Every person planning to create or update a heating system is interested in which radiators to use for this. The choice is really huge, but if you don’t know the features and key criteria, you can waste your money. Recently, you can increasingly hear about copper heating radiators. What is their advantage? This is what we will try to find out in this article.
- 1 Comparative review of popular models
- 2 Copper radiators
- 3 Main technical characteristics
- 4 Design features of copper batteries
- 5 Main advantages of copper batteries
- 6 Features of device operation
- 7 What to look for when buying?
Design features of copper radiators
Copper radiators last longer because they are not subject to corrosion.
The use of copper with a minimum amount of impurities allows you to reveal all the advantages of the material. Non-ferrous metal is not afraid of corrosion; it is strong and soft at the same time. The attractive appearance of copper batteries does not require painting. Heating devices are manufactured in various versions. Their design features affect the level of heat transfer.
Radiators are made of copper tubes of various diameters. To increase the heat transfer area, row plates made of non-ferrous metal are welded to them. Tubular elements come in horizontal and vertical directions. The devices consist of several sections. The number of pipes and plates depends on the model. There are options on the market with a protective casing made of metal or wood. Decorative cladding is matched to the interior of the home owners.
Structure of bimetallic radiators
Externally, bimetallic models resemble conventional aluminum radiators. The difference lies in the internal content. The design of composite products consists of two basic elements: an internal steel pipe and an external figure-ribbed body made of aluminum panels. Some radiators use copper instead of steel.
The coolant circulates through an internal steel or copper pipeline. Due to corrosion inertness, radiators do not rust and do not react with chemically active coolant. The external elements and the internal manifold are connected by spot welding or injection molding.
Based on their physical and operational properties, the batteries are suitable for installation in apartment buildings of any number of floors and for arranging a local heating system for cottage buildings.
The bimetallic structure determines the characteristics of the device. The steel core explains resistance to aggressive environments and endurance to pressure drops, the aluminum “shell” increases heat transfer and makes the radiator lighter
Advantages and disadvantages
Copper pipes and radiators can withstand pressure up to 16 atmospheres.
Despite the high cost, copper batteries are installed in private houses and apartments. The popularity of the devices is justified by the advantages of the material:
- high level of heat transfer;
- long-term operation;
- resistance to pressure up to 16 atmospheres;
- no deposits form on the inside of the pipes;
- coolant temperature up to 150°C;
- resistance to impurities present in the coolant.
Soft metal does not leak during a short-term increase in pressure. Copper batteries are lightweight and versatile in use.
Flaws:
- The devices are sensitive to abrasive particles. Their presence in the fluid flow accelerates wear of products.
- During installation, fittings made of ferrous metals must not be used. This leads to oxidation of copper.
- The high cost of copper heating radiators is the main disadvantage for most buyers.
Non-ferrous metal is not afraid of corrosion that occurs upon contact with water and air. But copper products are susceptible to oxidation due to a chemical reaction upon contact with aluminum or steel.
Technical and operational characteristics
Copper equipment has unique characteristics, so it can be installed not only in autonomous heating systems, but also in central ones. It is noteworthy that some models of copper heaters can be used for heating with both liquid and steam.
| Technical and operational characteristics | Range of values of existing models |
| Heat output (thermal power), kW | 0,1 — 2,195 |
| Working pressure, bar | 14-16 |
| Test pressure, bar | 20-50 |
| Required volume of coolant in the radiator, l | 0,26-4,81 |
| Maximum operating temperature, °C | 110-150 |
| Heated room area, m2 | 2-23 |
| Weight, kg | 1,6-22,6 |
| Warranty period, years | 20-25 |
| Service life, years | 35-50 |
| Connection type | Side, bottom |
| Thread of holes for connection to heating mains, inches | G ½, ¾ |
Heat transfer from heating radiators Comparison of indicators and calculation methods
Principle of operation
The temperature in copper radiators quickly rises and warms up the room.
Radiators are the part of the heating system responsible for heat transfer. The liquid circulating in the circuit is heated in the boiler. It flows through the pipeline into the batteries. High water temperature causes the metal to heat up. Copper has high thermal conductivity, an indicator that exceeds the characteristics of steel several times. The operation of radiators is based on physical processes:
- Thermal conductivity is the transfer of energy from heated bodies to colder ones. Pure copper, which is used in the production of batteries, has an indicator of 401 W/(m*K). This is one of the highest values among metals.
- Thermal radiation - hot metal emits infrared waves.
- Convection is the transfer of heat by air flow. Cold air masses pass through the radiator, their temperature rises. The heated flow rises to the ceiling. Heavy cold air takes its place, making the process continuous.
