In basements where vegetables and other food supplies are stored, it is especially important to establish air exchange. Otherwise, the room may become damp and the products will become unusable. Many people set up a garage cellar for storage, and you shouldn’t forget about ventilation in it: this can lead not only to dampness due to the accumulation of condensation, but also to the complete destruction of the entire building.
Garage owners often strive to use every square meter of land they own. It is for this purpose that a cellar or basement is equipped underground for storing valuables or preparations for the winter. Few people think that it is necessary to provide suitable conditions to maintain a stable microclimate in this room. However, even in a garage with a basement, proper ventilation is essential.
By ensuring optimal air exchange, many negative consequences can be avoided . These include:
- Formation of condensation on the walls. Because of this, the humidity in the cellar increases, which leads to the appearance of mold and mildew, which spoil the things in the room. If this happens where vegetable or fruit stocks are stored, they run the risk of spoiling very quickly.
- The top part of the garage cools down much faster than the underground part, so it will always be hotter in the basement than above ground. This can cause moisture to accumulate below, evaporate and rise into the garage. This will result in damage to the car or motorcycle, as well as the tools stored next to them.
- Sometimes garages store things that would cause too much inconvenience at home: various fuels and lubricants and chemicals. When they evaporate, toxic substances are released that are dangerous to people. If they accumulate indoors, a person faces poisoning and even death. Proper ventilation helps to avoid this threat: fresh air from the environment will constantly flow, diluting the concentration of toxins, and they themselves can gradually erode.
Therefore, although it may seem that installing hoods and fans in non-residential premises is an unnecessary luxury, you cannot do without them. Their absence can lead to many undesirable consequences that will negate the benefits of using additional space.
Features of winter garage ventilation
In most cases, garage ventilation in winter is arranged based on the temperature difference between the “internal” heat of the heated room and the “external” flow of the freezing environment.
Moreover, from the point of view of the energy efficiency of air exchange, such a basis looks very attractive - natural ventilation will work as if on its own, without consuming energy. However, from a functional point of view, “temperature” ventilation may be insufficient due to the low rate of outflow of air masses, which will lead to the accumulation of condensation of water vapor on the car and the walls of the garage. After all, a vehicle body soaked in moisture will rust in just a couple of seasons.
The car is in the garage
Therefore, in this article we will try to find a compromise between the speed and energy efficiency of garage ventilation in the cold season.
Internal insulation of the garage
Ventilation may not cope with condensation - you may need to insulate the garage from the inside to change the location of the dew point. To do this, choose moisture-resistant materials with low thermal conductivity. Most garages in Russia are insulated with polystyrene foam, although its modern analogues, polystyrene foam or penoizol, are thicker and insulate better.
To insulate a garage, it is not recommended to use mineral wool and other fibrous materials, which get wet, lose their properties and inevitably lead to local disasters in the garage.
Alexb4FORUMHOUSE Member
I insulated the ceiling in the garage with mineral wool, which I don’t recommend. When the temperature changed, condensation accumulated on the floor slab, and as soon as the stove was heated, it all began to flow down. The mineral wool was getting damp and was of no use.
When insulating a garage, remember that:
- Polystyrene foam and its derivatives are mounted on the sheathing, and sheets of finishing sheathing are attached to it.
- There is no point in installing thermal insulation in a damp and cold room, so before starting work, the garage is heated with a heat gun or a hair dryer.
- Thermal insulation will not work properly without sealing the joints between the materials. One of the reasons for the appearance of condensation is poor sealing of seams.
- In brick garages and shell rock garages, the walls are insulated on both sides. There is no external insulation in a metal garage.
How does typical garage ventilation work?
When arranging ventilation in a garage, a classic supply and exhaust system with longitudinal movement of air masses is used. Air flows move from the gate to the opposite wall, “entering” the garage through openings in the doors or supply valves and “leaving” the room through an exhaust hood located under the ceiling or in the lintel area.
The flow is stimulated either due to the difference in the height of the supply and exhaust valves, as well as the air temperature in the garage and outside, or through the use of a mechanical pressure unit - a fan built into the ventilation duct.
At the same time, truly strong ventilation in the garage is only possible if the flow is mechanically stimulated . In turn, absolutely free (in operation) ventilation is possible only in the case of natural stimulation of the air exchange flow.
However, in addition to efficiency and low cost, both options also have other advantages and disadvantages. And in order to come closer to understanding the idea of the optimal design of a ventilation system, we will have to study both the positive and negative aspects of natural and forced ventilation.
Pros and cons of natural ventilation
To naturally encourage inflow, we will have to drill many 1.5 cm holes in the bottom of the garage door leaf. Moreover, the total number of such “channels” should be equal to the number of square meters of garage area. For example, for an area of 20 “squares” you need at least 20 holes.
