Published on April 08, 2014 Category: Heat engineering |
Heating systems for buildings, heating mains, water pipelines, drainage systems, hydraulic circuits of machines and machines - all these are examples of systems consisting of pipelines. Hydraulic calculation of pipelines - especially complex, branched...
... is a very difficult and cumbersome task. Today, in the age of computers, solving it has become much easier when using special software. But good special programs are expensive and, as a rule, only hydraulic specialists have them.
In this article we will look at the hydraulic calculation of pipelines using the example of calculating in Excel a horizontal section of a pipeline of constant diameter using two methods and compare the results obtained. For “non-specialists”, the use of the program presented below will allow you to solve simple “everyday” and production problems. For specialists, these calculations can be used as tests or for making quick, simple estimates.
As a rule, hydraulic calculation of pipelines includes solving two problems:
1. During the design calculation, it is necessary to find the pressure loss in the pipeline section under consideration based on the known liquid flow rate. (Pressure loss is the difference in pressure between the entry point and the exit point.)
2. When performing a verification calculation (during an audit of existing systems), it is required to calculate the flow rate of liquid passing through the pipeline using a known pressure drop (the difference in pressure gauge readings at the inlet to the pipeline and at the outlet).
Let's start solving the first problem. You can easily solve the second problem yourself using the MS Excel “Parameter Selection” service. How to use this service is described in detail in the second half of the article “Transcendental Equations? “Parameter selection” in Excel!”
The following calculations in Excel can also be performed in the OOo Calc program from the free Open Office package.
The rules for color formatting Excel worksheet cells, which are used in the articles in this blog, are described in detail on the “ About the Blog ” page.
Reducing gas consumption
Saving gas is directly related to reducing heat loss. Enclosing structures such as walls, ceilings, and floors in the house must be protected from the influence of cold air or soil. Automatic adjustment of the operation of heating equipment is used for the effective interaction of the external climate and the operating intensity of the gas boiler.
Insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings
You can reduce gas consumption by insulating the walls.
The outer heat-protective layer creates a barrier to cooling surfaces in order to consume the least amount of fuel.
Statistics show that part of the heated air escapes through structures:
- roof - 35 - 45%;
- non-insulated window openings - 10 - 30%;
- thin walls - 25 - 45%;
- entrance doors - 5 - 15%.
Floors are protected with a material that has acceptable moisture permeability according to the norm, since when wet, the thermal insulation characteristics are lost. It is better to insulate the walls from the outside; the ceiling is insulated from the attic side.
Window replacement
Plastic windows let in less heat in winter
Modern metal-plastic frames with double- and triple-glazed windows do not allow air flow to pass through and prevent drafts. This leads to a reduction in losses through the gaps that existed in old wooden frames. For ventilation, tilt-and-turn mechanisms are provided for the doors, which contribute to the economical consumption of internal heat.
The glass in the structures is covered with a special energy-saving film, which allows ultraviolet and infrared rays to pass through, but prevents their reverse penetration. The glass is equipped with a network of elements that heat the area to thaw snow and ice. Existing frame structures are additionally insulated with plastic film on the outside or thick curtains are used.
other methods
It is beneficial to use modern gas-fuelled condensing boilers and install an automated coordination system. Thermal heads are installed on all radiators, and a hydraulic arrow is mounted on the unit’s piping, which saves 15–20% of heat.
Example initial conditions
For a more specific explanation of all the details of the hydraulic calculation, let’s take a specific example of an ordinary living space. We have a classic 2-room apartment in a panel house with a total area of 65.54 m2, which includes two rooms, a kitchen, separate toilet and bathroom, a double corridor, a twin balcony.
After commissioning, we received the following information regarding the readiness of the apartment. The described apartment includes walls made of monolithic reinforced concrete structures treated with putty and primer, profile windows with two-chamber glass, pressed interior doors, ceramic tiles on the bathroom floor.
A typical 9-storey panel house with four entrances. There are 3 apartments on each floor: one 2-room and two 3-room. The apartment is located on the fifth floor
In addition, the presented housing is already equipped with copper wiring, distributors and a separate panel, a gas stove, a bathtub, a washbasin, a toilet, a heated towel rail, and a sink.
