Here you will learn:
- Types of heating
- Alternative heating for a cottage or private house
- Pros and cons of different types of coolants
- What is the most profitable heating system in a cottage?
- Comparison of costs of different heating systems
- One- and two-pipe heating systems
- Basic elements of a water heating system
- Which heating radiators to choose
- Installation of a cottage heating system
Regardless of whether an old system is being modernized or it is being designed from scratch in a newly built house, the first thing to start with is becoming familiar with the regulatory documentation. It describes in detail how the equipment is put into operation and describes the subtleties and features of its further use.
After spending some time on this, you can be sure that the heating system will last for many years. From year to year, the requirements are adjusted and updated. But there are some principles that every cottage owner should know. The first thing that needs to be ensured when installing a heating system is explosion and fire safety.
For safe operation during the installation process, you need to ensure free access to the equipment for cleaning and regular checks.
The list of rules that will help make a private home not only cozy, but also safe to live in, should include the following aspects:
- The temperature of open heating system elements should not be higher than that recommended by the manufacturer.
- Equipment and all appliances should be properly insulated. This will avoid burns, eliminate the formation of moisture and reduce heat loss. In addition, hot elements can ignite dust, gas or aerosol in the room.
- When using a coolant, the temperature of the latter must be 20 degrees Celsius lower than its evaporation or self-ignition temperature. For example, if the system uses water, then it must be prevented from boiling. An excellent solution would be to raise the pressure.
There are also operational requirements for the heating system. After all, any equipment must be as strong, durable, easy to operate, silent and easy to repair as possible.
It is better to order equipment from trusted manufacturers. Such companies produce truly high-quality products, since they stand behind them with their own name.
By choosing a boiler, radiators and pipes that best meet the listed criteria, you can save yourself from many problems.
Types of heating
There are two types of heating of country houses: autonomous and centralized heating. They are divided into several subspecies, operating on different energy sources:
- Natural gas.
- Liquid fuel – gasoline, diesel, diesel oil.
- Solid fuel - firewood, pellets, coal.
- Electricity.
- Natural sources of energy.
Each of them has its own set of advantages that are beneficial to use under certain conditions.
Heating equipment for a country house
Alternative heating for a cottage or private house
Heat pumps or solar collectors are most often used as alternative sources of thermal energy. The latter can also be a source of electricity. The cost of such equipment at the moment is astronomical and only owners of large, very large residential properties, where such investments will pay off in the foreseeable future, can afford them. In developed countries, governments actively subsidize the use of such equipment. Well, in the former USSR, the use of heat pumps and solar collectors turns out to be much more expensive than gas, coal and even electricity.
Heat pumps
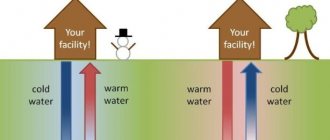
Heat pumps are a very real alternative to traditional heat generators and boilers.
The operating principle of this energy-saving system is somewhat reminiscent of an air conditioner, which transfers heat from indoors to outdoors. A heat pump transfers heat from the ground into a heated room and transfers cold back.
When a heat pump operates, energy is not spent on generating heat, but solely on moving it.
Heat pump operation diagram. Click to enlarge.
The functionality of this system makes it possible to obtain approximately 4.5 kW of thermal energy, spending only 1 kW of electrical energy on its transportation.
Heat pumps are highly efficient, reliable and cost-effective. Alternative heating of the described type has only one significant drawback - the decision to install it should be made only at the zero construction cycle.
This requirement is dictated by the large volume of excavation work.
Pros and cons of different types of coolants
Depending on the coolant, heating can be water, air, or electric. Some cottages are heated using open flames - fireplaces or stoves. Each type of coolant has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Water systems consist of a boiler, pipes and radiators. The cold coolant is heated in the boiler, then flows through pipes into radiators, where it gives off heat to the surrounding air. The cooled water is fed into the boiler and the cycle repeats again.
If the system is combined with underfloor heating, then the coolant flows from the radiators into the second circuit and only then returns to the heating device. The boiler itself can operate on gas, electricity, solid or liquid fuel.
Water heating with radiators
The principle of operation of the air system is simple: cold air enters the heat generator, from where it is supplied through air ducts to the rooms of the cottage. Warm flows displace cold ones, which also enter the heat generator, and the cycle repeats.
