The stove is considered a traditional design for heating buildings.
But if it is installed in a large house with several floors, then its power may not be enough to heat all rooms evenly. The solution here may be a furnace coil, which is also called a heat exchanger. It is connected to a heating device, then it is carried out through each room, thereby ensuring ideal and uniform heating of the entire building.
Design features
Most often, a metal tank with a capacity of up to 5 liters with built-in pipes acts as a heat exchanger. There is no direct contact with fire. The device allows you to heat cold water, which then flows into radiators or a removable tank of larger capacity located in the same or an adjacent room.
As a result, by heating the stove in one room, it will be possible to heat another. According to its design, the heat exchanger for a furnace can be external or internal.
This type is very similar to a tank filled with coolant. Inside the container there is a part of the pipe used to remove combustion products. In terms of its design, the external heat exchanger is more complex than the internal one, as it places increased demands on welding work.
However, its maintenance is much easier. If necessary, the tank can be dismantled to remove scale or eliminate leaks.
Interior
Mounted above the firebox directly inside the stove. It is easy to install, but if maintenance is necessary, certain difficulties may arise. Especially if the stove is made of brick.
To avoid this, at the time of design development it is worth taking care of the maintainability of the future heat exchanger.
Source of thermal energy for the system
The part of the system that provides the transport function is not of interest to us. The theory of its functioning is needed in order to make heating with your own hands. As a source that would heat the water, you can use a gas boiler or an electric one.
The fireplace as a water heater turns into a multifunctional device. He continues his mission to provide the external decoration of the room and create comfort from the opportunity to contemplate the combustion process, but to warm up all the rooms, they use a fireplace with water heating.
The rather low efficiency index, especially for a fireplace with an open firebox, does not allow us to hope for high-quality heating during periods of severe frost. But for a small house this option is quite suitable. If you provide the ability to connect and disconnect the fireplace from the heating system, then the ideal option can be realized.
Commissioned furnace
The idea is that the main heating is taken over by the device that is intended for this purpose. At the right moment, the fireplace turns on and provides additional energy. At dachas, when the owners leave for a while, the fireplace can be turned off and the main boiler left running.
Pros and cons of the oven
A conventional stove distributes heat unevenly: it is very hot right next to the stove, and the further you go, the colder it becomes. The presence of a water circuit allows the heat produced by the stove to be evenly distributed throughout the house.
Construction of a heating furnace with a water circuit
Thus, only one stove can heat several rooms in the house at the same time. The stove works almost the same as a solid fuel boiler. Only it doesn’t just heat up the coolant and water circuit. In addition, the walls and smoke channels are heated, which also play an important role in the heating process.
The heat exchanger (coil) is the main element of the stove. It is installed in the fuel part of the stove, and there the entire water heating system is connected to it.
The advantages of a furnace with a water circuit include the following features:
- First of all, for such a furnace there is no need to purchase expensive units and components.
- A properly built stove will serve you for a long time without requiring expensive repairs. Sometimes, you may only need a small cosmetic one.
- The stove can be created in any design: shape, size, decoration - all this is according to your taste and financial capabilities.
- If you compare a stove equipped with a water circuit and a solid fuel boiler, then with the help of the first one heats not only the coolant, but also the smoke outlets.
- The coil can be equipped with an already built stove. It can also be inserted into a cooking stove.
A stove option that fits perfectly into the interior of the room.
This type of heating also has disadvantages.
- When the heat exchanger is inserted into the fuel part, the latter's precious space is greatly reduced. The problem can be solved if the heat exchanger is built into the furnace during its construction. This part just needs to be increased. Well, if it is inserted into an already built structure, then there is no other way out except to add fuel incompletely, but in parts.
- With such a stove, the fire hazard increases. There is an open fire burning in the stove and fireplace, plus spare wood is often stored nearby. Do not leave this unit unattended.
- If the stove is operated incorrectly, carbon monoxide entering the home can lead to very dire consequences.
An image from which it becomes clear that it is better not to leave the unit unattended.
Experts advise using non-freezing liquid in such structures if people do not live in the house permanently, but, for example, only in the summer.
Installing a heat exchanger in a sauna stove
When choosing a heat exchanger, you should, first of all, take into account the volume and power of the furnace combustion chamber. A powerful furnace will most likely already contain a heat exchanger.
However, such water is best suited for heating the circuit. Since it has a high outlet temperature, which creates a pressure difference that forces the water to move through the pipes. The internal heat exchanger is not capable of producing large quantities of hot water.
- A solution to the problem can be a remote samovar tank. It should be taken into account that the smoke in a stove with an internal heat exchanger has a lower temperature than in a conventional stove. The difference can be 50-100 degrees. Therefore, the additional heat exchanger here must have a small volume of 20-80 liters.