And most importantly, the living rooms, bathroom and kitchen already have aluminum heating radiators. The question regarding the pipes and boiler remains open.
Calculation example
An example of performing hydraulic calculations using a program for low-pressure gas pipelines is given. In the proposed table, all the data that the designer must enter independently is highlighted in yellow.
These are listed in the paragraph on computer hydraulic calculations above. These are gas temperature, kinetic viscosity coefficient, and density.
In this case, calculations are carried out for boilers and stoves; therefore, it is necessary to specify the exact number of burners, which can be 2 or 4. Accuracy is important, because the program will automatically select the simultaneity coefficient.
In the picture, the columns in which the indicators must be entered by the designer himself are highlighted in yellow. Below is the formula for calculating the flow rate on the site
It is worth paying attention to the numbering of sections - they are not invented independently, but are taken from a previously drawn up diagram, where similar numbers are indicated. Next, the actual length of the gas pipeline and the so-called calculated length are written down, which is greater
This happens because in all areas where there is local resistance, it is necessary to increase the length by 5-10%. This is done in order to prevent insufficient gas pressure among consumers. The program does the calculations on its own
Next, the actual length of the gas pipeline and the so-called calculated length, which is longer, are written down. This happens because in all areas where there is local resistance, it is necessary to increase the length by 5-10%. This is done in order to prevent insufficient gas pressure among consumers. The program performs the calculations independently.
The total consumption in cubic meters, for which a separate column is provided, at each site is calculated in advance. If the building is multi-apartment, then you need to indicate the number of housing, starting from the maximum value, as can be seen in the corresponding column.
It is mandatory to enter into the table all elements of the gas pipeline, during the passage of which pressure is lost. The example shows a thermal shut-off valve, a shut-off valve and a meter. The value of the loss in each case was taken from the product passport.
Using one program you can make calculations for all types of gas pipelines. The picture shows calculations for a medium pressure network
The internal diameter of the pipe is indicated according to the technical specifications, if the gas company has any requirements, or from a previously drawn up diagram. In this case, in most areas it is prescribed at a size of 5 cm, because most of the gas pipeline runs along the facade, and the local city gas requires that the diameter be no less.
If you even superficially familiarize yourself with the given example of performing a hydraulic calculation, it is easy to notice that, in addition to the values entered by a person, there are a large number of others. This is all the result of the program, since after entering the numbers in the specific columns highlighted in yellow, the calculation work is completed for the person.
That is, the calculation itself occurs quite quickly, after which the received data can be sent for approval to the city gas department of your city.
Are there free calculation programs?
To simplify the calculation of the heating system of a private house, you can use special programs. Of course, there are not as many of them as graphic editors, but there is still a choice. Some are distributed free of charge, others in demo versions. In any case, it will be possible to make the necessary calculations once or twice without any material investments.
Oventrop CO software
The free software "Oventrop CO" is designed to perform hydraulic calculations for heating a country house.
Oventrop CO was created to provide graphical assistance during the heating design phase. It allows you to perform hydraulic calculations for both one-pipe and two-pipe systems. Working in it is simple and convenient: there are ready-made blocks, error control is provided, and a huge catalog of materials
Based on preliminary settings and selection of heating devices, pipelines and fittings, new systems can be designed. In addition, it is possible to adjust the existing circuit. It is carried out by selecting the power of existing equipment in accordance with the needs of heated rooms and premises.
Both of these options can be combined in this program, allowing you to adjust existing fragments and design new ones. For any calculation option, Oventrop CO selects the valve settings. In terms of performing hydraulic calculations, this program has wide capabilities: from selecting pipeline diameters to analyzing water flow in equipment. All results (tables, diagrams, drawings) can be printed or transferred to the Windows environment.
Software "Instal-Therm HCR"
The "Instal-Therm HCR" program allows you to calculate radiator and surface heating systems.
It comes with the InstalSystem TECE kit, which includes three more programs: Instal-San T (for designing cold and hot water supply), Instal-Heat&Energy (for calculating heat losses) and Instal-Scan (for scanning drawings).
