A gas nozzle is a godsend for heating a private home. This device has a number of advantages: simple design of the spray device, safety in operation and high efficiency, and therefore its use becomes economically feasible. A gas nozzle for a heating furnace is a device with the help of which a gas-air combustible mixture is created in order to ensure complete combustion of fuel in the combustion chamber. Fuel injectors have a wide range of applications in thermal power engineering. They are installed not only in household stoves, but also in heating boilers of low, medium and high power, operating on gaseous and liquid fuels.
Combustion process in a boiler
The chemical reaction inside the boiler is a combustion reaction between oxygen (O2) in the air and hydrocarbons (CHyOx) in the fuel, which release energy as heat. During the combustion process, water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are formed, the latter being especially dangerous in terms of air pollution and global warming.
Other combustion products of injector gas may also appear depending on the type of fuel and combustion conditions: oxides of nitrogen (NOx) or sulfur (SOx), which are responsible for acid rain. Carbon monoxide (CO), a dangerous toxic substance, can cause death if inhaled.
Correct adjustment of the device reduces the amount of harmful combustion products. CO2 emissions are reduced when the gas is completely burned. In order to reduce NOx emissions, it is recommended to use the correct combustion technology, which is ensured by the design of the burner device.
How to choose?
What you need to pay attention to when choosing a burner device for a boiler:
- productive power - noise level during operation (applies to supercharged models) - type of heating equipment for which the burner is purchased - type of fuel - pros and cons of this device - provide for possible malfunctions in the operation of the local gas supply line.
Taking these factors into account, you can choose the most suitable burner device for your boiler so that it operates as efficiently as possible without the burden of frequent preventative maintenance.
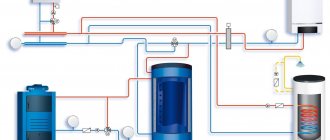
Space heating devices
They mix fuel and oxygen and, with the help of an ignition device, ensure complete combustion, which occurs in the combustion chamber, and the heat is transferred to water through a heat exchanger. Control devices regulate ignition, combustion speed, fuel and air supply, exhaust draft, water temperature, steam and water pressure in the boiler.
The hot water produced by the boiler moves through natural circulation through the in-house heating system of the entire building. The heating circuit may include hot water heat exchangers, air conditioning and ventilation units.
Tips for cleaning and care
- Close the valve for supplying natural gas to the device;
- Carefully remove the burner;
- Mark the location of the injectors and then unscrew them;
- Clean the nozzles with a brush or a special needle;
- The burner is cleaned with a stiff brush and purged with a pumping device;
- The nozzles for the gas boiler are installed back;
- The burner is attached to the boiler.
In order for a gas boiler to work without failures, you need to choose the right type of burner, carefully studying all the characteristics. In addition, the device should be carefully looked after, otherwise it can quickly fail.
Device classification
The industry produces a very large number of gas injectors of various types, purposes and designs, which are strictly classified by type of fuel and method of air supply. Air supply classification:
- Atmospheric burners are burners in which air is supplied naturally; it is captured in a Venturi tube by a gas stream using the principle of an injector.
- Forced air or pulse burners are equipped with a fan that provides air flow for combustion of the air-fuel mixture and removal of products resulting from fuel combustion.
The gas burner for the stove in the house is divided by type of fuel:
- Gas for burning gaseous fuel.
- Burner for burning liquid fuel.
What should you pay attention to?
To properly build a stove for your home or bathhouse yourself, you must follow certain subtleties. Whether you are building a small or large oven, pay attention to:
- For reliability, the brickwork of the stove is secured with the so-called bandaging of seams. Bandaging is alternating bricks with different sides. For example, the bottom brick is placed with the long (spoon) side forward, the middle one with the short side (called the butt side), then again with the spoon side. The dressing can be single-row or multi-row. Multi-row is more reliable and economical; it requires fewer incomplete bricks. Vertical dressing is required! Horizontal is desirable.