The air circulation mode can be natural or forced. In the first case, the heating in the cottage is disrupted if the windows or doors are open. And in the second you have to use electric fans.
To heat the cottage, you can use convectors, heaters or any type of electric heated floor (cable, carbon, etc.). These systems are the easiest to maintain because they are usually fully automated.
Scheme of air heating with a gas furnace
Electric heating of a cottage will cost much more than other types of heating. Another disadvantage: in the event of an accident, the house may be left without electricity and heating at the same time.
A stove or fireplace may be a good option for a small space, but it is unlikely to be suitable for a house with several rooms. In addition, you will have to give up the idea of organizing a convenient hot water system.
Autonomous heating of a private house
Heat pumps
The most universal alternative heating for a private home is the installation of heat pumps. They work on the well-known principle of a refrigerator, taking heat from a colder body and releasing it in the heating system.
The circuit is complex at first glance and consists of three devices: an evaporator, a heat exchanger and a compressor. There are a huge number of options for implementing heat pumps, but the most popular are:
The cheapest implementation option is air-to-air. In essence, it resembles a classic split system, but electricity is spent only on pumping heat from the street into the house, and not on heating air masses. This helps save money while keeping your home perfectly warm throughout the year.
The efficiency of the systems is very high. For 1 kW of electricity you can get up to 6-7 kW of heat. Modern inverters work great even at temperatures of -25 degrees and below.
“Air-water” is one of the common implementations of a heat pump, in which the role of a heat exchanger is played by a large-area coil installed in an open area. Additionally, it can be blown by a fan, causing the water inside to cool.
Such installations are characterized by a more affordable cost and simple installation. But they are capable of operating with high efficiency only at temperatures from +7 to +15 degrees. When the bar drops to a negative level, efficiency drops.
The most universal implementation of a heat pump is “ground-water”. It does not depend on the climate zone, since a layer of soil that does not freeze throughout the year is available everywhere.
In this scheme, the pipes are immersed into the ground to a depth where the temperature is maintained at 7-10 degrees throughout the year. Collectors can be located vertically or horizontally. In the first case, it is necessary to drill several very deep wells, in the second, to lay the coil at a certain depth.
The disadvantage is obvious. complex installation work that will require high financial investments. Before deciding to take such a step, you should calculate the economic benefits. In areas with short, warm winters, it is worth considering other options for alternative heating of private houses. Another limitation is that a large free area is required - up to several tens of square meters. m.
The implementation of a water-to-water heat pump is practically no different from the previous one, however, the collector pipes are laid in groundwater, which does not freeze throughout the year, or in a nearby body of water. It is cheaper due to the following advantages:
- Maximum well drilling depth – 15 m
- You can get by with 1-2 submersible pumps
Biofuel boilers
If there is no desire and opportunity to equip a complex system consisting of pipes in the ground, solar modules on the roof, you can replace the classic boiler with a model that runs on biological fuel. They require:
It is recommended to install such installations in conjunction with the previously discussed alternative sources. In situations where one of the heating devices does not work, you can use the second one.
When deciding on the installation and subsequent operation of alternative sources of thermal energy, it is necessary to answer the question: how quickly will they pay for themselves? Of course, the systems considered have advantages, including:
- The cost of energy produced is less than using traditional sources
- High efficiency
However, you should be aware of the high initial material costs, which can reach tens of thousands of dollars. The installation of such installations cannot be called simple, so the work is entrusted exclusively to a professional team that can provide a guarantee on the result.
Alternative heating of a private home is becoming in demand, which is becoming more profitable against the backdrop of rising prices for traditional sources of thermal energy. However, before you start converting your current heating system, you need to calculate everything by considering each of the proposed options.
It is also not recommended to abandon the traditional boiler. It must be left and in certain situations, when alternative heating does not fulfill its functions, it will remain possible to warm your home and not freeze
What is the most profitable heating system in a cottage?
If it is possible to connect to a gas main, this is an ideal option. Water heating in a cottage from a gas boiler was and remains the most profitable. It is best to use radiators as heating devices.
Warm floor in a cottage
An alternative to traditional batteries is water heated floors. However, in regions with harsh climates, underfloor heating alone will not be enough. You can choose a combined option: radiators and heated floors.
