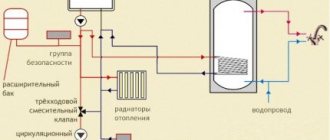
At different times, the issue of heating remains relevant for people. Perhaps one of the most popular heat sources are gas boilers - devices for generating thermal energy in premises for various purposes. First, you need to understand the principle of operation and structure of gas boilers of different types: wall-mounted, floor-mounted, double-circuit.
Gas boilers are used for two purposes:
- Heating (of premises, objects for various purposes);
- Heating water (for taking a bath, washing dishes, etc.).
According to the operating principle and depending on the purpose, gas boilers are divided into:
- Single-circuit;
- Dual-circuit.
Basic design of a wall-mounted gas boiler
The external structure of such a gas boiler includes:
A housing that protects the boiler itself from fire and from outside interference for its high-quality operation
Control panel for entering certain commands that regulate the heating temperature, respectively, and the water heating temperature. By design, the control panel can consist of either any rotary knobs or touch buttons- A display that clearly displays the temperature that we set using the control panel, what stage the heating is currently at, possible errors and failures in the system, with which you can determine exactly what problems have arisen with the boiler
- A pressure gauge (mechanical or electronic), with which we can see the pressure of liquids in the heating system.
It is worth noting that modern boilers operate only in closed systems with a water pressure in this system of 1 to 2 atm.
The internal structure of a gas boiler includes:
- Primary heat exchanger
- Gas-burner
- Pump
- Gas fittings
- Secondary heat exchanger
- Three-way valve
- Turbine (smoke exhauster)
Let's consider the operating principle of a gas boiler , examining in detail each element of the internal structure:
Installation Features
Installation of this type of equipment is a very responsible matter. To ensure its proper functioning and your own safety, you must approach this issue with the utmost care. First of all, you should pay attention to the following points:
- The place where it is planned to install the boiler must comply with all regulatory parameters. It is necessary to coordinate its location in advance with representatives of the gas service.
- The connection project is initially drawn up on paper and then sent for approval to the appropriate organization.
- After receiving permission, its employees will personally install the necessary metering devices to monitor fuel consumption.
- Before starting installation, you need to make sure that the unit is fully equipped. If some parts are missing, such a device cannot be installed. This may lead to an emergency situation.
- First of all, installation points are determined on the wall surfaces, only then do they begin the phased installation of all elements.
- Upon completion of the installation activities, the system is connected in series. Test filling the circuit with water, then heat the boiler.
- If you find any problems or smell gas, you should not try to fix the problem yourself. In such cases, you should immediately call a specialist who will assess the condition of the structure on the spot and carry out the necessary repair work.
Primary heat exchanger
gas boiler heat exchanger
It is a determining element in the operation of the boiler; it serves to transfer heat from the fire to the heating fluid further into the heating system. The design of the heat exchanger is usually the same for all types of gas boilers from manufacturers. Externally, it is a copper pipe with heating fluid flowing inside it. Such heat exchangers are called “copper”. Since the heat exchanger is located above the burner flame, the heat from the fire heats the copper pipe, which transfers the heat to the heating fluid. It is noteworthy that copper was chosen as a metal that successfully copes with the task of retaining heat and, if necessary, losing it quite quickly, because has a high heat transfer coefficient. Also, copper does not rust quickly, due to which its service life is quite long. In addition to the copper pipe, the heat exchanger is equipped with special plates that help smoothly distribute all the heat from the fire, thereby promoting uniform heating of the heat exchanger.
What does the number of circuits affect?
Gas heating in an apartment building, based on the number of circuits, can be double-circuit or single-circuit. What's the difference? Single-circuit ones perform only one task - they warm up the working fluid in heating systems. To increase the temperature of water used for household purposes, it is necessary to additionally install a capacitive water heater. Type of heating – indirect.
