Home » Insulation
Reading time 5 min Published 08/17/2019
Heating a home using liquid coolant is the most popular. The reliability of heating systems consisting of sets of equipment and pipelines depends on the coolant and its characteristics. The task of the coolant is to transfer the maximum amount of thermal energy at minimal cost.
Replacing one type of coolant with another is done to increase the efficiency of the heating system. But before you pump or replace new coolant into the system, you need to select the coolant itself.
Types of thermal media
The cheapest coolant is water. But the use of water is not always justified. Water should be used in heating systems that are not subject to corrosion. The use of water as a heat carrier has certain reservations. Such a coolant must be processed by distillation, this will protect the heating system from the formation of scale in it. The use of water that freezes at zero temperatures can destroy pipes in the event of an emergency shutdown.
Injecting special “anti-freeze” agents as a coolant allows you to ensure high-quality operation of the home heating system. The market for manufacturers of antifreeze for heating offers various types of thermal media, made on different bases and having certain characteristics, on which their final price depends.
Basic requirements for a coolant:
- The degree of viscosity of the thermal fluid with temperature changes;
- Inertness of antifreeze in relation to other materials;
- The thermal fluid must not be corrosive and be safe for residents in terms of toxicity and ignition;
- Thermal conductivity of the material;
- The price of the thermal fluid must correspond to its payback period.
Popular antifreezes for heating
Ethylene glycol-based antifreezes are divided into two categories depending on their freezing point: - 30 °C and - 65 °C. This type is cheap and cold resistant.
Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol has a significant drawback - high toxicity, which limits the conditions for its use. Ethylene glycol, which is colored red by manufacturers to warn of danger, is not used in open heating systems.
Propylene glycol, colored green by manufacturers, is safe to use. The coolant has a freezing point of 35 °C and can be used in systems with an open expansion tank.
Antifreeze made from glycerin is safe to use and has a freezing point of 30 °C. In comparison with ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, it has a number of advantages and can successfully replace them:
- protects corrosion nodes and does not damage parts and elements;
- compared to coolants based on ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, with a service life of no more than 5 years, glycerin-based antifreeze has a longer service life - up to 8 years;
- the liquid is sold in diluted form, ready for use;
Fact! Glycerin-based antifreeze can be used in heating systems as a replacement for another type of coolant, without flushing the pipes.
Starting a water heated floor
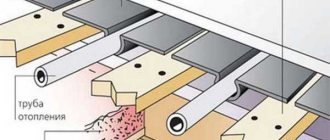
Water heated floor is a multi-layer device. Therefore, even the commissioning process, which seems simple, has its own characteristics. Before you begin installing the structure, you need to understand how to properly fill and turn on a warm water floor, and you also need to read the instructions for use.
The first start-up includes: filling, washing, draining, adjusting the system, warming up and drying the screed. The principle of operation depends on the coolant used and the type of heating; it can be closed or open. In addition, an important point when starting the floor is to ensure fluid circulation and remove air pockets from the circuit.
To properly put the device into operation - a water-heated floor - the outlet manifold must have a special tap. The crimping machine needed to check the floor can be rented.
But if water and not antifreeze is pumped into the pipeline, then it is better to have your own device. You will have to use the device frequently, since it is recommended to replace the coolant annually, and therefore test the system.
Filling the heating system with antifreeze
Before pouring antifreeze into the heating system with your own hands, you need to correctly calculate how much liquid will be needed and how much to buy. To carry out calculations, it is necessary to calculate the volume of the entire heating system.
There are special tables that allow you to accurately calculate how much antifreeze needs to be poured before initial use or replace one antifreeze liquid with another, based on calculations made per linear meter of pipe. Using such calculations and knowing the diameter of the pipes, you can calculate how much coolant is required per 10 m of the system. It remains to be clarified how much antifreeze needs to be added to fill the battery section. By adding up all the data, you can get the total volume of antifreeze required to fill the system. There is no single formula - filling depends on the diameter of the pipes and the volume of the radiators.
In most cases, the container in which the thermal fluid is sold contains information about the antifreeze sold and its density. Such data allows you to calculate how much water needs to be added to the liquid, which will serve as a heat carrier.
To refill the antifreeze with your own hands, you need to have a pump or special equipment that allows you to carry out the procedures of purging and flushing from used residues. For filling work you will need: a screwdriver, pliers, an adjustable wrench, hoses for pumping coolant, fixing clamps and sealing tape.
Securing beacons
Advice
To mark the level of the future floor to which the filling will be carried out, beacons for the screed are installed. The installation of beacons is usually carried out in large rooms where landmarks are needed to determine the horizon level.
Profiles with an edge size of 10 mm serve as beacons. Their installation is carried out at the same level in a horizontal plane. The distance between the beacons should be the same (50–70 cm) - this will make the screed easier.
Beacon installation algorithm:
- A laser level must be installed along a long wall.
