Temperature standards
Requirements for the temperature of the coolant are set out in documents that specify the standards that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State Construction Standards and Rules:
- DBN (V. 2.5-39 Heating networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 “Heat supply, ventilation and air conditioning system.”
For the calculated supply water temperature, the figure that is equal to the temperature of the water leaving the boiler, according to its passport details, is accepted.
For autonomous heating, it is necessary to decide what the temperature of the coolant should be, taking into account the following factors:
- Beginning and ending of the heating season based on the daily average outdoor temperature of +8 °C for 3 days;
- The average temperature inside heated residential and public buildings should be 20 °C, and for industrial buildings 16 °C;
- The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 “Heat supply, ventilation and air conditioning system” (clause 3.20), the limit values of the coolant are as follows:
- For a clinic - 85 °C (excluding psychiatric and drug departments, as well as administrative or home use premises);
- For residential, public, and also domestic buildings (not counting halls for sports, trade, spectators and passengers) - 90 ° C;
- For auditoriums, restaurants and premises for production of categories No and B – 105 °C;
- For catering companies (excluding restaurants) it is 115 °C;
- For production premises (categories B, D and D), where flammable dust and aerosols are emitted – 130 °C;
- For staircases, lobbies, pedestrian crossings, technical premises, residential buildings, industrial premises without the presence of flammable dust and aerosols – 150 °C.
Depending on external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 °C, dust and varnish begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit greater heating.
To calculate good indicators, specialized graphs and tables can be used, which set standards depending on the season:
- With an average reading outside the window of 0 °C, the supply for heating devices with different wiring is set at 40 to 45 °C, and the return temperature at 35 to 38 °C;
- At -20 °C, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °C, and the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °C;
- At -40 °C outside the window, absolutely all heating systems are set to the maximum possible values. On the supply side it is from 95 to 105 °C, and on the return side it is 70 °C.
Central heating
How does an elevator unit work?
At the elevator entrance there are valves that cut it off from the heating main. Along their flanges closest to the wall of the house, there is a division of areas of responsibility between homeowners and heat suppliers. The second pair of valves cuts off the elevator from the house.
The supply pipe is always at the top, the return pipe is always at the bottom. The heart of the elevator unit is the mixing unit, in which the nozzle is located. A stream of hotter water from the supply pipe flows into the water from the return pipe, drawing it into a repeated circulation cycle through the heating circuit.
By adjusting the diameter of the hole in the nozzle, you can change the temperature of the mixture entering the.
Strictly speaking, an elevator is not a room with pipes, but this unit. In it, supply water is mixed with return water.
What is the difference between the supply and return pipelines of the route?
In normal operation it is about 2-2.5 atmospheres. Typically, 6-7 kgf/cm2 enters the house on the supply side and 3.5-4.5 on the return side.
What is the difference in the heating system
The difference on the highway and the difference in the heating system are two completely different things. If the return pressure before and after the elevator does not differ, then instead of supply, a mixture is supplied to the house, the pressure of which exceeds the readings of the pressure gauge on the return by only 0.2-0.3 kgf/cm2. This corresponds to a height difference of 2-3 meters.
This difference is spent to overcome the hydraulic resistance of bottlings, risers and heating devices. Resistance is determined by the diameter of the channels through which water moves.
What diameter should be the risers, fillers and connections to radiators in an apartment building?
The exact values are determined by hydraulic calculation.
In most modern houses the following sections are used:
- Heating outlets are made from pipes DN50 - DN80.
- For risers, a pipe DN20 - DN25 is used.
- The connection to the radiator is made either equal to the diameter of the riser, or one step thinner.
The photo shows a more sensible solution. The diameter of the liner is not underestimated.
What to do if the return temperature is too low
In such cases:
- The nozzle is drilled out
. Its new diameter is agreed with the heat supplier. An increased diameter will not only raise the temperature of the mixture, it will also increase the drop. The circulation through the heating circuit will speed up. - In the event of a catastrophic lack of heat, the elevator is disassembled, the nozzle is removed, and the suction (pipe connecting the supply to the return) is turned off. The heating system receives water directly from the supply pipe. Temperature and pressure drop increase sharply.
