Causes of condensation in a stove chimney.
It is believed that for normal operation of a brick stove, the smoke at the exit from the stove into the chimney must have a temperature of at least 250 degrees Celsius.
At this temperature of the flue gases at the entrance to the chimney, at the upper end of the pipe there will be a temperature of about 105 degrees Celsius. (with a well-designed chimney)
This temperature regime allows you to avoid condensation of the chimney.
How to determine the temperature of the exhaust gases of the chimney
The temperature of the exhaust gases can be determined in a simple way. To do this, place a dry splinter across the view hole during combustion. After 30-40 minutes, remove the splinter and scrape off the sooty surface.
- — If the color of the splinter does not change, it means the temperature is within 150C,
- - If the splinter turns yellow (to the color of a white bread crust), then the temperature reaches 200C,
- — The splinter turned brown (to the color of the crust of rye bread) — the temperature rose to 250C.
- — A blackened splinter indicates a temperature of 300C,
- — When a splinter turns into coal, the temperature reaches 400C.
When firing the furnace, the temperature of the gases must be adjusted so that at the view it is within 250. Cracks and holes in the pipe and furnace through which cold air penetrates also contribute to the cooling of the gases and the formation of condensation. When the cross-section of the pipe or chimney channel is higher than required, the flue gases rise through it slowly and the cold outside air cools them in the pipe. The surface of the chimney walls also has a great influence on the draft force: the smoother they are, the stronger the draft. Roughness in the pipe retains soot. and reduce cravings.
When firing the furnace, the temperature of the gases must be adjusted so that at the view it is within 250C. Cracks and holes in the pipe and furnace through which cold air penetrates also contribute to the cooling of the gases and the formation of condensation. When the cross-section of the pipe or chimney channel is higher than required, the flue gases rise through it slowly and the cold outside air cools them in the pipe. The surface of the chimney walls also has a great influence on the draft force: the smoother they are, the stronger the draft. Roughness in the pipe retains soot. and reduce cravings.
Hello, dear readers! My name is Vitaly Ivanovich, and I build stoves, fireplaces and install heating equipment.
For more than 40 years, starting back in 1977 as a stove maker’s assistant, I have been studying this business and improving my skills. With retirement I have more free time and I decided to share my experience with you. Read for good health and ask questions in the comments!
Let's look at examples of condensation occurring in a chimney.
Smoldering mode.
“Condensaaaaat! “
This is exactly how you want to scream when you see people connecting metal stoves with smoldering mode to brick pipes.
All arguments usually cannot overcome the issue of price.
The user, having bought an inexpensive and quite nice stove like a “potbelly stove” in a store, connects it to a brick pipe left after dismantling a poorly functioning old brick stove.
As a result, this design condenses and stinks throughout the whole house.
The cause of condensation, in this case, is the smoldering mode.
Read more about smoldering mode here.
The final result, most often, is the destruction of the chimney.
Low temperature of gases leaving the furnace into the chimney.
An illiterate stove maker made too many channels or caps in a brick stove.
Result: Passing through many channels, the flue gases are too cooled, and their flow rate is also significantly reduced.
Condensation falling in the chimney destroys the brick.
One day, summer residents approached me with a request to relay the pipe.
The owner of the house assured that the brick in the chimney was falling apart because the stove maker soaked the brick.
I tried to explain:
- About condensation.
- About the fact that 7 channels are too many for her stove.
- About flow speed, gas temperature, etc.
As a result, her husband said: “Bullshit! The stove is good, very warm. And the black water flowing out of the valve is from the rain.”
I don’t know further about the history of that stove, because... there was nothing more to talk about.
This furnace was condensing due to the asbestos-cement pipe above it.
The chimney cross-section is too large.
Fortunately, asbestos-cement pipes are being installed less and less on new stoves.
The cross-section of asbestos-cement pipes is usually much larger than necessary for the furnaces to which they are connected.
A large chimney cross-section inevitably leads to condensation.
The asbestos-cement pipe itself is as sensitive to condensation as a light bulb, but the condensate will flow through it into the furnace.
Often, on old stoves, condensation even begins to flow out of the stove’s cleaning doors and seep through the seams.
Poor quality firewood can also lead to condensation in the chimney.
Read more about the quality of firewood here.
Requirements for chimney material
Materials used for the production of smoke exhaust devices must meet the following requirements:
- Resistance to high temperatures;
- High resistance to corrosion;
- Resistance to aggressive chemicals and environments.
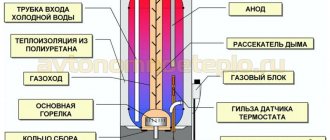
All these requirements for a chimney for a gas boiler have a real basis. Thus, the requirement for chemical inertness is due to the fact that in the chimney pipe during operation of a gas boiler there is a certain amount of condensate containing sulfuric acid. To ensure that such an environment does not damage the structure, it must be protected from corrosion and chemical attack. The intensity of condensation can be reduced by insulating the chimney.