- All seams, both horizontal and vertical, are coated with the solution.
- It is recommended to lay the bottom row with the brick surface facing forward; this will reliably strengthen the entire structure.
- The thickness of the seams between the stones should be up to 3 millimeters, but not less than 2 mm.
- No need to tap the bricks! Put them in place immediately, with clear movements. Moving stones or moving them is not allowed.
- If the stove is located in the house, calculate its position so that it does not come into contact with flammable surfaces. When building a stove into a wall, cover the opening with brick and metal. Seal the gap between the stove and the opening with non-combustible insulation.
- When installing metal equipment, the edges of the bricks are cut off. The gap between the cast iron and the brick is about half a centimeter. Then it is filled with a mixture of concrete and sand. This is done because metal and brick have different deformations when heated.
- Around the holes and doors, brick can be laid edgewise. This will give the whole building a certain charm and also strengthen the structure.
- For a gas firebox, install special ready-made gas burners. They must meet all safety standards and have degrees of protection: when the flame is blown out or flooded, the gas supply must automatically stop.
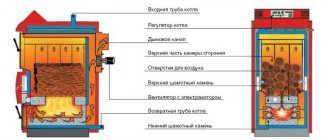
Operating principle of an atmospheric burner
The gas, entering the nozzle nozzle, increases its speed and creates a vacuum at the base of the torch, which sucks in part of the combustion air, the so-called primary air, forming a gas-air mixture.
The main air-gas mixture enters a series of holes (circular, inclined, straight) located on one or several tiers of the device. The mixture is ignited using a pilot light. The additional air required for combustion, called secondary air, is drawn into the flame by induction due to natural convection.
A homemade gas burner for heating with domestic gas has a percentage of primary air from 40 to 50%. All parts of the device (nozzles, mixing tubes) structurally ensure stable combustion of fuel without loss. However, this type of burner does not have the ability to manually control the combustion process. The combustion process is strictly ensured by the burner design and fuel parameters.
While the big advantage of boilers equipped with an atmospheric burner (power up to 1 MW) is the simplicity of the system, they have major disadvantages:
- no emergency shutdown of the combustion process during operation of a brick kiln in the event of a sudden stop in the fuel supply;
- excess air;
- poor combustion efficiency;
- significant production of NOx.
Foundation
Ideally, when constructing a building, the foundation for the furnace will already be laid. Until recently, this is exactly what they did in the villages. What to do if there is no foundation? Let's build it with our own hands.
You need to dig a hole, the perimeter of which will be slightly (see 15) larger than the perimeter of the stove. The bottom of the pit is covered with sand, and the sides are reinforced. Then the concrete mixture is poured.
The concrete must harden well; up to 2 weeks are allotted for this. When working, check the surface with a level; it must be flat and strictly horizontal and 10-16 cm below the main floor. A roofing felt sheet folded in half is placed on top, then a steel sheet and an insulation bedding.
For stoves used in outdoor dachas, the foundation is not deep and just above the ground. The same applies to stoves that will be in the garden.
Pulse burner design
It has a higher efficiency compared to natural ones, is more efficient and complex in design. The fuel burner consists mainly of seven elements:
- Fuel pump, it supplies the boiler with fuel from the tank (liquid fuel) and is equipped with a pressure regulator that returns the excess fuel required for combustion.
- The fan provides the combustion process with the air necessary to burn the fuel.
- A solenoid valve is a valve that operates automatically. It is used to supply a jet of fuel in sufficient quantity for combustion.
- The nozzles are the central part of the burner. The nozzle allows the fuel to be atomized very finely to promote thorough mixing with air to form a fuel-air mixture for combustion.
- A fuel heater, it allows the liquid fuel contained in the tank to be made less viscous to aid combustion. This initial viscosity is related to the storage temperature in the tank as well as the specific characteristics of the fuel.
- Electrodes, they allow you to ignite the gas-air mixture to create the desired flame.
