Heating devices are an essential element of any water heating system. They are usually the most expensive part. A good opportunity to save money would be to use homemade radiators. They are made from smooth round steel pipes or from profile pipes. The latter option is somewhat more expensive, but allows you to reduce the depth of the device and get a more aesthetic appearance.
The use of a profile pipe for the manufacture of heating registers has a number of features. When starting to work with your own hands or deciding to buy a “homemade” product, you need to carefully weigh the pros and cons. Studying the basic rules by which heating registers are made from a profile pipe will help you avoid mistakes when working independently and will make it possible to make a competent choice of the necessary parameters.
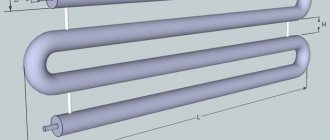
Steel pipe register
Key Features
The register is several parallel pipes held by vertical jumpers.
To construct a heating system, steel or cast iron products of round or rectangular cross-section are used. The layout of the elements is sectional or serpentine. The coil is a classic design with efficient heat transfer. In sectional registers, transitions are made close to the edge to increase the heat transfer rate.
Heating structures can be portable (contain heating elements that heat water) or stationary (connected to the boiler). The coolant moves from top to bottom. The pipes can be connected to the pipe by threaded connection or welding. Additional jumpers make the structure more rigid.
To heat 1 m2 you need 1 m of pipe with a diameter of 60 mm.
- ease of connecting the heat exchanger to the system;
- the ability to manufacture a structure according to specified parameters;
- The coolant can be water or steam.
Calculation of a heating structure made of round pipes
This calculation technique is not suitable for finned registers, since they have a larger surface area and heat transfer. Specific thermal power is calculated using the formula:
where Δt is the temperature difference between the air and the working medium of the pipe, K is the thermal conductivity coefficient (for metal it is equal to 11.63 W/m²*C), L is the length of one section, D is the diameter of the pipe, P is the number P = 3.14 .
When calculating the remaining sections, the resulting value is multiplied by a factor of 0.9.
Practical heating registers: what to choose for your home and apartment
On the market, everyone can choose heating registers for installation in an apartment or private house. On sale there are designs made of metal horizontally located pipes connected to each other by special jumpers, due to which water moves through the heating device. Modern registers have higher heat output than traditional Soviet batteries. The most popular aluminum registers have the best technical characteristics. Homemade batteries are used in small apartments or rooms, ensuring proper heating of the available space.
How to make a register with your own hands
To make a homemade heating register from pipes, you will need 3 profile pipes of rectangular section 60x80 mm and a wall thickness of 3 mm, as well as 4 round pipes with a diameter of 25 mm, plugs made of sheet material with a wall thickness of 3 mm.
- Holes for jumpers are measured and cut at the ends of the pipes. The central pipe is cut through on both sides.
- Lay out the profile pipes horizontally, lay jumpers between them strictly along the holes, then weld them.
- Now the product is installed vertically.
- Welded seams create tightness at pressures up to 13 atm.
Video: register installation procedure
Heat exchanger for bath
In the sauna, the energy of the stove is transferred to water. The curved pipe is placed inside the firebox, while the coil does not come into contact with the fire. As hot water rises, cold water replaces it. In a closed water circuit, a cycle occurs that increases the temperature in the entire system. The bath coil is made of stainless steel; other materials do not withstand such harsh operating conditions.
Craftsmen lay out the furnace, building a heat exchanger (register) inside it, which is then connected to a water tank. The optimal way to place the heat exchanger is opposite the opening through which flue gases flow into the smoke duct. The register design is U-shaped and welded from pipes. Sometimes a finished section of a cast iron battery is used. Due to the low natural pressure, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm and a length of no more than 2.5-3 m are used.
The register dimensions are selected depending on the furnace power. To heat 100 liters of water, you will need a pipe 2 m long and 40 mm in diameter. The thermal power of such a heat exchanger will be equal to 2 kW.
- It is better to install the heat exchanger simultaneously with the laying of the furnace after the foundation has been erected. In this case, the size of the firebox is easy to match with the size of the register.
- A distance of 10-15 mm is maintained between the heat exchanger pipes and the firebox. The coil does not come into contact with the flame; it is heated by the hot air. The curved pipe is connected to the tank through threaded connections.
- A curved pipe wound around a metal chimney can also heat water (the outlet temperature reaches 500 C).
- Experts use heat-resistant seals at the junction of the heat exchanger and water pipes.
