Choosing a coolant for a heating circuit is not a simple matter and requires some knowledge. It’s worth mentioning right away that the choice of coolant is only needed for buildings with autonomous heating. If the room is connected to centralized heating, then the heat supply organization will fill the system.
The coolant can be of 3 types:
- Liquid.
- Steam.
- Gas.
Heating of private households using steam or gas systems is extremely rare. Therefore, we will consider in more detail what types of liquids can be used as a coolant.
This:
- Water.
- Ethylene glycol.
- Propylene glycol.
The main requirements for coolants include the following:
- Specific heat.
- Viscosity.
- Fire safety.
- Toxicity of the substance.
Application of water
The method of transferring heat from a source to radiators using water is the simplest and at the same time the least expensive . Water accounts for at least 70% of the total number of liquids used.
Despite the apparent simplicity of application, there are a number of points that must be taken into account:
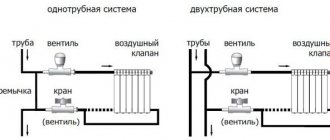
- Rigidity. There are solid particles in water. When heated above 70 degrees, the crystallization process begins, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of scale on the internal surfaces of the boiler heat exchanger, pipelines, and batteries. To combat this phenomenon, there are water softening devices that also purify water from mechanical pollution. Such devices are connected directly to the water supply. When connected in this way, there is no need to install an additional pump to fill the system. Filling occurs due to pressure in the water supply network.
- Temperature regime. When providing heat to a separate building, the supply temperature rarely exceeds 95 degrees. Most domestic heating boilers are also designed for this temperature as the maximum. At this temperature, the liquid does not boil. It must be remembered that at a temperature of 80 degrees, the process of deaeration begins (the release of air particles from the water). To prevent airing of the system, it is necessary to install air valves that will automatically release the air that appears.
- Freezing temperature. If the room is heated regularly, then this problem will not arise. If the heating of the room is not carried out on an ongoing basis, but from time to time, then it is necessary to take into account that at 0 degrees the water will freeze. Freezing of water in heating devices can lead to their failure for a long time or even to complete unusability.
Positive aspects of using water:
- Environmentally friendly substance.
- Has a high heat capacity.
- Does not require additional energy costs to ensure circulation.
- If it is necessary to fill the system , it is always available.
- Low cost.
Negative sides:
- Turns into ice at 0 °C.
- The need to install a water treatment device.
Alternative sources of home heating
Alternative sources of heating for the home are economical and safe.
When using alternative or renewable energy sources, such as the sun or earth's energy, the owner of the premises is also independent of external communications. In this case, collectors are used to collect the collected energy or heat pumps to supply it continuously. Such systems are completely safe for nature and save money for owners who do not have to pay for the supply of gas or electricity.
Most often, home owners who want to protect themselves as much as possible from economic crises and the lawlessness of public utilities install autonomous heating. For this system, specialists select the installation methods and format individually, adapting it to the characteristics of the room. Autonomous heating can be electric or gas, if it is possible or necessary to connect to fuel communications. For complete independence from external suppliers, boilers running on solid or liquid fuel are used. In addition, autonomous heating allows you to combine different energy sources, creating the most adaptable and convenient option for most buildings.
Ethylene glycol
In some conditions, there is a need to use a coolant with a fairly low freezing threshold. Such substances are called antifreeze. Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze makes up approximately 25% of all coolants.
Special additives are introduced into the composition of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze - inhibitors that slow down the rate of unwanted chemical processes under the influence of ethylene glycol.
Freezing temperature can reach -60 °C.
When using ethylene glycol, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Viscosity. Ethylene glycol is not used in its pure form; it is mixed with water. Depending on the concentration, the viscosity of the substance also changes. As the viscosity increases, the speed of movement of the coolant through the pipes also decreases. Because of this, it is necessary to increase the pump performance, which leads to an increase in the cost of heat generation.
- Thermal expansion. The coefficient of thermal expansion of this substance is on average 50% higher than that of water. Therefore, when heating, to prevent pressure build-up in heating devices, it is necessary to install an expansion tank. The same tank should also serve to replenish coolant when the temperature drops.
- Chemical properties. Due to its properties, ethylene glycol is aggressive to certain types of materials. For example, when using it, it is necessary to abandon rubber seals. You will need to replace them with paronite ones. Also, the use of galvanized pipes is not possible. Ethylene glycol dissolves zinc. When deciding to use ethylene glycol as a coolant, you must carefully study the passports of all installed heating devices for the possibility of its use.
- Filling the system. Filling the system with a water-glycol mixture is only possible using a booster pump. Given the increased viscosity of the mixture, it is necessary to select the correct pump parameters. Also, it is necessary to select the material for the tank from which the pump will fill the heating circuit with solution. When choosing a pump, you must take into account the parameters of the liquid that it will pump.