Liquid fuel boilers
When solid and, especially, liquid fuels are burned, a larger number of different oxides are formed. This is due to the impurities contained in the fuel, in particular sulfur. When water combines with sulfur oxides, sulfuric acid is formed. Dew from sulfuric acid vapor falls earlier than from water vapor. This leads to the fact that if the gas temperature in the chimney is not high enough, the pipe is subjected to strong aggressive influence. This factor must be taken into account when choosing a material.
If you look at it, both high and low temperatures inside the chimney affect its service life. To ensure that replacement of the chimney of a gas boiler or fireplace is not required soon after installation, you need to choose the right material. It is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the processes that occur inside the system, the effect of temperatures, the possible formation of condensation and other factors. If you do not have the necessary knowledge, it is better to consult a specialist. Attempts to save money by purchasing the cheapest material usually end in rapid failure of the chimney. Remember that the system must work properly. Select the chimney according to the type of equipment used.
Normal temperature of gases leaving the furnace
In order for the water present in hot gases to evaporate better, the temperature of the latter must be increased. On well-heated pipe walls, settled drops of moisture quickly evaporate.
The normal temperature of gases leaving the furnace before exiting into the pipe is 12O...14O°C, when leaving the pipe into the atmosphere - not lower than 100°C.
If the flue gases, when exiting into the chimney, that is, at the view, reach a temperature of about 250 ° C, then condensation does not form, draft improves, the stoves heat up faster, while consuming less fuel.
The temperature of the exhaust gases can be determined using a dry splinter, which is placed across the view hole during combustion. If after 30...40 minutes you remove the splinter and scrape off the sooty surface from it with a knife, you can set the temperature of the gases. The color of the splinter does not change at temperatures up to 150°C. If the torch turns yellow (to the color of a white bread crust), it means the temperature has reached 200°C;
Thus, when firing the furnace, the temperature of the gases must be adjusted so that at the viewer it is within 250°C.
You should know that in the summer, condensation either does not form at all or occurs in small quantities. The formation of condensate largely depends on the size of the grate, the correctly raised hearth and the design of the furnace in a Russian stove, the size of the channel, the thickness of the walls, clay and height of the chimney, the temperature of its heating, the humidity of the fuel used, the temperature of the gases leaving the chimney and the excess number of chimneys in the stove.
The height of the chimney must be at least 5...6 m, counting from the level of the ash chamber or the hearth of a Russian stove. The thickness of the pipe walls should be half a brick, 20 mm). Thinner pipe walls heat up quickly and cool down quickly, which leads to the formation of condensation.
Such pipes must be insulated. Various cracks in the pipe and the stove, through which cold air penetrates, also contribute to the cooling of gases and the formation of condensation. When the cross-section of the pipe channel (chimney) is higher than required for a given stove, the flue gases rise through it very slowly and the cold outside air cools them in the pipe.
Sometimes, to improve draft in stoves, it is necessary to rearrange the pipes, reducing the size of the chimney, lowering or raising the height of the pipe on the roof. This is done until a satisfactory result is obtained. Where the chimney narrows, right angles should be cut off to ensure a smoother transition of gases.
Do-it-yourself stove laying
What pipes are suitable for fireplaces?
The degree of reliability and efficiency of chimneys largely depends on the heating devices connected to them, and vice versa. Therefore, for each type of fireplace there is an optimal chimney option.
The use of thermally insulated modules along the entire length of the chimney (starting from the firebox) is justified in those rooms where the fireplace serves mainly decorative functions. Usually, in order to use the heat of the exhaust gases, the first 1.5-2 m of the chimney is assembled from single-wall pipes in compliance with the necessary fire safety measures.
The following requirements are imposed on the chimney of a classic masonry fireplace with an open firebox: its channel can only be direct-flow, with a cross-section of at least 1/10 of the cross-section of the firebox opening. A hearth fireplace in which the firebox is open on two or more sides (its “extreme” variety is “island” fireplace) are equipped with a smoke eliminator hood that goes into the chimney. The latter must have an increased cross-section, and quite often it is equipped with an exhaust device (smoke exhauster).
Pixels
"EcoFireplace"
The most common fireplaces today are those with a closed firebox. Their fundamental difference from the classic ones is that the air necessary for combustion does not enter through the combustion opening, but through the ash pan, and by manipulating the dampers, you regulate the intensity of combustion. The vast majority of fireplace inserts can be equipped with a modular stainless steel chimney.
"EcoFireplace"
Many fireplace inserts have an outlet pipe equipped with a damper. In a buried position, it partially blocks the chimney, limiting draft, and the combustion process slows down.
"EcoFireplace"
If the damper is open, flue gases escape unhindered - this is required at the ignition stage, as well as when it comes time to add firewood to the firebox. Sometimes the damper opens automatically at the same time as the firebox door.