- The tank for the pipe of a unit without an internal heat exchanger can be much larger - up to 150 liters.
- Manufacturing and installation of external tanks does not require additional effort. For this, metal sheets or ready-made tanks are used. They are installed simultaneously with the creation of the pipe. In this case, the pipe itself may have a shorter length, since at the outlet into the wall or roof the temperature in it will be significantly lower than usual.
- The difficulty in installing built-in heat exchangers is not associated with them themselves, since they are completely integrated into the stove, but with the installation of the heating circuit.
If an additional pump is not planned here, then the length of the pipes should not be more than 10 meters. For longer circuit lengths, forced circulation pumps should be installed.
Important! The unit with a built-in heat exchanger cannot be operated continuously without water. Since the design of the furnace is designed for cooling by water. Without it, the metal in the combustion chamber will overheat and deform.
When choosing and installing a heat exchanger, you should also not forget that any water containers require maintenance and regular descaling. Operating tanks in this regard is much easier.
Each owner chooses for himself how to make the bathhouse more comfortable and high-tech. But it will always be reasonable to combine several methods at once, and family and guests will certainly appreciate it.
Latest announcements
Gas boiler Protherm (Proterm) Bear 20 klom
New in box, everything is sealed, warranty receipt dated 09/1/19. I’m selling because it doesn’t fit our old system, but to return...
- Region: Moscow region
11.09.19
Water heating gas boiler VK-21(KSVA-2.0 GS)
We offer steel water heating boiler KSVa-2.0 Gs (VK-21). For a wholesale order (from 2 boilers) a price discount is possible Type...
- Region: Kirov region
05.08.19
Steam generator KV-300
We offer steam boiler KV-300 (KP-300). Steam capacity for normal steam, kg/hour – 300; - permissible excess...
- Region: Kirov region
28.06.19
Steam generator for 500 kg steam
Technical characteristics: — steam output — 500 kg/h; - boiler type - two-pass, fire-tube with reversible...
- Region: Kirov region
28.06.19
Steam generator for 1600 kg steam
Technical characteristics: — steam output — 1600 kg/h; - boiler type - two-pass, fire-tube with reversible...
- Region: Kirov region
28.06.19
Water heating boiler KSV-0.63
We offer a water heating boiler KSV-0.63. Technical data and characteristics: - rated heating capacity, ...
- Region: Kirov region
28.06.19
Water heating boiler 850 kW gas diesel
Technical characteristics: - nominal heating capacity - 0.85 MW; — Efficiency – 92%; - boiler type - two-pass, ...
- Region: Kirov region
28.06.19
Automatic coal boilers Lugaterm
The boiler model combines three main parts: a water-cooled firebox, a heat exchanger with automatic mechanical ...
- Region: Moscow
15.03.19
SOLID FUEL WATER BOILERS ON THE KVR MINE FIRES
Type of fuel: firewood of any moisture content Power from 0.2 to 2.5 MW Purpose: obtaining hot water at a nominal temperature ...
- Region: Kirov region
05.02.19
WATER HEATING BOILERS FOR WORKING WITH WOOD PROCESSING AND LAWMILLING WASTE KVM
Type of fuel: wood waste (sawdust, wood chips, bark) – without humidity limitation Power: from 0.2 to 2.5 MW Purpose: ...
- Region: Kirov region
05.02.19
Announcements by topic:
- Boilers and equipment for boiler houses
- Cooling towers
- Heat networks (all about pipelines)
- Materials
- Water treatment
- Cogeneration
- Autonomous heat supply
- Pumps, fans, smoke exhausters
- Pipeline accessories
- Heat exchange equipment
- Metering devices
- instrumentation and automation
- Repair equipment
- Heating devices
Design features
If the owner of the building has experience in bricklaying or stove work, the installation can be done with his own hands. Before connecting the water heating system, you will also need to make a heat exchange unit.
Despite the fact that the construction market offers a large selection of ready-made structures, self-production is more profitable. A manual installation allows you to take into account all the parameters of this particular stove, its placement and the dimensions of the fuel compartment.
Heat exchanger made of pipes
The design of a stove heating system with a water circuit involves installing a heat exchanger in the fuel compartment of the stove and connecting pipes to it to supply working fluid. For heating and cooking stoves and cookers, coils welded from pipes and placed in metal containers are well suited. Their production requires professionalism, and cleaning from combustion products is quite labor-intensive, but the tortuous surface will ensure rapid heating.
The 50 mm U-shaped pipes used in the design can be replaced with sections of 40x60 mm profile pipes. This will simplify the welding work and greatly facilitate installation. If the oven is not used for cooking, additional small diameter tubes are welded to the top of the heat exchange unit. The design, improved with your own hands, will give off much more heat.