Natural exhaust requires the installation of a ventilation hole in the upper part of the garage wall opposite the gate, the area of which is equal to the sum of the areas of 1.5 centimeter channels.
Ventilation equipped in this way demonstrates the following set of advantages:
- No need for power supply. No fan means no electricity bills.
- Minimum level of fire danger. There is no electric motor - no risk of sparking with subsequent detonation of gasoline vapors.
- No need for system maintenance. No moving parts - no repairs.
At the same time, natural ventilation in the garage, which is almost ideal in the summer, turns into a source of very serious problems in winter, since the cold season reveals the following disadvantages of such a scheme:
- Dependence of throughput on the permeability of the supply or exhaust channel. In winter, the 1.5-centimeter holes in the sash will be “overgrown” with frost in just one or two weeks, stopping the air exchange process.
- Dependence of draft in the channel on weather conditions. Heavy snowfall will simply close both the supply ducts and the exhaust pipe.
- Insufficient performance of a system designed to store a relatively “dry” car. After all, in winter, up to 100 kilograms of snow can stick to a vehicle, which will melt in a warm garage and saturate the air with excess moisture, which requires truly powerful ventilation to hide.
As you can see: the natural air exchange pattern is ideal only in summer, and in winter its effectiveness is questionable.
Advantages and disadvantages of forced ventilation
To force air exchange, we need a special fan with armature spark protection. It is built into the supply and exhaust ducts, mounted outside the garage - this arrangement will help reduce the risk of detonation of gasoline vapors.
Forced ventilation in the garage
This layout scheme gives the ventilation system the following advantages:
- The forced system will pump out any volume of air from the garage, providing any air exchange rate.
- The air exchange channels remain clean in any conditions, since high air speed makes it difficult for frost to form a plug. That is, forced ventilation of the garage in winter does not depend on the weather or temperature.
However, the practice of using pressure equipment guarantees the presence of the following problems:
- Dependence of the air exchange process on the availability of electricity in the network. No electricity - no ventilation.
- The need to pay for excess electricity consumption. Even the weakest fan will consume at least 10 kW per day.
- The need to organize periodic maintenance or replacement of fans. Sooner or later, even the most reliable unit will break down.
Simply put: the effectiveness of a forced system depends on money and the performance of pressure equipment . No money - no ventilation.
Combined winter ventilation in the garage - a balance of functionality and efficiency
The combined air exchange option involves natural inflow and mechanical-natural outflow of air. That is, we arrange natural ventilation, supplementing its exhaust branch with a pressure unit.
By taking advantage of this scheme, the garage owner will receive the following benefits:
- Minimum energy consumption with maximum performance.
- Minimum risk of fire - the fan is mounted on the wall outside.
- Possible transition to energy-saving natural ventilation mode.
As a result, even the cellar ventilation works flawlessly - the garage in winter and summer is full of fresh air, blowing the room from bottom to top.
Of course, this scheme has certain disadvantages, for example, the same dependence on electricity. But in this case, the “cons” of the design are offset by the total “pros” of the natural and forced ventilation scheme.
Therefore, the combined air exchange option can be considered an almost ideal solution to the problem of garage ventilation in winter. Well, in the summer you can switch your system to cheap natural air exchange, saving considerable money.
Ways to improve natural ventilation
Without using mechanical tools to enhance air exchange, you can achieve a stable renewal of the atmosphere in the garage in two ways - by heating the exhaust pipe and installing a deflector on it.
Warming up the exhaust duct
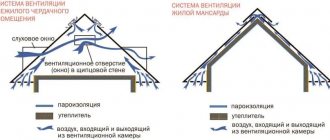
Warmed air is lighter than cold air masses entering through the supply air intake. Striving for the highest point, it exits through the exhaust ventilation duct, being replaced by fresh air from outside - the pressure of the internal (in the garage) and external (on the street) atmospheres should be equal.
When building natural ventilation in a car box, it is enough to follow the recommendations of this diagram
To improve the heating of air in the upper layer of the atmosphere inside a cold garage, you need to paint the exhaust duct black. As a result, the walls of the duct will absorb the maximum amount of solar energy and will heat the air inside the duct, causing it to move upward more intensely.
When planning natural ventilation taking into account the black color, you should not insulate the ventilation duct. However, for the “heating with an incandescent lamp” method, it is extremely necessary to thermally insulate the exhaust duct.
It gets cold in the garage in the fall. This is not a problem for a car, but for supply and exhaust ventilation it is very bad.
If the hot engine for the first hour after entering the box still serves as a source of heat for the air, then after a couple of hours in the unheated garage the temperature will be almost equal to the street temperature. And natural ventilation will stop working.
The wind flow blows over the deflector (diagram a), the air from the exhaust duct is divided into several directions (diagram b). In this case, multiple zones of low (-) and high (+) pressure appear
A regular 40-watt incandescent lamp will allow you to maintain air exchange and prevent icing of the exhaust duct (condensation will accumulate in it).
