Heating coils are units used to quickly heat air in buildings with large spaces: production workshops, shopping centers, sports and exhibition halls, as well as to create thermal curtains at the gates and oases with local heating in the right places inside such buildings.
The design of the heater combines three heating principles:
- heat exchanger with accelerated heat removal from a heated surface and fresh air blowing from a fan;
- a convector that organizes the flow of heated air upward and the intake of cooled air from below;
- a radiator that, having an elevated temperature, warms colder surfaces by radiating heat.
The device is a network of tubes in which coolant circulates. Through this network, the fan circulates air that is heated by contact with the surface of the thermal elements. In all such systems, the heat removal surface area is important: the larger it is, the more efficient the heat transfer of the heater. For this purpose, plates of more complex shapes are installed on the tubes or wire is wound. The coolant passing through the tubes heats the plates and the air between them to a given temperature, and the fan carries it into the room.
Operating principle and design of a water heater
Universal devices operating on water are installed in places with a well-established heat supply system.
A simple but quite effective design solution allows you to heat air in the range from + 70? C to + 100? C and is relevant for hangars, gyms, supermarkets, greenhouses, warehouses, large pavilions - that is, large premises that require additional heating. If you have ever used a household heat heater, you will easily understand the principle of operation of a water device. It also heats the air, but the role of an electric spiral enclosed in a small housing is played by a set of metal tubes through which the heated coolant circulates.
The heating process is as follows:
- hot water, heated to the required temperature (on average from + 80? C to + 180? C), from the heating pipes enters a heat exchanger consisting of small aluminum, steel, bimetallic or copper tubes;
- the tubes heat the air passing through the device;
- The built-in fan distributes heated air throughout the room and stimulates its movement in the opposite direction - towards the device.
There is no need to specially heat the water, since it is part of the heating system, so significant cost savings occur.
The design of a standard water heater is a hybrid of a heat exchanger, fan and convector. It is effective for heating large industrial premises, and, when choosing the right piping, also for cottages with a well-established ventilation system.
Waste oil heater and gas heater: options for the garage
In heating garages, homemade units that run on waste oil are often used. Such a device provides double savings - it serves as a waste oil recycler, and also does not require the purchase of expensive heating equipment.
A heater is a common option for heating a garage.
With the help of such a heater, you can heat rooms with an area of over 300 cubic meters, provided that the owner also took care of insulation. If the insulation is weak, then a normal temperature for life can be maintained in a room with a volume of up to 200 cubic meters. The oil consumption is equal to 300 ml per hour.
The heater can additionally be equipped with automation and special temperature sensors to determine the presence of a flame and temperature indicator. The design must include an oil pump, as well as fans for pressurizing and blowing the heat exchanger. The heater fans themselves are also equipped with automation. This is a simple thermal relay that is activated when the device warms up and when it cools down. The oil pump, operating in automatic mode, delivers used oil drop by drop into the perolysis cup. You can select the desired level and rate of oil supply.
To heat technical rooms, gas heaters are also used, which are low-power heating devices that run on liquefied gas. The fuel can be propane-butane or pure propane. Such equipment has an advantageous combination of small build and power, so the unit can be easily moved and used in limited space.
Electric heater with fan.
Water heater: design features
A water heater for fresh air ventilation is economical compared to its electric counterparts: in order to heat the same volume of air, 3 times less energy is used, and the performance is much higher. Savings are achieved by connecting to a central heating system. Using a thermostat, it is easy to set the required temperature balance.
Automatic control improves efficiency. The supply ventilation control panel with a water heater does not require additional modules and is a mechanism for controlling and diagnosing emergency situations.
The composition of the system is as follows:
- Temperature sensors for street and return water, supply air and degree of filter contamination.
- Dampers (for recirculation and air).
- Heater valve.
- Circulation pump.
- Capillary antifreeze thermostat.
- Fans (exhaust and supply) with control mechanism.
- Exhaust fan control.
- Fire alarm.
Design of a water duct heater type 60-35-2 (size - 60 cm x 35 cm, row - 2) made of galvanized steel, intended for ventilation and air conditioning systems.
Water and steam heaters are presented in three varieties:
- Smooth tube: a large number of hollow tubes are located close to each other; heat transfer is small.
- Plate: Finned tubes increase the heat transfer area.
- Bimetallic: pipes and collectors are made of copper, aluminum fins. The most effective model.
Benefits of professional installation
According to the rules, the installation and maintenance of ventilation systems, as well as control units, must be carried out by specialists with an engineering education. They bear full responsibility for incorrect selection, installation, connection of devices, as well as for maintaining technical devices in improper or unsafe condition.
To correctly determine the contents of a panel or cabinet, installers do a full monitoring of the ventilation network.
Then you need to do the following:
- analyze the load;
- choose the optimal scheme;
- determine the operating modes of devices in order to increase efficiency;
- select equipment.
The assembly itself takes a little time: all the devices are mounted one by one in several rows, the wires are carefully connected to the terminal blocks and laid along the lines in organized bundles, then taken out.
One of the connection options, where NK1 and NK2 are duct-type heating devices; M1 – 3-phase fan; A, B, C – network connection, N – neutral, PE – ground; Q – protective thermostat against overheating; Y – ignition protection thermostat
Professional installers have experience installing and operating control panels, so they are unlikely to make a mistake with the choice of model and the nuances of connecting devices. In addition, they are well versed in the diagrams of ventilation systems for apartments and country houses and can quickly determine if there is an error in the drawing.