Sheet steel heat exchanger
Devices of this type are used in furnaces intended exclusively for heating the room. To make them, you will need sheet metal half a centimeter thick, sections of rectangular pipes 40x60 mm, as well as round pipes of the same diameter for supplying water to the working surface. The dimensions of the heat exchangers depend on the size of the furnace fuel compartments.
A similar heating system can be used for a heating and cooking stove or a simple stove. To do this, the structure must be mounted so that the heated gases from the fuel chamber move towards the upper shelf of the register, flow around it and enter the smoke channels.
Choosing the design of the device
When choosing a suitable heat exchanger for a furnace, you should strive to ensure that the total surface area of the finished product is as large as possible. This will ensure the most efficient heating of the room.
Coil
The most widespread are registers (coils). Such heat exchangers are made from smooth-walled pipes with a diameter of 40 - 50 mm. Outwardly, they resemble a characteristic L-shaped grille. For their manufacture, you can use not only round, but also profile pipes with a similar cross-sectional area.
The return and hot water outlet can be located either on one side of the register or on different sides.
The output option is determined by the design features of the furnace itself and the piping layout of the heating system.
Tank
The next most popular are rectangular or cylindrical tanks, inside of which there is a pipe or coil. The length of such a heat exchanger depends on the parameters of the furnace firebox. The heat exchanger installed on the chimney usually has a cylindrical shape. There is a pipe running inside it, the diameter of which is equal to the diameter of the chimney. The pipes are welded from below. Can be used both for heating a room and for heating water.
This design requires special attention. Due to the rapid cooling of combustion products, the draft in the chimney itself is significantly reduced. This helps slow down fuel combustion.
Installing the product on a heating and cooking stove requires special attention. Care must be taken to ensure that hot gases pass over the top shelf and enter the chimney at the front of the firebox.
In this case, the cooking plate can be located directly above the heat exchanger. It is also possible to manufacture a register without a top shelf. The so-called shelf consists of lower and side parts connected to each other by pipes.
Inspection of welded joints and bends
Each welded joint is subjected to external inspection and measurement to identify displacement of the edges and fracture at the joint (Fig. 8). The displacement b of the welded edges refers to the parallel displacement of the pipe axes among themselves. Kink k is a deviation in the form of a skew of the axes of the joined pipes. The displacement of the edges and fracture of the joint is measured with a special ruler 400 mm long with a cutout in the middle, which is installed tightly along the generatrix of one of the pipes with a cutout at the joint, and the deviation is determined along the other pipe with a feeler gauge at a distance of 200 mm from the axis of the joint. Measurements are carried out in 3 - 4 places around the circumference of the joint.
The inspection reveals such defects as burning (melting) of pipes in places of contact with the jaws and the machine body, creeping edges, and incomplete removal of the outer burr.
a - displacement; b - fracture;
Figure 8 — Deviation of welded pipe edges
To check the quality of welds, as well as devices for automatic control of welding process parameters, express tests of control welded joints (samples) are carried out. Samples are received before the start of each shift. Welding is allowed to be performed only if there are positive results of express tests of control samples. As a rule, express samples are subjected to metallographic examination.
Checking the mechanical properties and metallographic examination of welded joints is carried out on samples made from control welded joints, or on samples of welded joints cut from the manufactured product. In the case of cutting from finished products, the volume of control joints must be at least 1% (but not less than three joints) of the total number of identical welded joints performed by each welder in one shift.
By running the ball with compressed air, the completeness of removal of internal flash (or metal leakage) is checked - ensuring the specified flow area in welded joints. When inspecting welded joints on straight pipes (braids), a ball with a diameter of 0.86 in.nom is used, on coils 0.8 in.nom. of pipes. The reduction in the diameter of the ball when monitoring the flow area in the coil is caused by the ovality of the pipes in the bends. A ball catcher is placed on the free end of the coil, which ensures safe operation.
Ovality control of pipe bends and heating surface coils is selective (at least 10% of bends of the same standard size). The maximum ovality along the entire bend length should not exceed the permissible value. The maximum and minimum outer diameters of the pipe at the bending point are measured in one control section.
The ovality of the section in places where pipes are bent can be determined
where and are, respectively, the maximum and minimum outer diameter of the pipe at the bending point, measured at one section of the section, m.
Permissible ovality for boiler heating surfaces
where R is the bending radius of the pipe, m;
— outer diameter of the pipe, m.
The thinning of the pipe wall at the bending point on the stretched (outer) side is determined selectively by an ultrasonic thickness gauge. It is recommended to check the thinning when changing bending tools, setting up the machine and accessories.