And finally, the last type is fireplace stoves.
The main distinguishing feature of such devices, which makes them resemble a real stove, is the presence of a built-in smoke channel, through which the flue gases are cooled to a fairly low temperature. In this regard, there is a need for a massive masonry or well-insulated modular chimney. Chimneys for fireplaces and their characteristics
| Fireplace type | Combustion feature | Efficiency, % | Exhaust gas temperature, °C | Chimney type |
| With open firebox | Air access is not limited | 15-20 | Up to 600* | Brick, heat-resistant concrete |
| With closed firebox | Air access may be limited | 70-80 | 400-500 | Brick, made of heat-resistant concrete, modular insulated from stainless steel or ceramic, within heated premises - single-circuit enameled steel |
| Fireplace stoves | Air access is limited, gases are cooled passing through integrated channels | Up to 85 | 160-230** | In addition to those listed above: soapmagnesite or soapchlorite - massive or with an internal pipe (steel, ceramic) |
* - when using hardwood, coal as fuel, as well as with excess draft, the temperature may exceed the specified value; ** - for fireplace stoves made of soapstone; for metal - up to 400 °C
Types of systems
The design of sauna stoves includes 2 types of chimneys:
- Indigenous. They are organized next to the stove, using a special pipe for connection, through which the smoke goes into the main channel. One chimney can be used for 2-3 stoves. The main thing is that its internal diameter has the appropriate parameters, and the pipes from each heating device are located at different heights;
- Systems with a mounted pipe are mounted directly on the stove pipe and discharged through the roof. This chimney option is the most common for sauna stoves.
Classification of chimneys according to installation location includes 2 types:
- External. Their main part is located on the street and fixed to the wall using a bracket. They are not particularly recommended for baths, as they quickly cool down, losing precious heat.
- Internal. These are vertical structures with good traction, located inside the building.
Depending on the material used, chimneys are:
- Brick. A traditional look, characterized by labor-intensive masonry and high requirements for compliance with all parameters. They have a lot of advantages: durability, fire safety, strength, good thermal insulation and heat accumulation. Disadvantages include the roughness and angularity of the inner surface on which soot deposits accumulate;
- A metal chimney is faster to install and costs less. It has a perfectly smooth surface, but weaker heat-retaining characteristics;
- A combined version, including 2 parts: the lower one is made of brick, the upper one is made of a modern sandwich pipe. Allows you to organize neat, small passages that are easier to cover with heat-resistant material.
Construction of a ceramic smoke channel
The most reliable and safe option for installing a chimney in a wooden house is a construction made of ceramic blocks. Its outer side practically does not heat up, which means there will be no problems with passage through the ceilings.
Let's consider the sequence of assembling a smoke channel from components of the German brand Schiedel Rondo Plus:
Let’s immediately make a reservation that the main one is constructed from ceramic modules, i.e. a separate pipe for which a separate foundation is arranged.
All technological holes are cut out along the construction site. Cutting is done with a regular grinder with a diamond blade.
To make geometrically accurate holes, the ceramic chimney kit includes a template. Further:
The ceramic chimney is assembled in a standard manner: modules are built up one after another. However, it is worth paying attention to the specifics of passages through the attic floor and through the roof.
In our example, the chimney and ventilation riser are located next to each other, which is why we had to slightly trim the rafters:
Dimensions and cross-section of the chimney
To calculate the cross-sectional area of the chimney pipe, you need to take into account the dimensions of the pipe that is in the gas boiler. As a result, the throughput of the chimney must be no less than the pipe itself. Two heating boilers can be connected to the chimney at once, but their inputs can only be placed at different levels, and the distance between them must be at least 0.5 m. The cross-section of the pipe when connecting two boilers is equal to the sum of their power multiplied by 5.5.
When figuring out what kind of chimney is needed for a gas boiler, you need to take into account not only its area, but also its cross-sectional shape. The cross-section of the chimney can be rectangular or round. The smoke flow moves inside the pipe along a spiral path, so the presence of different angles will interfere with it. It is because of this that it is advisable to give preference to a chimney with a round cross-section of pipes, which provide higher draft.
Principle of operation
- The fuel placed in the firebox of a fireplace (stove, boiler) is ignited, as a result, the process of generating heat starts, and with it smoke (soot, ash and other aggressive chemical compounds harmful to human health).
- The temperature of the combustion products is about 500⁰C, which means they become lighter and rush up the shaft. The influx of cold air starts the process of natural convection, increasing the traction force and thereby displacing combustion products outside.
- Oxygen-rich air naturally supports fuel combustion.
Use of wood based on its heat capacity
When choosing a type of firewood, it is worth considering the ratio of cost and heat capacity of a particular wood. As practice shows, the best option can be considered birch firewood, which has the best balance of these indicators. If you purchase more expensive firewood, the costs will be less effective.