It is enough to hang its cartridge under the opening of the vertical exhaust duct and leave it on. The heat generated by the lamp is enough to move air at a speed of 0.2-0.4 m/s.
Moreover, the air duct must be wrapped in thermal insulation material and make sure that no moisture enters the insulation. There is little heat from the incandescent lamp; it may not be enough for the full length of the exhaust pipe and the air will quickly cool down.
Note that the use of fluorescent or LED lamps does not improve air exchange - they generate significantly less thermal energy. Only incandescent lamps are suitable.
Installing a ventilation deflector
This device helps to increase the exhaust draft by up to 20% without the use of any mechanical devices - due to the formation of a low pressure zone at the head of the air duct.
Based on Bernoulli's law, deflectors change the movement of air flows due to their design (section).
The parameters of the TsAGI deflector elements are tied to the diameter of the exhaust ventilation duct. The numbers in the diagram indicate: hood head (1); diffuser glass (2); outer casing (3); hood struts (4); cap (5) (+)
The wind is forced around the curved body of the deflector, which leads to the formation of miniature zones of relative vacuum, causing the mass of air in the pipe to move upward.
Structurally, the ventilation deflector (using the example of the TsAGI project) consists of the following elements:
- A diffuser (glass) in the shape of a truncated conical pipe. The narrow side fits onto the exhaust pipe. Helps establish air pressure differences and increase traction.
- A cap (umbrella) that protects the air duct from the penetration of flying debris and precipitation.
- Outer body having a cylindrical shape. Creates low pressure zones by cutting wind flow.
The TsAGI deflector type is widely used to enhance the natural draft of ventilation pipes in Russia. Along with it, disc-shaped, weather vane, H-shaped and rotary deflectors are known.
By the way, domestic natural ventilation hoods are especially often equipped with a Grigorovich deflector.
The efficiency of exhaust deflectors of any design is directly related to atmospheric conditions, namely the presence of wind.
That is, in strong winds this device develops maximum thrust in the natural ventilation system, but in calm conditions it does not work at all.
The defining moment is the proximity of the roof ridge. The closer it is to the pipe, the higher it should be raised (+)
The deflector can not only improve draft, but also prevent “clogging” of the exhaust pipe during strong winds, which low-current natural ventilation cannot overcome.
In addition, the ventilation complex equipped with a deflector device is most protected from draft overturning.
We draw attention to the need to raise the headband of a hood equipped with a deflector above the roof plane by half a meter or more. The location conditions regarding the proximity of the roof ridge, discussed in the diagram above, also apply.
What kind of ventilation is suitable for a cellar in winter?
If the basement is small (usually 5-7 m²), then the effect of natural ventilation for good preservation of vegetables and canned goods during the cold season will be quite sufficient.
Features of air exchange in winter are characterized by increased draft, which decreases with the onset of warming outside.
The essence of natural ventilation is the presence of two pipes: exhaust and supply. The edge of the first is installed under the ceiling, and light warm air comes out through it, and the second should end below, not far from the floor, and an influx is carried out using this channel.
Natural ventilation can be simplified to a structure with one pipe - an exhaust pipe. There may also be an even more economical option when they equip a hole in the outer wall and cover it with a louvered grille.
If the cellar is located in a large room, then an arbitrary hood may not give the desired result. Then forced ventilation will come to the rescue to normalize air humidity. It differs from natural ventilation in the use of fans. This circulation works flawlessly even in calm weather.
There is another method of forced ventilation. At the top of the hood there is a turbine (rotating deflector), which creates additional draft.
Air flows set it in motion and rotate the fan, enhancing the exhaust effect.
Before installing ventilation, cellar owners may have a question about what type to choose. The fact is that if the area is relatively small, then installing a forced exhaust can cause harm to the stored products: too much ventilation can dry out the vegetables and they will lose their properties.
Which one to choose for DIY installation?
The main criterion for choosing the type of ventilation for a given basement under the garage is the area of the room.
- Owners of small garages (up to 50 sq. m.), who agree to carry out periodic inspections and cleaning of pipes, can limit themselves to a natural ventilation system.
- If the basement is located under a large garage intended for parking large trucks and buses, it should be equipped with forced ventilation, which provides air exchange using additional fans or other mechanical blowers.
Rules for installing natural ventilation
It is ideal when a hood is installed during the construction of a cellar, but if the device was not installed in a timely manner, then this is not critical. Every owner will be able to equip this simple structure in his basement.
Before you start building a natural hood, you should familiarize yourself with some recommendations:
- Before preparing to install the exhaust and supply pipes, you should take care of the insulation for them. This is done to avoid the formation of frost and then condensation. Particular attention should be paid to the exhaust pipe. To prevent it from becoming clogged with ice, it should be properly insulated from the outside. You can use special polystyrene foam for pipes.