For pipes with a diameter of up to 60 mm, bent without heating, high frequency currents (HFC), waviness (corrugations) on the inside of the bend and bulges on the stretched side should not exceed 0.5 mm in height with a minimum step of at least three heights.
Kinds
Types of heat exchangers are divided by design, location and material of manufacture. For each specific case, you can select a combination of these types.
By combining the design and material, and placing it correctly, you can significantly increase the efficiency of a brick kiln. It’s worth considering how to make a heat exchanger for a furnace without extra costs. By analyzing the types of existing structures, you can select the most optimal heat exchanger for a particular layout.
- Coil. It is created from a pipe, coiled in the form of a spiral, several meters long. Such a water heat exchanger for a furnace is installed in a container with a liquid coolant. The ends of the pipe are expanded into the walls, allowing the coolant to circulate inside, simultaneously heating the water in the tank. With the correctly calculated length of the coil, the material it is made of, and the number of rings, you can speed up the heating of the water. Also, the part of the coil that remains in the air increases the rate of heating of the room.
- Heat exchanger with container. The tank and heat exchanger pipe for the furnace are installed directly next to the combustion chamber. It is necessary to strictly observe the degree of inclination of the supplied pipes in order to achieve natural circulation. In some cases, it is necessary to install an electric pump for these purposes. This solution has its advantages - the water is heated directly by passing through a pipe that goes around the firebox. This solution increases the heating rate. Typically used for heating circuits.
- Pipe board. It consists of two completely sealed containers and a large number of small pipes. The main pipe-containers are located in different parts, near the combustion space and are connected by pipes. Heat exchange occurs at the joints. This design is used for heating large spaces, up to high-rise buildings. The operation of such a heat exchanger is complicated because precautions must be taken. The chemical composition of the water is important here; due to the formation of scale, wall breakthroughs are possible.
- Water jacket. This heat exchanger is the most difficult to create with your own hands. Its design consists of two sealed tanks located one inside the other. Efficient and easy to use - a heat exchanger for a stove made of pipes. It allows heat exchange to occur quickly, but is difficult to manufacture and requires professional skills.
Choosing material
The coil is traditionally made from a pipe, the length and diameter of which are determined by the desired level of heat transfer. The efficiency of the structure will depend on the thermal conductivity of the material used. The most commonly used pipes are:
- copper with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 380;
- steel with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 50;
- metal-plastic with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.3.
Copper or metal-plastic?
With the same level of heat transfer and equal transverse dimensions, the length of metal-plastic pipes will be 11, and steel pipes will be 7 times longer than copper ones.
That is why it is best to use annealed copper pipe to make a coil.
Such a material is characterized by sufficient plasticity, and therefore it can easily be given the desired shape, for example, by bending. The fitting is easily connected to the copper pipe with a thread.
We are looking for improvised means
Considering the high cost of materials, it would be appropriate to consider the possibility of using products that have already served their purpose, but have not yet fully exhausted their service life. This will not only reduce the cost of manufacturing the heat exchanger, but will reduce the time for installation work. As a rule, preference is given to:
- any heating radiators that do not leak;
- heated towel rails;
- radiators from cars and other products of similar design;
- instantaneous water heaters.
Coil installation method
You can install a coil heat exchanger on the chimney of a sauna stove or potbelly stove in a garage or shed. It will serve for heating or for heating water.
To work you will need:
- aluminum or copper tube up to 3 m long;
- 2 3/4″ fittings and a flexible hose for hot water;
- boiler with a float valve for filling with water and a valve for its use;
- tap for draining coolant from the system.
The system installation technology looks like this:
- The first step is to bend the tube so that its cross-section remains unchanged. For copper pipes less than 28mm in diameter, you can use a pipe bender without heating them. But steel, aluminum and products with large diameters require preheating with a blowtorch.
- For bending, you can use dry sand, filling the pipe with it and closing it with plugs on both sides. A spiral bend is made according to the sample, after which sand is poured in and the pipe is washed under water pressure.
- At the end parts of the tube, threads are cut for adapters for fittings, and then connected to the system.
- The resulting coil is mounted on the chimney. If you solder it with tin to the pipe, the heat transfer will be better. Preliminary degreasing is carried out with orthophosphoric acid.
- A storage tank is hung on a support or on the wall a little above the coil. Connect it to the heat exchanger with a flexible connection and install a tap at the bottom of the tank.
Note that for safe and long-term use of a heating coil, you need to install a pump that circulates water in the system and prevents overheating.
Methods for making coils
There are three main schemes for obtaining coils of boiler heating surfaces (Fig. 7): element-by-element, braided and by the method of sequential extension. Regardless of the method, the technological process for manufacturing coils includes: incoming inspection of pipes; sorting the original pipes by length; development of schemes for cutting pipes into elements; pipe cutting, trimming and cleaning of pipe ends. We choose the element-by-element method.