- Heavy welded structures are installed in brick kilns (it is difficult to find a place for it in an iron kiln).
- The chimney of a stove with a heat exchanger is cleaned more often, since an order of magnitude more soot is formed in it due to incomplete combustion of fuel.
- To heat the liquid even faster, a circulation pump is introduced into the system to artificially move water.
- The heat exchanger is filled with cold water before the oven heats up.
- In order to prevent pipes from bursting at sub-zero temperatures, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of completely draining water from the system.
A self-made register is a good opportunity to save money. Heat exchangers made of smooth or profiled products can withstand pressure and temperature surges, and their high heat transfer allows them to be used for heating large rooms.
For the heating system of large premises, it is not advisable to use conventional factory batteries and radiators. They have very little heat output and power. As an alternative, heating registers can be considered.
Heating devices called registers are several folding pipes located parallel to each other and connected to each other by jumpers. The coolant moves through the pipes, transferring heat to the iron walls of the register, which heat the air space in the room.
Water or antifreeze can be used as a coolant , which prevents the pipes of a disconnected system from freezing during the cool season. In independent heating registers with a cylindrical electric heater (TEH), the coolant can also be oil, then the independent register is considered the most powerful analogue of domestic oil radiators. They have become widespread due to their simplicity of design, reliability and a number of other advantages.
Error correction
Sometimes, incorrect measurements of a room lead to incorrect calculations. The installed heating radiator does not work efficiently and the room is cool. You should not immediately rush and make a new device, spending both time and money. There is a way to increase thermal output.
To do this, it is necessary to increase the heating area. The only option in this case is to weld ribs made of a metal sheet 1.0-2.0 mm thick to the pipe structure. The shape of the ribs can be different, the main thing is their area.
Therefore, for example, rectangular pieces with a length greater than the height of the radiator and a width of 100-150 mm are cut out of a sheet of iron. Semicircles with a diameter of 100 mm are cut into them on one side. On each piece of sheet there are two semicircles, the distance between which is determined by the gap between the two pipes in the battery.
The finished forms are welded to the heating structure. The more there are, the higher the heat transfer of the device.
Heating radiators are elements of engineering plumbing systems that are functionally designed to heat the air in a room. According to SNiP (2.03.01-84), radiators that comply with heat balance calculations should be used in any room. They are quite sufficient to maintain normal temperatures inside buildings.
However, for a garage or small workshop it is better to make a heating register yourself. In terms of dimensions and heat transfer, this device goes beyond the parameters of classical designs, but is much more suitable for these premises. The article we presented describes in detail the technology of its manufacture.
Advantages and disadvantages of devices
Homemade metal or aluminum devices differ from conventional radiators in their dimensions. They consist of some pipes whose diameter exceeds 32 mm. To organize the circulation of the coolant, the pipes are connected to each other by pipes.
What is the reason for the popularity of these heat supply devices? First of all, the prospect of independent production. You can make bimetallic devices, metal or aluminum pipes.
Before connecting the heating registers, you should carefully study all their sides.
Advantages:
- Long service life. For metal and aluminum modifications it can reach 25 years. In this case, the possibility of breakdown will be minimal.
- Significant heat dissipation. This is due to the fact that the power of the devices exceeds this parameter of traditional radiators and batteries. Due to the large size of the coolant.
- Easy installation and operation. Since anyone who is at least a little familiar with the instructions for organizing heat supply can correctly identify the devices, they can be used in buildings of all types. But most often they can be found in the heating system of industrial, administrative and commercial premises.
Read also: Wet shaving with an electric razor like this
But, in addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the possible disadvantages that a register made of a smooth metal pipe may have:
- Large coolant size. This leads to its rapid cooling.
- Lowest rate of air convection. Reduces the efficiency of heat supply.
- Unsightly appearance. Most often this applies to homemade systems.
Correctly calculated heating heat transfer directly depends on the design of the device. Currently, a number of types of these heat supply devices are used, differing not only in the production material used, but also in appearance.
Answers from experts
Tori:
plastic pipes and aluminum radiators.
LegendaSporta:
polypropylene.
mu.rza:
we bought polypropylene ones. each has its pros and cons. Read this, a very informative article about pipes
Vladislav Ushkalov:
Igor Shkurny:
Polypropylene... have less trouble with it... unless of course you have a soldering iron!!!!