- For the supply pipe, it is better to use a design without bends or with a minimum number of them, and it should also be without narrowing or expansion.
- It is necessary that the inlet vented outside be protected from snow getting into it. It is also worth worrying about the mesh on the upper edge of the pipe, which will prevent rodents from entering.
- In order for air masses to enter and leave the cellar evenly, the diameter of the supply and exhaust pipes must be the same.
- To protect against hypothermia in the basement in winter, sliding dampers should be placed in the pipes. At this time of year, it is necessary to ventilate the room in doses so as not to overcool the contents of the cellar, and thus not cause harm to the products instead of benefit.
Knowing these important nuances, you can begin installing natural ventilation equipment.
To install ventilation in the cellar, you need to make 2 holes in opposite sides of the ceiling. Pipes are inserted into the holes in different ways, depending on the function of each of them. The end of the exhaust pipe is fixed under the ceiling (at a height of 1.5-2 m above the floor), and above the building it should rise 30-50 cm. The supply pipe is located 30 cm from the ground. Ordinary sewer plastic pipes can be used as ventilation. Their optimal diameter is 100-250 cm2.
When the basement area is small, then a replacement for two pipes can be one, but a two-channel one with a wind catcher at the top edge.
You can check whether the ventilation in the cellar is working properly using a conventional fire source (matches or lighter). The lit flame should actively deflect when it is brought to the lower edge of one of the pipes, which will indicate the presence of air movement.
Preferred device circuits
How to make a hood in the garage with your own hands? For a typical small garage, it is recommended to choose the ventilation system shown in Figure 1 below:
This is a simple and quite effective option. In car owners' garages, you can often see a pipe as a real ventilation system for large rooms. To the question: “Why did you do it this way, do you need more work?”, the answer is: “How else?”, that is, people simply copy what they see in industrial buildings and practice black magic.
You can use a garage fan with a diameter of 150-250 mm, preferably a duct type (with flanges for embedding in the chimney). This creates a sufficient vacuum and removes all lighter-than-air gases and vapors within a few minutes.
Heavy components of smoke and gases, which usually disperse on the ground, are diluted by air entering through the air intake below or the gap between the floor and the door and rise upward. Within 10-15 minutes, the air in the garage will be completely replaced by fresh air from outside.
The figure shows that the air inlet and outlet are located almost diagonally along the parallelogram in the shape of which the garage is made. Therefore, there will be no stagnation zones.
An additional fan is especially important. You don't have to buy it, but if you do, it will be a big benefit. It perfectly balances the humidity in the garage. With its help, you can quickly dry your car and prevent very significant rusting of the metal.
This fan, even without heating, will dry your car within hours. The outdoor fan cover can be open or closed, it makes no difference. In winter, spring and autumn, drying is more important than in summer. The fan in the room should be portable, it is more convenient.
Where should you place an exhaust fan in your garage? If the garage has a basement or inspection shaft, they must be ventilated. This creates an area where polluted air can stagnate. A garage with a cellar or pit shows that the owner knows how to use a shovel or has access to high-level equipment.
In this case, in order not to clutter the garage with pipes, the ventilation can be routed into a separate shaft adjacent to the garage, as shown in Fig. 2:
The diameter of the pipes must be at least 100 mm. Pipes must be insulated from frost and condensation with mineral wool 3-5 cm thick. It is better to choose plastic pipes, as they do not rust. As you can see in the figure, such a short pipe will not provide much resistance to air flow. Its length does not exceed 1.5 meters.
The ventilation duct is covered with a casing with louvers, which can be easily welded from an iron sheet and primed against rust. It can also be made of wood and covered with galvanized metal sheet. The height of the coating above the ground is 30-50 cm. You can use a mesh on the pipe as protection against rodents - but they can climb anywhere. Air enters the basement or shaft through the air intake and openings in the shaft and staircase.
WARNING Working in a duct containing large quantities of heavier-than-air gases can be quite literally deadly. Even harmless carbon dioxide, which we drink along with mineral water, can kill a person when working in a mine with this gas. Therefore, when carrying out such work, it is necessary to install exhaust ventilation with an exhaust fan at floor level.
The fan can be reversible, in which case it can also be used to supply fresh air from below. Typically, air is drawn in from below because the indoor air is warmer than the air outside. When heated, it mixes with the air in the room and rises to the ceiling.
Therefore, hoods are usually located in the upper part. But, as we have already noted, there are cases when dirty air needs to be sucked in from below. In this case, the fan must create enough pressure to clear the air duct, but one may not be able to handle it.
Then two fans are installed in series, with a distance of at least 50 cm between them. Figure 3 illustrates this option.
In the second case, air is sucked in from below. If the fans are reversible, clean air can be pumped into the shaft from the street. In some cases, this method of ventilation may be more effective. It is possible to combine options 2 and 3, where dampers can be used to select the air intake point.