- Toxicity. Due to its high toxicity, ethylene glycol is not widely used. For humans, the lethal dose can be 50–500 mg. In open systems, the use of ethylene glycol is strictly prohibited. Materials exposed to ethylene glycol must be replaced.
Positive sides:
- Defrosting the system is almost impossible.
- Good heat capacity.
- Low probability of scale formation.
- Quite an attractive price.
Negative aspects - toxicity! This is what prevents ethylene glycol from gradually displacing water from its leading position. Ethylene glycol is deadly.
Finally, about coolants for electrode boilers
Electric water heaters of this type operate on the principle of a “soldier’s boiler” consisting of two blades connected to a 220 volt network. Water simultaneously serves as a coolant and electrolyte; heating occurs due to its conductivity, which depends on the content of magnesium and calcium salts.
This is why electrode boilers do not work with distillate and significantly lose power with under-salted water. According to the passport of the Galan heater, the resistance of the working fluid should be no more than 3200 Ohms per 1 cm.
If you pour regular ethylene glycol into an electrolysis heat generator, the substance will enter into a chemical reaction, foam and lose additives against corrosion and scale formation. The problem can be solved in 2 ways:
- A special antifreeze designed for electrode-type units is purchased. Special additives that resist foaming are dissolved in the working environment.
- A saline solution of the required concentration is prepared, as shown in the video below. Such water will begin to crystallize at a lower temperature, although it cannot be compared with antifreeze in terms of frost resistance.
You should pay attention to the preparation of tap water - pass it through a filter and let it sit for 1-3 days. A good solution is to buy a corrosion inhibitor separately and add it to the coolant for the heating system in advance.
Propylene glycol
The most reliable, safe and modern coolant is a product based on propylene glycol. It began to be used in the world in the 60s of the last century. Leading European countries have been using this antifreeze as the main coolant for 20 years. In our country, the share of propylene glycol is only 5%. In its physical properties it is very close to ethylene glycol. Freezing occurs at a temperature of 60 0 C. The coefficient of thermal expansion is only 5% higher than that of water.
When using propylene glycol, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Viscosity. Taking into account the increased viscosity compared to water, when designing a heating system it is necessary to select a circulation pump with increased performance. This will ensure a normal rate of heat transfer from the heating boiler to the heating radiators.
- Chemical properties. In terms of its chemical properties, this antifreeze is close to ethylene glycol. Before you start using it, you need to make sure that the selected equipment can use this coolant. Otherwise, you may damage the boiler and the heating system as a whole. The use of rubber seals, as well as tow, is also not possible.
- Filling the system. In order to fill the heating circuit with propylene glycol, it is necessary to use a make-up pump. At the lowest point of the heating system, it is necessary to provide space for connecting a booster pump. The system must be filled slowly. At the same time, all air valves must be open. This filling method will help avoid clogging the system with air.
Beware of Unknown Origin of Glycols
Today the market sells solutions from various manufacturers, both well-known and reliable, and low-quality basement-made ones. Beware of liquids of unknown origin, since their composition lacks a full package of inhibitors, stabilizers, antioxidants, anti-foam additives, and they also do not have appropriate documentation confirming quality and compliance with GOSTs.
Give preference to products based on liquids containing organic additives instead of previously used inorganic ones. It is also worth remembering to preserve the environment by choosing, for example, environmentally friendly propylene glycol.
Propylene glycol and ethylene glycol (ethanediol-1,2) are the simplest dihydric alcohols that have gained wide popularity, along with glycerin, as low-freezing liquids (antifreeze) in heating systems.
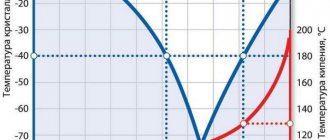
They are distinguished from other coolants by the fact that they perfectly withstand high temperatures when combined with water and begin to boil only at 105°C-110°C at normal atmospheric pressure and at 120°C-150°C at elevated pressure. Depending on the degree of dilution, their crystallization temperature ranges from -40°C to -70°C.
They may contain anti-corrosion additives to protect the internal elements of the system from corrosion and reduce foaming, which can significantly increase its service life.
Calculation of the amount of coolant
You can find out the required amount of coolant in 2 ways:
Settlement
It is necessary to sum up the amount of coolant in the boiler, radiators and pipelines. Data on the amount of coolant in the boiler and batteries can be taken from the passports.
The volume of liquid inside the pipe can be calculated using the formula:
- V = S (pipe cross-sectional area) x L (pipe length).
To simplify calculations, there is a table of volumes.