If you don’t figure it out in time and connect the devices according to an illiterate diagram - and this also happens - you can create an emergency situation.
The sale and distribution of panels and cabinets is carried out by many companies that produce or sell ventilation, refrigeration and heating equipment. For example, in Moscow this can be done in, “Roven”, “AV-automatics”, “Galvent”, etc.
Types of heaters
The heater is installed directly inside the ventilation duct, so it must match the size and shape of the shaft. Depending on the coolant used in the heater, there are three types of heaters:
- Mermen.
- Steam.
- Electrical.
Mermen
Most often, rectangular heaters are found, but you can also choose a round model.
The device consists of rows of tubes, removable side panels and covers.
Water circulates through the tube system, but it can also be ethylene glycol.
Through the side holes, the size of which must be specified when purchasing, the unit is connected to the building’s heating system.
There are certain requirements for the air that passes through the heater:
- It must not contain solid particles, fibers or sticky substances.
- Dust content is less than 0.5 mg/m3.
- Minimum inlet temperature -20°C.
You also need to select a device based on productivity (in m3/h). If this indicator is insufficient, the heater will not warm the air and the rooms will be cold.
If for some reason it is impossible to install a heater of the required power, you can sequentially install a number of devices of lower power.
Steam
They are mainly used in industrial establishments where steam is a by-product of the production process. Steam heaters indicate the maximum permissible pressure they can withstand. Typically this is from 0.5 to 1.2 Pa.
Design of water and steam heaters
The same heater can be used for both steam and water.
There are three types of devices:
- Smooth tube.
- Lamellar.
- Bimetallic.
Peculiarities:
- Smooth tubes consist of many thin hollow tubes located close to each other. Minus: the heat transfer of the model is not great.
- Lamellar. Here the tubes are finned, which increases the heat transfer area. More effective than the first.
- Bimetallic ones have copper pipes and collectors, and the fins are made of aluminum. The most effective.
Electrical
Suitable for a small ventilation system - integrating such a unit into a ventilation system is much easier than a water unit. If energy costs are too high, there is an option to install an electric heater paired with a recuperator.
It is a spiral heating element in a housing. There is a built-in thermostat to protect against overheating.
Classification of air heaters by tube shape
The devices are equipped with tubes directed across the air movement. To eliminate the risk of airing, water is directed through the pipes from bottom to top. The connecting flanges at the ends of the housing have holes located for connections with ventilation ducts. Depending on the shape of the tubes, there are several modifications of air heaters.
Smooth tube
Smooth-tube heater
The heaters are made of hollow pipes 20-32 mm in diameter, located at a distance of 0.5 cm from each other. The heating device can be selected according to the location of the tubes in the water heater:
- Corridor. The ends of the elements are welded into the upper and lower manifold. Water is directed through the inlet pipe to the distribution box. It moves through the pipes and heats them, being discharged as condensate or cooled liquid.
- Chess. It is highly resistant to air currents. The heater operates normally when the air dust content is less than 0.5 mg/mᶾ and the inlet water temperature is +20 degrees.
Smooth tube devices are suitable for low air flow.
Lamellar
Plate heater
Modifications with fins that increase heat transfer. The plates are rectangular and round. The elements are equipped with tubes on which a corrugated steel tape 1 cm wide and 0.4 mm thick is wound.
The medium-sized model is a three-row version, and the large one is available with 4 rows of pipes. The dimensions of the plates of medium variation with a thickness of 0.5 mm are 11.7x13.6 cm. Large ones differ from them only in length - 17.5 mm. Large plates are arranged in a zigzag pattern, and medium ones are arranged in the form of a corridor.
The type of calorific heating of plate devices can be determined by markings. Models SDT4009V are compatible with steam and are installed vertically. The STD3010G air heater can be connected horizontally to a water system.
Bimetallic
The bimetallic heater lasts longer due to its anti-corrosion properties.
The device has spiral-rolled fins, suitable for water coolant with a maximum temperature of 180 degrees. Bimetallic air heaters of the KSK3 and KPZ series are medium in size and are equipped with 3 rows of tubes. Large devices such as KSK4 and KP4 have 4 rows of pipes.
The similarity between both types of SSCs lies in their design. They consist of heat exchangers, side shields, tubular grilles and covers with baffles. The heat exchangers are made in the form of 2 tubes. The inner 1.6 cm in diameter is made of steel with aluminum outer fins. The transverse distance between the nozzles is 4.15 cm, the longitudinal distance is 3.6 cm.
What is forced ventilation
Creating a comfortable indoor microclimate is an important task. Air ventilation is one of the components of this process. Supply ventilation in an apartment or house copes well with these tasks. Depending on the model, the device provides:
- purifying the air from various impurities;
- temperature change depending on the specified parameters;
- maintaining optimal humidity levels;
- creating comfortable living conditions.
Supply ventilation device
To increase the speed of exchange of air masses, various devices are used
When understanding what supply ventilation looks like, you need to pay attention to what elements it consists of:
- Fan
. The operation of the entire system depends on its power level. - Filters
. Protect the premises from contamination from the street. - A heating element
. Supply ventilation with heated air helps not to experience discomfort from temperature changes. - Recuperator
. The device is used to reduce the cost of heating air using room heat. - Sound absorption system
. To minimize sound from device operation. - Air ducts
. Prefabricated supply ventilation consists of pipes made of plastic or light metals. Specifications vary by model.