The “Instal-Therm HCR” program is equipped with expanded catalogs of materials (pipes, water consumers, fittings, radiators, thermal insulation and shut-off and control valves). The calculation results are presented in the form of specifications for the materials and products offered by the program. The only drawback of the trial version is that it cannot be printed.
Computing capabilities of "Instal-Therm HCR": - selection by diameter of pipes and fittings, as well as tees, fittings, distributors, bushings and pipeline thermal insulation; — determination of the lifting height of pumps located in the mixers of the system or on the site; — hydraulic and thermal calculations of heating surfaces, automatic determination of the optimal inlet (supply) temperature; — selection of radiators taking into account cooling in the pipelines of the working fluid.
The trial version is free to use, but it has a number of limitations. Firstly, as with most shareware programs, the results cannot be printed, nor can they be exported. Secondly, only three projects can be created in each application of the package. True, you can change them as much as you like. Thirdly, the created project is saved in a modified format. Files with this extension will not be read by any other trial or even standard version.
Influence of pipe material on calculation
For the construction of gas pipelines, you can use pipes made only from certain materials: steel, polyethylene. In some cases, copper products are used. Metal-plastic structures will soon be widely used.
Each pipe has a roughness, which leads to linear resistance, which affects the process of gas movement. Moreover, this figure is significantly higher for steel products than for plastic ones.
Today, the necessary information can only be obtained for steel and polyethylene pipes. As a result, design and hydraulic calculations can only be carried out taking into account their characteristics, which is required by the relevant Code of Practice. The document also contains the data necessary for the calculation.
The roughness coefficient is always equal to the following values:
- for all polyethylene pipes, regardless of whether they are new or not, - 0.007 cm;
- for already used steel products - 0.1 cm;
- for new steel structures - 0.01 cm.
For any other types of pipes this indicator is not indicated in the Code of Practice. Therefore, they should not be used for the construction of a new gas pipeline, since Gorgaz specialists may require adjustments to be made. And these are again additional costs.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Features, advantages and disadvantages of natural and forced coolant circulation systems for heating systems:
Summarizing the hydraulic calculations, the result was specific physical characteristics of the future heating system.
Naturally, this is a simplified calculation scheme that provides approximate data regarding hydraulic calculations for the heating system of a typical two-room apartment.
Are you trying to do a hydraulic calculation of your heating system yourself? Or maybe you don’t agree with the material presented? We are waiting for your comments and questions - the feedback block is located below.
Hydraulic calculation of pipelines in Excel using SNiP 2.04.02-84 formulas.
This calculation determines friction losses in pipelines using empirical formulas without taking into account the coefficients of local resistance, but taking into account the resistance introduced by the joints.
On long pipelines, such as water supply and heating mains, the influence of local resistance is small compared to the roughness of the pipe walls and height differences, and often the coefficients of local resistance can be neglected in evaluation calculations.
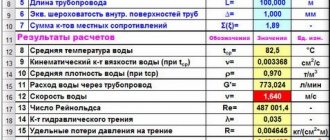
Initial data:
d and the length of the pipeline L previously entered in the previous calculation , as well as the calculated value of the water velocity v .
1.
Select the type of pipe from the drop-down list located above cells A30...E30:
New steel and new cast iron without internals. protective coating or with bitumen protective coating, v > 1.2 m/s
Calculation results:
Based on the selected type of pipe, Excel automatically extracts the values of empirical coefficients from the database table. The database table, taken from SNiP 2.04.02–84, is located on the same “CALCULATION” worksheet.
2.
The coefficient
m
is extracted
to cell D32: =INDEX(H31:H42,H29) =0,300
3.
Coefficient
A
is extracted
to cell D33: =INDEX(I31:I42,I29) =1,000
4.
Factor
1000 A 1
is extracted
to cell D34: =INDEX(J31:J42,J29) =21,000
5.
A factor of
1000 A 1 /(2 g )
is extracted
to cell D35: =INDEX(K31:K42,K29) =1,070
6.
Coefficient
C
is extracted
to cell D36: =INDEX(L31:L42,L29) =0,000
7.