To heat a house with a solid fuel boiler, it is not recommended to use types of wood such as spruce, pine or fir. The fact is that in this case, the combustion temperature of the wood in the boiler will not be high enough, and a lot of soot will accumulate on the chimneys.
Firewood made from alder, aspen, linden and poplar also has low thermal efficiency due to its porous structure. In addition, sometimes during the burning process alder and some other types of firewood shoot out coals. In the case of an open furnace, such micro-explosions can lead to fires.
It is worth noting that no matter what the wood is, if it is damp, it burns worse than dry wood and does not burn completely, leaving a lot of ash.
Types of chimneys
Brick chimney
Until recently, brick chimneys had virtually no alternative in both urban and rural construction. Being a universal structural material, brick allows you to vary the number of chimney channels and the thickness of the walls (you can make the necessary thickenings in the places where the floors and roofs pass, as well as when constructing the street part of the chimney).
Burda Media
The main problem for an external chimney is good insulation.
Burda Media
A masonry fireplace with an open firebox has a low (15-20%) efficiency, and it is quite difficult to heat a room with its help. But it will help create the atmosphere of a medieval castle in the house.
If construction technologies are followed, a brick chimney is very durable. However, it also has disadvantages. Due to the significant mass (a pipe with a cross-section of 260-130 mm and a height of 5 m, laid out in half a brick, weighs about 1.5 tons), it is necessary to build a foundation. And the construction of this entire structure will require a lot of time and effort. The channel cross-section (rectangular or square) is not optimal for traction. In addition, with periodic use in the cold season, the service life of a brick pipe is greatly reduced due to the aggressive effects of condensation.
To install a brick chimney, very highly qualified builders are required.
Common mistakes during construction
- Choosing low-quality or unsuitable bricks (weakly fired partition or wall bricks).
- The thickness of masonry joints is more than 5 mm.
- Edge laying; the use of stepped (“jagged”) masonry on sloping areas.
- Incorrect preparation of the solution (for example, if the ratio of the parts of clay and sand is chosen without taking into account the fat content of the clay), careless splitting or cutting of bricks.
- Inattentive filling and bandaging of masonry seams (presence of voids and double vertical seams).
Laying pipes close to structures made of combustible materials. The condition of the brick pipe requires constant monitoring. Previously, it was certainly whitewashed, since on a white surface it is easier to notice soot, indicating the presence of cracks.
Alexander Zhilyakov, :
The brick chimney has faithfully served man for centuries. Laying stoves and fireplaces from this material is almost an art. The paradox is that during the period of mass dacha construction in our country, this skill suffered serious damage. The consequences of the “work” of numerous unfortunate stove-makers were sad, and most importantly, they gave rise to distrust of brick fireboxes and chimneys. Therefore, favorable conditions have arisen and continue to exist for the promotion of factory-ready chimney systems to the domestic market.
Steel chimney
Stainless steel pipes can easily be considered the most widely used type of chimney today. Steel modular systems have a number of undeniable advantages. The main ones are light weight, ease of installation, a wide selection of pipes of different diameters and lengths, as well as shaped elements. Steel chimneys are manufactured in two versions - single- and double-circuit (the latter - in the form of a “sandwich” of two coaxial pipes with a layer of non-combustible thermal insulation).
The first ones are intended for installation in heated rooms, connecting a fireplace to an existing chimney, as well as sanitizing old brick pipes. The latter are a ready-made design solution, equally suitable for installing a chimney both inside and outside the building. A special type of stainless steel smoke channels are flexible single- and double-walled (without thermal insulation) corrugated hoses.
For the production of single-circuit chimneys and internal pipes of sandwich-type chimneys, alloyed heat- and acid-resistant sheet steel (usually 0.5-0.6 mm thick) is used. Single-circuit chimneys made of carbon steel, coated outside and inside with special black enamel, are even superior to stainless steel pipes in terms of heat resistance; They are also not afraid of condensation, but only if the coating is intact, which is easily damaged (say, when cleaning a chimney). The service life of uncoated pipes made of “black” steel with a thickness of 1 mm does not exceed 5 years.
Sandwich pipes
The casing (shell) of sandwich pipes is usually made of ordinary (non-heat-resistant) stainless steel, which is electrochemically polished to a mirror finish, and some manufacturers offer enamel painting in any color on the RAL scale. The use of a galvanized steel casing is justified only when installing a chimney inside a building. From the outside, such a pipe, if the chimney is actively used, will not last long: due to periodic heating, corrosion intensifies.
Alexey Matveev, :
Stainless steels used for the production of chimneys are divided into two categories: magnetic ferrite (in the American ASTM standardization system these are AISI 409, 430, 439, etc.) and non-magnetic austenitic (AISI 304, 316, 321, etc.) . According to our tests of AISI 409 steel (composition: 0.08% C, 1% Mn, 1% Si, 10.5-11.75% Cr, 0.75% Ti), the critical temperature value in the inner pipe of the insulated chimney fragment , at which the effect of intercrystalline corrosion became noticeable, was equal to 800-900 C. After 4 hours of exposure, the inner wall of the pipe was covered with a kind of “crocodile skin,” which indicates the beginning of the process of steel destruction. At 650 C no traces of corrosion were observed. The temperature in the pipe rises to 1000 C only when soot ignites (an extreme phenomenon that has a detrimental effect on the condition of almost any chimney). At operating temperatures up to 600 C, a stainless steel chimney can last for decades.