The principle of operation of supply ventilation
A characteristic feature of modern apartments is excessive sealing, so many are thinking about installing a forced air movement system. The supply ventilation system is ideal for this. It works like this:
- Air enters the air intake.
- Transported through an air duct thanks to the operation of a fan.
- After heating to the desired temperature, it enters the room.
Advantages of water fan heaters
- These air-heating units are compact, light in weight and conveniently mounted both on the wall and on the ceiling.
- Thanks to the wide variety of designs and colors, heaters will fit into any interior. The body of the devices is made of durable materials, which ensures resistance to corrosion and a long service life.
- In the warm season, a water heater can be used as a fan. Due to the specific water-air heat exchanger, high efficiency of the water fan heater is ensured with low energy consumption.
- These water heaters instantly heat up to the set temperature, are safe to use and are suitable for almost any room.
What is a water heater for supply ventilation
A water heater for supply ventilation is a water heater installed in ventilation ducts. These units are designed to heat or cool air coming from the street. They are also connected to an autonomous or central heating system and heat the air while it passes through the ventilation ducts.
You can order a water heater for heating and ventilation at home, garage, office, industrial workshop, store and other facilities. Devices with a powerful heat exchanger and fan are installed in shopping and service centers, large warehouses and sports facilities.
Low prices for Volcano water fan heaters and Teplomash air heaters.
If you have not found the answer to your question, please leave it in the comments below the article - and we will definitely answer you.
Review of modern models
To facilitate the selection and get an idea of water heaters from different manufacturers, the features and characteristics of several models will be described:
- The ZAO T.S.T plant produces heating devices for supply ventilation - KSK-3. The model is equipped with aluminum heating elements. Its body is made of carbon steel. These units operate with coolant in the following temperature range: from +70 degrees (outlet) to +150°C (input). The minimum air temperature in the supply air duct is -20 degrees. Maximum coolant temperature + 190 degrees. Working pressure is around 1.2 MPa. The working life declared by the manufacturer is 13.2 thousand hours, and the service life is 11 years.
- Volcano mini heat fans are compact in size and practical. They are produced by the Polish company of the same name. There are special blinds to change the direction of air flow. Power is 3-20 kW, productivity is 2 thousand cubic meters per hour. The unit has a double-row heat exchanger with protection class IP 44. The maximum operating pressure is no more than 1.6 MPa, and the maximum coolant temperature is +120 degrees. The heat exchanger volume is 1.12 liters. Suitable for heating air in industrial and domestic premises.
- Italian water heaters Galletti AREO work for heating and cooling air masses. They are equipped with a heat exchanger consisting of copper-aluminum tubes, a fan and a drainage tray. Power ranges from 8-130 kW. When operating in cooling mode, this figure is 3-40 kW. Working pressure – 10 bar. Coolant temperature +7…+95°С. The unit heats the air to +40 degrees or cools it to +10°C. Protection class – IP 55. Electric motor protection is provided.
Also on the trading market of industrial heating equipment are models of the following brands: Teplomash, Fraccaro, 2VV, Yahtec, Kroll, Tecnoclima, Pakole, Remko, Innovent, Zilon.
Electrical devices
Electric heaters for fresh air ventilation are very effective, but quite expensive heating devices. The temperature in the ventilation duct increases as a result of air coming into contact with hot spirals or plates made of refractory types of metals.
An increase in the temperature of the heating elements occurs due to a change in the electrical resistance of the heaters. This requires quite a lot of electrical energy.
The degree of heating of the coil or plate is directly proportional to the strength of the current that flows through the element. By increasing the voltage, you can decrease the current without changing the electrical power.
Advantages and disadvantages of electric heaters
Among the main advantages that characterize an electric heater, it is worth highlighting the following.
Simple installation process. Thus, it is much easier to connect a cable to the heater than to circulate water or other coolant inside it.
You don't have to worry about providing thermal insulation to the wiring. The power loss in the cable due to electrical resistance is much lower than the heat loss in any pipeline with coolant fluid.
Easy adjustment of suitable air temperature. To be able to set the temperature of the air supplied to the room at the required level, it is enough to install a simple temperature sensor in the power circuit of the heating device. In the case of a water heater, coordination of the boiler power, coolant temperature and air temperature will be required.
At the same time, the electric type of devices also has its disadvantages. First of all, this is the cost of the device, which is higher in comparison with water analogues. So, in the case of approximately the same power level, the price of an electric heater will be approximately 2 times higher than a device with a liquid coolant.
Quite high energy costs. Thus, to ensure heating of the air in the ventilation system of even a small room, electricity costs will be significant.
Heater: this is a device for heating air in different systems
Before you start choosing a device, you need to understand the very concept of what a heater is, as well as what types there are and what are the typical and functional features of each of them.
Air heaters are capable of heating both small and fairly spacious rooms
Air heaters are used to heat air in various systems:
- heating;
- air conditioning;
- ventilation.
Heating in thermal equipment is carried out due to the reaction between chemically aggressive substances in the middle. That is why the classification of air heaters is based on the type of heat exchanger. The device can be water, steam, freon and electric. A water heater for heating is used as a heat exchanger with an intermediate coolant. A steam heater is used to heat air in heating systems.
