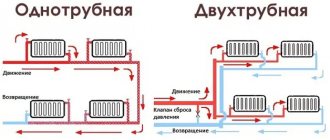
When it comes time to think about the heating system in your home, a lot of technical questions arise. Of course, you want to do everything correctly, thoroughly and inexpensively. But it’s not enough just to properly plan the system itself; you also need to take care of the water flowing in the veins of your home. Excessive water hardness and abrasive impurities in it can shorten the life of your system by decades. Today there are many ways to purify water. And you definitely shouldn’t skimp on them. Savings here will entail large expenses in the future, including replacement of machinery and equipment. When using water from a well or reservoir, several filters must be used to protect the coolant. There are four main and mandatory ones:
- ion exchange resin filter
- cascade mechanical cleaning filter
- universal filter mesh
- coarse filter
The uninitiated user, of course, will have natural questions. What are heating filters for, are they useful, do you need to use them all at once and at what stage? The questions are natural and require a detailed answer. It is worth planning the installation of filters at the design stage of your home. It is necessary to allocate space for them, taking into account installation and maintenance. Provide a connection system. If the moment was missed, the filters can be installed later, but this will entail additional labor costs. Therefore, if you are still at the planning stage, it’s time to study each filter in detail.
Why are filters needed for a heating system?
Either pure water is used as a coolant, because it has chemical additives. The liquid medium causes corrosion of the metal components of thermal routes - wiring, fittings, radiators. Rust particles enter the stream, circulating along with the coolant. In areas of narrow passages, changes in direction, and unevenness, traffic jams inevitably form - accumulations of small pollutants.
As a result, you may notice uneven heating of the radiators; due to inadequate exchange of the environment, it is necessary to increase the boiler power. Migrating dirt negatively affects the operation of the centrifugal pump and leads to its failure. Blockages that occur in the boiler heat exchanger are also dangerous.
Filtering devices are collection points that trap dirt and debris, allowing you to quickly and without additional material costs remove all foreign components from the coolant. Advantages of using the nodes in question:
- protection of an expensive boiler and pump from premature wear,
- eliminating the need for frequent coolant replacement,
- eliminating the procedure of flushing the system,
- ensuring maximum heat transfer from radiators,
- reduction of hydraulic resistance in control valves, fittings, pipes, connecting units.
As a result, the operation of the pump and boiler is rationalized and their energy consumption is reduced.
Why is untreated water dangerous for a gas boiler?
Why do you so desperately need a water filter in front of a gas boiler? What filter? What impurities have the most negative effect on boiler equipment? Actually, impurities in water can be very different. After all, there can be several sources of water:
- Central water supply;
- Nearest surface source;
- Underground source.
Each source has its own impurities, some more harmful than others, some others. But if you bring all the harmful impurities into one table, you’ll get something like this:
| Equipment | Impurities in water |
| Boiler room | Solids - garbage, sand Smell, color Metal salts Lime salts Bacteria, viruses Dissolved gases |
A filter in front of the heating boiler is necessary, and more than one. It all depends on two factors - the state of the water and financial capabilities. Using untreated water will actually cost the consumer much more. Danger lies even in seemingly good water coming from a central source. Such water involves all stages of purification, except one - softening. And lime water is especially destructive for a gas boiler!
What special negative does she have? Is it necessary to install a filter in front of a gas boiler? If the boiler is steam, then definitely! The steam must be crystal clear, purified, including from dissolved gases. When heated, limewater forms a dense coating on surfaces. And it's not easy to remove. But most importantly, it works as an insulator. Heat passes through such a coating, even a very thin one, very poorly. The surface under such a load suffers terrible overloads and either burns out or explodes. Therefore, a water softening filter in front of a gas boiler is a mandatory element of water treatment if the water is too hard.
Hard water and scale
There are two problems in terms of softening. Both hard water and the resulting scale cause damage to the system. The worst thing for the boiler is the result of lime water - scale. All cracks, scratches, breaks are due to the heat transfer block to the water. As for hard water, it brings negative consequences to human health both directly and indirectly.