Lizard:
I bought a house with completely defrosted metal pipes and cast iron radiators. I chose, consulted, changed to polypropylene and aluminum batteries. I bought one cast iron. and what? It was she who cracked in the very cold (there was no heating, and there was antifreeze in the pipes, but it did not help). I also changed it to aluminum. Further, in the well next to the house there is water supply for five houses, each has its own valve, the pipes are all iron. They rusted like hell. When it burst again, I raised a fuss, collected money from the people, and the local master replaced the filling of the well with polypropylene again. Now we are all calm. So polypropylene is perhaps more reliable. Some people claim that pipes made of polyethylene (very dense) are even more reliable and are not afraid of frost at all, but I don’t know.
Floors:
Iron pipes are 3-5 times cheaper and much more reliable than propylene and plastic. The disadvantage is corrosion of the metal from the inside, which cannot be gotten rid of in any way, but if the water is not drained from the system, then after cutting a 20-year-old pipe, it is as good as new inside (I myself have cut old heating pipes more than once - there is almost zero corrosion inside. And heating devices are more aesthetically pleasing than aluminum and bimetal. USSR cast iron is no longer in fashion, and the material consumption is appalling)))
Sergey Rudin:
Look here: agrosad m /catalog/tverdotoplivnie_kotli_1
Solo:
In a private house AOGV. ) There seem to be no other options.
Andrey:
rephrase the question. A radiator heating system is one thing, but pipes and radiators are a completely separate issue.
Alexander Bonn:
Gas boiler, steel radiators, welded pipe. Energy consumption: 10 sq. m = 1 kW. For a private house, warm floors (1st floor) and radiators are combined. But there must be an emergency heating system (electric or solid fuel).
Alasseia:
question about heating a spherical house in a vacuum, no information about the source of energy supply, no information about the house itself, what would I recommend - a project for heating your bungalow completed by a specialist
F F:
Boilers, boiler equipment. Heating 2 x storey house. : // forum .domostroy /#gazosnabjenie-vodoprovod-otoplenie-konditsionirovanie Gas wall-mounted boiler Heating, plumbing, sewerage for a house or cottage. Heating 2 x storey house.
Which radiators or pipes are better? - it is necessary to rely on the volume of coolant for the correct operation of the boiler! example - 70 sq. wooden house, - they wanted a fan system with aluminum. heating radiators, after calculating the amount of coolant, we chose a register system of pipes.
For a brick house, combine heated floors (1st floor) and radiators, a fan distribution system, and metal-plastic in a screed. Alexander Bonn +++
alexm66:
The question is very general: which is better, a foreign car or a VAZ - for which there is money and opportunity. I think the main criterion is the reliability of the equipment, and a competent installer will be able to make a workable system out of it, but an illiterate one will ruin any “luxury” equipment.
Design Features
Heating registers are used to a greater extent in industrial workshops, technical rooms, and, in addition, in apartments and private houses. Registers are common in many places with high sanitary requirements, for example, in medical organizations and schools.
According to the type of system, heating registers are divided into collapsible and coil devices:
- In sectional registers, pipes are connected to each other by jumpers of the smallest diameter - this type of connection is determined mainly by the ease of installation. The distance between the register pipes is calculated using the formula D+50 mm, where D is the pipe diameter. If the rule is followed, mutual irradiation of the pipes will be minimized, as a result, heat transfer increases.
- In coil-type registers, pipes are combined from the end using an outlet whose diameter is equal to the diameter of the pipes. The slight increase in the cost of the product is offset by the huge surface area, and as a result, by the greater efficiency of the heating device. In addition, the coil register has less hydraulic resistance than the sectional one, which makes it possible to use less powerful, but more economical and cheaper pumps in the heating system.
Pipe end caps can be either thin, convex or elliptical. It is recommended to use such plugs in systems with the highest coolant pressure, and, in addition, for decorating purposes, in order to add the most interesting appearance to the device. If necessary, the outer sector of the register is additionally equipped with a fitting for a degassing valve.
There is another variation - an independent register with a heating element . Equipment of this type does not require connection to a heating system, since the coolant is heated by electricity using an integrated heating element. During the design of such registers, the power of the heating element is selected according to the section of the device plane: overheating can provoke an excessive increase and leakage of coolant through the emergency valve. With low power of the heating element, the efficiency of the device will be lower than its possible capabilities.
The outer segment of the independent register is integrally equipped with a fitting, which is initially used to fill the coolant inside, and then used to connect an emergency valve or expansion tank - and in this case it is used to compensate for the expansion of the coolant during heating.