If we classify air heaters according to thermal and aerodynamic characteristics, then the types of air heaters are divided into three-row and four-row. Based on the number of connecting sizes, heaters of individual models are divided into 7 numbers.
Steel pipes, which have a ribbed surface on the outside, serve as a coolant transporter in the middle of the heater. Due to this design, the area increases and, as a result, such piping of the heater increases the efficiency of heat transfer. In the middle of the tubes with fins, a heating or cooling element in the form of water, steam or freon is transported. Air currents flow outside, which heat or cool during contact with the pipes.
Volcano air heater structure: 1 — movable adjustable blades, 2 — built-in diffuser with fan, 3 — heating elements, 4 — warm air supply
The general scheme is based on the following operating principle: the coolant has a high heat transfer coefficient when interacting with air flows. The rib trim on the device is metal plates that are simply mounted on tubes or wound like ribbons or wire.
What is supply ventilation with air heating
Complete set of compact heated ventilation for an apartment
Ventilation with a heat exchanger provides a continuous supply of heated fresh air flow. This creates a good microclimate. Ventilation providing heating of incoming air masses includes: central supply and exhaust equipment with a recuperator, which provides heating of air coming from the street. This occurs due to the temperature of the exhaust air being removed. The recuperator, passing air, does not mix it with the exhaust air masses. That is, air enters and exits through individual channels, the walls of which are located end-to-end.
Heating of the supply ventilation can be carried out using recirculation (air conditioners, heaters). Warm “exhaust air” is mixed with supply air, which is heated to the desired temperature and then supplied to the room.
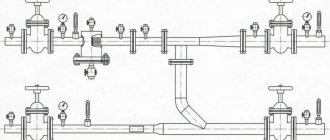
Strapping methods
The piping is a frame made of reinforcement, with the help of which the flow of hot water is regulated. The piping unit helps to monitor the performance of the supply ventilation heater, control it and maintain the desired temperature in the building. The location of the piping units is determined by the installation location, air exchange diagram, and technical parameters of the equipment. There are 2 installation options:
- Recirculated air masses are mixed with supply air.
- Only indoor air is recirculated according to a closed principle.
Taking this into account, there are 2 methods of strapping:
- 2-way valves - with uncontrolled reverse water flow;
- 3-way valves - when controlling water flow in a boiler room or boiler room.
Some produce piping units of various modifications, which are entire sets consisting of valves (balancing and check valves, two and three-way), pumps, bypasses, ball valves, pressure gauges, and cleaning filters.
Scheme of piping heater units for supply ventilation. (Ball valves installed at the inlet and outlet allow you to shut off the water, and a thermomanometer allows you to control temperature and pressure)
If natural ventilation is well established, then there are much more opportunities for successful operation of the equipment. The correct choice of piping in such cases is effective both for heating large areas in production and for private houses and cottages.
The heater used for ventilation is usually connected to the heating system directly at the air intake point. If forced ventilation is in effect, the air heater can be installed anywhere. Air heaters for supply ventilation allow you to create a comfortable temperature regime in both industrial and residential premises. It is only important to correctly decide on the choice of coolant, which will be the most effective (with minimal costs and maximum performance) under certain conditions. An automated system - such as a supply ventilation control panel with a water heater - will make the use of heating devices for supply ventilation convenient and safe.
Types of supply ventilation
These indoor air movement systems are classified according to a number of characteristics. According to the design of the ventilation network, the system is:
- Team
. When individual elements are connected using air ducts. - Monoblock supply ventilation
. In this option, most of the elements are combined in one housing.
According to the ventilation method, the supply system is divided into: local, complex and emergency. Based on the presence or absence of an air duct, the classification is:
- Ductless
. When fresh air enters the room through the supply opening. - Duct
. The supply occurs through an air duct system.
Ductless ventilation
The device ensures the injection of clean air into the room due to the operation of the supply unit, due to which the effect of an air curtain or oasis is formed in the intended area of the room. Ductless supply ventilation ensures the removal of contaminated air through a special hole or gap in the door and window. If you have a powerful fan that makes a lot of noise, it must be supplemented with a noise suppressor. Depending on the degree of complexity, supply ventilation is a device that is divided into three types:
- window valve
; - supply fan
; - Supply unit
.
In installations, a filter is installed to filter out impurities, and an air intake grille is installed to protect against debris. Supply and exhaust ventilation for an apartment can be equipped with a system for heating the incoming air; for this, a special element is used that prevents the temperature in the room from falling below a predetermined level. Each owner chooses one or another type for himself, depending on the final purpose of the acquisition and financial capabilities.
Duct ventilation
These devices are a set of air ducts that connect all rooms. What distinguishes them is the need for periodic maintenance to maintain quality of operation. Ducted supply ventilation has one drawback - a large network of air ducts that need to be hidden by the ceiling. This must be taken into account and installation done at the stage of renovation of the premises. The principle of operation of the system is simple - fresh air enters the room through the channels and with its flow displaces the exhaust air through the air intakes.
Often such forced ventilation is installed at large facilities, where heating requires large energy consumption. In order to lower them you can set:
- recuperator;
- water heater;
- VAV system.
Connection
The supply of air masses can be carried out in one of two options:
- Left version: the mixing unit and automatic control are installed on the left side, water is supplied from the top, outflow is at the bottom.