The coefficient of hydraulic resistance
i
in m.water column/m is calculated
in cell D37: =D35/1000*((D33+D36/D16)^D32)/((D7/1000)^(D32+1))*D16^2 =0,057
i=((1000A1/(2g))/1000)*(((A0+C/v)m)/((d/1000)(m+1)))*v2
8.
The calculated pressure loss in the pipeline
dP
in kg/cm2 and Pa is found accordingly
in cell D38: =D39/9.81/10000 =0,574497
dP = dP/ 9.81 10000
and in cell D39: =D37*9.81*1000*D8 =56358,1
dP = i * 9.81 *1000* L
Hydraulic calculation of the pipeline using the formulas of Appendix 10 SNiP 2.04.02–84 in Excel is completed!
Calculation of water volume and capacity of the expansion tank
The volume of the expansion tank must be equal to 1/10 of the total volume of liquid.
To calculate the performance characteristics of the expansion tank, which is mandatory for any closed-type heating system, you will need to understand the phenomenon of increasing the volume of liquid in it. This indicator is assessed taking into account changes in basic operating characteristics, including fluctuations in its temperature. In this case, it varies over a very wide range - from room temperature +20 degrees and up to operating values within 50-80 degrees.
It will be possible to calculate the volume of the expansion tank without unnecessary problems if you use a rough estimate proven in practice. It is based on equipment operating experience, according to which the volume of the expansion tank is approximately one tenth of the total amount of coolant circulating in the system
In this case, all its elements are taken into account, including heating radiators (batteries), as well as the water jacket of the boiler unit. To determine the exact value of the required indicator, you will need to take the passport of the equipment being used and find in it items relating to the capacity of the batteries and the working tank of the boiler
Once they are determined, it is not difficult to find excess coolant in the system. To do this, first calculate the cross-sectional area of polypropylene pipes, and then multiply the resulting value by the length of the pipeline. After summing up all branches of the heating system, the figures for radiators and boiler taken from the passport are added to them. One tenth is then subtracted from the total amount.
Gas supply to residential buildings
The use of gas for heating residential buildings and heating water in the warm season has become possible due to the relatively low cost of this fossil.
After undergoing primary processing, it is cleared of mechanical impurities and chemical additives. Thanks to a wide network of gas pipelines, it can be obtained in any locality and delivered to every home.
Scope of application of natural gas in residential buildings:
- Cooking food
- Heating water in the absence of central hot water supply
- Heating in the cold season
Cooking food. Most homes have gas stoves for cooking. They gained popularity not so much from the price of the stoves, but from the cost of fuel, ease of connection, and uninterrupted supply.
The advantages of gas stoves include ease of operation and low cost of maintenance and repair.
Heating water. The use of natural fuel to heat water in homes became popular in the middle of the last century.
A huge advantage of these systems was the presence of an already supplied source of natural gas to apartments and houses.
A serviceable and adjusted column provided stable hot water for the needs of each consumer in the absence of a central hot water supply.
Heating. This type of gas use has found wide application in private homes where central heating is not practical.
Each consumer, having an existing gas supply system in their arsenal, installed a heating boiler for their needs.
Depending on the area of the house, a boiler was purchased and a heat distribution system was installed throughout the house.
The consumer himself chose the temperature in his home depending on weather conditions and, accordingly, gas consumption.
Automation of pumping equipment
To function properly, such pumps must consume electricity. Today, electricity is not cheap, so many people are thinking about how to make the pump more economical in terms of energy consumption.
Installing a heating system in a private home is a necessary and extremely important task when you want to create the most comfortable temperature conditions for living in it. The most efficient heating unit is a piping with forced circulation of coolant through the main line. To achieve this task, the system should be retrofitted with a pumping unit
The only problem is that it is necessary to select such equipment in terms of performance, because the efficiency of the entire circuit depends on this. You will learn how to correctly calculate the power of a circulation pump for heating in this article.
To achieve this task, the system should be retrofitted with a pumping unit. The only problem is that it is necessary to select such equipment in terms of performance, because the efficiency of the entire circuit depends on this. You will learn how to correctly calculate the power of a circulation pump for heating in this article.
