The stability of operation and durability of the heat exchanger directly depend on regular maintenance and cleaning of elastic gaskets, plates, and other components and parts from contamination. For this purpose, special means are used for washing heat exchangers. Let's look at what they are below.
Figure 1 - Flushing agent
Types of pollution
The coolant liquid contains various dissolved elements, which disintegrate when heated, forming an insoluble precipitate - scale. In most cases, pollution forms:
- organic and fatty sediments;
- calcium carbonate;
- iron oxide;
- salt;
- limestone.
Plaque gradually builds up on the inner walls of the heating equipment. If you do not clean regularly, the thickness of the sediment increases. This impedes the circulation of the working medium, reduces the efficiency of the device and prevents its normal operation.
Booster Summary
This is very rare and expensive equipment. If you intend to buy it, then you will expect expenses in the range of 40,000 - 90,000 rubles. And for everyday tasks this is a rather unprofitable solution.
The booster itself is a container with a built-in pump that provides a change in the flow vector. Because of this, the efficiency of washing increases significantly. The devices are resistant to any reagents.
The most popular models are presented below:
| Booster | A country | Productivity (liters per hour) | Tank volume (l) | Working pressure (bar) | Price tag (RUB) |
| PIPAL PUMP ELIMINATE 20 V4V | Italy | 2600 | 18 | 1 | 38 000 |
| BWT Cillit SEK 28 | Germany | 2400 | 20 | 1,5 | 57 000 |
| TM Aquamax | Italy | 5000 | 30 | 1,2 | 53 500 |
Washing methods
Gasketed plate heat exchangers are washed using chemical and mechanical methods. The first option, as a rule, does not require disassembling the equipment, which is why it is the most popular. Mechanical cleaning is necessary when heavy contamination is detected. The technique involves dismantling the system and involves significant labor costs.
Figure 2 — Flushing the heat exchanger
Why is flushing necessary and what does it save from?
Since plate heat exchangers are being considered, you need to focus on the design features. Here the heat from the heated plates is transferred to the cold environment and then the coolant is transferred further. Made, such plates can be made of different materials, but the following are most often used:
| Type of heated device | Plate material |
| Heat exchanger | Copper Steel Cast iron Titanium |
The plates can be corrugated or flat. The plates are located close to each other, and the water wanders between them, gradually heating up. Naturally, if you use lime mineralized water, then very quickly unpleasant growths form between these thin plates.
And the longer you use low-quality water, the more negative consequences there will be. The heating quality will drop sharply! How does lime water work? When heated, it produces lime salts, which very quickly settle on heated surfaces. The worst thing about limescale is that it transmits heat very poorly. It turns out that the device begins to act up. Here, even washing the plate heat exchanger with your own hands will be of great help. And all because scale fouling of the plates disrupts the entire operation of the heat exchanger. The water comes out of it barely warm and the heating time increases significantly.
The worst case scenario is when the metal of the heat exchanger plates cannot withstand the overload. What can happen in this case:
- The metal will begin to crack;
- The metal will begin to flow;
- The metal will begin to explode.
In any case, scale build-up on the surface leads to equipment failure. Moreover, the breakdown is such that it becomes impossible to repair the equipment. That is, the reason for the urgent need to use liquid for flushing plate heat exchangers has been clarified. But this is where the competition between flushing and water treatment comes into play. But you should immediately warn that flushing will always be a loser. It does not save from scale, it does not prevent it, it only eliminates plaque that has already formed. And this is exclusively a struggle with the consequences.
What problem does flushing solve? Reagents and chemical liquids help eliminate plaque that has formed. At least somehow soften it, dissolve it and remove it from the surface. Rinsing is used even before mechanical cleaning. The plaque is so insidious that it literally eats into the surface. And it is very difficult to remove it. Even very strong chemicals are powerless.