- Right execution: the indicated mechanisms are on the right, the water supply tube is at the bottom, the “return” is at the top.
The tubes are placed on the side where the air valve is installed.
Water heaters are divided into 2 types according to the type of valve:
- two-way – when connected to a general heating supply;
- three-way – with a closed method of heat supply (for example, when connected to a boiler).
The type of valve is determined by the characteristics of the system supplying heat. These include:
- Type of system.
- Water temperature at the beginning of the process and during outflow.
- With central water supply, the difference between the pressure in the water supply and outflow pipes.
- When autonomous - the presence or absence of a pump installed on the inflow circuit.
The installation diagram must provide for the inadmissibility of installation in the following cases:
- with vertical pipe inlet and outlet;
- with top air intake.
Such restrictions are due to the possibility of snow masses entering the equipment inflow and further leakage of melt water into the electronic unit.
Place of installation of a duct heater for supply ventilation in the air exchange system (if there is a possibility of the temperature dropping below normal, it is obligatory to install an anti-freeze thermostat)
To avoid malfunctions of the automation unit, the temperature sensor must be located in the inside of the air blowing element at a distance of at least 0.5 m from the inflow mechanism.
Calculation of heater power
Let's determine the initial data that will be needed to correctly select the heater power for ventilation:
- The volume of air that will be distilled per hour (m3/h), i.e. the performance of the entire system is L.
- Temperature outside the window. – tul.
- The temperature to which the air needs to be heated is tcon.
- Tabular data (air density at a certain temperature, heat capacity of air at a certain temperature).
Instructions for calculation with example
Step 1. Air flow by mass (G in kg/h).
Formula: G = LxP
Where:
- L – air flow by volume (m3/h)
- P – average air density.
Example: Air coming in from the street is -5°C, and at the outlet the required temperature is +21°C.
Sum of temperatures (-5) + 21 = 16
Average value 16:2 = 8.
The table determines the density of this air: P = 1.26.
| Air density depending on temperature kg/m3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -50 | -45 | -40 | -35 | -30 | -25 | -20 | -15 | 10- | -5 | +5 | +10 | +15 | +20 | +25 | +30 | +35 | +40 | +45 | +50 | +60 | +65 | +70 | +75 | +80 | +85 | |
| 1,58 | 1,55 | 1,51 | 1,48 | 1,45 | 1,42 | 1,39 | 1,37 | 1,34 | 1,32 | 1,29 | 1,27 | 1,25 | 1,23 | 1,20 | 1,18 | 1,16 | 1,15 | 1,13 | 1,11 | 1,09 | 1,06 | 1,04 | 1,03 | 1,01 | 1,0 | 0,99 |
If the ventilation capacity is 1500 m3/h, then the calculations will be as follows:
G = 1500 x 1.26 = 1890 kg/h.
Step 2. Heat consumption (Q in W).
Formula: Q = GxС x (tcon – tul)
Where:
- G – air flow by mass;
- C – specific heat capacity of air entering from the street (tabular indicator);
- tcon – temperature to which the flow needs to be heated;
- tul – temperature of the flow entering from the street.
Example:
Using the table, we determine C for air with a temperature of -5° C. This is 1006.
| Heat capacity of air depending on temperature, J/(kg*K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -50 | -45 | -40 | -35 | -30 | -25 | -20 | -15 | 10- | -5 | +5 | +10 | +15 | +20 | +25 | +30 | +35 | +40 | +45 | +50 | +60 | +65 | +70 | +75 | +80 | +85 | |
| 1013 | 1012 | 1011 | 1010 | 1010 | 1009 | 1008 | 1007 | 1007 | 1006 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 1006 | 1006 | 1007 | 1007 | 1008 |
Substitute the data into the formula:
Q = (1890/3600*) x 1006 x (21 – (-5)) = 13731.9** W
*3600 is the hour converted to seconds.
**The resulting data is rounded up.
Result: to heat air from -5 to 21 °C in a system with a capacity of 1500 m3, a 14 kW heater is required
There are online calculators where by entering performance and temperatures you can get an approximate power indicator.
It is better to provide a power reserve (5-15%), since equipment performance often decreases over time.
Heating surface calculation
To calculate the heated surface area (m2) of a ventilation heater, use the following formula:
S = 1.2 Q: (k (tliquid – tair)
Where:
- 1.2 – cooling coefficient;
- Q – heat consumption, which we have already calculated earlier;
- k – heat transfer coefficient;
- tliquid – average temperature of the coolant in the pipes;
- tair is the average temperature of the flow coming from the street.
K (heat transfer) is a tabular indicator.
Average temperatures are calculated by finding the sum of the incoming and desired temperatures, which must be divided by 2.
The resulting result is rounded up.
Knowing the surface area of the heater for ventilation may be necessary when selecting the necessary equipment, as well as for purchasing the required amount of materials when independently manufacturing system elements.
Features of calculating steam heaters
As already mentioned, the heaters are used the same for water heating and for the use of steam. Calculations are carried out using the same formulas, only the coolant flow is calculated using the formula:
G=Q:m
Where:
- Q – heat consumption;
- m is an indicator of the heat released during steam condensation.
And the speed of steam movement through the pipes is not taken into account.
