Bimetal sectional radiator design
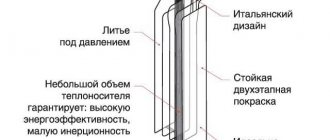
Bimetallic heating radiators are devices consisting of two main parts, each of which is made of different types of metal. This is precisely what determines the name given to the radiator. Typically, stainless steel is used to make the interior. These materials are characterized by high resistance to aggressive influences from the coolant. In this case, the pipes are located both vertically and horizontally, and coolant circulates through them.
The outer part of the radiator is nothing more than a casing with fins. Most often, the casing is made of aluminum, and this choice is due to high thermal conductivity and the short time required for complete heating. Aluminum quickly releases heat into the room, increasing the overall air temperature.
The two parts of the radiator are connected to each other using the high-pressure casting method. Spot welding can be used somewhat less frequently for these purposes. To secure individual sections, nipples and special gaskets made of paronite or silicone are used that can withstand constant exposure to high temperatures.
Sectional radiators consist of several sections, each of which has equally directed threads on both sides. Using this thread, the sections are mounted into each other - connecting nipples and sealing gaskets are screwed into them. Thus, the structure can be assembled from almost any number of sections, which allows in each individual case to ensure the required level of heat transfer for the room.
In appearance, a bimetallic radiator is practically no different from its aluminum counterparts. The only parameter by which they can be distinguished is weight. Since bimetallic models have an internal steel filling, it weighs significantly more.
Due to the ability to quickly and efficiently heat areas, as well as a long service life, you can buy a bimetallic heating radiator to heat rooms of any size. You just need to purchase a sufficient number of sections.
Steel heating radiators height 200 mm
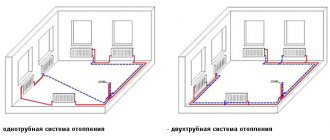
There are two types of heating implemented in steel panel heating radiators. These are heating by thermal radiation in the infrared spectrum and convection heating. The share of convection heat in such radiators is 60 – 75%. This combination of two heating options made it possible to achieve the fastest and most efficient heating of the room. The design of the individual panel is quite simple. Typically, a pair of steel plates made of sheets 1.2 - 1.25 mm thick, which after stamping acquire a profile in the form of vertical channels, are connected to each other by welding. Coolant circulates in the channels formed by stamping. Steel panel radiators can consist of a block with one (type 11), two (type 22) or three (type 33) panels. To increase the heat transfer surface, fins are welded to the panel. As the number of panels increases, the thermal power of the radiator increases. The radiators are also equipped with a removable convection grille and side plates. Panel radiators are available in three versions - with side (left and right), bottom and universal connections. Advanced models of panel radiators (usually models with bottom and universal connections) have a built-in thermostatic valve to be able to adjust and maintain a comfortable room temperature. For objects with special hygienic requirements, modifications with a smooth surface of the heating panel are available. The standard technical parameters of such devices allow their use in heating systems with a pressure of no more than 10 bar and a maximum temperature not exceeding 110 0C. The disadvantages of panel heating radiators include the need for cleanliness of the coolant. Oxygen, contaminants and chemical impurities in them can lead to active corrosion processes, which are undesirable in thin-walled steel panels. Also, the thin steel of the panels has low resistance to hydraulic shocks. The reliability of panel radiators in this regard is further reduced by the presence of welds, which are more susceptible to corrosion and pressure changes than the base metal of the plate. Therefore, it is better not to use such devices in centralized heating systems, where it is difficult to control the quality of the coolant. The considerable weight of radiators, which brings them closer to their cast-iron counterparts, also cannot be considered an advantage. But don’t forget about the advantages of steel panel heating radiators. Since such devices are produced, unlike sectional radiators, in a form completely ready for installation, their range, standard sizes and thermal power are very wide. They have low inertia, their heat transfer rates are also at a high level. And the simplicity of design and modern technology ensured the low price of panel radiators. In addition, among all types of heating devices, steel radiators have the lowest cost per kilowatt of heat, which is another important advantage. You can buy a panel heating radiator in the Moscow online store of your thermal partner “TavaGO”.
Bimetal and semi-bimetal: what is the difference?
Conventional bimetallic radiators have a casing made of aluminum. The rest of its parts are made of other metals. During the manufacturing process, steel cores are placed into special molds and then filled with molten aluminum. After solidification, this metal does not come into contact with the coolant in any way, and serves solely as a heat exchanger. Such batteries are best suited for installation as part of any heating systems.
If we talk about semi-bimetallic radiators, then in their design the steel pipe is present only in the vertical part of the radiator. The horizontal passages remain aluminum. It is possible to install such batteries as part of a central heating system, but since the coolant in such systems can rarely boast of purity and the absence of alkaline impurities, such radiators may last less than completely bimetallic ones.