The copper radiator has high efficiency. Its characteristics ensure a rapid increase in room temperature.
Monolithic or sectional?
The outer and inner parts of bimetallic radiators are connected by pouring aluminum into special molds where a steel (copper) core is placed. The operation is performed under high pressure. In this way it can be manufactured as a single monolithic structure,
so is
the sectional team.
Design of a monolithic radiator
In the first case, the heat exchange body is cast over a ready-made welded manifold, resulting in a battery in which there are no potential leak points, due to the lack of joints. Radiators of the second type are assembled from separate sections, fastening horizontal sections of pipes with steel nipples through heat-resistant (up to 200⁰C) sealing rings. The disadvantages of such models are obvious: the installation components are sensitive to the quality of the coolant and pressure surges in the system, which can lead to the appearance of corrosion on the aluminum body and leaks.
However, prefabricated radiators are repairable and allow you to easily replace a failed section, but if there is a problem with monolithic devices, this will be impossible. However, the service life of the latter, according to manufacturers, is up to half a century, and the key to their reliability is the cast structure itself. For comparison: the working pressure of some “monoliths” can reach 100 atm, and for sectional devices it is in the range of 16–35 atm (however, these values are sufficient with a margin for both urban and autonomous heating systems with a standard pressure of about 14 and 10 atm, respectively). The service life of prefabricated radiators is also considerable - 25–30 years.
Non-separable radiators are more expensive than collapsible ones, but for installation in urban heating systems they should be preferred - as they are more durable and better adapted to extreme operating conditions (unstable pressure, water hammer, etc.). As for the ability to reduce or increase the number of sections to adjust the thermal power of the radiator, this is an absolute advantage of sectional models. When purchasing a “monolith”, it is necessary to determine in advance exactly the required power of the device. It will not be difficult to make a choice, since the market offers a wide range of products with different sizes and characteristics.
Black radiator Royal Thermo BILINER 500 Noir Sable, 12 sections. Dimensions 574 x 971 x 87 mm, power 2060 W, weight 22 kg. Price from 9000 rub.
Radiator Rifar Monolit 500, 10 sections. Dimensions 577 x 800 x 100 mm, power 1960 W, weight 21 kg. Price from 8800 rub.
Radiator RADENA BIMETALL CS150, 8 sections. Dimensions 241 x 592 x 120 mm, power 960 W, weight 7 kg. Price from 4400 rub.
Radiator Global Style Extra, 10 sections. Dimensions 566 x 810 x 80 mm, power 1730 W, weight 18.7 kg, antifreeze + water. Price from 8400 rub.
Radiator RIFAR SUPReMO, 14 sections. Dimensions 575 x 1120 x 90 mm, power 2828 W, weight 30.8 kg, water + oil + antifreeze. Price from 13020 rub.
Black radiator Royal Thermo pianoforte, 12 sections. Dimensions 591 x 971 x 100 mm, power 2270 W, weight 26.4 kg, water + oil + antifreeze. Price from 13,320 rub.
Radiator Sira RS Bimetal 500, 6 sections. Dimensions 480 x 572 x 95 mm, power 1194 W, weight 11.52 kg, steam + water + oil + antifreeze. Price from 5300 rub.
Radiator Royal Thermo PianoForte Tower Silver Satin, 22 sections. Dimensions 1760 x 591 x 100 mm, power 3982 W, weight 48.4 kg, water + oil + antifreeze. Price from 5300 rub.
Which battery to choose
The cost of radiators is not the last criterion when purchasing a device. Aluminum batteries are sensitive to the composition of the coolant, have low operating pressure, and are sensitive to water hammer. They are not recommended for installation in apartments with central heating. Aluminum appliances will be the optimal budget solution for a private home. Copper batteries do not have these disadvantages. They are effective and resistant to aggressive influences.
When choosing between copper and aluminum cooling radiators, related factors are taken into account. The non-ferrous metal structure has a small diameter and is more susceptible to corrosion. Aluminum tubes with a cross-section twice as large are less likely to clog and last longer.
What should you consider when choosing a radiator?
To achieve the proper thermal effect, it is necessary to calculate the total power of the battery. Bimetallic equipment is not a cheap purchase, so you should take care of its durability. The conscientious execution of the radiator is guaranteed by trusted manufacturers.
Capability assessment - thermal calculation
Having decided on the appropriate technical characteristics and dimensions of bimetallic radiators, it is necessary to calculate the required number of sections.