The thermal insulation layer in sandwich pipes solves three problems at once: it prevents overcooling of flue gases from negatively affecting draft, does not allow the temperature of the internal walls of the chimney to drop to the dew point, and, finally, ensures a fire-safe temperature of the external walls.
The choice of insulating materials is small: usually it is basalt wool (or silicone wool, perlite sand (but it can only be filled in during the installation of the chimney).
Rosinox
Sections of pipes made up of several modules that rise above the roof are given stability by making stretch marks.
Burda Media
Steel chimney module
Such a very important characteristic of a chimney as gas tightness depends on the design of the pipe joints, so every manufacturer strives to bring it to perfection. Thus, sealing of some chimneys is ensured by centering couplings; The double annular protrusion formed at the joint is crimped with clamps included in the delivery of each module. Other chimneys have a cone-shaped connection in combination with a ring lip.
The vast majority of stainless steel chimneys are installed in the traditional way, and here a lot depends on the quality of the parts. Typically, the upper module is put on the lower one, but single-circuit, and when laying externally, double-circuit modules should be joined by inserting the upper one into the lower one, which will avoid condensate leakage through the joints.
Ceramic chimneys
Ceramic chimneys are the same “sandwiches”, but “cooked” according to a completely different recipe. The inner pipe is made of fireclay pottery, the middle layer is permanent basalt wool, the outer layer is made of lightweight concrete sections or mirror stainless steel.
Ceramic chimneys are resistant to high temperatures (up to 1000 °C), condensation, and at the same time have the main advantage of modular systems - they can be quickly and easily assembled.
Ceramic systems also have their disadvantages. Chimneys with a concrete casing have a significant mass (1 linear meter weighs from 80 kg), can only be used as main ones (free-standing), and do not allow obstacles to be bypassed. The “weak link” of such chimneys is the connection point. Manufacturers provide for the use of a metal module (modules), which has a shorter service life and therefore will require replacement in the future, which must be taken into account when building a fireplace.
Raab
Raab chimneys with stainless steel inner pipe and concrete casing: with ventilation duct…
Raab
...or without it.
And finally, metal does not combine well with ceramics because it has a high coefficient of thermal expansion: around the perimeter of the steel pipe where it enters the ceramic one, it is necessary to leave a fairly large (about 10 mm) gap, which is filled with asbestos cord or heat-resistant sealant.
However, the high reliability and durability of ceramic chimneys (the factory warranty is 30 years, and the actual service life, according to manufacturers, is more than 100 years) allows us to turn a blind eye to the listed shortcomings.
- Heating
3 simple rules that will help keep your chimney clean and avoid soot fires
Pipe location
The chimney pipe can only be positioned vertically. The deviation from the vertical axis can be no more than 30 degrees, or 1 meter in any direction. The chimney is connected to the gas boiler in such a way that a pipe section of at least 0.5 m in length comes out of the boiler.
The number of bends and turns in the chimney should be kept to a minimum if possible. If this is not possible, then it is possible to install bends and elbows, but their total number should not exceed 3. Horizontal sections of pipes can have a slope of no more than 0.01 degrees towards the boiler.
Solid fuel boilers
The choice of chimney for a solid fuel boiler, stove or fireplace is significantly different. The main criterion is that the material must be resistant to high temperatures. The fact is that the principle of their operation differs from gas boilers. The process of burning wood, coal or briquettes is accompanied by high temperature. As a consequence, the temperature of the combustion products exiting is also high. Despite the variety of modern materials, brick remains the best option. Popular metal pipes, including stainless steel ones, quickly burn out, so their service life is short. Plastic pipes are categorically not suitable for solid fuel boilers, since they cannot withstand high temperatures. Cheap asbestos pipes can be used, but they are designed for gas temperatures of no more than 300 degrees.
Rules for installing a chimney for a gas boiler
When installing chimney pipes for a gas boiler in a private house, you need to follow a number of rules:
- Chimney elements must be installed from bottom to top;
- Structural elements can only be fastened vertically;
- The pipe for the gas boiler should not be higher than 5 m;
- Bends and sagging of pipes in straight sections are not allowed;
- All pipe connection points must be treated with sealant;
- The chimney should not have more than three horizontal sections longer than 1 m;
- The head can only be placed above the zone of passage of air masses.