- The combustion head, which consists of two elements. The tip that directs the flame and the reflector that holds the flame in the stove.
The burner operating mode can be divided sequentially into stages:
- Pre-ignition. Turning on the fan, which allows the engine to run.
- Ignition. Opening of the solenoid valve, which directs fuel to the nozzle.
- Ignition. A spark is created to maintain a stable combustion flame.
- Operating mode. Turn off the igniter after the flame has stabilized.
- Stop. Closing the solenoid valve, turning off the burner and after 15 - 20 minutes of ventilation of the firebox in order to free the combustion space from explosive mixtures, turning off the fan.
Oven nozzle
Gas stove burner is used to burn gaseous fuels such as gas. They are available as atmospheric or pulse burners. When comparing the two systems, especially the blower burners provide very clean and efficient combustion of gas products in all power ranges by precisely controlling the supply of fuel and combustion air.
Modern and compact heaters currently use mainly flat burners, in which the flame is distributed over several nozzles over a larger area. The operator's hand makes the combustion particularly efficient and also cleaner due to the lower temperature. Particularly favorable and clean is the so-called catalytic combustion, in which the gas enters into a chemical oxidation reaction on the surface of the catalyst with oxygen from the air. This process does not require conventional ignition and is characterized by a very low flame temperature.
If the jets are installed incorrectly
Determining that the wrong jets are installed on the stove is quite simple.
This will be noticeable by the following signs:
- the burner ignites with a bang, goes out, burns with a hum and is unstable;
- the flame is low and hisses, extinguished;
- The color of the fire turns yellow and soot is formed.
All this indicates incomplete combustion of gas, which means there is a high risk of an emergency. Therefore, you need to replace the injectors with those provided by the manufacturer.
You can do this yourself, taking all precautions, or invite a specialist. But no matter how easy this work may seem, in the absence of basic knowledge about the structure of the stove, it is not worth taking on.
Liquid fuel combustion device
These burners are used to burn liquid fuels such as low sulfur fuel oil, diesel fuel or biofuels. Unlike gas, this type of fuel must be atomized to a gas state. If this is not done, large drops of fuel oil will enter the combustion chamber.
They will not be able to burn completely and will cause the formation of soot, which will settle on the heat exchanger and reduce the useful heating surface of the boiler. These burners at one time offered a pressurized combustion process, as blower burners, due to which the necessary air was mechanically supplied to the combustion point. According to the color of the flame, a distinction is made between so-called yellow and blue burners.
While yellow burners atomize liquid fuel, blue burners use part of the combustion heat to completely evaporate the fuel oil. This way, less soot is produced and combustion occurs at higher temperatures - hence the blue color.
Since clean combustion always depends on sufficient throughput of liquid fuel and its sufficient quantity, the use of such burners in everyday life is limited compared to gas burners.
Gas equipment safety system
The safety system allows you to continuously monitor the burner flame. This control is provided by either a photosensitive photocell generated by the flame or a photocell sensitive to light radiation. The system automatically warns the user in the following cases:
- flame does not appear when fuel is supplied;
- torch breakage during combustion;
- the burner does not work.
Thanks to this control system, the boiler does not have unburned fuel, which can cause an explosion of the gas-air mixture in the boiler furnace. To ensure reliable and trouble-free operation of the boiler, the burner must perform the following functions:
- fuel ignition;
- automatic fuel supply and processing;
- combustion air supply;
- complete combustion of fuel;
- power regulation.
Trouble-shooting
Having a boiler at home brings many advantages, but it also has a number of disadvantages, and the user does not always know what to do correctly. Boiler faults are common to many types. It is important to promptly determine the cause of these faults before calling emergency services. List of the most common and most likely faults.
First of all, if the boiler does not start, you need to check the circuit components:
- network voltage;
- faulty boiler fan switch or motor;
- damaged boiler cables;
- false triggering contacts of automation or commissioning equipment;
- availability of water, whether the gas boiler is powered to the minimum required level specified by the equipment manufacturer.
