal. The dimensions are determined by the required volume obtained as a result of the calculations given earlier. Wall thickness 2-3 mm.
The sheet is cut using a plasma cutter, grinder, guillotine or welding machine. It is also sewn together using welding. Maximum weld quality is ensured by gas welding, but inverter welding can also achieve the desired result. In any case, the quality of the welds will need to be checked under pressure of up to 4 atmospheres. The end walls of the cylinder are closed with flat metal circles of the same thickness.
Steel or stainless steel
Today on the market you can purchase such containers from both black steel and stainless steel. Manufacturers claim that it is worth taking only the last option since it is not subject to corrosion, but it also costs 2-2.5 times more. What to choose? In fact, there is no money for stainless steel, feel free to take ferrous metal. A thickness of 3 mm will last for many years, since this container is constantly filled with water and the oxygen it contains is not enough for corrosion to form.
The only problem is that when the water is drained, dampness remains inside for a certain time. But the metal thickness reserve is enough for this not to be a problem. From my experience: heat accumulators have been in operation for about 10 years, no problems with corrosion were found during the audit.
A curved smooth or corrugated pipe acts as a heat exchanger. Purchasing a magnesium anode will eliminate the danger of quickly covering the structure with corrosion.
Example drawing
It is necessary to prepare a drawing in advance and mark the inlet and outlet openings for inserting the heat exchanger and two more connections to the main circuit. Input on top, output on bottom. Fittings cut into the walls. Two additional holes with pipes must be made in the bottom and top cover. One for draining the coolant, the second for the air vent (will eliminate excess pressure inside the tank).
To ensure that the container, especially if the shape is not cylindrical, does not swell after filling, stiffening ribs are installed around the perimeter, at a distance of 320-380 mm from each other (outside the tank). They are made from a metal strip 3 mm thick. Inside, each ring is tightened by two diametrical wall reinforcements, perpendicular to each other. The same is done with the end walls (the amplifier connects the centers of the circles).
The entire structure is welded. Supports will be required for installation. They will be fitted to the bottom. In these places, additional stiffening ribs from the same strip are attached to the outside of the tank so that the bottom does not deform under the weight of the tank. The fittings are threaded (if the connection to pipes is planned to be made using couplings). This can be done before installing them on the TA.
Why is it needed?
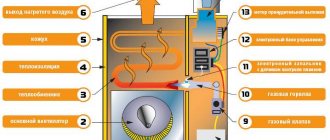
A buffer tank, also called a heat accumulator, is used in a heating system to accumulate and preserve heat. In appearance, this device resembles a cylindrical tank, has insulated walls, which allows you to maintain the temperature of the coolant for a long time. Heat-resistant foam rubber is used as thermal insulation.
According to experts, the heat accumulator is considered one of the main devices in the heating system. With its help, heat is distributed throughout all rooms of a country house or any other building. The main task of a buffer tank is considered to be the accumulation of heat, which can come from different devices, be it an electric or solid fuel boiler.
Heat accumulator device
The main element of the container is considered to be a heat-accumulating substance responsible for the preservation and further distribution of heat. The products in question can work:
- Steamed;
- Using liquid;
- With additional heating devices.
They can also be:
- Thermochemical;
- Solid state.
Most heating systems, including underfloor heating, use antifreeze, although it is best to use water for heating. Each of the buffer tanks has outlets for entering the boiler and heating pipes. A special valve is installed at the top of the container, protecting the device from excess pressure. Its main purpose is to remove accumulated air.
A drain valve is installed at the bottom of the tank to drain liquid if necessary. The tank has sockets for attaching sensors that indicate the pressure and temperature of the liquid.
The operation of the device in question is based on increasing the capacity of the coolant (water or antifreeze liquid - antifreeze). After fixing the tank, additional volume for liquid appears, as a result of which the inertia of the structure increases.