Selecting a cleaning chemical
When choosing a chemical reagent for cleaning a heat exchanger, the main rule is:
The components of the chemical reagent must be aggressive towards scale, but neutral towards the exchanger plates, elastic elements and other parts of the system. This is the only way to effectively remove contamination without harming the mechanisms of the unit.
Criteria for choosing a means for flushing heat exchangers:
- thickness and amount of plaque on the walls inside the equipment;
- material for the production of sealing gaskets and plates;
- chemical composition of pollution.
To reduce the risk of damage to the internal parts of the system, it is recommended to analyze the resulting sediment and, based on the data obtained, choose the most effective but safe remedy.
Chemical washing of a plate heat exchanger, cost and nuances
How does chemical washing work? How often? What is the cost of chemical flushing of plate heat exchangers? Why is it sometimes priced higher than timely developed and put into operation water treatment?
Heat exchangers can be washed with alkalis or acids. Cleaning should be done with diluted products. When working with hazardous chemicals, be sure to remember safety rules. It is necessary to use respirators, gloves, and dilute the products strictly according to the instructions.
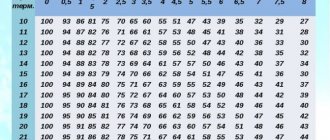
How often should heat exchanger surfaces be cleaned? It all depends on the speed at which surfaces become coated with plaque. If the water is too hard, you will have to clean the surfaces once a month. When working with a plate device, you need to take into account that the distance between the plates is narrow, and that the plates themselves are thin, which means it is very easy to damage them.
This should also be taken into account when choosing chemicals, since such processing has its own characteristics. Firstly, the consumer should not think that flushing a plate heat exchanger is cheap. Chemicals may not cost a lot of money, but they will have to be used often, this is the first feature, and any aggressive agent will leave its mark on surfaces. And their cost has nothing to do with it! Any aggressive agent is designed to dissolve any substances and any surfaces. Therefore, washing with such substances will damage the surfaces. They may not even dissolve the surfaces themselves, but when removing plaque using mechanics in the future, the surfaces will still not retain their original smoothness. If the thermal system does not include a water softening system, then rapid failure is guaranteed. And the most expensive means for washing plate heat exchangers are not helpful here. And most likely, the most expensive products are the most aggressive, which means they will destroy surfaces much more intensely. So, when choosing cleaning products, consumers deliberately reduce the service life of their equipment. Although a one-time flush may seem like a better investment.
Types of cleaning solutions
Three types of cleaning products are produced for cleaning plate heat exchangers:
- powders;
- concentrated liquids;
- ready-made solutions.
The first two types are called reagents. They require preparation before use. The products are diluted with water in the proportion specified by the manufacturer.
Figure 3 — Plaque in the heat exchanger pipe
Tools and filters
When comparing water filters and rinses, the initial investment in rinses will be lower, but the amount of use will quickly make them the more expensive option. Purifying water will always cost less in the long run than constantly dealing with the consequences of poor quality or poorly treated water. Reagents for washing plate heat exchangers will always lead to the destruction of surfaces, even if they work carefully with the surfaces. The composition of water, if it is not purified, is unknown, how it will change in the future, it is unknown what will get into such water, and how the new impurity and the old rinsing agent will react is unclear. One way or another, washing the surface with aggressive agents means gradually destroying the surfaces. As a result, the equipment will still have to be disassembled. The design features of any equipment involve bottlenecks where dissolved impurities can accumulate and clog narrow passages. When using purified water there will be no such problems at all.
AquaShield
Let's take and compare the cost of chemical washing of plate heat exchangers and the price of a regular simple AquaShield. Chemical washing for a year can result in the cost of one electromagnetic softener. AquaShield will prevent new scale from forming on equipment surfaces for a year. But at the same time, WITHOUT using new cleaning agents, it will help remove old scale. And the cost of its operation will only be electricity. And the device uses no more electricity than a regular light bulb per month. This comparison alone is enough to understand that flushing products can only be a temporary solution to problems.