Automated hydraulic calculation of heating system Excel
To make it more convenient to make hydraulic calculations, you can use various computer programs that allow you to perform accurate calculations. Excel is considered one of the most popular programs.
By the way, if you do not know the basics of hydraulics, then it will be difficult for you to do this, even in computer programs. This is due to the fact that some of them do not have decoding formulas and calculations of resistance in particularly complex circuits.
Nuances of some programs:
- OvertopCO and DanfossCO can calculate calculations for natural circulation systems;
- HERZ CO 3.5 – works according to the method of calculating specific pressure losses;
- Potok - copes well with calculations based on changing temperature differences along risers.
As for working in Excel, using spreadsheets is very convenient. You just need to know the sequence of actions and the exact calculation formulas. First, select the desired cell into which the data is entered. Further calculations occur through automatic application of formulas.
For example, in order to calculate the diameter of pipes, we need to know:
- The difference between hot and cold heat sources for a two-pipe system or fluid flow for a single-pipe system;
- The speed of movement of the heat source and its flow;
- Liquid density and parameters of the studied areas (their length in meters and the number of instruments located there).
To calculate the sizes of pipes within each section, it is convenient to use Excel tables.
Oventrop co program: choosing polypropylene pipes
Oventrop co is designed for quick calculations. Before work, the necessary settings are made and equipment elements are selected. In this case, various heating schemes are created. Changes are being made to them. This program for hydraulic calculation allows you to determine the coolant flow and select pipes of the required diameter. It helps to perform calculations for one-pipe and two-pipe structures. It's convenient to work with her. The program is equipped with ready-made blocks and material catalogs.
Adjustment of the existing structure is carried out by selecting power and the necessary equipment. The program helps you select the characteristics of the reinforcement.
The calculation results can be transferred to the operating system in a convenient way.
BGTG
Do you need gasification of a private home? Have you thought about gasifying your country house?
The state enterprise "Research Institute Belgiprotopgaz" develops gas supply projects (gas pipeline projects, boiler houses) for objects of various purposes:
- residential multi-storey buildings, holiday villages;
- shopping and entertainment centers, shops, catering establishments, sports complexes, administrative buildings;
- production and warehouse facilities;
- boiler rooms;
- agricultural facilities;
- sanatoriums, hospitals, hotels.
The company's clients have access to services for the development of technical documents (external and internal gas supply networks, selection of equipment) using innovative technologies. The company also provides services for supervision of objects under construction.
The design of gas supply systems is undoubtedly a very responsible area of activity, which is determined by the strategic importance of the designed objects that are classified as explosive. In the hands of the designer who directly creates the project, the possibilities for determining the quality, durability and, most importantly, the safety of the further use of his brainchild brought to life are concentrated.
An individual who has access to the design of gas distribution and gas consumption facilities and a personal license to design engineering equipment for networks and gas supply systems, having a regulatory and technical base, can also carry out projects.
The gas pipeline is an important element of the gas supply system, since 70-80% of all capital investments are spent on its construction. At the same time, of the total length of gas distribution networks, 80% are low-pressure gas pipelines and 20% are medium- and high-pressure gas pipelines.
Low-pressure gas pipelines serve to supply gas to residential buildings, public buildings and public utilities.
Medium pressure gas pipelines through gas control points (GRP) supply gas to low pressure gas pipelines, as well as industrial and municipal enterprises.
Through high-pressure gas pipelines, gas flows through gas distribution units (GRU) to industrial enterprises and medium-pressure gas pipelines. Communication between consumers and gas pipelines of various pressures is carried out through the gas distribution center (GRP) and the GRU.
Classification of gas pipelines
Modern gas pipelines are a whole system of complexes of structures designed to transport combustible fuel from places of its production to consumers. Therefore, according to their purpose, they are:
- Trunk – for transportation over long distances from production sites to destinations.
- Local – for collecting, distributing and supplying gas to settlements and enterprises.
Compressor stations are being built along the main routes, which are needed to maintain working pressure in the pipes and supply gas to designated points to consumers in the required volumes, calculated in advance. In them, the gas is purified, dried, compressed and cooled, and then returned to the gas pipeline at a certain pressure required for a given section of the fuel passage.