Double-circuit boilers cope well with both heating rooms and water. The circuit is heated to the required temperature in a flow-type heat exchanger. An alternative is a cylinder water heater.
Gas-burner
gas boiler burner
The principle of the burner design of a wall-mounted gas boiler is similar to the burner of a gas stove, with the only difference being the dimensions and appearance. As in a gas stove, the greater the boiler power, the larger the burner. It is noteworthy that the dimensions of the burner directly coincide with the dimensions of the heat exchanger, which allows the boiler to be ergonomic. This type of burner is called “injection”. Its operating principle is that gas and primary air are supplied to the burner. Inside it, mixing and formation of a gas-air mixture occurs. Next, the prepared mixture exits through the holes in the burner, mixes with secondary air and enters the combustion chamber, ignited using the electric ignition available in each boiler. The combustion chamber, as a rule, is closed with special covers and protected from heat leakage and overheating of the housing by asbestos plates. When gas burns, fire and smoke are generated.
Heat exchanger and burner of a gas boiler
Pump
Pump in a gas boiler
Serves to impart movement to the coolant. This device causes heating fluid to circulate from the heated primary heat exchanger to the radiators, heat them and move back to heat them. The pump usually has several speeds and is adjusted by a service engineer based on the size of your heating system.
Too high a pump speed can create additional noise and reduce the efficiency of the boiler. And too small will lead to uneven heating of the radiators. Therefore, for proper setup, it is very important to contact qualified service engineers.
Secondary heat exchanger
Responsible for heating water for household needs. Considering the design of a gas boiler, it is worth noting that this element is made of food-grade stainless steel plates. On one side, heated heating fluid moves through the heat exchanger, and on the other, cold water. When the heating fluid meets, it transfers its heat to cold water through a thin layer of metal. In this way, the water is heated and then flows into consumers’ taps. In this case, the heating fluid loses its temperature, entering the primary heat exchanger for subsequent heating. Such a heat exchanger has from 8 to 30 alternating layers and allows you to heat a fairly large amount of water.
Operation of the automation system
The operating principles used for automatic gas boilers are designed to ensure safe operation and achieve maintenance of a certain coolant temperature for some time. The devices are equipped with all kinds of sensors and thermostats.
Automatic protection systems allow you to turn off the gas supply during a temporary shutdown. The system will simply stop working. It will need to be restarted manually immediately after gas transportation through the network pipeline is resumed. This can be done in a few minutes.
Modern models have energy-saving features, as well as a method of frost protection. The temperature regime of the coolant is regulated using special sensors. If the thermometer drops to 5 degrees, the boiler will turn on automatically to warm up.
New models began to be equipped with self-diagnosis systems. During operation, the state of the main components is analyzed, after which the information is transmitted to the display via error codes. This technologically advanced method allows you to identify about 90 percent of probable faults.
Design of a double-circuit gas boiler
There is a slight difference in the device itself. In double-circuit gas boilers there is not one, but two heat exchangers - primary and secondary:
- The primary heat exchanger performs the same role as the heat exchanger of wall-mounted and floor-standing boilers - it serves to heat the room and is represented by a copper or steel tube. True, the latter is less profitable to use due to the fact that it is prone to corrosion. Copper has no such drawback.
- A secondary heat exchanger is precisely needed to heat water for household needs. It can be made of steel. It is affected by a temperature slightly lower than the temperature that reaches the primary heat exchanger. The point is in the mechanism of operation of the secondary heat exchanger itself. Two liquids move through the heat exchanger: one is the boiler coolant, the other is the very water that the owner plans to use for washing, for example. When these two liquids meet, the coolant shares heat with service water through a thin layer of metal, and then again enters the primary heat exchanger (restore the previous temperature). While the household water, having heated up, reaches the taps of sinks and bathtubs. This is how it heats up. The secondary heat exchanger most often has quite a few alternating layers, which helps to warm up an impressive amount of water well.