- On this wall we mark the line of the installation horizon.
- We make a retreat of 30–40 cm from the wall.
- We attach the first beacon profile to the solution.
- Align it with the line on the wall.
- We install subsequent beacons, observing the specified step.
- To transfer the horizon from the first profile, we use a building level.
- We continue the installation of beacons.
- We check all beacon profiles at the final stage.
- Leave them for 24 hours for the solution to harden.
Video about fixing beacons:
Features of antifreeze
Water is considered the cheapest and most accessible coolant for heating devices. But at low temperatures, a change in its physical properties occurs, which can lead to the failure of the entire floor heating system. To avoid negative consequences, a special solution, antifreeze, is used to fill the water circuits.
Such a liquid reagent is a substance that does not change its state at sufficiently low temperatures. The high anti-corrosion properties of antifreeze allow it to be used for pipelines made of various metals. At the same time, the finished coolant does not contribute to the deposition of various sediments and scale inside the water circuit.
Thanks to these properties, the use of antifreeze allows you to turn off the heating system in severe frosts without first draining the coolant. The reagent is especially popular in country houses, where owners do not have the opportunity to constantly monitor the quality of the operating process of heating equipment.
The types of antifreeze produced have different temperature indicators. On packaging with a viscous liquid, manufacturers indicate at what maximum values the coolant can be used.
Basically, the finished solution is designed for temperatures from -30 to -65 degrees. But when these limits are exceeded, it does not harden, as usually happens with water, but becomes gel-like. At the same time, the reagent retains all its original characteristics, and therefore is not capable of harming the floor heating system.
How to drain water from circuits
The peculiarity of a water heated floor is that, when installed correctly, it does not have a lower point and there is no tap there either. Therefore, to drain the system you will have to use a compressor. It is connected to the input (supply) manifold (do not confuse it, exactly to the input). If your collector assembly is factory-assembled, then it has special devices that prevent the coolant from flowing back. And if you connect the compressor to the “return” manifold, the coolant will not drain, but you may damage the unit.
So, on the supply manifold, at the special valve for filling water, remove the air vent, and, screwing the adapter in its place, connect the compressor output. On the return manifold, connect a hose to the drain valve, which is discharged into a bucket or into the sewer.
What do the collector elements look like that will need to be manipulated when draining/filling coolant?
Leave the shut-off valves of only one heated floor loop open. Turn on the compressor, water begins to come out under pressure (hold the drain hose). Leave the compressor on until airborne droplets begin to flow. Then turn it off, close the valves of the drained circuit, open the shut-off valves of the next circuit and turn on the compressor again. So, opening the shut-off valves one by one, drain the water from all circuits.
Since the length of the contours can be significant, a significant amount of liquid remains on the walls. It needs to be removed again. That is, repeat the procedure after a few hours. Only then can we say that the underfloor heating fluid has been completely drained.
Types of antifreeze and their properties
There are three main types of ready-made coolants on the modern market, which are successfully used in underfloor heating water circuits. Each individual group of antifreeze has its own composition, advantages and features of use.
Glycerin based solution
The coolant, the main component of which is glycerin, is successfully used for heating systems in houses of various types. Its main advantage is the absence of harmful components, which ensures its safe use in residential areas.
Glycerin-based antifreeze is non-flammable and has a relatively high level of heat transfer. The solution can withstand a maximum temperature of -30 degrees, which allows, if necessary, to turn off the heated floor system in severe frosts in winter.
The reagent consists of glycerin water and various additives that help improve its technical characteristics. For a metal pipeline, the mandatory presence of an anti-corrosion additive is required, since the use of a pure glycerin solution can lead to destruction of the system structure.
Antifreeze for heated floors based on glycerin
The main advantages of glycerin-based coolant include:
- safety and environmental friendliness of use;
- the presence of additives that prevent corrosion processes;
- Possibility of use for up to eight seasons in a row;
- fire safety;
- no negative impact on parts of the heating structure made of rubber or plastic;
- resistance to fairly low temperatures -30 degrees.
When the temperature limit is exceeded, glycerin antifreeze crystallizes. But at the same time it practically does not increase in volume. This property eliminates the possibility of pipeline rupture in the most severe frosts.
There are few disadvantages of using it:
- high viscosity of the solution, which requires the installation of high-power pumps;
- At elevated temperatures, the glycerin reagent can be converted into a substance with a pungent odor - acrolein.
When used in a floor heating system, parts made of plastic or non-polar rubber must be sufficiently durable and of high quality.
Ethylene glycol aqueous solution
Antifreeze with the lowest cost and fairly high efficiency. But its use is somewhat limited due to high toxicity. In this case, the freezing temperature of the viscous solution reaches -60 degrees. This characteristic allows the reagent to be used in the harshest winter conditions.
The coolant ethylene glycol contains special additives that prevent the rapid chemical process caused by the main substance.
What will be the basis?