In the absence of gas, you have to choose which energy source is the cheapest. It can be electricity, solid or liquid fuel. When making calculations, they are guided by the area and number of floors of the cottage. The type of building materials and thermal insulation features are also important.
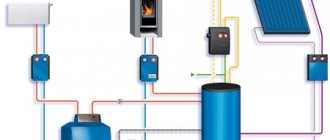
For a comfortable stay, you need to take care of the hot water supply. It often makes sense to connect a double-circuit boiler, which will provide both heating and the required volume of hot water.
Scheme of combined heating and hot water supply
Why electricity
Electric heating differs from classic water-stove and gas systems by being more economical and practical. We will leave the first aspect for discussion below, and describe the operational advantages here:
Electric heating is not only silent, but also environmentally friendly. It is transported safer than gas and does not emit harmful substances at all, both into the atmosphere and indoors. In the absence of waste, the need for exhaust chimneys and traction structures disappears. Heating using coal or wood is not at all comparable to electric systems. Heating with electricity does not require large one-time costs. You can make a comparison using gas as an example: to connect a house you must purchase equipment for each room, install communications, a boiler, and connect it to a common pipeline. Moreover, all this must be done together, since it is impossible to postpone connecting any part of the house to the system. And the electrical method allows you to organize sequential installation: first, the most important parts of the house are connected, and then, as funds accumulate, peripheral parts are connected. Thanks to the possibility of using a multi-tariff meter in a private house or apartment, as well as the constant development of technology in this area, electric heating is already the most economical among analogues
You should not focus on the high price of the equipment - it quickly pays for itself due to low energy consumption. Almost every method of organizing electric heating allows you to install it yourself, without many additional tools.
Of course, the use of electrical systems for heating cannot be called ideal. The work of high-quality heating of each home requires taking into account many features. In some regions, the cost of electricity can be so high that gas cannot be avoided. In old apartment buildings, it is difficult to switch to electric heating for two reasons: it is very difficult to disconnect from the central highway, and the electrical network will have to be reconnected, taking into account powerful equipment.
Despite this, the overall picture tips the scales towards electricity. For premises where there is no gas or where there is no possibility of supplying it, it is a real salvation.
Comparison of costs of different heating systems
Often, the choice of a specific heating system is based on the starting cost of the equipment and its subsequent installation. Based on this indicator, we obtain the following data:
- Electricity. Initial investments up to 20,000 rubles.
- Solid fuel. Purchasing equipment will require from 15 to 25 thousand rubles.
- Liquid fuel boilers. Installation will cost 40-50 thousand.
- Gas heating with own storage. Price 100-120 thousand rubles.
- Centralized gas main. Due to the high cost of communication and connection, the cost exceeds 300,000 rubles.
Ground-to-water heat pumps
These devices are the most versatile alternative sources of heating for suburban households in terms of dependence on the climate zone.
The principle of their operation is based on the fact that even at a depth of several tens of meters in permafrost areas, the soil temperature exceeds zero degrees.
Heat exchangers designed to extract heat from the ground are probes that are immersed in special wells. It requires the laying of pipelines, the length of which exceeds several dozen meters, and in addition to the high price of the pump, the cost of its installation itself is quite high. Thus, drilling one well costs approximately several thousand rubles per linear meter, but more than one is needed. In addition, you still need to install a pump and immerse probes in the well.
It will cost a little less to install a ground-water pump with a horizontally located collector. Heat exchangers are immersed in trenches below the freezing level. The disadvantage of such heating is the large area required to install a heat pump. The resulting heat is spent on heating water for domestic needs and transferring thermal energy to heating devices.
One- and two-pipe heating systems
In a single-pipe water heating system for a cottage, the circulation of coolant from the boiler and back is carried out along one line, which simultaneously plays the role of both supply and return. The whole scheme eventually closes into one large ring encircling the building. And to this ring, along the entire length of the pipe, the installation of heating radiators begins, with the help of which the coolant transfers energy to the living quarters.
The simplest diagram illustrating the principle of operation of a single-pipe heating system
Like any other complex system, single-pipe heating distribution has its advantages and disadvantages. What is a program for calculating the power of a heating boiler, you can read in our article.
Its advantages include the following.
- Saving on material - with a similar housing heating scheme, one third less pipes are required. Consequently, the cost of installing a heating system will be lower.