There are several areas where water leaves its mark before plaque forms. This includes washing and surface treatment. The secret is hidden in the contact of this type of water with any detergents. Lime salts react very poorly with washing alkalis. As a result, the dissolution of detergents deteriorates and they form a stone-like sediment in contact with salts. Every housewife who has ever washed a down jacket in hard water has seen what comes of this. There is a grayish-whitish coating with streaks over the entire surface of the jacket or coat. Which can then be washed, but this only makes it worse, stains appear in another place. And to rinse such a large thing with lime-tainted water, the costs are much higher. And divorces are still treacherous.
It turns out that the washing seems to be going well, but the laundry remains dirty, many times more water and detergents are used, and the result is even negative. People with ulcers or allergies are not recommended to drink lime water. Just like swimming in such water. It can cause irritation and allergies.
If you don’t have a softener, you need to get rid of scale and do it with enviable consistency. If deposits are not removed from the internal surface of a double-circuit boiler in time, it will burst, the household appliance will burn out, and the pan will become unusable ahead of time. That’s why we carried out various preventive cleanings of the gas boiler from scale and major cleanings. Today, with such development of the softening sphere, it is enough to install one or two softeners in an apartment to protect household appliances.
Root causes of boiler failure
As already mentioned, if the water in the system is limestone, then it is the first reason for the breakdown of boiler equipment. This is the main problem in thermal power engineering. Of course, a coarse filter in front of the boiler is just as important, but this is what will be installed by default if the water is supplied without primary purification, but softening may be delayed, the system is not cheap, and the boiler has not yet cracked. Unfortunately, a certain degree of carelessness in this regard still exists.
Another reason for boiler breakdowns is improper operation and improper care of boiler surfaces. And of course, poor quality water. There are no other root causes of breakdowns other than manufacturing defects. Any untreated water will instantly cause damage. Debris will clog the pipes, damage the surface, and the boiler will be irrevocably damaged. Therefore, expensive boiler equipment requires appropriate care. The consequences of hard water are the saddest, albeit in the long term.
Design features of the equipment
The following methods for separating impurities are used in filters for heating systems:
- settling devices are based on gravitational forces - when the flow speed decreases, sedimentation of solid particles is observed,
- in mesh variations, water passes through cells of a given size. Anything larger than these holes remains in the filter,
- in magnetic models, the active element attracts metal scale and particles of similar composition.
The simplest mud settling tanks are a cylindrical body with two pipes, with a flange plug at the bottom. There are jumpers in the cavity that change the direction of water flow. Magnetic models reduce the intensity of scale formation on internal surfaces.
Modern filters for water purification in a heating system combine 2 or all principles of medium processing.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of the filter is quite simple. Water enters the pipe and then goes into the internal cavity of the housing. And inside the body, suspended particles fall to the bottom in the form of sediment. The filter is installed inside the outlet pipe. The water passes through the filter and enters the heating system in purified form. To clean the mud trap from sediment, you need to remove the glass from the outlet pipe. The mud trap can be with a flange or threaded connection.
The sump device is a pipeline expansion unit that changes the direction of water flow, as well as filtering it with a mesh. Cutting off occurs under a special mesh, as well as the accumulation of large and medium fractions and precipitation.
The function of the mud collector is simple: it takes in contaminated water, purifies it and then removes the purified water. But it is recommended to periodically clean the lower part of the case from accumulated dirt.
But there is one nuance under which a mud filter for a heating system will work normally: the condition of a gradual increase in hydraulic resistance according to the readings of instruments on the pipeline line before and after the mud filter must be met.
Types of filters for heating systems
The most extensive classification is the identification of two categories:
- Coarse filters, mud collectors, use a mesh to collect solid inclusions whose diameter exceeds 300 microns.
- Fine cleaning models are capable of retaining suspended matter in the range of 5-300 microns.
The photo shows a fine filter for a heating system.
The latter are very rarely used in heating communications; they are more suitable for food and household needs. Therefore, it is advisable to consider 4 types of mud collectors common in the private sector.
Brass mesh oblique devices
They are optimal for local heating schemes and have a simple design. The products are equipped with threaded coupling connections, available in a variable range of sizes, which expands the possibilities of their use.
The monolithic cast brass body consists of a combination of two cylinders - horizontal and located at an angle to it. Both ends are equipped with threaded mounting couplings. At the end of the oblique cylinder there is a brass hexagonal plug sealed with a Teflon gasket. A steel mesh is located in the slope area. Before such a modification, a shut-off valve is installed to facilitate maintenance work and flushing.