Scale OFF
A simple descaling solution. It seems to work like Antiscale. It is diluted with water and poured into equipment where surfaces need to be cleaned. Depending on the degree of contamination, it is kept in contact with the surface to be cleaned for several hours, then rinsed with a powerful stream of water. This is an aggressive product; before use, you should read the instructions so as not to damage the work surfaces.
What other equipment can be used for washing plate heat exchangers?
Very often, various electrically driven mechanical brushes are used to wash heat exchangers, which helps remove old scale between the plates. The second option is a water softener for the boiler, which will help to create small water shocks in the plate heat exchangers, which will help dissolve old limescale deposits.
Price issue
How much does a descaling solution cost? On average, the price of the smallest 5-10 liter bottle ranges from 500-600 rubles per bottle. The price depends on the container, the area of sale, the chemicals used and the manufacturing companies. Sometimes chemicals developed for specific equipment are more expensive than mass-produced products.
Composition of the cleaning agent
Modern reagents and ready-made solutions are characterized by a wide range of chemical active ingredients in their composition. Concentrates may include:
- organic acids;
- acid corrosion inhibitors (prevent the destruction of system elements);
- chemical reagents;
- defoamers;
- components that form a protective film on internal surfaces.
The detergent must loosen carbonate contamination, transform it into a liquid state for removal from the system. Many manufacturers offer substances that change the color of the liquid to control the process. This eliminates the need to use test strips to measure pH levels at various stages of cleaning.
How to flush the system - 3 available methods
Without the use of specialized equipment, you can do the washing in the following ways:
- local cleaning of radiators;
- simple flushing of pipes and heating appliances with tap water;
- chemical (otherwise known as hydrochemical) cleaning of heating pipelines.
Reference. Centralized heating networks of apartment buildings are flushed using the hydropneumatic method. A powerful compressor is connected to the elevator unit located in the heating point. A mixture of water and air is pumped through the radiators and pipes of all apartments, tearing off particles of solid deposits, and even more so silt. The dirt is then dumped into the sewer.
Most homeowners do not have compressor units. In addition, you will need a mixing chamber and experience in performing such activities, otherwise you risk breaking the tightness of the joints. This means that the hydropneumatic method is of little use for self-flushing the system. We recommend starting by cleaning dead batteries.
Radiator cleaning
Identifying a problem battery is quite simple - with the heating running, feel the entire surface with your hand or measure the temperature at different points with a contact/non-contact thermometer, and then compare with the temperature of the supply line. If the sections heat up unevenly, flush the radiator.
In an apartment with central heating, flushing the battery is done as follows:
- We close the shut-off valves on the connections to the heating device. Using a gas wrench, unscrew the top plug with the Mayevsky tap, substitute the basin, and drain part of the coolant.
- Carefully open the tap on the supply line so that the water pressure throws debris out of the radiator. Of course, keep your basin under the stream. When the light coolant flows out, close the valve and put the plug in place.
- Similarly, we repeat the listed manipulations with the bottom plug. After rinsing, tighten the plug, open both taps, and bleed the air.
The described technology is applicable in private houses with automatic heating from the water supply. Just before flushing, it is better to close the valves on the boiler and expansion tank. In other cases, you need to remove the radiator and wash it separately. Connecting a cold water supply hose to the heating network is a risky option; when water is supplied “to a closed valve”, high pressure of 3...6 Bar can break the tightness of the system.
Disconnecting the battery gives one plus - the opportunity to look inside the supply pipes. Having seen deposits there that cover 1/3 or half of the flow area, it is easy to decide on further flushing of all heating pipelines.
Note. In an open system we have an expansion tank communicating with the atmosphere. If it is not possible to cut off the container with a tap, then it will not be possible to flush the battery through the recharge; the water will trample over the top and begin to drown the house.