Since double-circuit gas boilers have such a difference in design compared to single-circuit ones, their operating principle is somewhat different.
On the left is a three-way valve made of brass. On the right with a blue head there is a gas valve. The secondary heat exchanger shines at the back.
temperature sensor
A very important element, of course, is the temperature sensor; it is used in absolutely all units and is designed to control the temperature in the room. For example, you set the temperature to 25 degrees, the boiler worked out the body for this temperature, and then left the activity. The room gets colder, and the mark drops to 24 degrees. A heat sensor reacts to this, which sends a certain signal to the unit, which again begins to function and produce heat until the room temperature is again equal to 25 degrees.
Chimney design
The chimney structure of a gas boiler is extremely important for the operation of the boiler, since it is thanks to it that combustion products are removed from the apparatus. True, it is a tube, and there are no special devices in it. However, they come in different types:
- Metal. They are sandwich panels made of lines of different diameters, made of stainless steel. The voids between them are usually filled with a basalt thermal insulation layer. They are highly reliable. They are multi-layered and have high heat-insulating properties. But they are assembled from a large number of parts, which is not entirely convenient.
- Ceramic. Simpler, but no less durable models. They even resist the effects of chemical substances. They are ceramic pipes wrapped in mineral wool. However, they require additional installation of condenser collectors.
- Coaxial chimney. Easy to use and looks great. Does not require installation of any additional devices. Condensation does not accumulate, which is also its advantage. And it is something like a pipe-within-a-pipe design. Can be used for closed type boilers (those that take air from the street. Open systems take air from the house). That is, air enters the boiler through the outer pipe, and exits through the inner pipe, being exhausted.
Coaxial chimney
Previously, a brick chimney was quite popular. But they are quite difficult to install, and they are quite bulky.
Operating principle of boilers
So, single-circuit boilers work according to the following principle:
- Water is supplied to the boiler, which will act as a coolant.
- The pump supplies water to the heat exchanger, which, when heated by a burner, transfers heat to the incoming water.
- The coolant moves on, heating the room.
- The heat exchanger heats up to the set temperature. Then the system gradually extinguishes the burner and goes into waiting mode for a new command from the thermostat.
- The system removes gas combustion products.
Double-circuit ones operate using a more complex mechanism. Of course, heating the house occurs in the same way as with single-circuit boilers. However, there is still heating of water for domestic needs. A three-way valve helps with this:
- If it is necessary to heat water, the valve cuts off the coolant flow to the heating system. The valve is activated when the sink or bathtub faucet is opened.
- Then the water enters the secondary heat exchanger.
- The three-way valve then redirects water to the primary or secondary heat exchanger as needed.
That's all I wanted to convey. We hope this article was useful to you.
How do condensing devices work?
In conventional appliances, combustion products bypass the heat exchange surfaces and release part of the energy to the working environment of the heating system. Exhaust gases are discharged through a conventional chimney. In this case, a certain part of the heat is lost in the form of water vapor that appears during fuel combustion.
The operating principle of condensing gas boilers is somewhat different. The devices are capable of using the latent energy of water vapor. They are equipped with a blower fan that has a variable speed. In this regard, the combustion chamber is closed. Exhaust gases are discharged using a coaxial chimney.
Variable fan speed allows you to adjust the ratio of gas and supplied air. The condensing boiler does not function at its maximum efficiency in all cases. In order for the device to operate in economical mode, it is necessary to maintain the temperature of the coolant in the return pipeline less than 57 degrees.
The efficiency of the condensing device increases with decreasing operating temperature of the heating system. In other situations, the effectiveness is slightly reduced. Therefore, such a device is appropriate when used with heated floors, where the operating temperature range ranges from 40-45 degrees.
Unlike a conventional boiler, the condensing analogue has a larger heat exchanger area. In it, exhaust gases are cooled to a temperature below 40 degrees. The condensation process occurs directly in the heat exchanger, so it is made of corrosion-resistant materials.