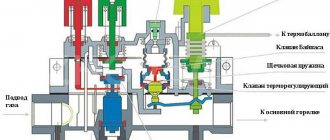
Hot water boiler –
a device that has a firebox, heated by the products of the fuel burned in it, and designed to heat water under pressure above atmospheric pressure and used as a coolant outside the device itself.
The heat generated by hot water boilers is used for heating, ventilation and hot water supply, and can also be used for various technological needs.
The maximum temperature of water leaving the boilers, depending on their heating capacity, can be 95, 115, 150 and 200 ºC.
All hot water boilers can be divided into gas-tube and water-tube. Based on the material from which hot water boilers are made, they can be divided into steel and cast iron. Cast iron boilers are more resistant to corrosion.
By the nature of water circulation (regardless of design), all water heating boilers are direct-flow.
A hot water boiler consists of a combustion device and heat-receiving surfaces, which for water-tube boilers are divided into combustion screens made of separate panels, which are a series of parallel pipes connected by input and output manifolds, and convective heating surfaces, in most cases assembled from coils.
Cast iron hot water boilers
operate at a water pressure in the system of no more than 0.6 MPa. The maximum temperature of heated water is 95 o C. It is allowed to operate boilers with temperatures up to 115 o C at an operating pressure in the heating system of at least 0.35 MPa. Currently, cast iron boilers are produced with a heating capacity that, as a rule, does not exceed 2 MW.
Cast iron boilers are assembled from separate cast sections connected to each other using separate conical nipples and tightened with coupling bolts that pass through the nipple holes. This design allows you to select the required heating surface of the boiler, as well as replace individual sections.
There are specialized cast iron sectional boilers designed for burning gaseous and liquid fuels, as well as for burning solid fuels. The latter can be converted to combustion of gaseous fuel with appropriate modifications.
Specialized boilers for burning gaseous fuels, for example, include the Fakel and Bratsk-1G boilers, as well as a large number of imported cast iron boilers.
steel water-tube boilers are widely used in heating boiler houses
the following types: TVG, KVG, KV-GM and PTVM.
Cogeneration water heating gas boiler TVG
is a direct-flow sectional heat generator with forced water circulation, equipped with a separate smoke exhauster and fan. TVG boilers are produced with a heating capacity of 4.65 MW (TVG-4) and 9.3 MW (TVG-8). A special feature of the boilers is their developed radiation surface. TVG-4 and TVG-8 boilers have three two-light screens and four burners. Double-light screens divide the firebox into four compartments. In addition, each boiler has two single-light screens located near the walls and a ceiling screen, partially transforming into a front screen.
The convective heating surface consists of two sections with upper and lower collectors connected to each other by eight risers, into each of which four U-shaped coils are welded. The coils are arranged parallel to the front of the boiler in a checkerboard pattern. To direct the movement of water along the coils, there are partitions in the risers.
For combustion of gas, hearth burners are used with a straight slot ending at the top with a sudden expansion. The burners are placed between vertical combustion screens.
Currently, instead of TVG boilers, gas hot water boilers of the KV-G type
heating capacity of 4.65 and 7.56 MW. These are direct-flow sectional boilers running on gas fuel. The boilers are designed to heat water from 70 to 150 ºC with high-quality regulation of heat output, i.e. with constant water flow through the boiler. The temperature of the water entering the boiler is maintained constant, equal to 70 ºC at all loads. KV-G boilers are a pipe system arranged in one transportable block. The pipe system consists of radiative and convective heating surfaces.
The radiation heating surfaces of KV-G boilers are formed by the left and right side screens, two double-light screens and a ceiling screen. The convective heating surface consists of U-shaped screens.
KV-G boilers use three hearth burners, which are located between sections of vertical combustion screens.
Steel direct-flow water heating boilers KV-GM
The unified series is produced in various standard sizes according to thermal performance. The boilers are intended for installation at thermal power plants, in industrial heating and heating boiler houses operating on gaseous and liquid fuels.