Basic formula: N=Ptot./Ppass., where Ptot. – required battery power for the entire room, Ppass. – thermal power of the section according to accompanying documents
The section’s heat transfer rate is taken from the radiator’s passport, and the total power must be calculated.
Calculation by area
The normalized value of thermal power per 1 sq.m of living space for the average climate zone, subject to standard ceilings (250-270 cm):
- the presence of one window and a wall with access to the street - 100 W;
- there is a window in the room, two walls adjacent to the street - 120 W;
- several windows and “external” walls – 130 W.
Example. The section power is 170 W, the total area of the heated room is 15 sq.m. Additional conditions: window – 1, external wall – 1, ceiling height – 270 cm.
N=(15*100)/170 = 8.82.
Rounding is done upward. This means that to heat the room it is necessary to use 9 sections of 170 W each.
Calculation by volume
SNiP separately regulates the amount of thermal power per 1 cubic meter of space in the amount of 41 W. Knowing the volume of the heated room, it is easy to calculate the heat transfer of the entire battery.
Example. Heating the room with the previous parameters. For the purity of the experiment, we leave the power of the section unchanged - 170 W.
N=(15*2.7*41)/170= 9.76.
It is necessary to install a radiator into 10 sections. The second calculation is considered more accurate. When calculating, attention should be paid to sources of heat loss indoors.
The calculated value must be increased by 10% if the apartment is located on the first/last floor, the room has large windows or the wall thickness does not exceed 250 mm
How to avoid fakes: radiator inspection
In addition to analyzing passport data, it would be useful to conduct a visual assessment of the product. Some manufacturers, in pursuit of customers, tend to “embellish” their products by introducing incorrect data into the documentation.
First of all, pay attention to the thickness of the core and aluminum “jacket”, overall dimensions, weight and quality of components.
Steel core. The minimum thickness of the steel tube is 3 mm. With smaller standard sizes, the declared strength of the product - resistance to water hammer and the development of corrosion processes - is significantly reduced.
The walls of thin metal provide access for the coolant to the aluminum “shell”, which, due to chemical activity, begins to quickly collapse
The result of a low-quality steel core is the formation of through holes and the creation of emergency situations in the heating network.
Radiator fins. Aluminum panels must be checked for strength - they should not bend from the efforts of the fingers of one hand. The minimum thickness of the panels is 1 mm.
It is better to choose models with profiled channels between the ribs. The formed confuser increases the speed of air flow, increasing the intensity of convective heat transfer.
To reduce the risk of injury, the outer edges of aluminum panels are rounded. There should be no streaks, uneven coloring or “gaps” on the surface.
Dimensions and weight. By individual order it is possible to produce radiators with a section width of less than 80 mm. However, store-bought models with inappropriate parameters are most likely fake.
To reduce costs, some manufacturers significantly reduce the width of the internal ribs, “masking” them behind standard-sized front panels. This measure worsens the heat transfer of a bimetallic radiator.
Battery components. It is almost impossible to check the quality of gaskets and nipples on site. Rely on the manufacturer's name and warranty period. Reliable companies guarantee up to 15-20 years of trouble-free operation.
Methods for installing copper radiators
To make efficient heating and not spoil the interior, choose one of two methods for installing batteries.
Wall mount
Copper radiator on legs with bottom connection.
Brackets are used for wall mounting of batteries. They are fixed to the supporting structure and serve as the basis for installing heating devices. The best option for placing radiators is a place under a window. According to building codes, the length of the device should be 50-75% of the size of the window structure. The rules require that batteries be installed at a distance of 60-100 mm from the floor, and 30-50 mm from the wall.
On legs
Floor placement has its advantages: it eliminates the load on the wall and simplifies installation. Such models are popular in interiors with panoramic windows. They are installed in cottages, country houses, offices. The disadvantage of batteries on legs is the limited connection; only floor-mounted pipes are suitable.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video review clearly demonstrates the design features of composite radiators and the basic requirements that a high-quality device must meet:
Full bimetallic radiators combine the positive characteristics of both materials. The batteries are distinguished by high thermal power, resistance to water hammer and excellent decorative properties. Their purchase is a justified investment provided that you purchase a certified product.
Tell us about how you chose a bimetallic heating device for your own apartment or country house. Share what argument was decisive in your choice? Please leave comments in the block below, ask questions, post thematic photographs.
Equipment for installing copper radiators
Shut-off valves can also be selected from a similar metal.
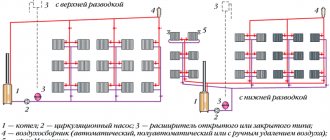
One of the factors for the safe operation of a heating system is the installation of shut-off valves.