Main selection criteria
Any specialist has a whole arsenal of tools that help him make the right choice. Each type of pipe has both positive and negative characteristics. Therefore, taking them into account, it is not difficult to find the optimal solution. Much also depends on knowing what heating systems exist and what engineering conditions must be met
Here is a list of basic initial data that must be taken into account when choosing heating pipes:
- Availability of forced or gravity heating system
- Laying method - internal or external
- Complex or simple system configuration.
- System pressure power
- Maximum water temperature
Below is a list of existing options. It will help you decide correctly which pipes to choose.
Materials for production
The materials used for the production of registers are VGP pipes and electric-welded steel pipes (according to GOST 10704−91 and others). The alloy has absolutely all the data needed for heating devices: resistance to high temperatures and pressure, the smallest thermal increase (in the established temperature range), significant thermal conductivity, shock resistance (which is important when used in industrial premises), and a long period of operation in heating systems.
In order to ensure the quality of welding and the reliability of the seams, the finished heating registers are subjected to pressing and hydraulic tests. The pointer is filled with liquid, and excess pressure is reached, usually 1.6 MPa. If a leak is detected, the liquid is combined, the detected holes are welded, after which the process is repeated.
Calculation
There are methods for calculating the characteristics of heating devices. They are distinguished by the accuracy of their calculations. However, to organize heat supply with the support of metal or aluminum heating registers, it is recommended to seek the services of specialists. Another option is to use special software .
However, in some cases it is necessary to properly think through the heating device yourself. To do this, you can use a simple diagram. You should first know the following characteristics:
- The general area of the heated building.
- The heat transfer coefficient of the register material used.
- Diameter of pipes used for manufacturing
Knowing the characteristics, you can calculate the power of the device.
Calculation of registers made of smooth pipes , their quantity and parameters required for heating a particular building can only be carried out approximately with a significant degree of error. This is explained by a large number of conditions on which the temperature in the room depends, such as: wall thickness, the thermal insulation properties of the room, the number and area of openings (and, in addition, the total area of the cracks in them), ventilation intensity, outside air temperature, wind speed.
Therefore, it is more correct to plan the number of parts in the registers and the number of heating devices themselves “with a reserve”, and you can control the temperature in the room by changing the operating modes of the heating boiler. However, there is an unofficial standard: for heating 1 sq. meter of a building with a ceiling height of 3 meters requires 1 meter of pipe with a diameter of 60 mm.
Pipes and a radiator in the heating system of a private house...
From the wording of the question it is not entirely clear whether the private house is yours or belongs to the customer...
If we assume that the house belongs to the customer of the work, then in order to avoid claims on his part, everything should be done in accordance with the project (contract).
If you equip your home with a heating system, then its elements should be chosen taking into account durability and ease of maintenance, naturally taking into account the “price of the issue” available to you personally. Usually everything works out when the work is carried out according to a ready-made project that suits everyone.
Now, in order. And so the pipes:
“...which pipes to choose: steel or ferrous metal?” There are only two types of ferrous metal - steel and cast iron. Cast iron differs from steel only in the percentage of carbon in the alloy and usually in the presence of certain alloying additives. Pipes for heat, water and gas supply systems previously (in the last century) were produced only from steel of various grades. This was due to their relatively low cost and the ability to quickly install systems. However, this is where the advantages of steel pipes ended. The main disadvantage of steel pipes is their poor resistance to corrosion and, as a result, low durability. Therefore, if you want to leave a legacy of a reliably operating heating system, then I do not recommend using ferrous metal pipes.
Currently, polymer and metal-polymer pipes are produced for use in heat-water-gas supply systems. Their structural difference is the reinforcing layer. Some use fiberglass, others use metal (usually aluminum).
Their main advantage is the impossibility of recycling the material under natural conditions. It is this quality that determines their exceptionally high resistance to corrosion destruction. In addition, polymer pipes have many other advantages over steel ones. When operated under certified conditions, the service life of polymer pipes is at least 50 years.
In accordance with modern design standards, pipelines of all systems must be laid covertly. In interior design, pipelines of engineering systems are not used. Pipelines of engineering systems are fixed to elements of load-bearing structures of buildings, in specially equipped channels, behind decorative lining. As a last resort, pipes are laid in special plastic boxes.
And now about: “which radiator is better to buy for a private house, the area of the house is approximately 60 square meters?”