Cast iron radiators that have served for more than 10 years will definitely have to be removed and cleaned with some kind of chemical, for example, a caustic soda solution (see the video below). The sediment at the bottom of each section rarely remains liquid and is unlikely to be removed using running water.
Rinsing with running water
The essence of the method is to remove dirt from the system using a large flow of water from the centralized water supply network. Let us immediately note the disadvantage of this option: only liquid sludge and suspended particles traveling along with the coolant can be washed out of pipes and heating appliances. If there are hard deposits in the batteries, it will not be possible to remove them.
How is this hydroflushing done:
- We connect the water supply hose to the make-up fitting. As you know, this pipe is cut into the lower point of the heating return line. We connect the drain hose to a break in the supply line (for example, instead of a circulation pump or at the junction of a faucet) and lead it to the sewer or to an area near the house.
- We clean the mud trap, open all radiator taps and balancing valves.
- The boiler must be isolated from the system using taps and must be washed separately. You should not drive all the dirt through its heat exchangers, especially for double-circuit heat generators.
- Open the water valve, gradually increasing the water flow. As you understand, backwashing begins, that is, the flow moves towards the coolant flow in operating mode.
- When the stream from the drain hose becomes transparent, turn off the water, swap the hoses and flush the heating in the other direction - along the movement of the coolant.
- At the end of the hydraulic cleaning, we refill the system, start the boiler, check the operation of the batteries and do balancing.
An important nuance. It should be understood that flushing is carried out due to the high flow of water through the heating pipelines, and not due to high pressure. You cannot supply water “to a closed valve”, only through an open drain hose. The heating network is not designed for water pressure.
A system with an open tank must first be prepared for flow rinsing. There are 2 options: cut off the expansion tank with a tap or plug the overflow tube. The second method is suitable for tanks without a top cover. If this is not done, the water will overfill the tank and flow out, leaving the area of the system left unwashed.
Chemical cleaning option
This is the most affordable way to thoroughly flush the heating system with your own hands.
To implement it you will need:
- vibration pump of a submersible household series, for example, “Rucheek” (or similar);
- a water filter in the form of a flask with 2–3 replaceable cartridges;
- special means for flushing heating networks and radiators;
- container for chemical solution;
- connecting fittings.
The procedure is carried out in 3 stages - preliminary removal of contaminants with running water, then chemical cleaning itself, and finally - final rinsing. The first and third stages are done using the technology described above using water supply; the second stage uses a submersible pump and filter.
How to flush the heating system chemically (stage 2):
- Prepare the washing solution in the barrel according to the instructions on the package. The amount of liquid corresponds to the volume of coolant in the heating network plus the container itself. We wrote how to choose the right chemical at the end of the article.
- Connect the pressure pipe of the pump to the heating supply, immerse the device in the barrel. The filter is placed on the drain line, which is directed into the same container, as shown in the video below.
- Remove the mesh from the standard mud pan and screw the empty plug back on. Otherwise you will have to clean it every 10 minutes.
- Turn on the pump, pump the reagent into the system. Make sure that the solution flows into the barrel from the drain hose and that there are no leaks.
- Flush heating lines until the water stream becomes lighter. Heavily contaminated filter cartridges must be replaced during the cleaning process.
- Wash the remaining chemicals from the radiator network with running water (stage 3).
Reminder. Chemical cleaning should only affect pipes, radiators and heated floors (if necessary). It is not recommended to pump the reagent through the boiler; it is better to clean the unit separately. An open type expansion tank should be cut off from the pipeline network or sealed.
Selection of detergents by type of contamination
| Type of pollution | Cleaning agent |
| Scale and metal deposits | Phosphoric, citric, nitric acids |
| Iron oxide | Inhibited mineral solution of high acidity |
| Organic compounds | Sodium alkali |
| Mineral contamination | Nitric acid |
| Fatty stains | Special solvents |
An alternative to chemicals is a mixture based on caustic soda and sodium carbonate. It is less harmful to human health, but is not able to eliminate all contaminants. It can be used to remove fats, oils, and biological substances.