In option 3, the pipe can be decorated with a recess with shelves for tools. This makes the pipes less noticeable and every centimeter of space is put to good use. Don't forget about ease of maintenance - everything should be designed so that it can be easily removed, replaced and reinstalled.
All the nuances of arranging cellar ventilation in the garage in winter
Often the cellar for storing food is located under the garage. In this case, it must also have ventilation. The exhaust duct is installed so that it passes through the garage space and through the roof. The traction force depends on the height of the pipe. If the garage roof is equipped with a ridge, then the edge of the pipe should be extended above it.
Ventilation of the cellar in the garage in winter requires periodic draft checks. It is necessary to inspect the pipe for icing and remove it in a timely manner. Or a situation may arise that condensate will drip from the exhaust device, then a removable container should be installed on the lower edges of the pipes. The liquid must be poured out on time.
Insulation of the exhaust and supply ducts is just as important as in the previous case. Pipes should be completely enveloped in thermal insulation material.
Installation of air flow in the basement and garage can be combined. One hole is divided into 2 sleeves, the first of which goes down into the cellar. As already discussed, the pipes in the room are located in opposite corners.
If it is necessary to reduce the percentage of moisture in the air, in addition to the hood, add containers with adsorbent. It could be a glass of rice or salt, or it could be brake fluid.
Solid garage floor
Another important measure for eliminating and preventing condensation in the garage is concreting the entire surface of the earthen floor and the inspection pit of the garage so that moisture from the soil does not enter the room. If for some reason this cannot be done right now, you need to find another way to completely cover the ground.
AfavaFORUMHOUSE Member
The most budget-friendly option is to lay roofing felt, linoleum, or whatever you find from this range under the garage.
The problem of condensation in the garage can be solved by installing a blind area (without it, rainwater may flow under the garage) and eliminating possible foundation defects.
The importance of garage ventilation in winter
Those people who store their car in a garage should take care of good ventilation of this room. This is especially important to ensure in winter. Ventilation in the garage in winter helps protect the vehicle from the harmful effects of moisture formed by condensation of air masses.
In winter, it is very important to install an efficient ventilation system in the garage.
The need for air exchange in the garage is caused by several other reasons. In a warm garage where fuels and lubricants are stored, toxic fumes accumulate in the air. They are dangerous to human health and require removal.
Common mistakes
Although the installation process is quite simple, many people make mistakes, as a result of which the ventilation structure malfunctions, does not fully cope with condensate removal, or does not work at all. The most common errors occur, as a rule, at the installation stage:
- Using a simple hole in the wall instead of a channel. This decision can be especially harmful if the cellar contains vegetables: there is no guarantee that the air will ventilate from the room, and not, on the contrary, enter it, and if this happens in winter, the food will freeze and it will be impossible to eat it. The equipped channels must have a certain cross-section and elevation angle.
- If the ventilation system in the basement in the garage is made according to a natural pattern, it would be a mistake to install the pipes horizontally: in this case, the draft practically disappears, resuming only with external air movements. If it still seems advisable to install pipes in this direction, it is necessary to place them with a slight angle of inclination (up to 10-12 degrees). A completely horizontal design will only work if it is equipped with a forced air distillation device.
- If the outlet is too low, the thrust is greatly reduced. For this reason, it is recommended to install the pipe above the roof of the garage.
The need for ventilation in the garage
Garage ventilation in winter is very important. Due to the difference in temperature on a frosty street and in a warm, hermetically sealed garage, condensation forms on the surfaces of walls and furniture. Prolonged exposure to moisture has a detrimental effect on the structure and all objects located in it.
Wooden shelves and tool cabinets begin to rot, concrete surfaces begin to crack and become moldy, and the body of the machine and its parts suffer from corrosion. Some of the moisture evaporates, but due to the tightness of the structure, the moisture does not leave its boundaries. This is why many car owners feel damp when opening the garage in winter. In summer there is a noticeable damp coolness.
Without ventilation at any time of the year, the vehicle is at great risk.
And in case of bad winter weather with ice and snow, a person himself can harm the building, the car and himself. After trips, snow often remains on the wheels, hood, and roof of the vehicle; in this case, it is better to use tubular snow guards on the roof. Once in a warm garage, the snow begins to melt.
Therefore, it is more expedient to create high-quality air exchange, spending a little money on it, than to carry out a major overhaul of the car after a few years. The difference in cost of these works differs several times.
Garage roof insulation
When they get tired of the drops falling from the garage ceiling every time the heater is turned on, car owners think about insulating the ceiling.
The easiest way to insulate a garage ceiling is to pour a thick layer of brick chips or expanded clay onto the roof. These materials:
- perfectly absorb moisture;
- dry well.
Typically, these bulk materials are covered on top with roofing felt, which is placed on a screed, or plywood (OSB). This design lasts for 10 years.