The chimney must be securely attached to the wall located next to it. Straight sections of the pipe must be fixed at a distance of no more than 1.5 m, while all connections of the chimney elements themselves must be securely fastened to each other. In order for the assembled structure to be as reliable and durable as possible, its elements must be further strengthened using metal clamps.
Installation features
- Installation is done from bottom to top.
- The assembly of a modular pipeline is carried out by inserting one pipe into another; the joints are additionally treated with fire-resistant sealant and fixed with clamps.
- The pipeline is attached to the supporting structure with special brackets every 2 meters, avoiding deflections and constrictions.
- Connecting seams should not be placed in the areas of floors and roofing pie. In addition, the so-called “fire cutting” of 150 or 300 mm is performed here for pipes with and without insulation, respectively.
- If the roof is classified as flammable, a spark arrester made of metal mesh with 5x5 mm holes is mounted on the pipe.
- The walls around the fireplace shaft must be lined with fire-resistant material (clinker, tiles or iron sheets).
- When the circuit is drained horizontally through the wall, inspection and cleaning modules are installed in them.
- To prevent precipitation and debris from getting inside, weather vanes and deflectors are installed on top of the pipe.
Correct temperature in the steam room
A lot can be said about the rules of classic health bath procedures, but in this article we will dwell in detail on the temperature. If we talk about the temperature in the steam room that is most suitable for health in all respects, then this indicator lies between 50 ° C and 70 ° C. In the classical Russian bathhouse, the stoves were always built of brick and, as a rule, they had closed heaters.
A ladle of water was poured onto the stones, heated red from the direct flame, which instantly turned into light, hot, finely dispersed steam, most comfortable for both the respiratory tract and the skin. A cloud of steam rose to the ceiling and a person lying on the shelf was gradually doused with small portions of this steam using brooms.
When designing your own sauna, it is important to understand that in addition to the correct temperature to obtain the full range of positive effects of steaming on the body, the sauna must also have a certain humidity. The optimal indicator is within 60%
It is this combination of temperature and humidity that provides ideal conditions for healing the entire body.
It is possible to ensure that the steam room has both the specified temperature and the correct humidity at the same time only if the stove is in it with a closed heater
To obtain high-quality finely dispersed steam, it is very important that the stones in the furnace are heated to at least 300 °C. And if the heater is open, then when the stones in it are heated to such an extent, the stove itself will be so hot that the temperature of the steam room will go beyond 70 ° C
If you rely on Wikipedia, the combustion temperature of firewood is in the range of 800–1000 °C (approximately), and ignition and smoldering of wood begins at 300 °C. In reality, this range is even wider - from 450 to 1050 °C. Not very accurate data, right? There is an explanation for this - the temperature in the center of the flame depends on many conditions. Those who want to achieve efficient combustion of wood in a stove or solid fuel boiler would do well to familiarize themselves with these factors.
Hot topic
In stoves and fireplaces, the temperature of the exhaust gases is quite high, and therefore it is most reasonable to use brick or concrete chimneys with them, which, of course, does not exclude the possibility of using steel or clay structures. In principle, asbestos-cement analogues are also suitable, but in accordance with the standards, the flue gases in this case should not be heated above 300°C. It is advisable to provide a separate smoke exhaust channel for each stove, but you can connect two stove fireboxes to one chimney if they are located on the same floor. When connecting chimneys, cuts should be provided in them with a height of at least 1 m from the bottom of the joint.
If stoves are allowed to be placed only in one- or two-story buildings, and each floor must have its own chimney for heat generators, then solid fuel fireplaces with closed fireboxes can be installed even in multi-story residential and public buildings. In this case, they must be connected to a collective smoke exhaust system through an air seal at least 2 m long, which prevents the spread of combustion products.
Chimneys made of technical ceramics are resistant to moisture and acids, as well as temperatures up to 1250°C
Errors in the construction of brick chimneys may also relate to the quality and features of the masonry or the choice of brick. In this case, you cannot use its lightly fired wall or partition varieties. The thickness of masonry joints should not exceed 5 mm, and installation of bars on edges is not allowed. Significant miscalculations include the stepped shape of the inclined sections of the channel, which leads to the formation of turbulence and a decrease in thrust. Inaccurate splitting of bricks, improper preparation of the mortar, the presence of voids in masonry joints and double vertical joints - all this causes problems when operating brick chimneys.
When constructing such structures, the use of hollow or porous bricks is not allowed. For laying furnaces of stoves and fireplaces, as well as chimneys, only fire-resistant ceramic products are used. Their production technology involves firing at a temperature of 1300–1350°C, and the color of the finished product varies - from almost white to light brown, more often straw with brown inclusions. Taking into account the design features of various types of furnace fireboxes, straight and wedge-shaped (end and edge) refractory bricks are produced.
The condition of a brick chimney must be periodically monitored: to simplify this task, the structures are whitewashed, since black soot, indicating the presence of cracks and leaks of flue gases, is clearly visible on a light-colored surface.
When does firewood produce more heat?