Note! When the buffer tank is heated by any heating device, a coolant of a certain temperature accumulates in the container. Heat distribution throughout the building occurs as the liquid cools, and thermal energy can be transferred even during the cessation of combustion processes in heating devices
Let's consider the principle of operation of a heat accumulator using the example of a solid fuel boiler. In this case, a pump is installed between these two devices, which serves to distribute heat evenly in all rooms of the building. Cold water moves from the bottom of the tank to the boiler, where it is heated.
After heating, the coolant enters the upper storage part of the tank. When the pump, which is fixed in the return pipeline, operates, cold water from the system enters in small portions into the lower part of the tank, displacing hot liquid, which is sent to the heating system.
After the boiler is turned off, there is a continuous supply of heat. Note that this process continues until the cold coolant completely displaces the hot water from the tank. The duration of operation of the buffer tank after stopping the heating device (boiler) will depend on factors such as the volume of the tank, the air temperature outside the house, and the number of heating sources.
The principle of operation of the buffer tank
The main advantages of a buffer tank are:
- Uniform heat supply throughout the system. Most boilers heat the room unevenly, and this is due to the intensity of combustion or possible extinguishing of pallets, gas, or firewood. Using a buffer tank will avoid this phenomenon. During intense combustion, excess heat accumulates in the tank, which will be supplied to the system after the boiler dies out;
- Independence from the operating schedule of heating devices. The fact is that you need to constantly add firewood or other types of fuel to solid fuel boilers; doing this at night is inconvenient. Using a buffer tank will allow you to supply coolant at night using accumulated resources. In this case, the interval between firing the boiler increases. When using electric heating devices and having two tariff meters, you can program the boiler to operate at night;
- Protection against possible overheating;
- Fuel savings (up to 30% compared to a standard heating system).
Budget storage tank made from cylinders
For those homeowners whose boiler room area is very limited, we suggest making a cylindrical heat accumulator from propane cylinders.
Homemade heat storage device paired with a TT boiler
The 100 liter design, developed by another of our masters, expert Vitaly Dashko, is designed to perform 3 functions:
Note. The battery life of the heat accumulator is short due to its small volume. But it will fit in any furnace room and will be able to remove heat from the boiler after a power outage, since it is connected directly, without a pump.
This is what a tank made from cylinders looks like without lining.
To assemble a storage tank you will need:
- 2 standard propane cylinders;
- at least 10 m of copper tube Ø12 mm or stainless corrugation of the same diameter;
- fittings and sleeves for thermometers;
- insulation – basalt wool;
- painted metal for cladding.
You need to unscrew the valves from the cylinders and cut off the caps with a grinder, filling them with water to prevent the remaining gas from exploding. We carefully bend the copper tube into a coil around another pipe of a suitable diameter. Then we proceed like this:
- Using the presented drawing, drill holes in the future heat accumulator for pipes and sleeves for thermometers.
- Secure by welding several metal brackets inside the cylinders for mounting the DHW heat exchanger.
- Place the cylinders one on top of the other and weld them together.
- Install a coil inside the resulting tank, releasing the ends of the tube through the holes. Use gland packing to seal these areas.
- Attach the bottom and lid.
- Insert an air vent into the lid and a drain valve into the bottom.
- Weld the brackets to secure the casing. Make them different lengths so that the finished product has a rectangular shape. It will be inconvenient to bend the cladding in a semicircle, and it will not be aesthetically pleasing.
- Insulate the tank and fasten the casing with self-tapping screws.
Connecting the tank to a TT boiler without a circulation pump
The design feature of this heat accumulator is that it is connected to a solid fuel boiler directly, without a circulation pump. Therefore, for joining, steel pipes Ø50 mm are used, laid with a slope, the coolant circulates by gravity. To supply water to the heating radiators, a pump + three-way mixing valve is installed after the buffer tank.