Local gas pipelines located in populated areas are classified:
- Depending on the type of gas, it can be transported: natural, liquefied hydrocarbon, mixed, etc.
- By pressure - in different areas gas can be of low, medium and high pressure.
- By location - external (street) and internal, above-ground and underground.
What is hydraulic calculation
This is the third stage in the process of creating a heating network. It is a system of calculations that allows you to determine:
- pipe diameter and capacity;
- local pressure losses in areas;
- hydraulic linkage requirements;
- system-wide pressure losses;
- optimal water consumption.
According to the data obtained, pumps are selected.
For seasonal housing, in the absence of electricity, a heating system with natural coolant circulation is suitable (link to review).
The main goal of hydraulic calculation is to ensure that the calculated costs for the circuit elements match the actual (operating) costs. The amount of coolant entering the radiators must create a thermal balance inside the house, taking into account the external temperatures and those set by the user for each room according to its functional purpose (basement +5, bedroom +18, etc.).
Complex tasks - cost minimization:
- capital – installation of pipes of optimal diameter and quality;
- operational:
- dependence of energy consumption on the hydraulic resistance of the system;
- stability and reliability;
- noiselessness.
Replacing the centralized heat supply mode with an individual one simplifies the calculation methodology
For autonomous mode, 4 methods of hydraulic calculation of the heating system are applicable:
- by specific losses (standard calculation of pipe diameter);
- by lengths reduced to one equivalent;
- according to conductivity and resistance characteristics;
- comparison of dynamic pressures.
The first two methods are used with a constant temperature difference in the network.
The last two will help distribute hot water among the rings of the system if the temperature difference in the network no longer corresponds to the difference in the risers/branches.
Selection of radiators and lengths of pipeline sections
It is necessary to decide on the type of heating devices and indicate their location on the floor plan. Next, a decision must be made on the final configuration of the heating system, the type of pipeline (single-pipe or two-pipe), valves for shut-off and regulation (valves, regulators, valves, pressure, flow and temperature sensors).
Then the drawn diagram indicates the number of thermal loads and the exact length of the sections for which the calculation is made. Finally, a “circulating ring” is defined. It is a closed circuit that includes all consecutive pipeline sections in which an increased flow of coolant is expected at a distance from the source emitting heat energy to the furthest heating device (with a double-circuit system) or to the instrument branch (with a single-pipe system) and back to the heating mechanism.
PC computing option
Performing calculus using a computer is the least labor-intensive - all that is required of a person is to insert the necessary data into the appropriate columns.
Therefore, hydraulic calculations are done in a few minutes, and this operation does not require a large amount of knowledge, which is necessary when using formulas.
To perform it correctly, it is necessary to take the following data from the technical specifications:
- gas density;
- coefficient of kinetic viscosity;
- gas temperature in your region.
The necessary technical conditions are obtained from the city gas department of the locality in which the gas pipeline will be built. Actually, the design of any pipeline begins with the receipt of this document, because it contains all the basic requirements for its design.
The use of special programs is the simplest method of hydraulic calculation, eliminating the search and study of formulas for calculations
Next, the developer needs to find out the gas consumption for each device that is planned to be connected to the gas pipeline. For example, if fuel will be transported to a private house, then stoves for cooking, all kinds of heating boilers are most often used there, and their passports always contain the necessary numbers.
In addition, you will need to know the number of burners for each stove that will be connected to the pipe.
At the next stage of collecting the necessary data, information is selected about the pressure drop at the installation sites of any equipment - this could be a meter, a shut-off valve, a thermal shut-off valve, a filter, or other elements.
In this case, it is easy to find the necessary numbers - they are contained in a special table attached to the passport of each product
The designer should pay attention to the fact that the pressure drop at maximum gas consumption must be indicated
From the special table attached to the product data sheet, you can find out information about pressure loss when connecting devices to the network
At the next stage, it is recommended to find out what the blue fuel pressure will be at the insertion point. Such information may contain the technical conditions of your city gas, a previously drawn up diagram of the future gas pipeline.
If the network consists of several sections, then they must be numbered and the actual length indicated. In addition, for each one, all variable indicators should be written down separately - this is the total flow rate of any device that will be used, pressure drop, and other values.