Figure 7. Element-by-element diagram of coil manufacturing
With the element-by-element manufacturing method, prepared straight pipes are first bent on machines followed by plastering, then the bent elements are welded together into a coil (Fig. 7).
Disadvantages of stove heating with a water circuit
- Loss of usable space. A heat exchanger built into the firebox significantly reduces its size, so this factor must be taken into account when laying the firebox. Well, if the heat exchanger is built into an existing structure, the only solution is to frequently add fuel.
- Increased fire hazard. Since a stove or fireplace requires the presence of an open fire and a fuel supply nearby, it is not recommended to leave such a stove unattended for a long time.
Having organized stove heating in the house, you must constantly monitor fire safety
Carbon monoxide. If used incorrectly, carbon monoxide, which is dangerous to human life, can enter residential premises.
Advice. If heating with a water circuit is installed in a country house where no one lives regularly, especially in winter, then in order to avoid freezing of the water in the circuit, it is better to use an antifreeze liquid.
Why do you need a heat exchanger in a bathhouse?
In the steam room, the heat comes from the stove and the stones on it, which accumulate heat and release it. In other rooms, heat comes from special structures that partly resemble a heating system.
The sauna heating system is based on water. The heat exchanger can be of different sizes and shapes. It can be a water tank, which is heated directly from the stove, or a water jacket made of pipes through which liquid circulates.
The main tasks of the heat exchanger:
- Heating of rooms other than the steam room;
- Energy saving;
- Creating a cozy atmosphere;
- Creation of warm and hot water for a bath.
Important! In a bathhouse, hot water is usually needed in a larger volume than in a regular home. So it is required for washing, to create cleanliness in the room, for the operation of vats with herbs, steam barrels and other original devices. Therefore, the heat exchanger must be designed for the required amount of water and its turnover.
Let's start installation
The sequence of work depends on the design features of the heat exchanger.
Installation of a device with a register
When installing in an old furnace, you will have to dismantle part of the masonry. The sequence of work is as follows:
- We prepare the foundation for the coil right in the firebox cavity.
- We install the coil.
- We lay the disassembled row of bricks, leaving space for the inlet and outlet parts of the pipes.
- We connect the heat exchanger to the heating system.
Before use, the tank must be checked for leaks. You can make sure there are no leaks by filling it with water, preferably under pressure.
Installation of a device with a container
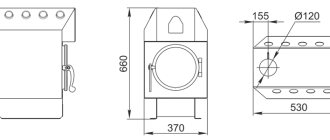
The best option for a stove or fireplace. Made from a metal tank and two copper tubes. The tank volume is usually about 20 liters. In the absence of a finished product, a tank of sufficient volume is made by hand by welding sheet steel.
For the manufacture of the heat exchanger, a material thicker than 2.5 mm should be used. Welding should be done in such a way that the thickness of the formed seam is minimal.
The tank must be installed 1 meter above the floor level, but no further than 3 meters from the stove. Two holes are made in the tank: one near the bottom, the second at the highest point on the opposite side. The efficiency of heat transfer depends on the location of the lines.
It is necessary to strive to ensure that the minimum deviation of the lower outlet in the direction of the floor is 2 degrees. The top one should be connected at a 20 degree angle in the opposite direction.
The drain valve is being installed in the storage tank. There is another tap designed to drain the entire system, which is installed at the lowest point. After checking the tightness, the system is ready for operation. The efficiency of such a stove with a heat exchanger can be appreciated in the cold season.
Types of heat exchangers
Coil
A simple device can be effective in different ways - depending on the type. Classification is carried out according to several criteria. Different models of factory or homemade heat exchangers, for example, in a bathhouse, differ:
- design,
- installation location,
- material.
These factors influence each other and the features of the heat exchange unit as a whole: its cost, efficiency, productivity, system volume, installation complexity, etc.
Design
Design differences largely depend on the purpose of the product. For example, heating water for washing requires a significant volume and intense heat transfer. And use only for heating requires a gradual transfer of heat to the coolant.
- A coil is a pipe bent at different angles. Warms up quickly, but often does not have enough volume. Suitable for installation in a wood-burning firebox, behind the firebox, in a heater, on a chimney (if the coil is spiral-shaped).
- A register is an analogue of a pipe radiator, perhaps the most popular, universal, and energy efficient. As a rule, these are several large-diameter pipes connected by thin tubes. The choice of a specific form and installation location is limited by the author’s imagination, as well as the general design.