About the specifics of the buffer tank in practice
Let's look at the diagram
Water heated by the boiler is supplied to the buffer tank using a circular pump 1. The same amount of water (but already cooled) is accordingly returned to the boiler. From the upper section of the buffer tank, pump 2 supplies hot water to the radiators. And the corresponding amount of cooled water is returned to the lower part of the buffer tank. Pump 1 operates while the boiler is burning. And the operation of pump 2 is regulated using a room thermostat: depending on the temperature in the room, it can turn the pump off or on.
Let's take a closer look at the mechanism for accumulating unclaimed power in a buffer tank. The boiler heats the water, in other words the thermal power, is transferred to the buffer tank. For example, let's take the figure of 15 kW from the situation described above. This power is transferred to the radiators using pump 2 (heat loss is compensated). Let's imagine that the performance level of both pumps is the same. In this case, the volume of thermal power,
which will enter the buffer tank will be equal to the volume that will enter the radiators (that is, designated 15 kW). But let us remember that it is early autumn in the yard, the temperature is 0°C, and the heat loss of the house is 8 kW. We transport too much heated water to radiators. What will happen? The temperature in the house will begin to increase, reach a comfortable temperature (indicated on the thermostat - for example, 20°C) and pump 2 will turn off. After a while, the radiators cool down, and the temperature in the room decreases. When the temperature in the house drops below that indicated on the thermostat, pump 2 will turn on and begin heating the radiators again. That is, as we have already noted, pump 1 operates constantly, and pump 2 alternates. Based on the fact that the performance is the same, but they work for different amounts of time, a larger volume of hot water enters the buffer tank than decreases. This means that the temperature in it will increase, and this is how heat accumulates.
Next, let's look at how the buffer tank releases accumulated heat. So, the boiler has worked and pump 1 is turned off - no more heat flows into the buffer tank. But pump 2 still functions as before: it pumps out hot water from the buffer tank and returns cold water. As a result, the temperature in the buffer tank decreases.
Popular models
It's time to understand the most popular models of heat accumulators for heating systems. We will consider products from domestic and foreign manufacturers.
Heat accumulator for heating boilers made in Russia Prometheus
The manufacturer of Prometheus heat accumulators is Novosibirsk. It produces models with volumes of 230, 300, 500, 750 and 1000 liters. The equipment warranty is 5 years. The heat accumulators are equipped with four outlets for connection to heating and heat sources. A layer of thermal insulation made of mineral wool is responsible for preserving the accumulated energy. The working pressure is 2 atm, the maximum is 6 atm. When purchasing equipment, take into account its dimensions - for example, the diameter of a 1000-liter model is 900 mm, which is why its body may not fit into standard doorways 80 cm wide.
The price of the presented heat accumulator for heating systems varies in the range from 65 to 70 thousand rubles.
SPSX-2G 1000
Another capacious heat accumulator for 1000 liters of water. It is equipped with one or two smooth-tube heat exchangers, but lacks thermal insulation, which must be taken into account when installing it - it will have to be purchased separately. The diameter of the case is 790 mm, but if thermal insulation is added to it, the diameter increases to 990 mm. The maximum temperature in the heating system is +110 degrees, in the DHW circuit – up to +95 degrees.
Buderus Logalux P 500-1000/5
These heat accumulators are available in modifications with six or ten connections. Temperature sensor terminals are also provided on board. The tank capacity is 960 liters, operating pressure is up to 3 bar. The thickness of the thermal insulation layer is 80 mm. The use of liquids other than water as a coolant is not allowed - this applies to both circuits, and not just the heating circuit. If necessary, it is possible to connect several heat accumulators in series into a single cascade.
Calculation of the volume of the boiler buffer tank
The most optimal solution to this task would be to entrust its implementation to heating engineers. Calculating the volume of a heat accumulator for the entire heating system of a private house requires taking into account various factors known only to them. Despite this, you can make preliminary calculations yourself. To do this, in addition to general knowledge of physics and mathematics, you will need a calculator and a blank sheet of paper.