What to do if the return temperature is too high
- The standard measure is to weld the nozzle and re-drill it, with a smaller diameter.
- When an urgent solution is needed without stopping the heating, the difference at the entrance to the elevator is reduced with the help of shut-off valves. This can be done with an inlet valve on the return line, controlling the process using a pressure gauge. This solution has three disadvantages:
- The pressure in the heating system will increase. After all, we limit the outflow of water; the lower pressure in the system will become closer to the supply pressure.
The wear of the cheeks and valve stem will accelerate sharply: they will be in a turbulent flow of hot water with suspensions.
- There is always the possibility of worn cheeks falling. If they completely shut off the water, the heating (primarily the access heating) will defrost within two to three hours.
Why do you need high pressure in the line?
Indeed, in private houses with autonomous heating systems, an excess pressure of only 1.5 atmospheres is used. And, of course, more pressure means much higher costs for stronger pipes and power supply for injection pumps.
The need for greater pressure is associated with the number of floors in apartment buildings. Yes, circulation requires a minimum drop; but the water needs to be raised to the level of the jumper between the risers. Each atmosphere of excess pressure corresponds to a water column of 10 meters.
Knowing the pressure in the line, it is not difficult to calculate the maximum height of a house that can be heated without the use of additional pumps. The calculation instructions are simple: 10 meters multiplied by the return pressure. A return pipeline pressure of 4.5 kgf/cm2 corresponds to a water column of 45 meters, which, with a height of one floor of 3 meters, will give us 15 floors.
By the way, hot water supply in apartment buildings is supplied from the same elevator - from the supply (at a water temperature of no higher than 90 C) or return. If there is a lack of pressure, the upper floors will remain without water.
Good values in a personal heating system
Individual heating helps to avoid most of the problems that arise with a centralized network, and the comfortable temperature of the coolant can change according to the season. In the case of autonomous heating, the concept of norms includes the heat output of the heating device per unit area of the room where the device is located. The heat regime in this situation is ensured by the design characteristics of the radiators.
The main thing is to ensure that the coolant in the network does not cool below 70 °C. A value of 80 °C is considered good. With a gas water heater, it is easier to control heating, since manufacturers limit the possibility of heating the coolant to 90 °C. By using sensors to regulate the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be adjusted.
It is a little more difficult with solid fuel devices; they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And in such a situation it is unrealistic to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob. Control of heating of the coolant is quite relative with high errors and is done using rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Boilers powered by electricity allow you to slowly adjust the heating of the coolant from 30 to 90 °C. They are equipped with a good overheating protection system.
Parameter control methods
System regulation Heating can be adjusted. Methods:
- quantitative;
The parameters are changed by increasing or decreasing the amount of coolant supplied. Pumps increase the pressure in the system, valves reduce the speed of the carrier.
- qualitative;
With quality, the parameters of the coolant change, additives are added that change the characteristic indicators.
- mixed.
Uses both methods.
Method for reducing heat loss
The first, main condition for reducing heat loss is good thermal insulation.
The system needs to be optimized. Adjust a comfortable temperature inside living rooms, follow the recommendations for temperature conditions in utility and non-residential premises.
Comfort in home
Coordination of coolant and boiler temperatures
Regulators help set the temperature of the coolant and boiler. These are devices that form automated control and adjustment of supply and return temperatures.
The return temperature depends on the amount of liquid passing through it. Regulators cover the liquid supply and increase the difference between supply and return to the level that is necessary, and the necessary indicators are placed on the meter.
If it is necessary to expand the flow, an increase pump can be added to the network, which is controlled by a regulator. To reduce the heating of the supply, a “cold start” is used: that part of the liquid that has passed through the network is again transported from the return to the inlet.