Let me assume that you need a heating device for your home, and not a source of thermal energy. If this is the case, then it is usually chosen according to two parameters - the required power and as an element of the interior of the room, naturally, based on financial capabilities. The power of a heating device for a “regular” living space made of stone-reinforced concrete structures with “standard” thermal insulation is selected at the rate of 1 kW per 10 sq.m. area. But it is far from a fact that the temperature in the room after such a “selection” will be comfortable. Typically, one heating device is installed in each room. In large rooms and taking into account the requirements of space-planning solutions, several heating devices can be installed. If a decision is made to use radiators of standard designs as heating devices, then most likely they will need to be covered with decorative grilles, which will inevitably reduce their efficiency.
Today, in terms of design and technical characteristics, the most efficient heating device is the fan coil. None of the radiators can compare with it in terms of operating efficiency and heat transfer.
Fan coil units are currently produced in a fairly large number of models, differing significantly in a number of capacities and appearance. All of them fit easily and naturally into any interior.
That’s basically all about which pipes and radiator are better in the heating system of a private house...
If you have any questions, I will answer them in personal correspondence. Good luck!
Connection
Connecting devices to the heating system can be done using welding, threaded and flange connections - the selection of one or another type of connection depends on the useful features of the heating system. If the device consists of a significant number of parts and pipes of larger diameter, it is important to use stands and fasteners that support the register not only at the bottom, but also in the middle, in order to share the weight and not form an excessive load on the lower sector. Please note that for best performance, it is preferable to install the register closer to the floor.
Design characteristics
Radiators made of smooth steel pipes are most often used. Welding of smooth pipes can be registered and serpentine. Registered ones can have 2 types of pipe connections - column and thread. Column - connecting each pipe to each other on both sides using jumpers. When connecting “thread”, the jumpers are installed alternately, first on one side, then on the other. This ensures a consistent connection, and the coolant flows around all the pipes one by one.
The heater radiator can be welded not only from round, but also from square pipes. They are not much different, but they are more difficult to work with and have higher hydraulic resistance. Although such radiators are much more compact.
In this case, the contact area of the metal with the air is much larger, which increases heat transfer. Such heating registers do not look very presentable, but they heat the room well, despite the temperature outside the window.
DIY making
One of the advantages of using registers in heating systems is the possibility of their independent production. For this purpose, round metal pipes are most often used. Despite the fact that the heat transfer coefficient of the heating register in this case will not be perfect, the production process will not require special skills.
To make this heating element yourself, you will need a pipe with a diameter of 40 to 70 mm. The largest cross-sectional value will lead to significant heat losses during coolant circulation.
make a heating device with your own hands according to the following work plan:
- Calculation of the optimal characteristics of the heating device - pipe diameter, total length of the section.
- Formation of a drawing to calculate the optimal amount of material used.
- Carrying out work on the production of a heating register.
- Checking the structure for leaks.
Read also: How to turn a bolt on a lathe
To accomplish this task, you will need a steel pipe specialized for forming the main registers and a line of the smallest diameter. With its help, heating devices will be combined with each other and the heating system. In addition, special end caps for the pipes will be required.
At the first stage , use a grinder to cut the pipes to the required length. It is not recommended to use a welding machine for this, since a weld will form at the ends of the heating register from the convex pipe.
Then holes are made to connect the pipes. The pipes are welded using a welding machine and end caps are installed. To ensure safe operation, the air vent and bleed valve must be identified. They are installed at the top of the system, but on the opposite side relative to the place of connection to the heating.
In some cases, improvements are made to the traditional design of a steel or bimetallic register. It consists of installing an electric heating element. A homemade heating device will produce heat using a heating element. But for this, it is necessary to determine the shut-off valves during installation so that the coolant can circulate only inside the heating device. This makes a good source of heat.
Correct installation of heating devices can be carried out in 2 ways - using threaded connections or using a welding machine. It all depends on the single mass of the structure, its dimensions and the characteristics of the heat supply system. In general, experts advise following the same instructions as when installing radiators.
Heating devices are an essential element of any water heating system. They are usually the most expensive part. A good opportunity to save money would be to use homemade radiators. They are made from smooth round steel pipes or from profile pipes. The latter option is somewhat more expensive, but allows you to reduce the depth of the device and get a more aesthetic appearance.
The use of a profile pipe for the manufacture of heating registers has a number of features. When starting to work with your own hands or deciding to buy a “homemade” product, you need to carefully weigh the pros and cons. Studying the basic rules by which heating registers are made from a profile pipe will help you avoid mistakes when working independently and will make it possible to make a competent choice of the necessary parameters.