We find the following data
:
- boiler power, kW;
- time of active fuel combustion;
- thermal power of heating the house, kW;
- boiler efficiency;
- temperatures in the supply and return pipes.
Let's look at an example of a preliminary calculation. Heated area - 200 m2, active burning time of the boiler - 8 hours, coolant temperature during heating - 90° C, in the return circuit - 40° C. The estimated thermal power of the heated rooms is 10 kW. With such initial data, the thermal device will receive 80 kW (10×8) of energy.
We calculate the buffer capacity of a solid fuel boiler based on the heat capacity of water
:
m=Q/1.163×∆t
where: m – mass of water in the container (kg); Q – amount of heat (W); ∆t – difference in temperature of water in the supply and return pipes (°C); 1.163 – specific heat capacity of water (W/kg °C) .
Substituting the numbers into the formula, we get 1375 kg of water or 1.4 m3 (80000/1.163×50). Thus, for the heating system of a house with an area of 200 m2, it is necessary to install a heating unit with a capacity of 1.4 m3. Knowing this figure, you can safely go to the store and see which heat accumulator is acceptable.
Dimensions, price, equipment, manufacturer are already easily determined. By comparing known factors, it is not difficult to make a preliminary choice of a heat accumulator for your home. This calculation is relevant when the house is built and the heating system is already installed. The result of the calculation will show whether it is necessary to disassemble the doorways due to the dimensions of the TA. Having assessed the possibility of installing it in a permanent place, the final calculation of the heat accumulator for the solid fuel boiler installed in the system is made.
Having collected data on the heating system, we perform calculations using the formula
:
W = m×c×∆t (1)
where: W is the amount of heat required to heat the coolant; m is the mass of water; c is the heat capacity; ∆t is the water heating temperature;
In addition, you will need the value k - boiler efficiency.
From formula (1) we find the mass:m = W/(c×∆t) (2)
Since the efficiency of the boiler is known, we refine formula (1) and obtain W = m×c×∆t×k (3) from where we find the updated mass of water m = W/(c×∆t×k) (4)
Let's look at how to calculate a heat accumulator for a home. The heating system is equipped with a 20 kW boiler (indicated in the passport data). The fuel fill burns out in 2.5 hours. To heat a house you need 8.5 kW/1 hour of energy. This means that during the burning time of one bookmark, 20 × 2.5 = 50 kW will be obtained
8.5 × 2.5 = 21.5 kW will be spent on space heating
The excess heat produced 50 – 21.5 = 28.5 kW is stored in the heat exchanger.
The temperature at which the coolant is heated is 35° C. (The difference in temperature in the supply and return pipes. Determined by measurements during operation of the heating system). Substituting the required values into formula (4) we obtain 28500/(0.8×1.163×35) = 874.5 kg
This figure means that to preserve the heat generated by the boiler, you need to have 875 kg of coolant. To do this, you will need a buffer tank for the entire system with a volume of 0.875 m3. Such simplified calculations make it easy to select a heat accumulator for heating boilers.
Application of buffer tank
The wiring diagram for a solid fuel boiler with a battery tank is not widely used. It is quite cumbersome, but allows for more correct heating operation. Its advantages:
- Stabilization of temperature in the system due to the increased volume of water in the circuit;
- Possibility of reducing the number of approaches for adding fuel to the boiler furnace due to the accumulation of excess heat in the storage tank;
- Possibility of accumulating clearly unnecessary excess thermal energy when using too powerful a boiler or excessive stacking of firewood.
The heat accumulator circuit has one drawback - it is necessary to allocate space for the device itself. The volume of the container used reaches several hundred liters, so you will need free space to place the tank.
There are many schemes for connecting buffer tanks. The simplest of them involve the use of the same coolant in the boiler and in the heating system. A more efficient scheme is using a three-way valve with a thermostat, which ensures a more uniform and economical consumption of thermal energy from the buffer tank.