- Due to the main line, which simultaneously performs both the supply and return roles, the cost of effort and time for installing the entire system as a whole is reduced.
- Compactness - with single-pipe wiring, heating system communications take up less space. They are much easier to hide in a wall or behind a decorative box.
- Simplicity - it is much easier to independently equip such a heating system for your cottage.
Single-pipe heating with bottom wiring
But for the low price and simplicity, you have to put up with one, but very significant drawback of such a scheme - the inability to achieve uniform heat distribution across all radiators. At the beginning of the heating pipe, the batteries will be excessively hot, and at the end, on the contrary, they will be barely warm.
Advice! If for some reason you want to install a single-pipe heating system, then you can solve the problem of uneven heat distribution as follows: from the boiler to the farthest point of the line, gradually increase the number of sections in the radiator. Due to this, the heat transfer of the system will be more uniform. The downside of this approach is the increased costs of radiators, which call into question the main advantage of single-pipe wiring - low cost.
Vertical wiring of a single-pipe circuit is suitable for apartment buildings or with natural coolant circulation. For a cottage, it makes sense to give preference to a horizontal system. Often the main line is “hidden” in the wall or under the floor surface
"Leningradka" is the most advanced of single-pipe heating systems. Each radiator is connected through tees and bends and is equipped with shut-off valves. With its help, the owner of a house with a one-pipe system can disconnect a separate battery from the main without turning off the entire circuit as a whole
A more modern and advanced heating system arrangement is a two-pipe layout. Here, instead of one line, two are used - the first for supplying coolant to the radiators, the second for discharging it back to the boiler. These pipes are called “supply” and “return” respectively.
A picture illustrating the principle of operation of a two-pipe heating system
In many ways, the advantages and disadvantages of one- and two-pipe heating systems are mutually opposite. So, the advantages of the “supply” and “return” scheme include the following.
- More uniform distribution of thermal energy across radiators. With a competent approach to regulation on the supply line, all heating radiators in the cottage will have approximately the same temperature. The situation when there is boiling water in the first radiator and lukewarm water in the second does not happen here.
- Smaller diameter of pipes required for laying such a heating system.
- The ability to regulate the temperature in each individual room using a thermostat and a tap on the supply line to the battery.
A two-pipe heating system has its drawbacks, two of them - increased costs for materials and the need to spend more time and effort on installing heating. Moreover, the first drawback is considered controversial by many owners of country houses - yes, for heating with “supply” and “return” more pipes are needed, but at the same time their diameter is smaller. You will also need more compact (and therefore cheaper) fittings, connectors and shut-off valves.
Example of vertical and horizontal heating schemes
With this diagram you can easily understand the difference between one- and two-pipe water heating pipes.
Interesting! The best distribution of thermal energy between heating radiators can be achieved using radial wiring - when from the boiler to each individual radiator there are its own “supply” and “return” lines, laid under the floor surface. Such a scheme requires a lot of time and money to install, but the result will be high heating efficiency.
An example of a radial two-pipe heating system from a distribution manifold
Collector heating supply for a cottage
Collector heating of the cottage
How to properly install heating in a cottage if its area is equal to or exceeds 200 m². Even installing a two-pipe system in this case will be impractical. To solve this issue, it is best to use collector piping.
Currently, this is one of the most difficult ways to organize heating of a cottage with your own hands. To uniformly distribute the coolant over a large area of the building, a multipath piping scheme is used. Immediately after the boiler, the main and return collectors are installed, to which several independent lines are connected. Unlike the two-pipe heating system of a cottage, the collector system provides the ability to regulate the operation of the heat supply for each individual circuit. For this purpose, control devices are installed - thermostats and flow meters.
The features of collector heating for a do-it-yourself cottage include:
- Uniform distribution of heat over all circuits, regardless of their distance;
- Possibility of using small diameter pipes – up to 20 mm. This is due to the small length of each node of the system;
- Increased pipe consumption. In order to properly install collector heating in a cottage, it is necessary to draw up a pipeline installation diagram in advance. They can be wall or floor mounted;
- Mandatory installation of a pump for each circuit. This is due to the high hydraulic resistance that occurs in the collector. It may interfere with coolant circulation.
When choosing a ready-made heating supply project for a cottage or when drawing it up yourself, you need to take into account the heat losses of the building. The design power of the entire system will depend on them.