Floor waterproofing
In order for the heating system to work more efficiently, it is important to take into account other factors that affect the internal climate in the house. For example, often paying great attention to the insulation of windows, walls, doors and ceilings, they completely forget about the huge floor areas in the house. To insulate them, you can use modern waterproofing of the subfloor.
Insulation options
There are three main types of waterproofing the floor in an apartment before screeding. It is simply necessary not only for heat conservation, but also for sound insulation and protection of the lower floors from water leaks in case of accidents. The floor can be insulated as follows:
- Pasting. Special insulating materials are laid in even layers on top of each other and securely fastened.
- By painting. There are special mixtures that are applied with a brush to the insulated surface in several layers. The main disadvantage of this method is its fragility.
- By pouring. A special cement-bitumen mortar is prepared and poured evenly into the room.
- By pouring. This method is used in houses without a basement. An insulation cushion is made from crushed stone and sand.
- Combined. Most often, several methods are used at once.
Design of heating registers
Heating devices in the form of registers are a structure of several vertical or horizontal pipelines connected to each other using jumpers. In this case, the connecting elements can have different shapes and sizes. Depending on their location, classification is performed.
Register structure
For the manufacture of heating registers, smooth carbon steel pipes with a round cross-section, as well as square and rectangular ones, are used. Their combined use is possible. Stainless and galvanized steel, aluminum, copper, and brass can also be good materials for registers, but they are much more expensive and more difficult to process with your own hands.
Heating registers made of steel profile pipes are considered the simplest to make. They can be made in two main configurations: sectional type and coil type (S-shaped).
In a sectional type register, several sections of profiled metal with capped ends are arranged in parallel and connected to each other by round tubes of smaller cross-section. The jumpers ensure that the rows of the device are filled with coolant from both sides simultaneously. Moreover, the closer to the edge the transition pipes are installed, the higher the heat transfer of the device.
In a coil register, the liquid passes in an S-shape through rows of profile pipes, gradually cooling. To add rigidity to the structure, additional blind jumpers are used. Horizontal rows are connected in pairs by a snake using tubes of a smaller cross-section, like in sectional models, or sections of the main profile. The latter option is preferable due to lower hydraulic resistance and greater heat transfer.
Connecting pipes are made with threads or welding. The most effective option for connecting a heating device is a top-down diagram. For low models and in the case of forced circulation of coolant, entry and exit from below may be justified.
The design of the register must include a Mayevsky valve or an automatic air vent. It is located at the end of the top row on a threaded fitting to allow replacement. A prerequisite for installation is to maintain a slope of 0.05% in the direction of coolant movement.
Registers can be either stationary or portable. The former work as elements of a general heating system, the latter perform the task of local heating. The heat source for a separate mobile register is a heating element with a power of 1.5-6 W, mounted in the housing.
Important! The distance between register rows significantly affects heat transfer. The closer the pipes are to each other, the greater their mutual influence, which reduces the efficiency of the device. It is recommended to place the rows at a distance of at least the height of the profile pipe, increased by 50 mm.
In addition to large horizontal registers, small vertical models are also in demand. If you carry out the work carefully, you can get homemade cheap heating radiators from profile pipes that are almost as aesthetically pleasing as modern sectional radiators.
In some cases, steel registers can be a good addition to the heating units already installed in the room. Despite the lower heat transfer than radiators of a similar size, their use may be more appropriate due to their lower cost.
High vertical registers are very convenient for high rooms or near high window openings. They can successfully fit into the interiors of rooms with unusual design solutions. By experimenting a little with color and shape, you can get a creative decoration from simple heating devices.
Advantages and disadvantages of profile pipe
Most often, heating registers are made from smooth round-section water and gas pipes. They are cheaper, have better hydraulic characteristics for transporting coolant, and greater tensile strength with a small wall thickness. What is the reason for the use of profile pipes for the manufacture of registers?
Heating radiators made from rolled metal of square and rectangular cross-section have a number of important advantages:
- compactness of the device in depth;
- the ability to give an attractive appearance;
- the surface area is greater than that of a round pipe of the same height;
- additional opportunities for creative design of non-standard premises;
- They are relatively easy to make with your own hands and do not rotate during operation;
- can be made from pipe scraps left over after construction work.
However, there are also plenty of disadvantages:
- the profile pipe is not intended for transporting liquid;
- lower resistance to water hammer and high pressure;
- The length of the welds is longer than that of similar round pipe registers, which increases the likelihood of leaks and reduces the overall reliability of the device.
Read also: Barrel polishing paste
Thus, before deciding on the advisability of using registers made of profile pipes, you should evaluate all possible options, carefully analyze the operating conditions and the requirements that heating devices must meet in each specific case.