- A diplomat is one or more interconnected containers with pipes. This is a common model, easy to assemble and install. A sauna stove with a heat exchanger of this type will provide heat, heat, and hot water. Disadvantages - a significant volume reduces the heating rate and limits the choice of installation location. The primitive form does not contribute to complete heat transfer, interfering with the heating of parts of the stove itself. Therefore, it is only suitable for installation inside the heater (if we are talking about a sauna), behind it or behind the firebox.
- Water jacket is a casing installed on parts of the heat generator that are heated from the inside. Often this is a cylinder with pipes placed on the chimney. Difficult for DIY assembly, prone to leaks, but does not require disassembling the stove for installation and is quite effective.
Water jacket
Diplomat
Register
The choice of model is usually associated not so much with efficiency and price, but with the complexity of installation. For example, some modifications of water “shirts”, “coils” and “diplomats” are installed without disassembling the stove. The maximum is upgrading part of the pipe or replacing the cast iron stove (for cooking) with a “diplomat”.
Heat transfer registers are generally preferred over other devices. However, they are installed only during the construction of a new stove or serious alteration of the old one.
Material
Copper heat exchanger
When designing a stove or fireplace with any heat exchanger, the engineer (or stove maker) takes into account the parameters of the materials. Necessary properties are fire resistance, elasticity, corrosion resistance, heat capacity, thermal conductivity. Only metals have these characteristics.
- Steel is excellent in all respects except corrosion resistance. However, if the coolant is always filled, it will not rust.
- Stainless steel has no disadvantages other than high price and difficulty in welding. Galvanized steel is almost never used due to toxic emissions associated with high temperatures.
- Cast iron, the disadvantages of which are the difficulty of welding and the high probability of cracking (due to sudden temperature changes due to uneven heating).
- Copper, which is good for everyone, except for the high price and connecting parts by soldering. Solder does not “hold” strong heat if the water is drained, so the use of copper is limited.
The choice is usually related to the availability or accessibility of the material. You can often find sauna stoves with a cast iron heat exchanger, which is a modified battery. The modification consists of welding the joints of the sections and plugs in the extra holes. Thus, a heat exchange register is obtained that has all the necessary properties. Its disadvantage is its bulkiness, which limits the choice of location.
Do-it-yourself stove heating with a water circuit, step-by-step construction
First, before you start building the stove, you need to prepare the foundation. To do this, you need to dig a pit, the depth of which is 150–200 millimeters. Fill the bottom with layers of broken brick, crushed stone and rubble. Then fill everything with cement mortar. The foundation should rise several centimeters above the floor. Place waterproofing material on the screed.
Construction process of a water loop furnace
Main features of brick laying
The stove must be built from quality materials. Walls can be built from bricks with normal firing, but for the firebox, purchase refractory bricks.
- Before starting laying, the bricks must be wetted. To do this, immerse them in water for a while. When air bubbles stop coming out of them, you can start laying.
- All rows and corners must be tied.
- Apply the cement mortar to the entire rad at once. Its layer should be about 5 millimeters. Refresh the mortar on the end right before laying brick on it.
- When you get to the firebox, don't apply the clay with a trowel. Do it with your hands.
- Every five rows, carefully cut off excess cement from the seams and wipe them with a damp sponge.
- The walls of the stove must be vertical and horizontal. Use a spirit level constantly during laying to check this.
Advantages of combined heating systems
- Cost-effectiveness of the system. Construction of a stove or re-equipment of an already finished one will not require serious financial investments, and as a heating device it does not require complex and expensive maintenance.
- You can combine a stove with a fireplace and get not only a heating device, but also a unique decorative element that can become the main attraction of the interior.
- The house creates a special coziness and atmosphere that can only be created with the help of this living heating method.
- Relatively high efficiency. If the stove is built by a competent specialist according to a good design, its productivity will be quite high, up to 60% in comparison, for example, with an oil-fuel boiler.
Application specifics
Standard stove heating implies an uneven distribution of thermal energy - the further from the source, the colder. After connecting the radiators and filling with water, the stoves act as analogues of solid fuel boilers, providing heating of the coolant, smoke channels and walls. During combustion, such a system will allow heat to be transferred from the coil to the radiators, and after the fuel dies out, it will use the energy of the heated walls of the furnace.
When installing a heat exchanger, it is worth considering that its installation will reduce the usable volume of the fuel compartment and fuel will have to be added much more often. Correct design of the water circuit and its relationship with the dimensions of the heating chamber will help eliminate this problem. A good alternative would be to install a long-burning stove.
Such an upgrade of the heating system has its own nuances. The energy released during the combustion of wood will heat the heat exchange unit and the working fluid placed in it, but the walls of the furnace will not change their temperature.
The upper part of the housing with the smoke channels will be heated. If the building is used for temporary residence, the furnace will be turned on irregularly and can lead to freezing of the liquid inside the pipes. In order to prevent accidents, it is recommended to replace water with antifreeze.