If you don’t want to spoil a good roof made of corrugated sheets, there is an option to glue sheets of 55mm EPP or other insulation onto the mounting foam from the inside.
Types of ventilation
For frosty winter conditions characteristic of the Russian territory, ventilation should be as efficient as possible.
When there is a large difference in temperature inside and outside the room, the condensation process occurs many times more intensely than in the summer. Therefore, ventilation with the highest efficiency should be selected. According to SNIP building codes, this refers to the air exchange rate.
You can achieve the desired ventilation and get rid of the harmful effects of moisture using the following types of ventilation:
- natural;
- forced;
- combined.
When deciding to choose suitable ventilation for a private garage, you should pay attention to the advantages and disadvantages of all its available varieties. In addition, the cost of materials and equipment that can be used during the installation process is no less important.
The most budget option is natural ventilation. It functions thanks to the laws of physics. The draft required for ventilation is generated due to the difference in air temperature inside and outside the room. But in order to achieve this phenomenon, care should be taken to ensure the correct location of the exhaust and supply openings.
With garages that have through cutouts in the gates, it will be easier to install the ventilation system. This gap can be used as a supply window. All that remains is to choose a suitable place for the hood. But, do not forget that even this simple choice has its own characteristics that affect the quality of air exchange in the garage.
Recommendations from experts
When installing ventilation in the garage cellar, the following points should be taken into account:
- The functioning of a natural structure largely depends on climatic conditions, weather, season and temperature. The peak efficiency of such a system occurs in the late autumn months and winter, when the difference between temperature conditions is so strong that air circulates throughout the room without the use of equipment.
- If a natural system is installed in the cellar, you should carefully monitor temperature fluctuations: getting a large volume of cold air inside leads to freezing and can harm the things and products stored inside. If the temperature drops sharply, the ducts from the outside should be partially blocked. Usually, for a very frosty winter, the vents are left open only a quarter; in the fall and spring, they can be opened halfway.
- In summer, the difference between the temperature inside and outside is minimal, the movement of air masses practically stops. For this reason, if a garage with a cellar is located on a site in the southern region, it is not advisable to arrange natural ventilation: you should give preference to a combined scheme so that the fan is turned on during the warm season.
- If the cellar is small, you can arrange a system from one pipe, but you will need to divide it into an outlet and a receiving channel. Each of them is equipped with its own valve, which is necessary to regulate the flow intensity.
Conclusion: if the garage has a cellar or basement used for storing workpieces, tools, fresh vegetables or cereals, the creation of a ventilation structure is mandatory. A combined system is considered the most effective, and natural ventilation is the least expensive. Regardless of the type of structure, it is quite possible to install it yourself; it will require a minimum of tools, and the work will take on average 1-2 days.
How to ensure natural air exchange?
Having their own private house with a garage in the yard, many people spend a lot of time there. The harmful effects of toxic fumes, as well as moisture itself, are dangerous to human health.
Toxic fumes, as well as moisture itself, are exactly what is dangerous to the health of a person who spends a lot of time in the garage
Therefore, it is necessary to create favorable microclimatic conditions. This can be done using natural air exchange. To obtain it you should:
- Select locations for the supply and exhaust openings. The hood is located at a height of 15–20 cm under the ceiling, and the inflow is located in the diagonally opposite corner, at a distance of 15 cm from the floor.
- A pipe is installed in the supply window, the street end of which should be located vertically. An “umbrella” is placed on its end to protect from snow and rain. The same procedure is performed with the exhaust window.
- Inside, decorative grilles are installed at the ends of the pipes.
Owners of such ventilation systems are advised to monitor the condition of the exhaust and supply pipes, especially during cold spells and frosts. Often, ice forms in their cavity, which impairs traction. In addition, if it is not removed, it will melt in the spring and flood the garage.
One of the disadvantages of the natural ventilation system is the variability of draft. After all, ventilation itself depends on weather conditions. Therefore, some garage owners install dampers on the supply and exhaust openings, rather than decorative grilles. They allow you to adjust the air exchange rate as needed. In addition, it is possible to even completely stop ventilation.
Natural exhaust device
Ventilation of the basement under the garage can be achieved in one very simple way: you need to make a ventilation duct in the wall. Alternatively, the same channel can be made from blocks laid on the side face. The scheme is very simple, but is capable of providing air exchange in the basement. A metal mesh should be installed on the duct to protect against large bugs and birds.
Correct installation of natural ventilation.
The traditional version of natural ventilation involves placing two pipes in different corners of the shaft. One air duct will be responsible for supply ventilation, and the other will be responsible for exhaust ventilation. This scheme works in any basements and cellars, which are located not only under the garage, but also in other places (including open spaces).
For the most effective air exchange and for air to rise and fall through the pipes, the end of the supply pipe should be at a height of 40-45 cm from the floor. The end of the exhaust pipe should be located just below the ceiling. Pipes can be made from almost anything (asbestos cement, tin, PVC, etc.).