To organize economical heating of a private home, you need to extract maximum thermal energy from wood, and then transfer it to the premises with minimal losses. The second condition depends on the efficiency of the heat source, but the first one depends precisely on the temperature of burning wood in the furnace or boiler. The higher it is, the more heat is released.
The amount of heat generated when wood burns (heat output) is influenced by the following factors:
- caloric content (the amount of thermal energy that can be obtained from a unit of fuel);
- natural moisture content in wood;
- volume of supplied air and its temperature.
In practice, all of the above parameters are interconnected. The calorie content of fuel supersaturated with moisture is approximately 2 times lower than that of dry wood. And without the required volume of air, it will begin to smolder and emit minimal heat. That is, the real combustion temperature of wood is not a constant value and cannot be accurately indicated in theoretical considerations.
For reference. There is a simple way to determine what fire temperature is reached when burning wood in an open firebox. Use an infrared pyrometer that measures the heating of surfaces from a distance, as the master stove maker did in his video. It demonstrates testing of a barbecue fireplace insert; measurements are taken in the second half of the video.
Now let's look at each factor separately.
About the calorific value of fuel
Different types of wood differ in density and weight, and also contain different amounts of carbon and hydrogen - the main components that produce heat during the combustion process. As a rule, denser and heavier species, such as oak and ash, provide more energy than poplar or alder. We present to your attention a table with data on the density, specific heat and combustion temperature of various types of wood.
Note. The table shows the values of the mass and volumetric heat of combustion of dry fuel per 1 kg and per 1 m³ of storage. The maximum temperature is based on ideal combustion conditions with excess air.
If we compare the calorific value by volume, it is noticeable that oak or birch logs will emit more heat than less dense coniferous species. And although the conditions for burning wood in a stove, potbelly stove or boiler are far from ideal, the trend will still persist. That is, the flame temperature directly depends on the calorific value of the selected wood species.
Maintenance and cleaning
Preventive maintenance and cleaning of the chimney duct is carried out at least 2 times a year, before the onset of the heating season and at its end. The inspection must be carried out by representatives of regulatory organizations, and they also issue a conclusion on the suitability or unsuitability of the chimney circuit for operation. If you have the appropriate knowledge and skills, the home owner can also periodically inspect it. In this case, the channel is checked for:
- presence of traction;
- integrity of partitions;
- circuit tightness;
- presence of blockages.
If the thickness of ash deposits is more than 2 mm, cleaning is carried out. To do this, use a special ball weight, a brush and a stiff brush with an extended folding handle or on a steel cable. Starting cleaning from the top and gradually unfolding the handle, they move into the depths of the shaft. The fireplace insert is first closed to prevent soot from penetrating into the room, the furniture is covered, and the windows and doors are closed.
Cleaning can also be done using chemicals. When burned, the so-called “miracle logs” release chemical compounds that are harmless to humans, under the influence of which the soot lags behind the walls.
Once every ten years, a major overhaul of brick structures is carried out, replacing the mortar in the seams.
It is prohibited to burn off soot and use chlorine-containing cleaning products.
Useful tips
The high combustion temperature of firewood is the key to efficient heating of a private home. Even manufacturers of TT boilers and wood-burning stoves indicate in the instructions that the best efficiency of the heat generator is observed precisely when operating at maximum mode.
Finally, we will give a few recommendations on how to achieve high heat output, and therefore energy savings:
- If you have to purchase firewood, do not buy low-calorie species, such as willow and poplar. The first is too saturated with moisture, and the second has low density. Remember that you pay for cubic meters, not kilograms of solid fuel.
- Dry the logs as much as possible. Freshly cut wood reaches a moisture content of 20-25% after at least one and a half years of drying in an open woodshed.
- Try not to operate the boiler in the vaunted smoldering mode, which supposedly helps save money. As you can see from the photo, the fire temperature during normal combustion is 800 °C, and smoldering wood will give no more than 450 °C. You can't heat a house with such heat transfer.
- Carbon monoxide CO is not only flammable, but also toxic. Trying to save fuel, we cut off the air supply to the firebox and provoke its release. Not only is potential fuel wasted outside, but it also pollutes the environment.
- Do not supply air to the firebox from the street, so as not to waste energy heating it. When choosing a solid fuel boiler, pay attention to models with a heating channel. They are easy to distinguish by the fan installed on the top panel, and not in the ash pan door.
Of course, it is impossible to continuously maintain a high temperature in the chamber, because the need for heat at home also changes and depends on many factors. To accumulate excess energy, there are heat accumulators, also known as buffer tanks. As a last resort, purchase a heat generator with forced draft, where during periods when the fan is turned off, the air supply is completely blocked.
Source
How many degrees in a brick kiln?
At brick kilns
there is a brick mass that accumulates thermal energy.
This allows the stove to release heat gradually, maintaining the air temperature in the house throughout the day; The average temperature of brickwork
outside is about 55-60
degrees
.