A simultaneity coefficient will be required. It takes into account the possibility of joint work of all gas consumers connected to the network. For example, all heating equipment located in an apartment building or private house.
Such data is used by a hydraulic calculation program to determine the maximum load on any section or entire gas pipeline.
For each individual apartment or house, the specified coefficient does not need to be calculated, since its values are known and indicated in the table below:
A table with simultaneity coefficients, data from which is used for any type of calculation. It is enough to select the column corresponding to a specific household appliance and take the desired number
If at some facility it is planned to use more than two heating boilers, furnaces, and storage tank water heaters, then the simultaneity indicator will always be 0.85. This is what you will need to indicate in the corresponding column used for the calculation of the program.
Next, you should indicate the diameter of the pipes, and you will also need their roughness coefficients, which will be used in the construction of the pipeline. These values are standard and can be easily found in the Rulebook.
A few important notes
As noted above, there are circulation pumps with a “dry” and “wet” rotor, as well as with an automatic or manual speed control system. Experts recommend using pumps whose rotor is completely immersed in water, not only because of the reduced noise level, but also because such models cope with the load more successfully. The pump is installed in such a way that the rotor shaft is horizontal. Read more about installation here.
In the production of high-quality models, durable steel is used, as well as ceramic shaft and bearings. The service life of such a device is at least 20 years. You should not choose a pump with a cast iron body for a hot water supply system, since under such conditions it will quickly collapse. Preference should be given to stainless steel, brass or bronze.
If noise appears in the system when the pump is operating, this does not always indicate a breakdown. Often the cause of this phenomenon is air remaining in the system after startup. Before starting the system, air should be released through special valves. After the system has operated for several minutes, you need to repeat this procedure and then adjust the pump.
If the start is made using a manually controlled pump, you must first set the device to maximum operating speed; in adjustable models, when starting the heating system, you should simply turn off the lock.
Determination of the number of gas control points for hydraulic fracturing
Gas control points are designed to reduce gas pressure and maintain it at a given level, regardless of flow.
With a known estimated consumption of gaseous fuel by the city area, the number of hydraulic fracturing is determined based on the optimal productivity of hydraulic fracturing (V = 1500-2000 m3/hour) according to the formula:
n = , (27)
where n is the number of hydraulic fracturing units, pcs.;
Vр — estimated gas consumption by city area, m3/hour;
Vopt—optimal hydraulic fracturing performance, m3/hour;
n=586,751/1950=3,008 pcs.
After determining the number of hydraulic fracturing stations, their location is outlined on the general plan of the city area, installing them in the center of the gasified area within the neighborhoods.
Why is it necessary to calculate a gas pipeline?
Throughout all sections of the gas pipeline, calculations are carried out to identify places where possible resistance is likely to appear in the pipes, changing the fuel supply rate.
If all the calculations are done correctly, then you can select the most suitable equipment and create an economical and efficient design for the entire gas system design.
This will eliminate unnecessary, inflated indicators during operation and costs in construction, which could occur when planning and installing the system without hydraulic calculations of the gas pipeline.
There is a better opportunity to select the required cross-sectional size and pipe materials for a more efficient, fast and stable supply of blue fuel to the planned points of the gas pipeline system.
The optimal operating mode of the entire gas pipeline is ensured.
Developers receive financial benefits by saving on the purchase of technical equipment and building materials.
The gas pipeline is correctly calculated taking into account the maximum levels of fuel consumption during periods of mass consumption. All industrial, municipal, individual and household needs are taken into account.
How to work in EXCEL
Using Excel tables is very convenient, since the results of hydraulic calculations are always reduced to tabular form. It is enough to determine the sequence of actions and prepare exact formulas.
Entering initial data
Select a cell and enter a value. All other information is simply taken into account.
- the D15 value is recalculated in liters, this makes it easier to perceive the flow rate;
- cell D16 - add formatting according to the condition: “If v does not fall within the range of 0.25...1.5 m/s, then the cell background is red/the font is white.”
For pipelines with a difference in inlet and outlet heights, static pressure is added to the results: 1 kg/cm2 per 10 m.