The regulator redistributes the supply and return flows based on the data collected by the meter, and ensures the strict temperature standards of the heating network.
Factors influencing blood pressure
Measuring instruments in the elevator unit room note any disruption in the supply or drainage of water from the building.
Increased pressure in the heating radiators of an apartment building can be created by the following factors:
- the temperature of the hot resource is too high compared to the established norm;
- the diameter of the pipe distribution was reduced due to unauthorized reconstruction by residents of the apartment heating scheme;
- formation of air jams in the end radiators of floors;
- the use of centrifugal pumps of greater power than provided for in the plan;
- part of the system is not working or is blocked.
A decrease in agent pressure also indicates a problem with the heating circuit.
When the pressure drops, you need to pay attention to the following possible aspects:
- emergency situations when supply pipelines rupture;
- malfunction or unsatisfactory operation of the circulation pump;
- failure of the safety unit;
- rupture of the expansion tank resonator.
Silting or clogging of the filter in front of the elevator unit also contributes to a drop in pressure.
A leak
The leakage of water from the heating circuit is the most common factor in reducing the pressure of the coolant. Most often, ruptures occur at the junction of pipes with the boiler and heating equipment.
A break is also possible in other arbitrary places if the owner of the apartment or house did not conduct a visual inspection before the start of the season, or installed defective elements.
A hot agent leak can occur in several ways:
- Through a rupture in the diffuser of the expansion tank. Such an accident cannot be visually determined due to the presence of water inside the container. To check, you need to press your finger on the valve that pumps air into the tank. When water leaks out of the spool, we can talk about a membrane crack.
- When the resource boils in the heat exchanger, through the relief valve.
- Microcracks, corroded areas of measuring instruments, and loose connections can also contribute to a drop in pressure and leakage of water.
The surest way to determine a possible leak is to turn off the circulation pump. The static pressure indicator will differ from the calculated characteristics.
Air outlet
After filling the artificial heating system with water, its pressure decreases when air leaves the circuit. Pre-boiler preparation - deaeration of water with chemical reagents - will help to avoid this problem.
The latter reduce the amount of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the coolant to the calculated level. The heating circuit is filled with a slow supply from below - through the relief valve, with cold water.
Aluminum radiators
Installing lightweight batteries - aluminum, leads to the reaction of oxygen with the metal, thereby forming an oxidizing film. The released hydrogen leaves through an automatic air vent.
A similar process is often observed in newly installed aluminum batteries, and the reaction stops after the film covers the entire internal surface of the radiator
Therefore, when installing new heating equipment, you should pay attention to the fact that the pressure in the central heating may drop and the volume of the thermal agent will have to be supplemented
Ways to reduce heat loss
The above information will help to be used for professional calculation of the coolant temperature norm and will recommend how to determine situations when it is necessary to use a regulator.
However, it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is influenced not only by the temperature of the coolant, the air from the street and the strength of the wind. The degree of facade insulation, windows and doors in the house should also be provided for.
To reduce heat loss from your home, you need to take care of its maximum thermal insulation. Thermally insulated walls, sealed doors, and plastic windows can help reduce heat loss. This will also reduce heating costs.
Normative base
Ensuring optimal thermal conditions in a room is based on several regulatory documents. Here are the most important ones:
Attention! If you have any questions, you can chat for free with a lawyer at the bottom of the screen or call Moscow; Saint Petersburg; Free call for all of Russia
- Federal Law dated 07.12.11 No. 416-FZ in Art. 7 (Chapter No. 3) fixes the general provisions of the rules on the basis of which the thermal regime in buildings is regulated.
- Government Resolution No. 354, adopted on 05/06/11. The “Rules for the Provision of Utility Services” approved by him fix the standards for the supply of thermal energy to owners and users of residential real estate and premises in apartment buildings.