For two and three-story cottages with a large area, a heat supply system with several distribution manifolds is best suited.
Shut-off and control valves: how they work
These are the parts of the system that control the flow of coolant. They completely or partially block the flow sections of the pipes. They are divided into three types:
- Shut-off valves - for example, a ball valve. It has two positions: open and close. The body is made of brass. The water supply process is controlled by a handle. The following valves are installed in the system:
- to shut off the radiator to carry out maintenance,
- for covering risers and branches,
- to turn off heating or pumping devices for repair purposes,
- for filling and emptying the entire system.
Sectional view of ball valve
- Shut-off and control – there are 3 types of parts:
— Balancing valves, they are mounted on the return line at the beginning of the branch, on the riser or at the radiator outlet. These parts regulate the amount of liquid in the pipe. If you partially block the cross-section of the pipeline, you can reduce water consumption in a specific section of the system.
Balancing valve
— Automatic pressure regulators are needed if there are many radiators in the house. They work in tandem with a balance valve: one regulates the flow, the other adjusts it according to the indicators of the radiator thermostats.
Pressure regulators
— Thermostatic radiator valves – reduce and accelerate the flow of hot water in the radiator at will. It is considered an important element for management - it helps to save on energy.
Thermostatic radiator valves
- Mixing-regulating - regulates the temperature of the liquid in the system.
Thermostatic mixing valve
Shut-off and control valves help distribute heat evenly throughout the house. It controls the movement of coolant and temperature. This saves the owner money and makes the system as a whole safe to operate.
Basic elements of a water heating system
The main elements of a water heating system include:
- boiler;
- a device that supplies air to the combustion chamber;
- equipment responsible for removing combustion products;
- pumping units that circulate coolant through the heating circuit;
- pipelines and fittings (fittings, shut-off valves, etc.);
- radiators (cast iron, steel, aluminum, etc.).
Selecting a boiler by the number of circuits
To heat the cottage, you can choose a single-circuit or double-circuit boiler. What is the difference between these models of boiler equipment? A single-circuit boiler is designed only to heat the coolant intended for circulation through the heating system. Indirect heating boilers are connected to single-circuit models, which supply the facility with hot water for technical purposes. Dual-circuit models provide for operation of the unit in two directions that do not intersect with each other. One circuit is responsible only for heating, the other for hot water supply.
Selecting a boiler by type of fuel
The most economical and convenient type of fuel for modern boilers has always been and remains main gas. The efficiency of gas boilers is not disputed, since their efficiency is 95%, and in some models this figure goes beyond 100%. We are talking about condensing units capable of “pulling” heat from combustion products, which in other models simply fly away “down the chimney”.
Heating a country cottage with a wall-mounted gas boiler is one of the popular methods of heating living space in gasified regions
However, not all territories are gasified, so boiler equipment that runs on solid and liquid fuels, as well as electricity, is very popular. Using electric boilers for heating a cottage is even more convenient and safer than gas, provided that the region has stable operation of electrical networks. Many owners are stopped by the cost of electricity, as well as the limited supply rate for one facility. The requirement to connect an electric boiler to a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V is also not to everyone’s liking or affordability. Electric heating of cottages can be made more economical by using alternative sources of electricity (wind turbines, solar panels, etc.).
In cottages built in remote regions, cut off from gas and electric mains, liquid fuel boilers are installed. The fuel used in these units is diesel fuel (diesel fuel) or used oil, if there is a source of constant replenishment. Solid fuel units operating on coal, wood, peat briquettes, pellets, etc. are very common.
Heating a country cottage with a solid fuel boiler running on pellets - granulated wood pellets having a cylindrical shape and a certain size
Selecting a boiler by power
Having decided on the type of boiler equipment according to the fuel criterion, we begin to select a boiler of the required power. The higher this indicator, the more expensive the model, so you must not miscalculate when determining the power of the unit purchased for a particular cottage. You can’t follow the path: the less the better. Since in this case the equipment cannot fully cope with the task of heating the entire area of a country house to a comfortable temperature.
The unit’s low power will be especially noticeable on cold days, when the thermometer will show abnormally low temperatures outside the window. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase boilers with a slightly higher power than the calculations show, but not significantly higher. Why overpay money and then force the equipment to work “idle”?