To clean it, you need to turn off the coolant supply, place a container to collect liquid and dirt, unscrew the plug with a wrench and remove the mesh. The latter is treated with a polymer brush under strong pressure of water.
Cast iron oblique magnetic models
Their design is similar to the previous variation, the differences lie in the material - the plug and body are made of cast iron. The filter mesh is the same steel, it is used with a paronite gasket.
In the photo, a magnetic cast iron mesh filter FMFch Du 50
The filtration unit is complemented by a stand on which disk-shaped magnets are installed at a given interval; they are not subject to corrosion. Thanks to this rigid inclusion, two-way filtration is ensured: mechanical impurities remain in the mesh, scale and metal particles are captured by the magnetic block. High quality of coolant processing is ensured.
The installation and maintenance procedure is fully consistent with brass variations with one addition - magnetic disks also need to be washed.
Flange magnetic filters for heating systems
The modification is in many ways similar to the previous version, but it is larger in size and is designed to service larger diameter pipelines. The threaded plug in this case is replaced by a flange plug; sometimes a clogged drain hole is provided here, allowing liquid and dirt to be drained without dismantling the entire plug.
When selecting and installing such products, it is necessary to take into account the installation and operational parameters of length and height, and also provide a place for removing the plug, removing the magnetic block, and the mesh.
Subscriber mud traps
They can be horizontal or vertical, the latter being more common. The devices have an impressive service life and are easy to use. Thanks to the large internal volume, the frequency of preventive maintenance is significantly reduced.
The cylindrical body is made of steel pipe. There are nozzles with a flange on both sides. The passing coolant undergoes two stages of purification: small suspensions are retained by the mesh, before large particles are deposited under the influence of centrifugal and gravitational forces. Reliable and simple design, affordable cost contribute to the widespread use of subscriber filters in autonomous heating systems.
On the specialized market there are self-cleaning mud collectors, supplemented with an air vent - dissolved gases are separated and removed in them.
Design
Dirt trap with drain cock.
The design of the mesh filter consists of the following parts:
- Brass, bronze, cast iron or stainless steel body. There are models with both flange and coupling connections to the pipeline. Brass and bronze are used to make filters ranging from ½ to 2 inches in diameter. Cast iron and steel are typically used to produce filters with a diameter of 1½ inches, but smaller models are also available;
- Cork. Connects to the housing either with a flange or thread. Allows you to remove the filter element for further cleaning or replacement. To avoid leakage, the plug is equipped with a sealing gasket (ring);
- The filter element is in the form of a fine-mesh cylindrical mesh. The mesh is made of stainless steel and connected to each other using electric contact welding.
Filter with tap.
Some filter models are equipped with magnets that attract iron-containing particles.
Mesh filters can vary in degree of purification:
- rough cleaning (cell sizes from 300 to 500 micrometers);
- finer cleaning (ability to retain particles with a size of 100 microns).
Installing a filter in the heating system
Pipelines of medium and small diameter (these are the ones that are usually used when installing autonomous heat supply) are equipped with coupling filters. Such products have threaded areas on both sides. On the case there are hexagons used to insert the key during assembly or dismantling - open-end, gas, adjustable.
Methods for installing a filter in the system
If large-diameter pipes are used, this means a flange connection using an O-ring, which is tightened with bolts. Installation is quite labor-intensive, but removing this component is easy - you don’t have to disassemble an entire section of wiring.
Filters installed “tightly” have pipes on both sides with a chamfer intended for making a weld. They have a non-removable design and are becoming increasingly rare due to the impracticality and complexity of replacement.
Maintenance and cleaning features
Self-cleaning filters have a special tap at the bottom: to remove accumulated dirt from the device, just turn the lever. At the same time, the filter mesh is also cleaned by the flow of water.
Better flushing is ensured with the help of a bypass bypass equipped with a valve - it must be provided for at the stage of installing the filter. Here, servicing comes down to redirecting the coolant flow from the reverse side. In this case, you can successfully free the mesh cells even from densely embedded solid inclusions. The contaminants are then removed through the drain valve.
Flushing models are very convenient to use. In this section of the system, the liquid supply is turned off, the flange plug or plug is removed from the device, and the filter component is removed. After washing the latter, the device is assembled in the reverse order.
Finally, non-flush mud collectors require complete dismantling, so they are extremely rarely used in autonomous heating networks. Here the maintenance is based on the actual output of the device from the circuit.