Mayevsky crane
For normal operation of the water heating system, the batteries must be equipped with a Mayevsky tap. This device serves to remove air accumulated in the pipes. It is installed on the top of the battery. The shut-off valve is opened after starting the system to bleed trapped air and prevent the formation of plugs. After turning the valve one turn, a hissing sound appears, characteristic of air escaping. The tap is kept open until a trickle of water appears.
Shut-off valves
Taps and valves are necessary to regulate the amount of coolant in the batteries, as well as forced drainage. Shut-off valves allow you to shut off the flow of water in the event of a radiator failure. It is made of brass, the connection to the pipe is threaded. Thermostatic valves, depending on the model, require manual adjustment or are automatic.
Bypass
A bypass pipe is installed between the inlet and outlet lines. Its diameter is less than the cross-section of the connected pipes. The jumper allows the coolant to bypass the battery. The element is typical for a single-pipe heating system. A tap can be installed on the bypass, then the movement of water is controlled.
When installing copper radiators, ferrous metal fittings should not be used. To avoid a chemical reaction, all connecting parts must be made of brass.
Comparative review of popular models
The choice of copper batteries, as noted above, is huge. But when choosing a particular model, focus not only on the cost, but also on the performance characteristics of the device. So, depending on the individual parameters of the heated room, you can select devices that are designed for 10-22 m2 of area. In this case, the heat transfer of one device ranges from 1 to 3 kilowatts. Do not forget about the large weight of the radiator - some models can weigh up to 13 kilograms.
The table below shows the most popular models. Check out their features to make the right choice.
| SR-800-1000 Power – 2.4 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 80x100x100 cm Price – 75,000 rubles | SA-550-1000 Power – 1.7 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 55x100x10 cm Price – 51,400 rubles |
| Classic Style 2195 W Power – 2.195 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 42x83x11 cm Price – 34,850 rubles | Classic Style pomni 1517 RK Power 1.517 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 83x11x42 cm Price 20,950 rubles |
| “Thermia 20/40 RB” Power – 0.24 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 21x40x12.5 cm Price – 2500 rubles | Copperi Art V Power – 0.98 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 180x75x10 cm Price – 107,400 rubles |
Variety of copper radiators
Copper plate radiator in a metal casing
When choosing a suitable radiator option, it is worth assessing their appearance and technical characteristics. The main thing is the heat transfer of the device, it shows how much area the device is capable of heating. Batteries can be installed in rooms with high humidity. There are various models of heated towel rails available for bathrooms. In stores you can find radiators made of copper, both domestic and imported. Products from China are not recommended; they are cheaper due to the use of thin sheets of copper. Radiators have a limited service life. An alternative to buying an expensive radiator is a bimetallic model. The coolant in them is made of copper, and the external panels are made of aluminum.
Among the variety of heating devices, copper radiators stand out with a minimum of disadvantages. They are universal in use and have high heat transfer. Significant cost is the only disadvantage of the devices.
Characteristics of copper-aluminum heating devices
Gone are the days of inconvenient and ineffective heat transfer, cast iron batteries. The struggle to save energy and minimize heating costs forces us to insulate our own home, purchase double-glazed windows with reduced heat loss, and use modern heating devices. Thanks to this, in this publication we will analyze the key characteristics of copper-aluminum heating devices.
Copper-aluminum heating devices, which have better convection of warm air, are better suited in appearance to the modern interior style of our residential buildings. Severe shapes and perfect design, the absence of corners with sharp ends and good performance compel us to select this particular type of heating radiator.
The key advantage of copper-aluminum heating devices
The copper tubes through which the coolant moves in the middle of the heating device have a neutral reaction with the copper pipe coil of the boiler for heating. In other words, there is no potential difference leading to electrochemical corrosion, as in heating networks with metal batteries.
The compatibility of copper-aluminum heating devices with different types of adapters, boilers, steel and copper pipes and many types of thermal media allows them to be used everywhere in industrial and residential premises. The durability and duration of trouble-free operation of the heating system becomes significantly greater when using heating devices of this type.
The remarkable heat transfer of copper pipes, on which aluminum plates are mounted vertically, causes air masses to heat up much faster when compared with aluminum heating devices, not to mention cast iron radiators. Convection heat transfer of copper-aluminum batteries reaches 85%, which significantly speeds up the heating of indoor air and saves fuel resources.
The small volume of the heating device makes it possible to quickly heat the aluminum plates to working values. The heat generation power of a typical part with a size of 60×80 cm and a capacity of 0.8 liters is 1400 W, at a coolant temperature of about +70? C.