Boilers KV-GM-4
and
KV-GM-6.5
with a heating capacity of 4.65 and 7.56 MW, respectively, are designed to heat water from 70 to 150 ºC with high-quality regulation of heat supply. The boilers have a single profile and differ in the size (depth) of the combustion chamber and convection shaft.
The boilers are equipped with one rotary gas-oil burner of the RGMG type with the corresponding heating capacity. The combustion chamber of the boilers, like the convective shaft, is completely shielded with membrane panels.
The convective heating surface consists of two packages. Each package is assembled from U-shaped screens.
Boilers KV-GM-10-150
,
KV-GM-20-150
and
KV-GM-30-150
provide water heating up to 150 ºC with a difference in water inlet and outlet temperatures equal to 80 ºC, and operate with constant water flow at all loads.
The boilers are direct-flow, have a single cross-sectional profile and differ only in the depth of the firebox and convective flue.
The boiler furnaces are equipped with one gas-oil burner mounted on the front wall with a rotary nozzle of the RGMG type.
The firebox is completely screened and divided by an intermediate double-row rotating screen into a combustion chamber and an afterburning chamber.
Packages of convective heating surfaces are located in a vertical flue with completely shielded walls.
Boilers KV-GM-50-150
and
KV-GM-100-150
are made of water-tube, direct-flow with a U-shaped closed arrangement of heating surfaces.
The boilers are designed to produce hot water with a temperature of 150 ºC in free-standing boiler houses for use in heating, ventilation and hot water supply systems for industrial and domestic facilities and at thermal power plants as peak-backup heat sources. The boilers are used to operate both in main mode and in peak mode (to heat network water from 70 to 150 ºC and from 110 to 150 ºC, respectively). Boilers must operate with a constant flow of water.
The boiler furnaces are equipped with gas-oil burners with rotary nozzles of the type RGMG-20 (two burners on the KV-GM-50-150 boiler) and RGMG-30 (three burners on the KV-GM-100-150 boiler).
Production of water heaters PP, GDP, VPE. Delivery to the regions of the Russian Federation and Kazakhstan.
KV-G boilers (gas hot water boiler) (Fig. 71) are produced with a heating capacity of 4 and 6.5 Gcal/h (4.65 and 7.56 MW) instead of TVG boilers. These are direct-flow sectional boilers operating on gas fuel and are a pipe system arranged in one transportable block. The pipe system consists of radiation and convective heating surfaces, similar to shell-and-tube heaters and heat exchangers.
The radiation surface includes four fire screens and a ceiling screen. The pipes of the outer single-light combustion screens and the ceiling along the entire height (length) are connected to each other by metal plates. Each combustion screen is a separate section consisting of straight pipes welded into the upper and lower manifolds.
For a given direction of water movement along the combustion screens, the upper collectors have a blind partition offset from the center (15 and 23 pipes). The combustion screens are connected to each other by bypass pipes.
Rice. 71. Pipe system (part) of the hot water boiler KVG-6.5-150: collectors: 1 - return water inlet; 6 and 9 - rear; 8 and 10 - upper side convective parts; 11 — hot water outlet; 15 — upper ceiling screens; 16 - front; 17 — lower combustion screens; partitions: 2 - made of pipes; 3 - in the pipes of the convective part; 13 - in the upper collectors of the combustion screens; 4 — packages of coils; screens: 5 - convective; 12 - ceiling, turning into front; 18 - lateral; 7 and 14 bypass pipes
The convective heating surface consists of two sections - right and left, each with seven pipes 0 51 x 2.5 mm, welded with one end into the upper and the other into the lower collectors, i.e. they represent the lower and side parts of the heating surface. Four packages of three-pipe coils 0 28×3 mm are welded into the side pipes. To direct the movement of water in the coils, blind partitions are installed in the side pipes.