Attention Based on these documents, management companies are engaged in the acquisition of thermal energy and collecting fees from owners to pay for supplies. The provisions are disclosed in more detail in the agreement between the heat supplier and the management company, as well as in the internal instructions of the management company
However, they cannot contradict basic regulatory documents approved at the federal level.
It is no less important than the presentation! Heating system return: what is it?
The strength and productivity of a heating system depends on the good performance of all parts included in it.
These include : a boiler for heating the coolant, heating devices connected to it and to each other in a certain way, an expansion tank, a circular pump, shut-off and control valves, pipe wire of the required diameter.
Creating very efficient heating system is possible thanks to specialized knowledge and experience in this area of life. The return pipe wire plays a very important role in the heating process of the room.
With forced circulation
This system is divided into two types:
The difference between them is quite big. The layout of the pipes, their number, and the sets of shut-off, control and control valves differ.
According to SNiP 41-01-2003 (“Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”), the maximum coolant temperature in these heating systems is:
- two-pipe heating system - up to 95°C;
- single-pipe - up to 115°C;
The optimal temperature is from 85°C to 90°C (due to the fact that at 100°C, water already boils. When this value is reached, special measures must be used to stop boiling).
The amount of heat emitted by the radiator depends on the installation location and the method of connecting the pipes. Thermal output can be reduced by 32% due to poor pipe placement.
The best option is a diagonal connection, when hot water comes from the top and return flow from the bottom of the opposite side. This is how radiators are tested during testing.
The worst thing is when hot water comes from below, and cold water comes from above on the same side.
Types of heating schemes
For buildings with several floors, a single-pipe direct distribution system is sometimes used. It does not have a clear division of pipes into the supply of liquid to the heating devices and the return, thanks to which the complete circuit is figuratively divided into two identical parts. The riser coming out of the boiler is called the supply, and the pipes coming out of the last heating device are called the return. The advantages of this scheme:
- saving time and financial costs;
- convenience and simplicity of installation work;
- beautiful view;
- the absence of a return riser and the methodical placement of heating devices (the coolant is supplied to the 1st, after the 2nd, 3rd and so on ).
For a single pipe system, a vertical wiring design with a vertical circuit and heat supply from above is popular.
With a two-pipe wiring system, we mean the installation of two closed, parallel-connected circuits, one of them provides the function of supplying the heat carrier to the device for heating the room (heat exchanger), the second - the function of its removal (return).
Heating devices are connected in several ways:
- Lower (or saddle, crescent-shaped). Takes into account the connection of the supply and return to the lower connecting holes of the heating device. An air vent and a plug are installed on the upper holes. Used for systems in which pipes are hidden under the floor or baseboard. Suitable for multi-section heating devices; with a small number of sections, heat loss reaches up to 15%.
- The lateral method is popular. The pipes are connected to the heat exchanger on one side: the heat carrier supply is through the top, the return line is through the bottom. Not suitable for devices with a large number of sections.
Photo 2. Heating circuit with two pipes with a side connection type. The supply and return temperatures are indicated.
- The diagonal (or lateral cross ) method involves supplying hot water from above, connecting the return line from below and on the other side. Suitable for heating devices with at least 14 sections.
- The third option for organizing a heating circuit is considered a hybrid method, which is based on the simultaneous use of one-pipe and two-pipe systems. For example, the collector circuit involves supplying a heat carrier through a single riser; subsequent on-site wiring is carried out according to an individual plan.
Working principle on how to increase productivity
A single circuit does not provide equal heating of the radiators; heat transfer decreases as it moves away from the boiler (the latter heating devices receive coolant cooler than the first ones). The disadvantage of such a system is the high pressure values of the coolant.
Reference. The productivity of a single pipe system increases if there is a bypass or circulation pumps formed on each floor.
Advantages of the two-pipe heat supply option:
- heating the required number of devices in the same way, regardless of their distance to the heat source;
- adjusting the temperature regime, carrying out repair activities on an individual device does not affect the operation of others.
Minuses:
- complexity of the wiring diagram;
- complexity of installation and connection.