Selecting parameters
The heating register parameters are determined based on the required heat output. The most accurate values are provided by a detailed thermal engineering calculation of heat loss through the building envelope, but since it is quite labor-intensive, we will consider alternative options.
Very approximately, for a typical insulated room with a height of no more than 3 m, you can take 1 kW of thermal power per 10 m 2. More accurate values can be determined from the table below, depending on the quality of thermal insulation and the volume of the room.
Q=K ·F · ∆t,
K – heat transfer coefficient, W/(m 2 0 C) , for a single pipe K = 11.3 W/( m 2 0 C );
F – pipe surface area, m 2, F = 2· (a+b) · l ,
where a and b are the dimensions of the cross-sectional sides, and l is the length of the pipe, respectively, m;
∆t – temperature difference, 0 C, ∆t= 0.5·(t1 + t2) – tк ,
where t1 and t2 are the coolant temperatures at the inlet and outlet of the device; tk – temperature in the room.
The required pipe length is calculated by dividing the required thermal power by the heat output of 1 m of pipe. The number of rows is determined by rounding up and is determined by the availability of free space and the configuration of the room. For the obtained number, the heat transfer value is specified taking into account the mutual irradiation of the pipes using a reduction factor of 0.9 for each row.
The length of the register can be taken structurally, taking into account the characteristics of the room and the location of the equipment. For example, if there is a large window, then it is desirable that the length of the threads be no less than the size of the window, creating a wide thermal curtain for cold air.
Advice! In some cases, it makes sense to take the length of the register across the entire width of the room. This will ensure the most even heating of the room. For objects such as greenhouses, this is especially important.
The cross-section of the profile pipe is taken either based on the available material, or is selected by trial calculations and finding the optimal combination of cross-section and length of rows of the heating register. The most commonly used pipes are 60*40, 60*60 and 80*60 with a wall thickness of 3 mm. Large cross sections are not desirable, since the increased volume of coolant will create additional load on the boiler.
Note: it is better not to skimp on wall thickness. The thicker the pipe wall, the longer the heating device will last. It will be able to withstand large pressure surges and is more resistant to corrosion.
Based on the calculations carried out, the final selection of heating register parameters is made and a drawing is drawn up. According to the accepted dimensions, a heating device is ordered or the register is made by hand.
Size calculation
Making your own pipe heating device is not very difficult. But there is one important point here - to correctly calculate the dimensions of the device. After all, such an indicator as heat transfer will depend on them.
Required indicators
The calculation is not easy, because it requires some criteria for the premises itself. For example: glazing area, number of entrance doors, what windows are installed, whether the floor, walls and ceiling are thermally insulated.
It’s difficult to take all this into account, so there is a simpler option that takes into account only two indicators:
The heating radiator is selected based on the heat transfer per 10 m² equal to 1 kW of thermal energy. The ceiling height should not exceed 2.8 m.
How can this help when assembling a homemade heating device? To do this, you will have to compare it with a conventional cast iron radiator of the MS-140-500 brand. The heat output of one section is 160 W, volume is 1.45 liters. What does this give us?
You can determine exactly how many sections will be needed if you use a cast iron device. The total volume of coolant that will fit in one battery is determined from the number of sections. And knowing this number, you can approximately determine the volume of the pipe radiator.
The thing is that the thermal conductivity of steel is 54 W/m*K, and that of cast iron is 46 W/m*K. That is, a small downward error will not have any effect on the quality of heat transfer.
Calculation example
Conventionally, we will assume that an eight-section cast-iron heating device corresponds to the above-described ratio. Its volume is 8x1.45=11.6 liters.
Now we can calculate the length of a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm, which we will use to assemble a homemade battery. The standard cross-sectional area of the pipes is 708.5 mm². We divide the volume by the cross-section, we get the length (we convert liters to mm³): 116000:708.5= 1640 mm. Or 1.64 m.
A slight deviation in both directions will not greatly affect the heat transfer. Therefore, you can choose either 1.6 or 1.7 m.
Making registers yourself
Steel registers have a fairly simple design and do not require much skill to create. Almost any person who has experience working with a welding machine can make homemade heating radiators from a profile pipe. Unlike round ones, they are conveniently fixed in place, which makes welding easier.
Required materials and tools
Before starting work, you need to stock up on everything you need. Let us consider in detail what is required for the simplest three-row register.