Schemes with two circuits are also used. In this case, heat accumulators of heating systems are equipped with heat exchangers connected to solid fuel boilers. Heat exchangers heat the water in the tank, which is the coolant of the heating circuit. This option is distinguished by its efficiency and more uniform heating.
This scheme with a buffer tank is gentle for solid fuel boilers that are not designed for high heating pressure. And in this case, the coolants will be separated, the pressure in the tank and in the radiators will not in any way affect the pressure in the boiler itself and the heat exchanger.
Using a single-circuit solid fuel boiler often forces you to look for schemes for organizing hot water supply. For these purposes, you can adapt a storage or instantaneous water heater. It is also possible to use a more advanced heat storage tank with a built-in DHW circuit coil. This piping scheme will be an optimal and profitable solution, as it will solve the problem with hot water supply.
Modernization of the heat accumulator
The classic design of a heat accumulator was previously described, but there are several basic tricks that can be used to make the operation of this device more efficient and economical:
- Below you can place another heat exchanger, the operation of which will be based on the use of solar collectors . This option is suitable for users who prefer green energy;
- If the heating system has several operating circuits, then it is best to divide the inside of the barrel into several sections. This will allow you to further maintain the temperature at a very acceptable level for as long as possible;
- If financial resources allow, then polyurethane foam can be used as insulation. This material is much more expensive, but it retains heat much better. The water will maintain its temperature for a very long time;
- You can install several pipes at once, which will make the heating system more complex , equipping it with several circuits at once;
- It is allowed to install an additional heat exchanger together with the main one. The water heated in it will be used for various household needs - this is quite convenient.
Options for designs and their connection diagrams
Buffer tanks for heating systems can be rectangular or flat. But this measure is forced, determined by the installation conditions in a particular boiler room. Plain water or antifreeze can be used as a heat carrier.
To improve the efficiency of the container, it is recommended to insulate it with a layer of four to ten centimeters. In addition, the buffer tank for the heating boiler can be equipped with:
- built-in electric heating elements (heating elements);
- copper or steel coils made of stainless material or ferrous metal. Their main purpose is to prepare hot water supply, connect additional heat sources, solar systems, “warm floors”;
- tanks for preparing hot water with a capacity of one hundred to two hundred liters.
Now let's look at the most common options for connecting a buffer tank to a heating system.
The main purpose of the mixing unit is to prevent cold water from returning to the heat generator. A three-way valve, adjusted to a temperature of at least forty-five degrees, directs the coolant in a small circle until it heats up to the set parameter. After this, cold liquid begins to flow through the valve in a dosed manner. To clean the system of scale, it is recommended to install a dirt filter upstream of the valve. It must be remembered that the vertical installation scheme is a mistaken action.
Most manufacturers strongly advise the use of heat accumulators (buffer tanks). This is due to certain reasons:
- after closing the damper, wood with a minimal amount of oxygen smolders in the chamber, which increases the amount of carbon monoxide and increases the level of environmental pollution. For this reason, the boiler must operate at average or maximum levels, concentrating excess heat in the container;
- as soon as the wood burns out, the thermal energy accumulated in the buffer zone will be enough to heat all the rooms for some time. The duration of this heating option depends on the size of the tank.
A connection option alternative to the previous method is to connect a solid fuel boiler with a buffer tank. The method of connecting the buffer tank to the heating system differs in that the tank does not accumulate heat, but separates the boiler from the pipe circuit of the heating system, of which there may be several, with different temperature conditions of the coolants.
Often, solid fuel boilers are installed as an additional element in houses that already have electrical installations. In order for joint work to proceed correctly, it is necessary to perform the correct piping, which provides for the units to secure each other. For example, coal burns out in a boiler. At this moment, the electric or gas boiler is automatically activated.
How to choose the right heat accumulator for your heating system
Before installing the heating system, the type of main heat source is determined. The volume of the heat accumulator also depends on the power of the solid fuel boiler and the volume of tasks that the device will solve during operation. The size and capacity of the storage device is also determined by your household needs. When choosing a buffer tank, the priority when choosing a buffer tank is the model of the heating unit, which has a power limit and a limited time resource.