What to look for when choosing a duct dehumidifier
The main parameter that characterizes a duct dehumidifier is its productivity, measured in liters per day. In other words: productivity is how many liters this model can “squeeze” out of the air in 24 hours.
For a private house with a small pool, a device that removes 10-50 liters of moisture per day may be sufficient. For large multi-storey buildings with a pool surface of 25-100 m2, a capacity of up to 350 liters may be needed. water in 24 hours.
In addition to performance, in equipment documents the manufacturer usually indicates:
- How much space is the device designed for?
- Dimensions of the installation and its functionality.
- Dimensions of cross-section of pipes for connecting air ducts.
User reviews
If high-quality equipment was purchased and the installation was carried out with the assistance of professionals, then the feedback on the use of this type of heaters will be extremely positive.
Igor. Volgograd.
Installing a two-row water heater in the greenhouse made it possible to completely cover the heat demand, while keeping heating costs to a minimum.
Novel. Dmitrov.
It was possible to completely heat a private house after installing water heaters. Thanks to the blinds, the flow of hot air can be easily adjusted.
Nikolai. Voronezh.
I installed the steam heater myself, despite the fact that the store strongly recommended using the services of an installation team.
Heating coils are very efficient devices. Having a relatively small size, such devices are capable of significantly changing the temperature regime in any room with minimal time.
Calculation of heater power
To carry out the calculation, the following data is required:
- Volume or mass of supply air to be heated. It can calculate volume flow (cubic m/h) or mass flow (kg/h).
- The initial air temperature, which is equal to the outside air temperature.
- The target temperature to which the supply air must be heated before being supplied to the premises.
- The temperature regime of the coolant, which is used to heat the air.
Instructions for calculation
When calculating the heater used for supply ventilation, it is necessary to calculate the heating surface area and the required power. You need to start by calculating the cross-sectional area of the heat exchanger along the front:
Af = Lρ / 3600 (ϑρ), here:
- L – supply air flow rate by volume, m³/h;
- ρ – value of the density of external air, kg/m³;
- ϑρ – mass velocity of air masses in the design section, kg/(s m²).
Calculation of heater power
The frontal cross-section indicator is necessary for awareness of the size of the heat exchanger. Next, you need to use the nearest larger device for the calculation. If, according to calculations, the cross-sectional area is too large, you will need to opt for several heaters mounted in parallel to obtain the required area.
The real mass velocity indicator must be calculated taking into account the actual front area of the selected heaters:
ϑρ = Lρ / 3600 Af.fact
Next, the required amount of heat to heat the air flow is calculated using the formula:
Q = 0.278Gc (tп – tн), where:
- Q – amount of heat, W;
- G – mass flow of heated air, kg/h;
- c – the specific heat capacity of the air mixture is taken to be 1.005 kJ/kg °C;
- tп – inflow temperature, °С;
- tн – initial air temperature from the street.
Since the fan is installed in the supply ventilation before the heat exchanger, the mass flow G is calculated taking into account the air density outside. G = Lρн
G = Lρн
Otherwise, the density is determined by the temperature of the air after it is heated. The calculated amount of heat allows us to calculate the coolant costs in the heater (kg/h) to transfer this heat to the air being passed through:
Gw = Q / cw (tg – t0)
In this formula:
- cw – heat capacity value for water, kJ/kg °C;
- tg – design temperature of water in the supply pipeline, °C;
- t0 – design water temperature in the return pipeline, °C.
The specific heat capacity of water is a reference indicator. The temperature characteristics of the coolant used for calculations are taken based on real indicators under existing conditions. If there is a boiler room or connection to a central heating network, the characteristics of their coolants will be needed for the calculation. Having information about the coolant flow rate, you can calculate the speed (m/s) of its movement through the heater pipes:
w = Gw / 3600 ρwAmp, here:
- Amp – cross-sectional area of the heat exchanger tubes, m²;
- ρw – density of water at the average temperature of the coolant in the heater, °C.
Calculation of the average temperature of water circulating through the heater is carried out using the formula:
(tg + t0) / 2
The speed calculated using the above formula will be valid for a set of heat exchangers connected in series. If parallel piping is performed, the cross-sectional area of the pipes will more than double. In turn, this will cause a decrease in the speed of movement of the coolant. Such a reduction will not bring an increase in productivity, but will cause a decrease in temperature in the return pipeline. In order not to encounter an excessive increase in the hydraulic resistance of the heat exchanger, it is not necessary to accept a coolant movement speed of more than 0.2 m/s.
Efficiency of using air heaters instead of heating radiators
The coolant circulating through water heating radiators transfers thermal energy to the surrounding air through thermal radiation, as well as through the upward movement of convection flows of heated air and the entry of cooled air from below.
The heater, in addition to these two passive methods of transferring thermal energy, drives air through a system of heated elements with a much larger area and intensively transfers heat to them. Assessing the efficiency of heaters and fans allows for a simple calculation of the cost of installed equipment for the same tasks.
An example of heating a vehicle maintenance service room with air heaters.
For example, it is necessary to compare the cost of radiators and heaters for heating the showroom of a car dealership, taking into account compliance with SNIP standards.
The heating main is the same, the coolant is the same temperature, piping and installation can be ignored in a simplified calculation of the costs of the main equipment. For a simple calculation, we take the known norm of 1 kW per 10 m2 of heated area. A hall with an area of 50x20 = 1000 m2 requires a minimum of 1000/10 = 100 kW. Taking into account a margin of 15%, the calculated minimum required heating capacity of heating equipment is 115 kW.