Why clean the heat exchanger?
Copper or its alloys are usually used in the manufacture of coils. The choice of metal is not accidental: copper has good thermal conductivity. However, there is a drawback, which is the intensive formation of oxide deposits. It is impossible to remove it mechanically.
During operation of the boiler, the oxide layer becomes larger and larger, thereby reducing the thermal conductivity of the coil. The efficiency of gas equipment can decrease by 15-30 percent, and this is noticeable in winter. The outside of the heat exchanger is literally “sticky” with soot, and scale forms inside. If you don’t wash it, it can get to such a state that you have to think about how to change the heat exchanger on a gas boiler.
Gas service specialists recommend preventive cleaning of the heat exchanger once a year, but practice shows that it is enough to clean the heat exchanger once every 2-3 years to be sure of its readiness for the heating season.
Flushing a gas boiler
A gas boiler can be cleaned at home. The need to do this arises when the following symptoms occur:
- the characteristic hum of the circulation pump, which indicates an overload of the system;
- burner operating without interruption;
- long heating of the radiator;
- low water pressure (double-circuit boilers);
- increase in gas consumption.
The following preparations are applicable for home cleaning:
- Lemon acid. It effectively removes scale if the solution is heated to 60 degrees. Suitable for cleaning systems made of brass, copper, stainless steel.
- Sulfamic and adipic acids. Sufficient for regular cleaning with light soiling. Eliminate metal oxides. Suitable for equipment made from different metals.
- Hydrochloric acid. Removes heavy sediment. Used for heat exchangers made of copper and steel. However, it can be dangerous for products made of other metals.
- Orthophosphoric acid. Removes scale and dirt. An additional benefit is the formation of a protective film.
- Water-soluble gels. They are slightly aggressive towards equipment elements and remove dirt well.
When cleaning boilers and heat exchangers, it is important to take precautions - wear goggles, gloves, and respirators.
Figure 4 - Protection of the respiratory system, eyesight and hands when flushing the heat exchanger with chemicals
Current and major repairs of heat exchangers
Routine repair of a heat exchanger is the prompt elimination of defects in heat exchange equipment. The need for such an event as heat exchanger repair may arise in situations such as:
- leakage in one or more places between the plates;
- flow of media from circuit to circuit.
Overhaul of a heat exchanger is a complex of the following measures:
- replacing all seals after their service life has expired (4-6 years);
- complete cleaning of heat exchangers from deposits and scale;
- inspection of the plates for signs of corrosion, rejection of such plates.
Our company provides round-the-clock service for any heat exchangers (emergency service for cleaning and washing the plates in the heat exchanger), as well as an emergency repair service for heat exchangers of any complexity. We also carry out work to maintain the constant functionality of your equipment.
You can enter into a service contract or arrange individual visits. The important thing is that you can control the situation without allowing problems to arise.
We always have in stock the main components and spare parts for the types of heating equipment we service.
As you can see from the photo, timely maintenance is an IMPORTANT condition for stable operation. The seals and some plates have become unusable - they need to be washed.
Warm Company specialists clean the plates in an acid bath and wash the plates under pressure.
What will cleaning the boiler do?
Boiler cleaning is a regular and integral procedure that requires certain knowledge and skills. Salt deposits accumulate inside the heat exchanger, and soot and soot accumulate in the chimney channels and the chimney itself
Therefore, in order for the equipment to be in proper condition, it is important to clean all elements of the boiler
As a rule, full power will be required in the midst of winter, which leads to the risk of being left without heating, and urgent repairs and cleaning of the boiler will cost a significant amount. To avoid this situation, you need to periodically perform work on flushing the heating boiler. You can clean the heat exchanger of a gas boiler yourself, spending several hours.