The most productive system of two pipes, which is also often selected for heating luxury housing, is considered an excellent choice for private construction
The process of installing a two-pipe type system is best carried out with the installation of a circulation pump, which makes it possible to use pipes of smaller diameter.
After it, in order to protect the recirculation circuit from squeezing, a check valve is installed.
When installing a system without a bypass, the rule is followed : supply is possible if there is a slope from or to the boiler. A coolant with a higher temperature enters the heating device through the inlet (Slope from the boiler to the device for heating the room) and heats it, and then exits through the return (Slope from the heating device to the boiler), but with a lower temperature. Qualified craftsmen often resort to replacing the recirculation pump ring with a system of 3 or 4-way mixing devices.
Main! With gravitational circulation, the entire pipe line from the riser to the heating devices does not have to be long.
Specifics
Long-term operation of boiler room equipment is possible with a properly designed pipe branching system, which provides some kind of temperature difference between the pipes supplying and discharging the coolant.
Attention! The presence of a fundamental difference in temperature values is considered the basis for the formation of abundant condensation on the firebox.
Drops of water, especially in combination with carbon monoxide formed during fire (in the case of equipment operating on solid fuel), quickly corrode the walls of the chamber, the impermeability of the main element is broken, and the boiler fails.
An acceptable solution in this situation is to connect an additional water heating device - an electric water heater. It is placed next to the boiler in a special way so that the coolant, having passed through all the devices of the system, enters it and then into the boiler.
Photo 3. Heating system with a storage water heater to heat the water. The device is placed next to a gas water heater.
Why is it hot in the kitchen and freezing in the bedroom? Adjusting heating radiators in an apartment
- Central heating systems, which are installed in multi-storey buildings , are often based on coolants, where the supply occurs strictly vertically from top to bottom. In such houses, it is hot on the upper floors and cold on the lower floors, so it will not be possible to adjust the heating level accordingly.
- If houses use a single-pipe network , then heat from the central riser is supplied to each battery and returned back, which ensures uniform heat on all floors of the building. In such cases, it is easier to install heat control valves - the installation takes place on the supply pipe and the heat continues to spread evenly.
- For a two-pipe system, two risers are already installed - heat is supplied to the radiator and in the opposite direction, respectively, the adjustment valve can be installed in two places - on each of the radiators.
- the system operates from an individual boiler ;
- a special three-way valve was installed ;
- The coolant is forcibly .
How different should the rhythm of feed and return be?
Why “should it be 45...55”? What if I heat the house with warm walls and floors? – at 55 you can already boil the eggs (softened). What if I have small (baseboard) heating appliances? - at 45 you will freeze even today.
“45...55” are ordinary stereotypes of thinking, formed on the usual diagram of heating devices such as “1 elbow per 2 m2”.
Less is better. However, it will be completely “0” only if there is absolutely no heat transfer (heating). You can switch the pump to mode 2 or even 1.
A delta of 20 degrees is considered wonderful. However, if this mouth does not exist and the batteries are hot, then this is also good. This means that the battery power is less than the boiler power. And the uncooled water goes back to the boiler. So in your case, the boiler will turn on less often (it already receives hot water). You can reduce the flow rate. Then the delta will be higher, but the boiler will also turn on more often. Strictly speaking, if heat loss in the pipes is neglected, the efficiency of the system will not change. The amount of energy the boiler consumes will increase the temperature in the house. So what?
I have a solid fuel boiler, it does not turn off and will not turn on either)))
By hand kmk less than 20 degrees.
Well, this is when it already goes out. Although I can set the electric boiler to 65 degrees. It will warm up
And by the way, why is it not recommended what to do when it’s already completely burned out, turn off the supply to it and wait until it boils.