Mechanism of operation
A metal stove placed in a house, garage or bathhouse must be equipped with a chimney to remove carbon monoxide and organize draft. During the process of heating the furnace, this pipe can reach very high temperatures, about 200-500 ℃, which is unsafe for people in the room.
If you install a heat exchanger on the chimney, you can significantly increase the efficiency of the stove, and also protect yourself from direct contact with a hot surface. In a tank or coil installed on the chimney, the coolant will be water, however, you can also install an air heat exchanger on the chimney pipe. Due to the direct contact of the chimney with the coolant, their temperature indicators are balanced, that is, the water or air gradually heats up, and the walls of the pipe cool down.
As the temperature of the water inside the register rises onto the pipe, it rises upward, where it enters the water tank through a special fitting. Through the inlet fitting located at the bottom of the heat exchanger, cold water enters it, replacing warm water. This circulation continues constantly, and the water can heat up to very high values.
An air radiator on a chimney pipe has a similar operating principle. Cold air enters the heat exchanger from below, and after heating it rises up and is supplied through the pipeline to the heated rooms. In addition, the radiator fins also give off heat. An air heat exchanger is optimal for heating attics in a country house or dressing rooms of a bathhouse, if such rooms are heated only from time to time. It is not advisable to organize water heating in them, since you will have to constantly fill and drain water from the system.
Quality indicators
Quality indicators serve to evaluate the operational merits of the unit, the main ones being: technical level, reliability and durability, structural, aesthetic and ergonomic characteristics of the unit.
A. Technical level.
There are absolute, relative and long-term technical levels.
The absolute technical level of a product is characterized by its performance indicators. Their number should be minimal. In order to avoid multiplicity and vagueness in assessing the absolute level, it is necessary to limit ourselves to only the most important of them - productivity, efficiency, process continuity, degree of automation.
The relative technical level characterizes the degree of perfection of a product when comparing (according to relevant indicators) its absolute technical level with the level of the best modern world - domestic and foreign - samples and models of similar purposes.
The promising technical level determines the intended and planned trends in the development of a given industry in the form of a set of its promising indicators.
B. Durability and reliability.
These indicators are the most important of the quality indicators.
Durability is the ability of a unit to remain operational with as few interruptions as possible for maintenance and repairs until destruction or another limiting state. The main quantitative indicators of durability are technical resource and service life.
Technical resource - the total operating time of the unit during the period of operation.
Service life is the calendar duration of operation of the unit until destruction or to another limiting state (for example, until the first major overhaul). The service life is limited by the physical and moral wear and tear of the unit.
Reliability is a property of a unit, determined by the reliability, durability and maintainability of the unit. Quantitative indicators of reliability: operating time, probability of failure-free operation, availability factor.
Running time is the duration or volume of operation of a unit, measured by the number of cycles, the number of manufactured products, or other units.
The probability of failure-free operation is the probability that, under certain modes and operating conditions, no failure occurs within a given operating time. Availability factor is the ratio of the operating time of the unit in units of time over a certain period of operation to the sum of this operating time and the time spent on finding and eliminating failures during the same period of operation.
B. Ergonomics and technical aesthetics.
Creation of modern heat exchangers that meet the best designs and international standards in terms of quality, ease of maintenance and appearance. The design of an industrial heat exchanger must be based on technical specifications and, at the same time, on the requirements put forward by new scientific disciplines - ergonomics and technical aesthetics.
Ergonomics is a scientific discipline that studies the functional capabilities of a person in labor processes in order to create perfect tools and optimal working conditions for him. Technical aesthetics is a scientific discipline, the subject of which is the field of activity of the artist-designer. The goal of artistic design is (in close connection with technical design) the creation of industrial facilities that best meet the needs of operating personnel, that best meet the operating conditions, have high aesthetic qualities, and are in harmony with the environment and setting.
A beautiful appearance usually corresponds to a rational and economical design. The appearance of the product largely depends on its color. Color is the most important factor, not only determining the aesthetic level of production, but also influencing worker fatigue, labor productivity and product quality.
Furnace heat exchangers
Coil arrangement diagram
The diagram shows one of the coil options. This type of exchanger is good to place in heating and cooking stoves, because its structure easily allows you to place a stove on top.
In order to reduce the labor intensity of the manufacturing process, you can make a few changes to this design and replace the upper and lower U-shaped pipes with a profile pipe. In addition, vertical pipes are also replaced with rectangular profiles if necessary.
If a coil of a similar design is installed in ovens where there is no hob, then to increase the efficiency of the exchanger, it is advisable to add several horizontal pipes. Treatment and removal of water can be done from different sides, it depends on the design of the furnace and the design of the water circuit.