Registration of results
The author's color scheme carries a functional load:
- Light turquoise cells contain the original data - they can be changed.
- Pale green cells are entered constants or data that is little subject to change.
- Yellow cells are auxiliary preliminary calculations.
- Light yellow cells—calculation results.
- Fonts: blue - original data;
- black - intermediate/non-main results;
- red - the main and final results of the hydraulic calculation.
Results in Excel table
Example from Alexander Vorobyov
An example of a simple hydraulic calculation in Excel for a horizontal pipeline section.
- pipe length 100 meters;
- ø108 mm;
- wall thickness 4 mm.
Table of local resistance calculation results
By complicating calculations in Excel step by step, you better master the theory and partially save on design work. Thanks to a competent approach, your heating system will become optimal in terms of costs and heat transfer.
Consequences of calculation errors and ways to correct them
It is obvious that hydraulic calculation is a rather complex and important stage in heating development. To facilitate such calculations, a whole mathematical apparatus has been developed; there are numerous versions of computer programs designed to automate the process of its implementation.
Despite this, no one is immune from mistakes. Among the most common is the choice of power of thermal appliances without carrying out the calculation indicated above. In this case, in addition to the higher cost of the radiator batteries themselves (if the power is greater than required), the system will be costly, consuming an increased amount of fuel and requiring more for its maintenance. Simply put, the rooms will be hot, the windows are constantly open and you will have to pay extra for heating the street. In case of reduced power, heating attempts will lead to the boiler operating at increased power and will also require high financial costs. Correcting such an error is quite difficult; you may need to completely redo the entire heating.
installation of radiator batteries, violation of battery installation rules
The next group of errors relates to the error in determining the required power of the heat source and heating devices. If the boiler power is obviously higher than the power of the heating devices, it will work inefficiently, consuming more fuel. There is a double cost overrun: at the time of purchase of such a boiler and during operation. To correct the situation, such a boiler, radiators or pump, or even all the pipes of the system, will have to be changed.
When calculating the required boiler power, an error may be made in determining the heat loss of the building. As a result, the power of the thermal energy generator will be overestimated. The result will be excessive fuel consumption. To correct the error, you will have to replace the boiler.
An erroneous calculation of system balancing, violation of the requirements for approximate equality of branches, etc. may lead to the need to install a more powerful pump that allows the carrier to be delivered to distant heating devices in a heated state. However, in this case, “sound accompaniment” may appear in the form of a hum, whistle, etc. If such errors are made in a warm water floor system, then the result of installing a powerful pump may be a “singing floor.”
If there are errors in determining the required amount of coolant or the gravity system is switched to forced circulation, its volume may be too large and distant heating devices will not work. As before, attempts to solve the problem by increasing the heating intensity will lead to excessive gas consumption and wear and tear of the boiler. The issue can be resolved by using a new pump and hydraulic switch, i.e. the heating unit will still have to be redone.
After all, we can definitely say that carrying out a hydraulic calculation of a heating system will guarantee minimizing costs at all stages of design, design, installation and long-term operation of a highly efficient water heating system.
Calculation of hydraulics of heating channels
Properly calculated hydraulics allow you to correctly distribute the diameter of the pipes throughout the system
Hydraulic calculation of a heating system usually comes down to selecting the diameters of pipes laid in individual sections of the network. When carrying it out, the following factors must be taken into account:
- the pressure value and its drops in the pipeline at a given coolant circulation rate;
- its expected consumption;
- typical dimensions of used tubular products.
When calculating the first of these parameters, it is important to take into account the power of the pumping equipment. It should be enough to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the heating circuits. In this case, the total length of polypropylene pipes is of decisive importance, with an increase in which the total hydraulic resistance of the systems as a whole increases
Based on the results of the calculation, the indicators necessary for the subsequent installation of the heating system and meeting the requirements of current standards are determined
In this case, the total length of polypropylene pipes is of decisive importance, with an increase in which the total hydraulic resistance of the systems as a whole increases. Based on the results of the calculation, the indicators necessary for the subsequent installation of the heating system and meeting the requirements of current standards are determined.