If the boiler failure is not caused by any of these problems, the following procedure:
- Pay attention to the noises made by the boiler, because they are often the first witnesses of destruction. They can also be due to hot water trapped inside the firebox or due to the presence of air in the heating system due to clogged air ducts.
- Pipe rupture. It usually occurs due to problems with a jammed boiler feed valve, various scale-forming deposits in the boiler, or a malfunction of the condensate drainage systems.
- Failures due to exceeding the pressure and temperature readings, their corresponding sensors can trigger, for example, due to a broken thermometer or, conversely, which is especially dangerous as a result of real overheating of the boiler.
- The heating circuits are not working, possibly due to poor quality of feed water and scale formation in the boiler pipes.
- A problem occurs with the burner (flame breaks, gas accumulation causes detonation and explosion).
For some of these problems, mainly pressure or temperature, the boiler monitor displays an error message, then the system shuts down and automatically restarts. If the problem persists after restarting, it is best to call a professional to troubleshoot the problem. It should be noted, however, that most of these failures can be avoided.
The best prevention is to have your boiler inspected, maintained and cleaned annually, usually by a professional. This will prevent the pipes from clogging and bursting. Prevention is better than restoration, and a simple annual inspection will protect the equipment and the health of users from possible emergency situations.
Best answers
What does pressure have to do with it? Remember chemistry - the number of molecules in the same volume is the same for different gases. And the heat of combustion of one molecule of butane is greater than that of methane. Consequently, in order for the burner to operate normally, less propane-butane must be supplied per unit time; for this purpose, smaller jets are installed on the bottled gas. And if you leave them, there will not be enough oxygen, and the burner will begin to smoke. And if you lower the pressure, the rate of gas flow will decrease, it will warm up and the flame will jump inside the burner. So the jets will have to be changed.
In my opinion, it’s not a matter of pressure, but the fact that in the cylinders there is propane butane and natural gas, a slightly different mixture .. accordingly, the combustion temperature is different... so due to the jets it is compensated for... or rather, the amount of gas passed through them
Yes, each stove has its own set for bottled gas, but we (as a rule) don’t know how to store them….
The most efficient devices of 2018
The most efficient certified boilers and gas burners this year:
- Bosch Greenstar series. The boiler is small, very quiet, environmentally friendly and uses economical condensing technology providing an AFUE rating of 95%. Greenstar is available in two models - combi for spatial and point-less water heating or space heating, which can be used with domestic hot water tanks. It is equipped with a heat exchanger with a 5-year warranty.
- Bradford White Brute Elite Series. The boiler with 95% efficiency has a condensing multi-pass stainless steel heat exchanger with an advanced modulation system. Innovative design features make Brute Elite easy to install in both new and existing heating systems.
- Bradford White Brute Elite 125 Series. Customizable combi based heating only models are 95% efficient with a combi unit providing heating and hot water from one unit. Requires only one gas connection, one ventilation system and built-in expansion tank and boiler pump, and is easily accessible for repairs.
- Buderus GB142 series. Condensing gas boiler. Using state-of-the-art condensing technology with 95% AFUE, the Boer Buderus GB142 wall-mounted condenser maximizes the heating value of every m3 of natural gas or liquefied propane.
- Boiler Alpine Series. This is a natural or liquefied gas condensing hot water boiler with a stainless steel heat exchanger. Equipped with Sage2 boiler control system. 1 TM, which supports multiple firing speeds, is also equipped with an external reset and a touch interface.
- Carrier BMW Performance Series. 95% AFUE. Stainless steel. The modulating condensing boiler is equipped with a unique vertically oriented stainless steel heat exchanger, 5 to 1 ratio, compact design with light weight, compact wall mounting, primary and secondary piping, with a 15-year warranty.
Having familiarized yourself with the design and operating principle of gas burners and popular models, you can easily choose exactly what suits your needs.