Solar collectors
Despite the fact that heating a country house with solar panels is almost impossible in harsh climates, it is impossible not to consider this type of alternative source of energy and heat.
The greatest efficiency can be achieved only with intense solar radiation - only in this case the temperature in the premises will be as comfortable as possible.
Varieties
Solar systems for heating the coolant (in our case it is a water-glycol solution) can be divided into passive and active.
The first ones are combined into one so-called “water heater”, which is located on the roof. The coolant reservoir is located above the collector level, and cold water is supplied to the tank from below.
Scheme of operation of a flat solar collector. Click to enlarge.
The latter have a structural difference from passive solar heating systems: the solar collectors themselves are placed on the roof of the house, and the coolant reservoir is located in the house.
The coolant is water, circulates in the heating system using a pump.
Most often, solar collectors are used for household needs - heating water in storage tanks.
But in this case, in winter you will have to drain all the water from the tank to avoid freezing.
There are two different types of solar collectors: flat plate and vacuum (tube).
A flat-plate collector is a solar absorber with glazing on the top, having a layer of foil-coated thermal insulation on the inside.
Diagram of the operation of a pipe manifold. Click to enlarge.
The absorber is a flat sheet of metal connected to a piping system.
It “collects” solar heat, transferring it to the coolant. The glass should not reflect glare - to achieve maximum effect from light energy.
A tube collector differs from a flat one only in the presence of vacuum glass pipes collected in one bundle.
An absorber made of a sheet of steel is inserted into each tube - it can be rotated inside to even out the sunlight.
Tube solar collectors are more expensive to install and maintain, but they provide a greater effect than flat ones due to longer retention of solar heat.
Both types of heating systems are mounted on the roof of the house - in the inclined part.
Recently, manufacturers have been offering so-called “solar” roofs, in which solar panels are already installed, but this option has not become widespread due to the leakage of the roof covering.
Which heating radiators to choose
Despite the types of heating systems, in any case, special equipment is required to supply heat to the cottage: heating radiators, radiators. All heating equipment can be divided into 4 types:
1) Cast iron radiators are an excellent coolant. But they are not without the risk of water hammer, which can lead to damage when the heating season begins. Since the inner surface of the radiator is rough, it is capable of accumulating limescale deposits, which block the flow of heat into the room. When choosing a cast iron radiator for a cottage, you should take into account that a local heating system is installed.
2) Steel radiators are more resistant to water hammer and do not have the disadvantages of cast iron radiators; they transfer heat better. But they are not resistant to corrosion; rust may form on the inner wall, which requires careful maintenance of the batteries, or they will require too frequent replacement.
3) Aluminum radiators have a lightweight design, conduct heat well, are resistant to corrosion, but are not able to withstand water hammer. If the cottage uses a local heating system, then such a radiator can be an excellent solution.
4) Bimetallic radiators are the most efficient. They are resistant to corrosion, water hammer, do not form scale on the inner surface, and give off more heat. Among the shortcomings, only the high price was identified.
Number of radiator sections: how to correctly calculate
Number of battery sections: wise selection
The calculation of the heating system is carried out with the obligatory selection of the number of radiator sections. A fairly simple formula can also be used here - the area of the room that is meant to be heated must be multiplied by 100 and divided by the power of the battery section.
- Room area. As a rule, all radiators are designed to heat only one room, and therefore the total area of the house is not needed. The only exception is if next to the room that is heated there is some room that is not equipped with a heating system;
- The number 100, which appears in the formula for calculating the number of radiator sections for a heating system, is not taken out of thin air. According to SNiP requirements, about 100 W of power is used per square meter of living space. This is quite enough to maintain a comfortable temperature;
- As for the power of the heating radiator section, it is individual and depends, first of all, on the material of the batteries. If it is impossible to accurately determine the parameter, then for calculations you can take 180-200 W - this corresponds to the average power of a section of modern radiators.
Having received all the data, you can begin calculating the heating batteries. If we take as a basis the size of the room as 20 m2, and the power of the sections as 180 W, then the number of heating radiator elements can be calculated as follows:
n=20*100|180=11
Advice. As is the case with the boiler power, the number of battery sections must be taken “with a reserve”, this will allow you not to worry about severe frosts.