Cleaning the heat exchanger mechanically
Having removed the heat exchanger, you can begin cleaning it mechanically. Of course, you can choose the second option (using chemically active substances), but it will be described below.
Having gone through the removal process step by step and taking the heat exchanger out, users are presented with an unattractive picture: a large amount of deposits and soot both inside the pipes and between the cooling plates. The mechanical cleaning method involves the use of a metal cable with a brush at the end, as well as various scrapers and blades. Using this tool, harmful deposits are removed from both internal and external surfaces.
The outer surface of the heat exchanger can be cleaned using a hard bristle toothbrush.
To make the process of removing dirt faster, you can “soak” the device in water with the addition of detergents. Then plaque or scale will be removed much easier and without effort. When using a cable, it must be slowly pushed into the device, while turning it clockwise.
Using a metal brush on a rod when cleaning a floor-standing boiler
Steel brush with a diameter of 40 mm and a working surface length of 100 mm
After the inside is cleaned, you need to rinse the heat exchanger using a hose that can be connected to a centralized water supply. It doesn’t require a lot of pressure; even an ordinary stream of water is enough to wash away dirt, plaque and other deposits.
Contamination from the outer surface, especially between the blades, should be removed carefully, as this can lead to damage to the heat exchanger and disruption of its operation.
Introduction
Heat exchanger is a device that exchanges heat between the internal and external environment. During the heating process, scale, various deposits, and contaminants are formed. Due to the formations, the heat exchanger loses its heating properties, which is why it is necessary to timely clean the heat exchange devices. Several cleaning schemes are used for cleaning:
- periodic,
- unscheduled.
After cleaning, the necessary properties of the heat exchanger are restored. The worst enemy of the heat exchange element is scale; during the heating process, salt deposits, metals and other substances settle on the heater, which affect the operation of the heat exchanger, which can subsequently lead to breakdown. Scale and plaque clog the channels between the plates, which leads to a decrease in the volume of liquid involved in heat exchange; heating does not occur fully; the liquid that circulates in the heat exchanger is not heated to the required temperature. This factor causes the device to fail very quickly.
Cleaning Frequency
There are no strict requirements for rules on the frequency of flushing heat exchangers - there are only recommendations indicated in the Operation Manual attached to each device. Recommendations should be adjusted in accordance with the specifics of use - the chemical properties of heat-carrying media, their physical contamination, etc. In particular, it is indicated to carry out cleaning when contaminating deposits of any nature with a thickness of more than 0.3 mm are detected during a routine inspection on heat exchange surfaces.
In practice, the presence of such deposits may be indicated by an excessive decrease in the thermal characteristics of the device recorded by external measuring instruments. Some manufacturers produce modern heat exchangers with a certain “margin”, i.e., taking into account the thermal resistance of contaminants. For them, the presence of deposits exceeding 0.3 mm is allowed - if the heat transfer parameters are within normal limits.
additional information
Since contaminants (especially scale) can play the role of a kind of “patches” in the heat exchanger, sealing possible cracks or violations of the integrity of joints, after the chemical and/or mechanical cleaning procedure, it is mandatory to conduct hydraulic tests of the heat exchanger. If damage is detected, it seems reasonable to decide on the economic feasibility of repairing or further operating the device - in some cases (especially when the service life is approaching), it may be more profitable to replace the damaged block element or the entire heat exchanger assembly with a more modern and efficient one.
JSC TsEEVT produces heat exchangers of standard and improved characteristics, of various designs and purposes, with a wide range of applications. It is possible to use devices manufactured by TsEEVT JSC both as part of new systems and as a replacement for worn-out heat exchangers. In each individual case, the heat exchanger is calculated individually, for specific tasks and technical characteristics specified by the customer.
To clarify any technical or practical issues, it is enough to contact the company’s representative office in any convenient way from those indicated in the “Contacts” section of this website or fill out an application by filling out an electronic form.