Interesting materials:
How to give vitamins to chickens? How to decorate a flower pot with rope? How is composite reinforcement made? How to divide barberry? How to cheaply paint a wooden fence? How to disinfect bulbs? How to add an NFC chip to a smartphone? How to add plasticizer to concrete? How to achieve lush flowering of clematis? How long should the ceiling dry after flooding?
Elements of modular chimneys - complete set
Using modular chimneys, you can create smoke exhaust routes of any design, length, with various offsets, turns and detours. To create such structures, as well as for connecting pipe modules, fastening them and other actions, there is a wide range of components. Let's list them:
- Deflector. It is mounted on the chimney head to protect the pipe from the effects of wind and precipitation. It also helps to optimize the chimney draft and increase the efficiency of the chimney by about 20%.
- Clamp for stretching. It is used for reliable fixation of a chimney whose height above the roof of a building exceeds 1.2 meters. Allows you to design chimneys of any height. It is also used for fixing external chimneys, regardless of the height of the pipe.
- Skirt. It is used to seal the area where the pipe exits the roof, to protect the connection between the roofing unit and the chimney from precipitation, as well as for decorative purposes.
- Roofing element. Also called roof penetration. Used to pass a chimney pipe through the roof.
- Connecting clamp. It is used for reliable joining of modular parts of the chimney to each other.
- Flange. It is used to protect and insulate flammable materials in areas where the chimney adjoins them.
- Wall mounting bracket. Used for reliable fastening of the chimney trunk to walls and surfaces
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any device, pipes of this type have their pros and cons. They have few disadvantages, but they are important:
- considerable price for the components of the structure;
- relatively short service life;
- gradual loss of tightness due to temperature changes.
The advantages of chimneys with sandwich-type pipes are as follows:
- Easy and clear installation. This distinguishes such smoke exhaust systems from devices whose installation requires calling a specialist.
- Small pipe sizes.
- The versatility of chimney pipes can go both into the walls and into the ceiling.
- Many layers that prevent condensation from accumulating on the pipes and serve as protection against the appearance of soot.
- This chimney is not afraid of the effects of chemicals and aggressive environments that appear during their use.
- Fire safety. Such chimneys are currently considered the best in terms of this parameter.
To improve the operation of the chimney, it is better to install a draft regulator.
The main characteristics that a chimney should have
Regardless of what material the chimney is made of and what design it has, this product must comply with the basic parameters of fire and operational safety. So, the chimney must:
- Be made of non-flammable materials
- Be suitable for the specific type of heating equipment used
- Maintain the temperatures provided by the equipment - both operating and peak
- Withstand temperature changes and climatic influences
- Features simple installation
- Have a long service life
- Be completely sealed
- Have insulation at points of passage through walls, ceilings, and roofs
Let's take a closer look at each type of chimney pipe.
Painting of stainless steel chimneys
Since a fireplace or stove is not only a source of heat, but also a full-fledged participant in the home interior, some manufacturers of steel chimneys offer design solutions for chimneys. The external contour of the chimney for the stove and fireplace can be painted in any color according to the RAL or RR palette. This service opens up wide opportunities for consumers to create beautiful interior solutions involving not only a heating device, but also a chimney.
Technical features of steel chimneys
The diameters of single-wall and double-wall chimneys, as a rule, range from 104 mm to 300 mm. In double-walled chimneys, high-quality fire-resistant basalt wool is used, a layer of which is located between the outer and inner contours. The thickness of the thermal insulation is usually 50 mm and 100 mm. For home fireplaces and stoves, it is recommended to use 50 mm insulation. The thickness of the steel chimney walls is usually 0.5 mm - 0.1 mm. For the manufacture of chimneys for fireplaces and stoves, austenitic high-alloy steel grades AISI 321 is used for the internal circuit and AISI 304 for the external circuit. High-quality steel chimneys use an internal thermal compensation system, which eliminates deformation of linear elements due to the natural temperature expansion of the metal.
It is worth noting that the standard warehouse program of most manufacturers of steel chimneys includes a product range of pipes of basic diameters and steel thickness, insulation. At the same time, today it is not difficult to find a manufacturer who makes chimneys of any diameter, insulation thickness and steel to order. Thus, in the case of using a heating device with non-standard technical connection parameters, it is possible to order a pipe with specific characteristics on an individual basis.
How to choose
It is difficult to unequivocally answer the question of which chimney to choose. There is a main rule here: the choice of a chimney should in no case be based on its cost. In this case, this is not the main thing. You need to start from the following things:
- depending on the selected heating type;
- on the type of unit you have chosen;
- on how the chimney will be installed. If you invite a specialist to do this, that’s one thing, but if you rely on your own strength, that’s a completely different matter; the job should be up to you;
- much will depend on the intensity with which your heating system will be operated.
Calculate everything and give a correct assessment of your knowledge and experience in installing a chimney, and then make your choice.