Comparative characteristics of copper-aluminum heating devices with other heating devices
When comparing copper-aluminum heating devices with other design radiators, we see their definite advantage in many technical specifications. One of the main advantages of bimetal radiators is their integral body, which makes it possible to maintain much higher pressure than other batteries. Radiators of this design have both side and bottom connections, which make it possible to advantageously hide the heating pipes into the floor.
If we take a typical cast iron radiator with 6 sections, a six-section metal, steel radiator with a size of 60×80 cm and a copper-aluminum heating device of similar indicators, we get the following comparative data:
- Cast iron 0.9 MPa 18 liters of liquid 36 kg 600 W.
- Steel 1.0 MPa 1.2 liters of liquid 6.5 kg 800 W.
- Metal 1.5 MPa 1.8 liters of liquid 9.6 kg 1200 W.
- Copper-aluminum 1.5 MPa 0.8 liters of liquid 6.9 kg 1400 W.
As you can see, the use of copper-aluminum heating devices provides savings not only in the amount of heated coolant, but also in high power with relatively similar sizes. The low weight of bimetallic batteries makes it possible to mount them directly on plasterboard walls, which is much cheaper and faster than installing cast iron radiators.
How to calculate the number of sections
To understand how many sections will be enough to effectively heat the room, you will need to calculate the area. Based on SNiP (building codes), for 1 m² you will need a battery with a minimum power level of 100 W.
The area of the room is calculated as follows: the length is multiplied by the width, the result is multiplied by the power and divided by the power required for one battery. These are approximate calculations that are relevant for housing with normal ceiling heights.
Review of bimetallic battery manufacturers
Now there are many companies producing various models of heating equipment. Each model differs not only in technical, but also in visual characteristics, as well as a set of additional options. Let's look at the best bimetallic batteries.
Warma
The company produces cast sectional radiators. We use high-precision equipment installed at factories in China. These models are used to heat residential, administrative buildings and industrial facilities. Each device successfully resists corrosion and is not afraid of water hammer. They are produced in a modern, laconic design, so they fit into most interiors.
The manufacturer provides a 10-year warranty on the equipment. Compared to its competitors, Warma offers customers affordable prices for radiators with 4–12 sections. Price - from 2600 rubles.
Tenard
The company is responsible for the production of full-bimetallic batteries that are installed in central or autonomous heating networks. Thanks to three-row fins, heat transfer becomes even more efficient. The side ribs have a slight slope, resulting in the formation of a convective flow diffuser. This type of fin serves as an intermediate support for the vertical channel. The coolant can be non-freezing liquids.
Price - from 2800 rubles.
Prices for bimetallic heating radiators Tenard
bimetallic heating radiators Tenard
Radena
These are high-strength sectional heating batteries made in Italy. To connect the sections, steel nipples and paronite gaskets are used. The internal part of the section has the form of a welded pipe frame made of carbon steel, which makes the radiator not only strong, but also durable.
A distinctive feature of the products is their small size, which saves free space in the room. The range also includes models designed specifically for housing with low window sills. The equipment is suitable for heating residential and administrative premises.
Price - from 2560 rubles.
Prices for bimetallic heating radiators Radena
Radena bimetallic heating radiators
Rifar
Products manufactured under the Rifar brand are in demand for central heating systems. The company constantly conducts technical monitoring, therefore it promptly expands its range and produces new accessories. For a large and poorly insulated room, the Base 500 model is ideal. Monolithic products with thin fins are not only durable, but also highly efficient.
The Base 200 model, in turn, can be easily combined with French windows thanks to the closed rear surface of the sections. Only specially prepared water serves as the coolant. Warranty period – 10 years. Price - from 6800 rubles.
Prices for bimetallic heating radiators Rifar
bimetallic heating radiators Rifar
Fondital
Products manufactured under this name are not only reliable and affordable, but also save energy. The company is expanding production facilities and automating installations. This makes it possible to produce lightweight and economical devices with minimal heat inertia.
Each model has a special design suitable for living spaces. If necessary, you can increase the number of sections, making heating even more efficient. Bimetal can easily withstand pressure up to 40 bar and can be used in central heating systems with aggressive coolant.
Price - from 4680 rubles.
Global
Global is an Italian manufacturer of sectional batteries. The range consists of two models: Global Style and Global Style Plus - both are installed in modern engineering systems. They can use antifreeze as a coolant. The devices are ideal for centralized heating systems.
At the top of the radiator there is a convection window that improves heat transfer and prevents overheating. Powder paint is used to paint equipment, which is resistant to moisture and mechanical damage.
Price - from 8400 rubles.