Thus, a garage with a basement can be ventilated using natural exhaust. Of course, this approach is not ideal, but it can still provide both the garage and the basement with more or less clean air.
The work is carried out in stages:
- The exhaust duct is fixed so that one end is at a height of 150-200 cm above the floor. The outer end of the pipe is installed above the garage roof to a height of 40-45 cm.
- The supply air duct is mounted in the opposite corner with a corresponding offset from the floor. The pipe should extend outward by 20-30 cm.
- The ventilation duct must be protected from rodents and birds with a metal mesh. In addition, it is recommended to cover the exhaust channels with rain caps.
To control the ventilation of the basement under the garage, it will be necessary to install dampers that regulate the air flow during the cold season, when it is important not to freeze the room so that the food in the pit does not freeze.
The cheapest and easiest way to ventilate a basement garage is to make a hole in the bottom of the wall instead of a supply pipe and cover it with mesh.
Advantages and disadvantages of natural air exchange
Winter ventilation in the garage should provide sufficient air exchange to extend the service life of all parts and devices of the building.
Opening the gate for ventilation for a few minutes every day and closing it is impractical and ineffective. The garage is not always located next to a private house or apartment of its owner. Therefore, you should take care of equipping the garage with a ventilation system.
The simplest option is natural ventilation. Its advantages are:
- sufficient air exchange to extend the service life of building materials, furniture and the vehicle itself;
- cheapness;
- ease of installation;
- independence from the power grid.
Arranging a room with such ventilation also has its disadvantages. The main one is the possibility of weak traction. This phenomenon occurs especially often in the summer. On warm days, when the air temperature outside becomes equal to the temperature inside the garage, air exchange worsens. Sometimes, there is a complete lack of traction. And this makes such a ventilation system ineffective.
But this problem is not difficult to solve. Increased draft in the supply and exhaust device is achieved by a conventional fan, which is often used for toilets and baths in a private house or apartment. But its installation itself makes the ventilation system a combined one. That is, the air flow is carried out by natural forces, and the exhaust is provided by a fan. This scheme has high efficiency, and purchasing a fan will not be expensive.
Why ventilate your garage?
Of course, a garage is a technical object, not a residential one, although some car owners may disagree with this statement.
If the car owner spends a significant part of his personal time in the garage, and also uses the basement or the garage itself to store food supplies, it is all the more necessary to take care of proper air exchange in such a specific room. First of all, this is a high concentration of exhaust gases, fuel vapors and other technical fluids. Even a short stay in such an atmosphere is very harmful to human health.
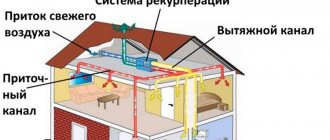
To maintain normal working conditions in the garage, stored equipment and machines, ventilation is necessary, which constantly removes contaminated air and supplies fresh air instead. The ventilation system is especially important in insulated garages, where the movement of air through the structure is hampered by thermal insulation. A well-maintained exhaust system will promptly remove harmful volatile chemicals that can harm the health of owners. The garage exhaust system is necessary for regular drying of the structure, which, due to the difference in external and internal temperatures, condenses in a confined space. Garage natural ventilation system. Air exchange system for an insulated garage. Drainage for owners. Exhaust air ducts of the ventilation system
The second problem associated with improper garage ventilation is excess moisture. Water vapor accumulates indoors and condenses on various surfaces, including the car. As a result, the risk and rate of corrosion increases dramatically - in other words, the car rusts.
Often vegetables, canned food, other food products or things that do not have a place in a house or apartment are stored in garages or cellars underground. Contact with moisture and exposure to technical vapors will have a detrimental effect on all these products. However, this problem can be solved simply by ensuring effective ventilation.
If ventilation is poor, drops of condensation may form on the walls and ceiling of the garage. This condensation leaks into the vehicle and can cause corrosion.
Features of the forced ventilation system
The forced ventilation system is provided by two fans installed on the supply and exhaust openings. That is, its installation begins in the same way as if natural ventilation is used.
It is necessary to drill through holes in the walls, install pipes and protective elements in them from rodents, birds and precipitation. But, 2 fans are installed on the inside of the building. The use of such a system is effective in large garages, as well as in existing pits.
There are several options for arranging forced air exchange. In addition to overhead devices that provide good ventilation of the room, duct fans can also be used. They are installed inside the pipes.
Such systems can be equipped with an automatic on/off system. In addition, it is possible to additionally install heating elements that prevent ice from forming on frosty winter days.
One of the most expensive, but also effective devices of a forced ventilation system is climate control equipment with additional heating, air conditioning and air filtration. But its main disadvantage is its high cost. Such devices are often used for multi-level garages, as well as for rooms attached to houses.
Rules and regulations
When ventilating your garage, remember the SNiP rules that must be followed - otherwise the likelihood of receiving a fine is higher than ever.