Criteria for choosing bimetallic radiators
When choosing a bimetallic radiator, you should take into account a number of criteria, which will directly determine the quality of the system and the duration of its operation. We are talking about the following selection criteria:
- Reliability of the design. Since the radiator is constantly exposed to increased pressure, its design must be prepared to work in such conditions. This issue is especially acute if you intend to use a radiator as part of a central heating system;
- Manufacturing materials. The materials from which the radiator is made must be able to easily withstand the effects of alkalis contained in low-quality coolants, and also be resistant to corrosive processes;
- Strength. The radiator must be resistant to mechanical loads. This is more about the outer case. When choosing a model, this point can be checked by applying some pressure on the ribs with your fingers. If they bend, then you have a low-quality model;
- Pipe thickness. Radiator pipes must have a width of at least 3 mm. Otherwise, they will quickly become unusable and require complete replacement;
- Gaskets and nipples. As we noted above, these elements are used to secure the radiator sections, and they must provide reliable and durable fasteners;
Width of ribs. The front part of the fin in a high-quality radiator necessarily exceeds the 70 mm mark in width. Taking into account all these criteria, you can choose the highest quality and reliable bimetallic radiator.
Calculation of the number of sections of bimetallic radiators
First, multiply the area of the room by the height of the ceiling. We get the volume of the room. Then we divide the resulting volume by a factor of 30. The resulting number is the power in kW that is necessary to heat this room. If the room is corner, i.e. has not one, but two walls bordering the street, then we add 20% to the resulting power. Also, if the glazing area is unusually large, each square meter of glass is considered as an additional 0.1 kW to the radiator power.
So, after the necessary calculations, we have obtained the radiator power, but how can we convert it into the required number of sections? It's simple! The resulting power is divided by the heat output of one section in kW. Thus, we get the required number of sections. The heat transfer of the section is indicated in the product characteristics on the website.
And another important point is the height of the radiator. There must be at least 10 cm from the floor level to the bottom edge of the radiator, and there must be at least 10 cm from the top of the radiator to the window sill. This is necessary for free air circulation.
Example: a room of 18 sq.m., ceiling height 2.7 m., has two street walls, glazing area 3 sq.m., window sill height 1 m.
- 18x2.7/30=1.62 kW is needed to heat the room;
- add 10% for heat losses for each street wall: 1.62+20%=1.944 kW;
- add 0.3 kW (3 sq.m. glazing) - we get 1.944 + 0.3 = 2.244 kW;
- divide by the heat transfer of one section 0.185 kW: 2.244/0.185 = 12.129. Rounding up, we get 12 sections
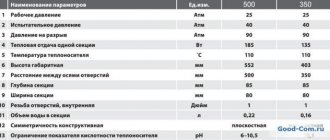
Aluminum sectional radiators with a center distance of 200 mm
In previous years, when heating radiators were either steel or cast iron, many chose the latter. Cast iron radiators had their advantages - they retained heat for a long time, provided better heating, and were less susceptible to internal deposits. But the disadvantages are also obvious - such batteries heated well only at a high temperature of the coolant in the heating system, they warmed up very slowly and had high thermal inertia. With the advent of aluminum radiators on the market, the picture has changed dramatically. Aluminum alloys have high thermal conductivity and structural strength. Lightweight compact radiators are made from them, the modern design of which combines the principle of heating by convection and thermal radiation. And the small volume of circulating coolant, combined with low thermal inertia, saves money on boiler fuel consumption. And what is also important is that such radiators can be used in low-temperature operating modes of heating systems, which further reduces energy costs for heating. When choosing aluminum heating radiators, one must proceed from the calculation that the thermal power of a section of 0.1 kW can heat 1 m2 of a room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m. The sectional design of aluminum radiators allows you to assemble stacked blocks from any number of sections. The standard provides a thermal curtain from the convective flow of the radiator when covering at least 75% of the width of the window opening. It prevents cold air from entering the room from the window. But it is not advisable to add more than 14-16 sections, because in this case the radiator will not warm up completely, which reduces its thermal efficiency. The sections are assembled into a radiator using nipples made of stainless steel or steel with anti-corrosion coating. To ensure a tight connection, they are sealed with rubber, silicone or paronite gaskets. The internal surface of each section undergoes multi-stage anti-corrosion treatment, and later it is painted with powder enamel. The price of an aluminum heating radiator will depend, first of all, on the manufacturer. Most of all, this market segment is represented by models from Italian manufacturers, who have become trendsetters in the industry. But there are also domestic models that are in no way inferior in quality, adapted for our heating systems, and, importantly, more affordable. As a rule, the cost is indicated for one section, and from here it is easy to calculate the cost of the entire kit, which will also include connecting fittings and an installation kit. It is recommended to additionally equip the radiators with an automatic or manual air vent (Mayevsky valve), and to comfortably maintain the temperature in the room, it would not be superfluous to install a thermostatic valve. When you start building a country house, or decide to replace the batteries in your apartment, you should take care of truly efficient heating of your home. In this case, sectional aluminum radiators with a high heat transfer coefficient are the best choice. You can buy an aluminum radiator for installation in a country house, private house, apartment or office in our thermal comfort store “TavaGO”.