In houses where the floors are made of concrete, as well as on the base (provided the base of the floor is located on a sand cushion), the common method of concrete screed is used. Important! If your house has wooden floors, this method is unacceptable for you. The beams simply will not withstand the load, no matter how thin the layer of concrete screed is. In such situations, a lightweight option is used, its description can be found below.
The first step when installing a heated floor is to prepare the base. The base must be flat; the presence of depressions or protrusions is unacceptable. The difference can be a maximum of 5 mm. If there are defects or stronger differences, you should:
- Fill with fine crushed stone in a thin layer (grain up to 5 mm) and level it.
- Cover the finished leveling layer with film.
- When laying heated floors, use wooden boards to walk on them, otherwise the crushed stone layer itself will create unevenness.
Criterias of choice
The selection of antifreeze for floor heating systems is carried out taking into account all the technical and structural features of the heating equipment. Since the main function of ready-made coolants is protection against freezing, when choosing a solution you should pay attention to the temperature limit for its use.
When using antifreeze for heated floors in residential premises, it is first necessary to consider such an indicator as complete safety of use and the absence of toxic substances in the composition.
To choose an effective coolant for a floor heating system, you should consider the following points:
- presence and composition of additives;
- the ability to combine with metals, plastic, zinc or rubber;
- temperature threshold;
- duration of use.
Additives that improve the properties of antifreeze must meet the design requirements of floor heating equipment. If a metal circuit is installed, it is recommended to pay attention to the quality of anti-corrosion additives. To protect rubber elements, special softening agents are required.
Why do you need to remove air?
The formation of voids reduces the efficiency of the heating system. Pumping equipment, like other components, operates less efficiently. To ensure comfortable indoor temperature conditions for users, more resources have to be spent.
As such voids increase, the pressure gradually decreases. After reaching the maximum minimum level, the corresponding signal is sent to the boiler control unit. In addition to electronic devices, mechanical means for similar purposes are used. This is an emergency situation, so the automation turns off the supply of gas or other fuel.
To turn it on again, you have to manually increase the pressure. But there are a lot of gaseous inclusions in fresh water, so negative processes are accelerated. The equipment will turn off more often.
It should be remembered that oxidation, which destroys metals, occurs in the presence of water and oxygen. Adding a new coolant activates the corresponding negative processes. In this operating mode, the durability of heating equipment is reduced.
It is necessary to exclude the appearance of air “plugs” in the heat exchange units of boilers. These parts are exposed to very high temperatures.
The reasons listed above are enough to understand the need for preventive measures. Carrying them out will prevent complex breakdowns and costs associated with restoration work.
Rules for using antifreeze
The use of ready-made high-quality coolants allows you to increase the efficiency of heated floors. Regardless of the type of antifreeze for the heating system, during the operation of the solution, the following basic requirements should be adhered to:
- For metal pipes of heated floors, antifreeze is used, which contains additional anti-corrosion additives.
- Due to the high level of viscosity of the finished coolants, the installation of circulating pumps with high power is required. In this case, the pipeline must have a diameter of more than 20 millimeters.
- It is necessary to replace antifreeze on time. The period of use of the solution depends on its type. For reagents based on propylene glycol and ethylene glycol, the service life is about five years. Glycerin antifreezes have a longer service life - up to ten seasons.
- Before using ready-made coolants, check the tightness of all connections. This point is of particular importance when using ethylene glycol, since its contact with the finishing coating leads to the destruction of the material, and human inhalation of vapors can cause serious poisoning.
- Antifreeze should be used for the floor heating system after the water circuits have been completely flushed. Metal pipes should not have rust or various deposits in the form of scale inside.
Antifreeze for underfloor heating is the best way to protect the system in winter. Its use allows you to easily turn off heating equipment for a long time on the coldest days.
The effectiveness of using ready-made coolants depends on the correct selection of the composition and its compliance with the technical requirements for installing heated floors. When purchasing such a liquid, you should always pay attention to the compatibility of the product with various materials, and also take into account the characteristics of the additives included in the composition.
Coolant refilling process
Before filling the water heated floor with coolant, all valves on the collector unit are closed, and the hose is connected to the inlet tip. When it is planned to flush the system, a hose is installed at the outlet, the opposite end of which is inserted into the sewer system, drainage pit or into a special container.
Filling begins with the first loop, for which the valves on this circuit are opened, and all the others are left closed. The pipes are filled with liquid and air is released, resulting in a hissing sound in the air vent valves.
The pump is turned on for a short period, the noise of the valves is heard again, after which it is turned off. Next, wait until the air is completely released and turn on the pumping equipment again. The process is repeated until all air pockets are eliminated and the second loop begins to be filled.
Before filling the second circuit, the valves of the already filled circuit are closed. The procedure is carried out until all loops of the system are filled. Then all inlet and outlet valves on the circuits are opened, and the coolant is pumped until the air is completely removed. The system is now prepared for testing or launching water heated floors.