- Profile pipe in accordance with the design parameters. Dimensions can be from 30x30x3 to 80x80x3 mm.
- A round pipe with the same wall thickness with a diameter of 25 or 32 mm depending on the cross-section of the profile pipe.
- Steel sheet 3 mm thick.
- Branch pipes with external or internal threads in accordance with the diameter and type of connection – 2 pcs.
- Steel coupling with internal thread with a diameter of 15 mm and Mayevsky tap.
- Welding machine.
- Drill.
- Bulgarian.
- Hammer.
- Marker or metal rod.
- Roulette.
- The profile pipe is cut into pieces of the required length in accordance with the drawing.
- The round pipe is cut into 4 pieces of 10 cm each.
- 6 plugs are cut from sheet metal in accordance with the size and shape of the profile pipe. They should be 3-5 mm smaller than the cross-section of the pipe. This will allow you to neatly hide the weld in the gap.
- The pipes are laid on a flat horizontal surface strictly parallel at a distance of 10 cm. You can use two wooden beams for support. The ends are aligned in one line. Marks are made for the holes at a distance of about 5-10 cm from the edge.
- Using a cutter or drill, the intended holes are cut in accordance with the diameter of the jumpers.
Work order
- The jumpers are fixed in place and secured by welding at 2-3 points.
- Having positioned the structure vertically, the jumpers are finally welded. It is recommended to first make a thin seam at low current, which will allow the gaps to be filled well. Next, a thick main seam is performed at increased current.
- The internal space of the register is cleared of metal debris and slag.
- The plugs are applied, tacked and welded to the ends of the profile pipes.
- Welding seams are processed. The protruding parts are knocked down with a hammer, then each seam is cleaned with a grinder.
- Holes in the register are drilled depending on the selected connection diagram. In this case, it is better to place them not in the center of the ends, but slightly higher or lower.
- Connecting pipes are welded to the holes.
- The seams are cleaned and all holes except one are plugged. The register is filled with water under pressure and the welding quality is checked. The seams must withstand pressure up to 13 atm.
- The outer surface is cleaned, degreased and painted with heat-resistant paint.
- A fitting is welded to the top row and a Mayevsky valve is installed.
Sometimes supports are welded to the register, but devices without them are more versatile. If necessary, you can always use a stand, but the weight is less and you can still mount it on the wall.
Which metal is better
To begin with, we note that structures of this kind can be intended both for heat transfer, performing the function of radiators, and for heat intake, when a tubular register is mounted directly in the combustion chamber of a boiler or furnace.
Plus, in some models, instead of a coolant liquid, heated gas is used, for example, a radiator chimney pipe.
- Steel pipes for heating radiators are deservedly considered leaders in this market sector. Of course, the heat transfer of steel is not as high as that of aluminum or copper; it is susceptible to corrosion and requires regular maintenance. But these shortcomings are more than compensated for by the affordable price, as well as a wide range of types and sizes. In addition, it is much easier to weld ordinary ferrous metal than non-ferrous metal.
- Stainless steel is used extremely rarely for such structures. Apart from the fact that its cost, to put it mildly, is far from budget, argon welding is used for soldering stainless steel, and not every professional welder can work with it.
Important: in this case there is simply no point in using galvanized iron. Thin zinc coating simply burns out during the welding process.
As a result, the already weak weld is further affected by corrosion.
The use of copper tubular registers is justified only in the case of copper wiring throughout the house. The heat transfer of copper is four times higher than that of ferrous metals, so here we can talk about heating with pipes without radiators, or rather with a minimum number of radiators. But, firstly, the price of copper is incredibly high, and secondly, this metal is very demanding in terms of operating conditions.
Copper heating wiring.
- Copper systems require a finely purified coolant that does not have solid abrasive inclusions.
- In such systems, fittings must be copper or compatible metals such as bronze, nickel, chrome or brass. Moreover, it is strictly forbidden to combine aluminum with copper.
- Copper pipelines necessarily require high-quality grounding, as there is a danger of electrochemical corrosion.
- Copper is a soft material, so the system needs additional protection; naturally, casings and shields also cost money.
The cast iron radiator heating pipes shown in the photo are still used in industrial buildings and technical rooms. But the weight of such a design is much higher than that of a household cast-iron battery. Considering the unesthetic appearance and rather low efficiency, they are not popular.
Tubular cast iron batteries.
Tip: cast iron tubular registers are ideally suited for installation in the combustion chamber. Optimal heat capacity, low price and unpretentiousness in terms of coolant make them leaders in this area.