The radiation surface is separated from the convective surface by a partition made of horizontally placed pipes 0 28×3 mm, connected to each other by metal plates. This partition in the upper part is at the level of the upper coils. Thus, through the space left above, the products of fuel combustion from the radiation heating surface pass into the convective heating surface, heating the coils, and then through the flues and chimney they are removed into the atmosphere.
To clean scale and sludge, all collectors of vertical and ceiling screens have removable hatches at the ends, and the upper collectors of combustion screens have removable hatches on top (one at a time).
Requirements for industrial gas boiler houses
Gas boiler houses are fire hazardous facilities; they are subject to special requirements at the stages of design, installation and operation. The basic requirements are enshrined in SNiP II-35 - “Boiler installations”.
Requirements for pumps are specified in SP 89.13330.2012. Water and steam must comply with GOST 20995-75, 2761-84, and the chemical water treatment system must comply with SNiP 2.04.02-84 “Water Supply”. More detailed information on the requirements and rules can be found in the book “Boiler installations of industrial enterprises” (L.N. Sidelkovsky, V.N. Yurenev).
Industrial boiler boiler boilers are installed in a separate building, whose fire resistance is determined by production requirements. For installation of large-sized elements and components of the boiler, installation openings must be provided.
The design and construction of industrial boiler houses is carried out taking into account existing building plans and utilities in the area of the proposed construction.
The project should include a boiler room, a pump room, a fuel facility, premises for chemical water treatment and instrumentation.
Construction of a hot water boiler using solid fuel
The main components of this unit are:
- Firebox: Usually made of thick cast iron sheets, but sometimes manufacturers use firebricks instead.
- Ash chamber (located under the firebox and separated from it by a grate).
- Heat exchanger (located in the upper part of the firebox). Usually made of cast iron.
- A water heating tank for domestic needs is installed both above the firebox and on the side.
- Pipe for connection to the chimney.
- A housing with doors opposite the firebox and ash chamber. The inside is insulated with a heat insulator based on basalt fiber with heat-reflecting screens.
- Some models have a fan.
Types: low temperature, high temperature
There are also boilers of varying levels of combustion and heat transfer. For example, there are options for long-term and short-term combustion, and there are also other types.
Characteristics:
- Low temperature model – up to 115 degrees. Great savings in fuel consumption, but there is also an accumulation of condensate, so careful operation is required.
- High temperature model – up to 150 degrees and above. Reliability is stable, the level of operation is high. Quiet operation, minimal waste emissions, and safety control systems.
Principle of operation
This unit is a direct combustion boiler, that is, fuel is burned in it in the most common, uncomplicated way. The resulting ash is poured into the ash chamber, from where it must be removed periodically.
The most convenient to maintain are boilers in which the manufacturer has installed a pull-out tray in the ash chamber.
Fuel loading and ash removal are carried out traditionally - through the corresponding doors in the housing. The difference from conventional solid fuel heaters is the increased size of the firebox and the presence of a water heating tank. Note that boilers of this type are not double-circuit. Here, rather, we are talking about an indirect heating boiler (and partly direct), built into the boiler body.
Operating principle of the boiler
But indirect heating here is not entirely ordinary. As is known, in indirect heating boilers, heat is delivered to the heated medium using water or other coolant fluid (oil, antifreeze), which fills the heating circuit. In a water heating boiler, thermal energy is transferred using air: inside the water heating tank there are tubes connected to a heat exchanger installed in the firebox, and this entire system is essentially empty, that is, it is filled with air that circulates in it.
At first glance, such a solution may seem strange, because we are accustomed to seeing water as a coolant, the heat capacity of which is 800 times greater than the heat capacity of air. But everything falls into place if we remember that the intensity of heat transfer depends not on heat capacity, but on the temperature difference. Air, due to its low heat capacity, heats up faster than water, which means it will give off heat more actively. Since all components are located inside the boiler body, there is no heat loss, so there is no need to use a coolant with a large heat capacity.
Boiler room ventilation and combustion air heating circuit
This circuit is the internal circuit of the boiler room, the heat from which is used for its own needs. It is an independent circuit separated by a heat exchanger.