And below there is condensation, and it is very angry with firewood (sulfur, and ultimately sulfuric acid). Accelerated rust of the pipe coil. It's not very scary for cast iron. And steel can “eat up” in a season or two (there were posts on SOK). When it has already burned out, there are no problems - there is no more condensation. But at the kindling step - well, maybe for quite a long time - the boiler itself is cold + the return flow is cool. That is why they provide protection against cold return in the form of a controlled circular pump directly on the boiler piping. It does not stop working very simply: until the return temperature reaches +65°C, the water moves in a small circle (almost like a thermostatic valve in a car). Most manufacturers build a circular pump directly into the boiler.
Data. Solid fuel 25 kW on coal. On wood I think below.
The heated area is 100 sq.m. There is no insulation of any 15 cm timber, the floors and ceilings are actually 20 cm of cotton wool)), not caulked. There are 8 design radiators with a total power of approximately 12 kW. And an indirect heating water heater is connected. But DHW is not consumed much, so it does not play a significant role in the calculation (I turn it off altogether, when the boiler has cooled down, the indirect heating water heater will also cool down (( )
And I wouldn’t say that it’s very warm in my large rooms. You can't breathe in the bathroom or bedroom. But in the living room and kitchen room it’s so-so, 20 degrees, but I’d like 25)) But all approaches to design radiators are hot.
PS there are suspicions that this is what heats up, but in general it sucks.
In an apartment, I would throw it away))) but on a summer cottage you need 15 of them. It turns out to be expensive, but these are very cheap.
Maybe change to cast iron, or leave it as is for now.
Something practically free no matter what. I have about 1 heating device that costs 5 thousand. In the end there are 2 pieces, plus thermal and connection, etc. and TP)))
I know Denis, but what’s the point, he won’t honor the 70% discount))))
How to make radiators hot, looking for solutions
If you find that the return is too cold, you should take a number of steps to find the causes and troubleshoot problems. First of all, you need to check that the connection is correct. If the connection is not made correctly, the down pipe will be hot when it should be slightly warm. The pipes should be connected according to the diagram.
To avoid air pockets that impede the flow of coolant, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a Mayevsky valve or bleeder for air removal. Before bleeding the air, you need to turn off the supply, open the tap and let out the air. Then the tap is turned off and the heating valves open.
Often the cause of cold return is the control valve: the cross-section is narrowed. In this case, the tap must be dismantled and the cross-section increased using a special tool. But it is better to buy a new faucet and replace it.
The reason may be clogged pipes. You need to check them for passability, remove dirt and deposits, and clean them well. If passability cannot be restored, the clogged areas should be replaced with new ones.
If the coolant flow rate is insufficient, you need to check whether there is a circulation pump and whether it meets the power requirements. If it is missing, it is advisable to install it, and if there is a lack of power, replace or upgrade it.
Knowing the reasons why heating may not work efficiently, you can independently identify and eliminate malfunctions. Comfort in the house during the cold season depends on the quality of heating. If you carry out the installation work yourself, you can save on hiring third-party labor.
When autumn confidently strides across the country, snow is flying above the Arctic Circle, and in the Urals night temperatures stay below 8 degrees, then the word form “heating season” sounds appropriate. People remember past winters and try to understand the normal temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
Prudent owners of individual buildings carefully inspect the valves and nozzles of boilers. By October 1, residents of an apartment building are waiting like Santa Claus for a plumber from the management company. The Lord of valves and valves brings warmth, and with it joy, fun and confidence in the future.
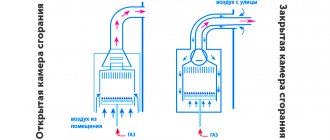
Why is a valve needed?
The correct design of a heating system is developed taking into account the difference in temperature values in the coolant supply and return pipes.
Often, instead of installing a boiler, another protection option is used that ensures long-term operation of solid fuel boiler equipment.
It helps to connect a bypass , which is a specially embedded pipe that allows the cooled coolant to change the direction of movement around the boiler.
The bypass ensures circulation of the coolant through the so-called small circuit. When forming this circuit, a thermostatic or three-way valve is installed at the junction of the bypass and return .