Read more about them in SNiP 21-02*99. Remember that the amount of fresh air must be at least 180 liters per hour, and the entire internal volume of the garage must be replaced at least 6 times a day.
What do you get by installing ventilation?
- Due to the influx of fresh air, you normalize the temperature in the room, achieving maximum comfort for yourself;
- eliminate the environment favorable for condensation and dampness;
- remove from the premises harmful gases and impurities that are dangerous to human life and are inevitable when storing flammable substances;
- extend the life of your car by protecting it from corrosion;
- you get the opportunity to store in the garage not only components and tools, but also food;
- achieve a pleasant microclimate for repairs and relaxation in the garage.
In the inspection hole
It is ideal to carry out work directly at the time of installation. Otherwise, you will have to tear down the entire structure and rebuild it.
Ventilation in the inspection pit is carried out by creating an additional channel immediately after leveling the bottom and walls. For this you will need a plastic pipe. Ideally, if it has a cross-sectional diameter of at least 10 cm. It is inserted into a horizontal trench so that the lower end almost touches the bottom, and is brought out through the wall.
As a result, even with a platform placed on top, excellent air circulation is ensured. And this is with a minimal investment of effort and money into the project.
Look at how other garage owners do it.
Briefly about the main thing
A garage needs a well-thought-out ventilation system, because insufficient or ineffective air exchange can make the room uncomfortable for both the car and its owner. The situation can be corrected by organizing natural, forced or mixed ventilation.
The device of natural ventilation is considered the simplest option, which does not require financial investments and special skills. You should start by calculating the minimum permissible pipe diameter that can adequately ventilate a room of a given size. If the garage has an inspection hole or basement, the system is slightly modified.
Calculation of ventilation network resistance
The higher the speed of air movement in the ventilation duct, the higher the resistance to the movement of air masses in the ventilation complex. This unpleasant phenomenon is called “loss of pressure.”
If the cross-section of the ventilation air ducts is gradually increased, it will be possible to achieve a stable air speed along its entire length. At the same time, the resistance to air movement will not increase
The ventilation unit must develop an air pressure sufficient to cope with the resistance of the air distribution network. This is the only way to achieve the required air flow in the ventilation system.
The speed of air moving through the ventilation ducts is determined by the formula:
V=L/(3600•S)
Wherein:
- V – design speed of pumping air masses, m3/h;
- S – cross-sectional area of the air duct, m2;
- L – required air flow, m3/h.
The choice of the optimal fan model for a ventilation system should be made by comparing two parameters - the static pressure developed by the ventilation unit and the calculated pressure loss in the system.
By placing the ventilation unit in the center of a branched air duct system, it will be possible to stabilize the air supply speed along its entire length
Pressure losses in an extended ventilation complex of complex architecture are determined by the summation of resistance to air movement in its curved sections and stacked elements:
- in the check valve;
- in noise suppressors;
- in diffusers;
- in fine filters;
- in other equipment.
There is no need to independently calculate the pressure loss in each such “obstacle”. It is enough to use pressure loss graphs in relation to air flow, offered by manufacturers of ventilation ducts and related equipment.
However, when calculating a ventilation complex of a simplified design (without prefabricated elements), it is permissible to use typical pressure loss values. For example, in basements with an area of 50-150 m2, the resistance losses of air ducts will be about 70-100 Pa.
SNiP on dimensions and ventilation
SNiP rules provide for ventilation in garages without a basement (as in non-residential premises) with the following features:
- Constant air circulation is organized, and its parameters do not depend on the material from which the garage is built, whether it is brick, concrete or metal.
- The standards provide for an air exchange of 180 cubic meters per hour per passenger car. Conditions can be ensured using natural, forced or mixed ventilation systems.
- Additional (increased multiple) air exchange standards apply for rooms in which vehicle maintenance is carried out (repair, assembly, painting). In this case, the volume of the box is multiplied by the coefficient (multiplicity) of air exchange (standards are indicated for different types of work). For example, the coefficient for service stations is 6-8.
- The rules provide for the possibility of heating or not heating the garage space. Winter temperature +5°C is considered the most rational for storing a car. The owner would be more comfortable at +10-15°C, but in such conditions, ice and snow on the car create a humid environment.
Painting or welding work requires increased ventilation Source project-home.ru
To determine the amount of air that needs to be replaced in the garage per hour, perform the following calculations:
- The volume of the garage is calculated by multiplying its length, width and height. For example, for a building with dimensions of 6x4x2.5 m, the volume will be 60 cubic meters.
- If the owner is engaged in repairs and minor restoration, a coefficient for a service station of 6-8 is used.
- Multiplying the unit volume and the multiplicity gives 360-480 cubic meters per hour. This is the volume of air that should change every hour. Such circulation can be organized using only a mechanical ventilation system with the installation of round duct fans.