A three-way mixing valve is installed on the heating side of the supply pipeline, which maintains the set temperature on the heated circuit of the heat exchanger according to the temperature sensor. The temperature is maintained by mixing coolant from the return pipe from the heat exchanger.
On the heating side, a circulation pump is installed on the return pipeline, which circulates the coolant through the heat exchanger. The pump runs all the time while the circuit is on, with a constant flow rate.
On the heated side of the heat exchanger, ventilation equipment (ventilation unit, air heaters) is connected, providing standardized ventilation in the boiler room and/or heating of combustion air.
Anti-freezing liquids based on glycol are used as a coolant. This necessitates the need to separate the ventilation circuit with a heat exchanger. On the glycol side, a circulation pump is installed on the return line, which circulates the coolant through the ventilation equipment. The pump runs all the time while the circuit is on, with a constant flow rate.
To compensate for temperature expansions, an expansion tank is provided in the radiator heating circuit, equipped with a safety valve that protects the tank from excess pressure by releasing the coolant. The coolant is discharged into a specially installed glycol solution storage tank. The glycol circuit is also fed from it using a special make-up pump.
Advantages and disadvantages
As mentioned above, this type of water heater is in great demand today. This can be explained by the following advantages:
- The device is completely autonomous, that is, its operation does not depend on the functioning of any centralized power supply network.
- Fuel is cheaper than gas, especially if waste from the wood processing industry or agriculture is used.
- To install a solid fuel hot water boiler, you do not need to obtain a permit and invite specialists, as is the case with a gas boiler.
- Compared to conventional solid fuel boilers, hot water boilers are lightweight, and the requirements placed on them are more lenient.
- Such devices are rarely equipped with automation, so failures almost never occur.
- Boiler maintenance consists of very simple actions (removing soot and ash), so it does not require any special knowledge or high qualifications.
- Durability. The hot water boiler can be used for decades, which is confirmed by the warranty provided by the manufacturer: it is usually 15 years.
- The cost is more than affordable.
At the same time, the potential user should know in advance about the characteristic disadvantages:
- The operation of the water heater cannot be automated. The user himself has to add fuel and monitor the temperature of the water in the tank.
- Since they strive to make the hot water boiler extremely simple and cheap, no measures are provided to increase its efficiency. Accordingly, it is very voracious and will require a fairly large supply of fuel.
In order to correctly connect the boiler to the heating system, you need to know some nuances. Wiring of a solid fuel heating boiler - diagram and additional circuits.
We'll tell you what an inverter is used for for heating boilers here.
Owners of gas boilers must know how this equipment works in order to be able to carry out simple repairs without calling a specialist for every reason. For more information about the design of a gas boiler, see this page.
Main characteristics
| Geography of delivery | any region of the Russian Federation and the CIS |
| Guarantee | 24 months |
| Short description | Modern hot water boiler houses are highly efficient heating systems that can be used to heat rooms of different sizes and types. With us you can choose a boiler room of suitable power quickly and easily |
Questionnaire for ordering a boiler room Implemented objects Calculate the cost of the boiler room
Cost calculation in 1 click!
Boilers with water circuit
Today, it is possible to ensure the operation of the heating system and heat water for domestic needs using just one device - a boiler with a water circuit.
This device is a regular heating boiler in which a boiler is installed. The latter, as in the case of a hot water boiler, can be located both above the firebox and on the side of it.
The simplest and at the same time the most famous representative of this category of equipment is titanium.
The heat exchanger located inside the firebox is connected to the heating circuit, as a result of which the coolant is pumped through it - now water. Part of this coolant is supplied through a separate branch to a heat exchanger installed inside the boiler, due to which the water in the boiler is heated.
In order for a heater to supply heat to two systems at the same time, it must have significant performance. Therefore, developers use various design solutions to ensure complete combustion of fuel and assimilation of the maximum possible amount of energy released.