When using radiators . We take one of the most common bimetallic radiators Rifar Base 500 x10 (10 sections), one such panel produces 2.04 kW. The minimum required number of radiators will be 115/2.04 = 57 pcs. It’s immediately worth considering that placing 57 radiators in such a room is unreasonable and practically impossible. If the price of a device for 10 sections is 7,000 rubles, the cost of purchasing radiators will be 57 * 7000 = 399,000 rubles .
When heating with air heaters . To heat a rectangular area in order to distribute heat evenly, we select from 5 Ballu BHP-W3-20-S water heaters with a capacity of 3200 m3/hour each with a similar total power: 25 * 5 = 125 kW. Equipment costs will be 22900*5 = 114,500 rubles .
The initial cost of heaters is almost 4 times less than the purchase of efficient bimetallic radiators.
When comparing the installed capacities of radiators and heaters by price, it is necessary to take into account in the calculation that one of the main indicators of standard heaters is the productivity of warm air. With a ceiling height of 6 meters in our example, the volume of the exhibition hall will be 1000 * 6 = 6,000 m3. Five air heaters with a capacity of 3200 m3/hour will refresh the air in the hall almost three times per hour, which will ensure its normal quality for workers and visitors not only in temperature, but also in composition.
The main area of application of air heaters is the organization of heating of rooms with large spaces for air movement:
- production workshops, hangars, warehouses;
- gyms, exhibition pavilions, shopping centers;
- agricultural farms, greenhouses.
Compact devices that allow you to quickly heat air from 70°C to 100°C, easily integrated into the overall automatic heating control system, are advisable to use in buildings with reliable access to coolant (water, steam, electricity).
Heat transfer from heating radiators: comparison of indicators and calculation methods
The advantages of water heaters are:
- High profitability of use (low cost of equipment, high heat transfer, ease and low cost of installation, minimal operating costs).
- Fast air heating, ease of change and localization of heat flow (thermal curtains and oases).
- Reliable design, ease of automation and modern design.
- Safe to use even in high-risk buildings.
- Extremely compact dimensions with high heating output.
The disadvantages of these devices are related to the properties of the coolant:
- At temperatures below zero, the heater is easy to freeze. If water is not drained from the pipes in time, they can break if disconnected from the main line.
- When using water with a large amount of impurities, the device can also be damaged, so using it at home without filters and connecting it to a central system is impractical.
- It is worth noting that air heaters dry out the air greatly. When used, for example, in a showroom, humidifying climate control technology is required.
Local ventilation
This type of ventilation works on the principle of exhaust systems. Types of local ventilation (supply and exhaust) involve the extraction of air directly from the place of formation of harmful substances. This allows you to stop their spread throughout the room, localize and remove them.
It is worth noting that modern local ventilation systems are specially equipped with powerful filters due to the nature of their application. This solution allows you to purify the air up to 98% and reuse it in the future.
In rooms where various types of work or food preparation are carried out, mixed air exchange systems are often created. They represent general ventilation of one of the above types, and local ventilation, which prevents substances from evaporating and spreading throughout the room.
Depending on the design, ventilation systems can also be either ducted or non-ducted. The first type involves the installation of branches that are spread throughout the building. It has one or two inputs and one output. The second type assumes the absence of channels, and the systems themselves are built into walls or floor slabs.
Principle of operation
Heated supply ventilation is very simple in operating principle. At the first stage, air is drawn in through the air intake and filtered from large debris and insects. After this, air is transferred directly to the device body.
At the next stage, the incoming air is specifically purified from all small particles. To do this, there are several thin filters in the inlet for varying degrees of purification.
After thorough cleaning, the air flows directly to the heating elements. If the device has the ability to control heating, then it occurs only within the specified parameters. After heating, another cleaning process starts, during which the air is freed not only from dust, but also from pollen, other allergens and odors.
As a result, purified and sufficiently warm air enters the room, the temperature of which can be controlled from the control panel.
Application specifics
The specificity of using devices of this type for heating lies not only in the peculiarities of using a particular energy carrier, but also in the size and power of the devices. If heating is carried out using gas or solid fuel, the fan heater must still be connected to the electrical network, which makes such systems dependent on the presence of current in the network.
Advantages and disadvantages
In addition to the fact that a constant power supply must be provided to power the fan motor, such devices have the following disadvantages:
- Increased noise level during operation.
- Quite a complex connection diagram.
- The need to constantly monitor pressure in water and steam installations.
The advantages of heating systems include:
- High efficiency when heating large areas.
- Minimum load on the electrical network (for water and steam models).
- Safe from fire and electric shock.
Important! Despite the presence of some disadvantages, the installation of heaters of this type is the most preferable at production facilities.
Operating conditions and features
The water heater is connected to the DHW and return pipes
The operating principle of a water heater for heating, equipped with a fan, is based on the heat exchange of two working media. Hot water is used as the primary coolant, air is used as the secondary coolant. Heating of air masses is carried out by transferring the heat of hot water to the cold air flow. The efficiency of heat transfer depends on the temperature difference - it must be large.
When operating the devices, several requirements must be met:
- Before installation in a large room, performance indicators are calculated.
- Household models are compact and compatible with steam or water heating.