It should be noted that for rooms located at the end or on the corner of a building, the result obtained must be multiplied by 1.2. Thus, it will be possible to achieve the most optimal values and determine a sufficient number of radiator sections to heat a country cottage.
Insulation
Economical heating systems will never work effectively if there are cracks and holes in the window openings or walls, and the enclosing structures do not have sufficient thermal insulation. With rational home insulation, energy savings are quite significant, regardless of the boiler model and type of fuel used. In this case, the equipment will be able to work less intensively, resulting in reduced fuel consumption.
A house can be insulated not only at the construction stage. The option of installing additional thermal insulation during operation is quite viable. Heat losses during the cold season must be minimized. When building a private house, you should consider that when constructing the box, the enclosing structures have a thickness appropriate to the climate of the region. And it directly depends on the type of material used. Additionally, the walls, as well as the ceilings of the upper and lower floors must be thermally insulated.
Modern technologies make it possible to reduce the thickness of insulating layers. But when insulating structures, you should not get carried away with too thin materials. After all, if they are damaged, the cold will certainly penetrate into the “weak” areas, and heat loss will become inevitable.
Expanded polystyrene has proven itself positively as a heat insulator. Recently, it is often used to insulate already built houses. Today, expanded polystyrene, characterized by a low thermal conductivity, is one of the recognized leaders in terms of price and quality. It is precisely this that experts recommend using for suburban residential buildings.
Regarding windows and doors, the following can be said. All gaps between boxes and openings must be carefully sealed so that cold air cannot seep into the house in winter.
Properly performed insulation will reduce the consumption of thermal energy by almost 2 times, which will significantly save the material resources of the home owner. You will have to pay less for electricity or gas, and you will need to store coal and firewood for the winter in reduced quantities. In addition, it will be possible to purchase a less powerful boiler.
Installation of a cottage heating system
After the boiler room has been arranged, radiators are installed according to the heating scheme of the cottage. The main parameters by which consumers choose radiators are: size, power and the material from which they are made.
Internal wiring
When installing a cottage heating system, special attention should be paid to the material of the pipes. Today, there are several types of pipes that are traditionally used in heating systems. Let's take a closer look at these types.
- Steel pipes. Durable, resistant to pressure changes, but difficult to install and susceptible to corrosion. Over the years, a layer of rust settles on the inner walls, which can impede the flow of water.
- Metal-plastic pipes. Durable, flexible and easy to install. Convenient to use with complex geometry of the heating system. But they also have a number of weak points: they are destroyed by mechanical stress and ultraviolet radiation, and are also flammable.
- Propylene pipes. The most popular material, which is undoubtedly due to the price of such pipes. They are the most economical compared to pipes of other materials. They have only one drawback - good flammability. Otherwise, it is an ideal material for heating pipes. They do not rust, do not crack, are easily welded using special “irons”, and are durable in use.
- Stainless steel pipes. They are usually used in non-residential premises: basements, laundries, billiard rooms. They have good heat transfer, so high that they can heat a room without installing radiators. A variety is corrugated stainless steel pipes. In addition to the above, they have one more advantage: they easily “go around” corners and turns without additional joints.
Crimping
Before starting the heating system, it is necessary to check all components and connections. To do this, the system is pressurized. That is, they pump air or water under pressure 2-2.5 times higher than the working pressure and leave it for a day. During this time, leaks are detected and eliminated at the junctions of system parts. For the first time, it is recommended to heat the boiler to no more than 40 C. After filling the entire system with water, each radiator is checked for warming up and the entire heating system as a whole. After checking, the heating power of the boiler can be increased.
Filters: why are they needed?
Often repairing a heating system from blockages is a dubious pleasure and is expensive. It is much better to protect the equipment. Filters protect the system from lime, rust, and scale. This will extend the life of the equipment and prevent sudden repairs. The main thing is not to forget to change them in a timely manner.
There are several types of filters:
| Coarse filter |
| Fine filter |
| Magnetic filter |
Filters are also mechanical and electronic. Their main difference is the size of the particles retained. Electronic models perform deeper cleaning, down to 0.01 microns.
Tips for choosing and installing filters:
— Check whether the filter and system materials are compatible;
— Install in front of the pipe entrance to the boiler or in front of the pump;
— To clean and change filters without problems, install them in a convenient place;
— During the heating season, filters need to be cleaned once every 30-40 days.