Coolant: water
Such installations use the cheapest natural coolant - water. They are quite suitable for heating a hangar, warehouse or other large-scale indoor space. But water can create scale inside the system, which improved boiler models can reduce or clean.
Such boilers are usually designed to heat:
- stock;
- residential buildings (utilities);
- production premises (workshop, covered platforms);
- premises of agricultural significance;
- vegetable stores or granaries;
- institutions and administrative buildings;
- other large objects and structures.
Proton water boiler
Price
Water heating boilers are characterized by a fairly wide range of prices.
- boiler "Karakan 8-TPE" (power - 8 kW): 12,200 rubles;
- boiler "Sibir KVO 15 TPE" (power - 15 kW): 17,400 rubles;
- boiler "Hephaestus-15" (power - 15 kW): 21,570 rub. (combined, that is, it has a built-in heating element);
- boiler "Karakan 12-TGEV" (power - 12 kW, additionally equipped with a gas burner, heating element, water heating tank): 21,700 rubles.
Imported boilers are much more expensive, for example:
- boiler “BURNit WBS 25” (Bulgaria, 25 kW, can additionally operate on gas, diesel fuel and oil): RUB 86,250;
- Viadrus Hercules U22C-2 (Czech Republic, 11.7 kW): 44 thousand rubles;
Buderus Logano S111-2 (Germany, 12 kW) costs 53,440 rubles.
If there is no gas supply, owners of private houses have a choice - to purchase a solid fuel or liquid fuel boiler. A diesel fuel boiler has a number of advantages, which is why many people prefer this type of heater.
What is a distribution comb and how to install it correctly, read in this material.
Fuel: firewood, pellets, gas, diesel, fuel oil
Models may also differ in the use of different coolants.
There are boilers:
- wood - medium-cost solid fuel;
- gas - cheap;
- diesel – medium-cost;
- fuel oil - medium-cost;
- pellets - expensive peat granules.
The most economical is a gas hot water heater. For floor-standing installations, solid fuel coolant options are more often used, but gas or diesel can also be used.
DIY making
It’s easy to make a simple hot water boiler yourself. Here's what you need to consider:
- The choice of firebox material should take into account what type of fuel you plan to use. Coal is characterized by a much higher combustion temperature than wood, so sheets for making a coal boiler firebox should be thicker - thin steel will quickly burn out.
- The ideal material is special heat-resistant boiler steel. In second place is alloyed heat-resistant steel with additions of chromium and molybdenum, for example, grades 12ХМ or 12Х1МФ. If you plan to use ordinary steel, then it should have a grade lower than steel 35. In steels of higher grades, when heated, a hardening effect occurs, as a result of which they become brittle.
Kits consisting of a fan, a temperature sensor and a controller are available for sale (for example, from the Polish company KG Elektronik), with the help of which it is easy to organize forced air supply into the firebox (see above for the description of the operation of a boiler with a fan).
Types: fire tube, water tube
The special design advantages of hot water boilers are that you can choose any of two options: fire-tube (or gas-tube) or water-tube.
Characteristics:
- The fire tube model is a special system of tubes supplying heated energy, automatic burners with blowing fan devices. In domestic conditions, these options are not used.
- Water tube model - special boiling tubes move the coolant. Warm up quickly, overloads occur, but explosions are practically excluded.
For electrical cable
| Pipe diameter | Wall thickness | Price for 1 p.m. VAT included |
| TU 6-49-53883187-01-05 SDR 17.6 | ||
| 16 s | 2 | 9,43 |
| 20 s | 2 | 12,10 |
| 25 s | 2 | 15,48 |
| 32 s | 2 | 20,26 |
| 40 s | 2,3 | 27,71 |
| 50 s | 2,9 | 42,99 |
| 63 s | 3,6 | 63,88 |
| 110 s | 6,3 | 149,75 |
| 160 s | 9,1 | 315,88 |
| 225 s | 12,8 | 619,44 |
| 315 s | 17,9 | 1890,00 |
| 400 s | 22,7 | 3138,75 |
For electrical cable