- The use of water with a temperature of more than 180 degrees in the mains is unacceptable - the heater will fail.
- For large rooms, a heater power control system is used in the form of a mixer with a three- or two-way valve.
- The maximum density of aggressive impurities in the air during operation of the device is specified in GN 2.2.5.686-98 and GOST 12.1.007-76.
- The energy efficiency of the heater depends on the heat transfer coefficient. The value is indicated in the passport.
- Before installation in a home workshop or garage, it is necessary to install filters to remove chemical impurities.
- Three-row models are suitable for ventilation communications that supply outside air at temperatures from 0 to -40 degrees.
- Four-row modifications are launched in winter only at a rate of temperature increase of up to 30 degrees per hour.
- The units are not suitable for forced or artificial ventilation - they pump air through duct elements.
Installation Tips
Heaters with sensors in the greenhouse maintain the desired temperature.
The water heater is installed in rooms connected to the central heating main. When installing yourself, you should follow the recommendations of specialists:
- The diagonal of the heater depends on the bending characteristics of the channels, the type of damper and structural elements.
- To protect the heater from freezing, installation is carried out in rooms with a temperature not lower than 0 degrees.
- Before installation, it is necessary to inspect the plates and tubes for integrity.
- Weld-on flanges are easiest to connect end-to-end.
- Direct-flow air vent valves are located at the top of the outlet and supply manifolds.
- The joints between the device and the ventilation system are sealed.
- Wall-mounted models are installed by fastening the console with two self-tapping screws.
If you have no experience connecting and tying the system, it is better to entrust the work to specialists.
Choosing a location for installing supply ventilation
Depending on the type of supply ventilation system and its purpose, the location for installation is selected. More details about each variety:
Monoblock designs
Monoblock-type systems are installed, as a rule, in the attics of residential buildings, and the shafts are located under the ceiling, which makes it possible to hide them when finishing the room.
In production workshops, installation takes place in specially designated rooms with an extensive communications network throughout the building.
Prefabricated
They are usually installed according to the building design, which specifies in detail the installation location of each system and the laying of air lines. Due to the size of the installation, its installation is possible either under the ceiling, in which case communications can be hidden during finishing, or along the outer wall of the room.
Regardless of the type of installation, the liquid-type heater part is connected to the heating system.
There is also a difference in the installation of structures that differ in the method of ventilation.
General exchange
Just like other types, it is installed at the stage of rough work according to the house design. Communications are laid under the ceiling of the rooms. Supply air ducts are brought closer to the floor. In the kitchen it could be a stove hood, in the bathroom it could be a ceiling fan.
Local
Local ventilation systems can be installed both during rough work and after finishing is completed. Some types of air supply devices can be mounted on a window vent. For wall installation, a hole is sometimes made in the wall of the room.
Prefabricated local ventilation systems are installed under the ceiling or in the walls of the room. This makes it possible to carefully cover communications with finishing materials.
Varieties according to installation method
Depending on the housing design, you can choose a fan heater:
- Floor type. Installed without fastenings, quickly connected to the water supply. Mobile models are easy to move to a new location.
- Wall type. The wall heater is equipped with a mounting console for adjusting the vertical position. The element is secured with anchor bolts, after which the water circuit is connected.
Household appliances are single-circuit, connected only to hot or cold water supply.
Wall
Floor
Selection of air exhaust equipment
a kitchen hood can be an interior decoration
We will remove air from the most “polluted” rooms: the bathroom and kitchen, using a time-tested exhaust fan.
Choose exhaust fans equipped with humidity and motion sensors. Such devices do their job better using less electricity.
A fan is installed instead of the exhaust grille. It is advisable to equip the hood with a check valve. This inexpensive device is a plastic curtain on a horizontal axis shifted upward. The valve blocks air flow from the ventilation system, preventing reverse draft.
If the fan is equipped with sensors, electric current is supplied to it continuously. Simpler models are powered from a light switch or activated by a separate button. The second option for the kitchen is preferable.
It is impossible not to mention a device that is widely used to remove exhaust air - a kitchen hood. The effectiveness of the hood is explained by the fact that it captures vapors and odors directly in the area where they appear
When choosing, you should pay attention to the following parameters:
- type (flat, island, dome, built-in);
- dimensions;
- operating principle (air recirculation or exhaust);
- performance;
- noise level;
- control method (touch or mechanical).
| Model | Type | Operating modes | Productivity (cub.m/h) | Power , W) | Control type |
| Hansa OKS 653 SWN | domed | Exhaust\ circulation | 620 | 160 | Sensor |
| Hotpiont HLB 6.7 | built-in | Exhaust\ circulation | Buttons | ||
| Elikor 60 IX | domed | retraction | 430 | 185 | Buttons |
| Cata CN-600 | domed | Exhaust\ circulation | 583 | 80 | Buttons |
| Snindo Avior 60 SS\BG | domed | Exhaust\ circulation | 800 | 238 | Sensor |
| Krona Kamilla 2M | built-in | Exhaust\ circulation | 550 | 200 | Buttons |
| Gorenie WHT961 | domed | Exhaust\ circulation | 755 | 288 | Sensor |
| Samsung HDC9A90 | domed | retraction | 861 | Sensor |
Table 2. Characteristics of some models of kitchen hoods
By installing exhaust devices, you get supply and exhaust ventilation with mechanical drive and heating.