The main nuances of creating a coil with your own hands
There are some rules that should be considered when creating a coil yourself:
- Voids may form in the heat exchanger, which should not be more than five millimeters. Otherwise, due to exposure to hot gas vapors from the furnace, the water in the device may boil;
- For the coil, pipes more than three millimeters thick are taken, otherwise, with a smaller pipe wall size, burnout of the elements may occur;
- When the device is located internally, a gap of twelve millimeters must be left between the firebox compartment and the heat exchanger device to compensate for the possible expansion of metal parts during the heating of water.
Economic indicators
A. Thermohydrodynamic perfection.
The power spent on pumping coolants in the heat exchanger determines to a large extent the heat transfer coefficient, i.e., the overall heating performance of the device. Therefore, an important indicator of the perfection of a heat exchanger is the degree to which power is used to pump coolant to ensure the required heat exchange.
The thermohydrodynamic perfection of the apparatus can be characterized by the ratio of two types of energy: heat Q transferred through the heat exchange surface, and work N spent on overcoming hydrodynamic resistance and expressed in the same units for all flows. Thus, the measure of the use of work expended on heat transfer can be expressed by the relation
E = Q/N
The greater the value of E, the more perfect, other things being equal, the heat exchanger or its heat exchange surface from a thermohydrodynamic (energy) point of view. The energy coefficient E is a dimensionless quantity, therefore the numerator and denominator of the expression E = Q/N can be referred to an arbitrary, but the same unit, for example, to a unit of heat exchange surface (thermal indicator), to a unit of mass of the heat exchange surface (mass indicator) or to unit of volume (volume indicator). When comparing apparatuses, the value of E can be related to all heat and to all work expended, or to a unit of surface, mass or volume of the apparatus.
The analysis shows that, all other things being equal, a change in the coolant speed has different effects on various quantities characterizing the operation of the heat exchanger: the heat transfer coefficient changes proportionally to the speed (or flow rate) to the power of 0.6-0.8, the hydrodynamic resistance is proportional to the speed to the power 1.7-1.8, and the power for pumping coolant is to the power of 2.75.
With an increase in the speed of the coolant, the power to pump it grows much faster than the amount of heat transferred, i.e. for a certain apparatus or a certain heat exchange surface, the value of the energy coefficient E decreases with increasing speed of the coolant. Therefore, the absolute value of the coefficient E cannot serve as a measure of the thermohydrodynamic perfection of a heat exchange apparatus, but is useful only when comparing two or more apparatuses.
B. Efficiency.
The thermal indicator of the perfection of a heat exchanger is its efficiency coefficient (efficiency):
n=Q2/Q1
where Q1 is the maximum possible amount of heat that can be transferred from a hot coolant to a cold one under given conditions; Q2 is the amount of heat transferred from the hot coolant to the cold one, or the heat expended in the technological process.
The maximum possible amount of heat, or available heat, depends on the initial temperatures and water equivalents of the coolants.
How to install a water circuit
Installation occurs in the same way as installation with any other heating system. The only point that needs to be taken into account is that the “return” for stove heating is located higher.
There are three types of coolant circulation:
- Natural. For natural circulation, pipe installation must be carried out at the maximum permissible slope. In addition, in the place where the pipe leaves the furnace, it is necessary to install an “acceleration manifold”: for this, the pipe is directed vertically to a height of 1–1.5 m, and then down to the radiators at an angle.
Forced. This type of circulation increases efficiency by up to 30%. A circular pump is added to the circuit, which creates coolant pressure. However, it is undesirable to arrange a system with only one type of forced circulation, because in the event of power outages or pump failure, water will not circulate, which will lead to boiling of the coolant in the system.
Combined. For this type of circulation, it is necessary to combine the installation of pipes with a slope, as described in the first paragraph, with the pump. In this case, the pump is connected to the system via a parallel line, as indicated in Diagram 4. With this combination, the pump will operate in the presence of electricity; in its absence, circulation will occur naturally.
Flaws
Despite many advantages, the installation of a heating element on a chimney pipe also has disadvantages . One of them, the most important, is a sharp decrease in the smoke temperature at the installation site of the heat exchanger. This can lead to deterioration of traction and the formation of condensation, increased soot deposition inside the pipe.
In addition, when connecting a heating system, for example, a garage, you need to calculate the volume of coolant to avoid boiling water and bursting pipes . Welds must be completely sealed.
Any heat exchanger design significantly increases the efficiency of the furnace . For trouble-free operation of the system, it is necessary to carry out a visual inspection of all its elements at least twice a year , and, if necessary, timely repairs, descaling, replacement of gaskets and other necessary maintenance work. In this case, water heating and heating systems will operate flawlessly for a long time.