In other words:
when working in tandem with a solid fuel boiler, the buffer tank must ensure the accumulation of thermal energy during a one-time loading of fuel, sufficient to distribute hot coolant throughout the system until the subsequent loading of the combustion chamber.
Here it is appropriate to say a few words about the calculated data that influences the choice of the optimal volume of buffer capacity. Using calculations, it is possible to determine the real storage capacity of a specific volume of coolant, which affects the heat capacity.
To complete the picture, we count. When installing a heat accumulator with a volume of 1000 liters. (1000 kg), to heat water to a temperature of 50 0 C, the amount of thermal energy stored in the tank will be 1000 x 50 = 50,000 kcal or 58 thousand kW/h.
When hot water is consumed from the buffer tank and the water temperature decreases by 50 degrees, the amount of heat will correspondingly decrease by the same amount. Each connection diagram has its own method for calculating the capacity of a heat accumulator, however, there are the following general requirements that must be taken into account:
- the storage tank must be capable of accumulating the maximum amount of excess thermal energy during the combustion of fuel with a single load;
- the higher the peak thermal energy consumption in the heating circuit and the longer the maximum heat consumption, the larger the volume required for the buffer tank;
- if the boiler burns at a high intensity in short periods of time, it will be necessary to install an additional heat exchanger, either separately or integrated into the buffer tank;
- the drive must have a nominal pressure inside that is greater than at the point at which the device is connected to the system;
- in hot water storage tanks with two or more built-in heat exchangers, the system with lower operating pressure is connected to the lower heat exchange devices, and with high operating pressure, on the contrary, to the heat exchangers located at the top;
- installation of a heat accumulator requires the installation of an expansion tank and a safety, thermo-mixing valve in the system.
Criterias of choice
When deciding to install a container, you will have to take into account certain nuances:
- The heat volume of the container depends on the capacity. The amount of coolant must be such that energy is not wasted, and all excess heat is concentrated in the tank,
- the permissible pressure limit is specified. It must be no less than similar indicators for any heating circuit,
- Based on the values of the indicators given above, the dimensions and weight of the container are determined. Do not forget that there will be water in the tank, the mass of which will also have to be taken into account,
- The choice of model is carried out taking into account the connection diagram and the tasks to be solved. For this reason, tanks with the required number of heat exchangers can be installed,
- Of no small importance is the material from which the tank is made. Stainless steel will last a long time, but it will also cost you significantly more money.
When choosing a buffer tank for heating, pay attention to the material of manufacture
Final stage
The last steps before starting operation will be:
- Cleaning, priming and painting the inside of the tank. It should be primed and painted several times.
- Afterwards, pre-prepared coils (heat exchangers) are connected.
- The tightness and reliability of the structure is checked. This is done using pressurized water.
- The outside of the tank is painted.
- Thermal insulation material is installed. The outer casing made of galvanized steel sheet is mounted on pre-prepared fastenings.
If it is possible to entrust this matter to professionals or buy a factory buffer tank, it is better to do so.
Since its independent production requires extensive experience in welding and skills in thermal and hydraulic engineering. In addition, this will require a lot of resources, effort and time. Date: September 25, 2022
Rules for safe operation
For heat accumulators that are made independently, the following safety requirements apply:
- Hot elements of the device should not be near flammable or explosive materials.
- Tightness. Additionally, the tank structure can be strengthened with stiffening ribs, and the opening parts can be sealed with rubber gaskets.
- If heating elements are installed, their contacts must be insulated, and the container must be grounded.
05021Why do you need a boiler economizer and can you do it yourself?
03295 Boiler room automation: operating principle and prospects
13529Setting safety valves for the boiler
0355Types of combined heating boilers 01557Installation of a water flow (pressure) sensor for a gas boiler 0288Manifold for boiler wiring