Radiator water volume:
- aluminum radiator - 1 section - 0.450 liters;
- bimetallic radiator - 1 section - 0.250 liters;
- old cast iron battery – 1 section – 1,700 liters;
Volume of water in 1 linear meter of pipe:
- ø15 (G ½”) - 0.177 liters;
- ø20 (G ¾”) - 0.310 liters;
- ø25 (G 1.0″) - 0.490 liters;
- ø32 (G 1¼”) - 0.800 liters;
Experienced
To determine the volume experimentally, it is necessary to completely fill the heating circuit with water. Then you need to carefully drain the water, measuring the volume with a measuring container.
When filling with water, it is necessary to slightly open the tap installed in the water treatment system area. In this case, the air valves must be open. This way you can avoid airing the system.
Water is drained from the heating circuit through a drain valve into the sewerage system or make-up tank. Filling the system with propylene glycol must be done using a booster pump.
As with water, filling must be done at a low speed. Considering the cost of propylene glycol, the systems only need to be drained into the make-up tank.
The frequency of replacing water in the heating circuit is usually one heating season. For antifreeze, the frequency set by the manufacturer is 5 years.
What volume should be filled?
The amount of liquid poured into the heating system depends on various factors. The main ones are:
- heating boiler volume;
- type of heating system;
- quality of materials for manufacturing pipes and radiators;
- area of the heated room.
Calculation of the volume of liquid for filling the system is carried out based on the recommendations of the manufacturers. The boiler technical data sheet contains information about what coolant can be used and in what volume.
Cost and selection criteria
The most accessible type of coolant is water.
The cost of ethylene glycol per 1 kilogram ranges from 50 to 70 rubles. Propylene glycol is the most expensive representative: its cost per 1 kilogram ranges from 80 to 130 rubles, depending on the packaging and country of origin.
As can already be seen, the coolant can significantly affect the characteristics of the heating system.
Water has the highest heat capacity of the representatives described above , so there is no need to increase the power of heating radiators, its viscosity indicators are optimal, it moves well both in systems with natural circulation and forced circulation.
In the passports of circulation pumps, in the equipment characteristics, the pressure and flow rate are indicated based on the calculation of the viscosity of water. The loads on pumping equipment are standard, and boilers, as a rule, are designed to operate according to a thermal schedule of 95-70, which is 5 degrees below the boiling point of water.
The heat capacity parameters of antifreeze are quite good, but smaller compared to water, so additional sections of radiators or more frequent installation of heated floor pipes will be needed. Due to its increased toxicity, it is better not to use ethylene glycol in residential areas.
Propylene glycol, although much more expensive than water, guarantees stable and safe operation of the heating system during the cold season.
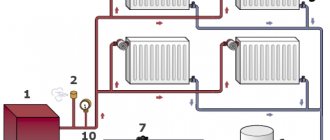
Types of heating systems
Experts distinguish two heating systems.
Construction specialists primarily classify heating systems by the type of coolant used. There are water and air heating systems for houses. When using a water system, heat is delivered to the house by water heated in special heating elements, for example, in a boiler room. Water, usually using pumps, is supplied to the radiator system and thus heats the house. The air system uses a network of ventilation equipment through which heated air fills the entire room. Alternative heat sources have also recently become increasingly popular. These include solar panels, biogas heating and much more.
Water heating systems
Basically, water heating systems are powered by gas boilers.
Water systems are also divided into several categories based on the principle of using different heating equipment. There are radiator systems, baseboard systems and warm water floors. Most water heating systems operate from gas boilers. You can find more detailed information about gas boilers here. They are quite environmentally friendly, highly efficient, and the most modern models have maximum automation functions, which makes them safe and easy to install and operate. In addition, gas heating can be used in completely autonomous systems, independent of city communications, which is why they are often used in country and private homes. The disadvantage of a gas boiler is the need to manually control the fuel supply to the heating element.
Air heating systems
When using air systems, the main heat carrier is heated air, which spreads throughout the room, displacing cold masses. The center of such a system is a programmable thermostat, which allows you to set the required temperature and create a unique microclimate necessary for this room. The main advantage of an air heating system is energy savings because there is no intermediate heating element as in a water heating system. Thus, the air temperature is much easier to regulate and adequately respond to weather changes outside the walls of the house. In addition, in warm weather, this system can work as a ventilation system, saturating the room with fresh air.
Blitz tips
- The choice of coolant must be made during the design process.
- Ethylene glycol mixtures are strictly prohibited for use in double-circuit boilers.
- The use of propylene glycol is true in relatively small heating circuits and only in the absence of leaks.
For normal functioning of the heating system in severe frosts, it is recommended to use a special coolant. On the modern market you can find various substances that prevent the heating system from freezing. But propylene glycol-based coolant is considered safer and more effective. This product has many positive characteristics and its own characteristics of use.
How to use propylene glycol based coolant?
Before replacing propylene glycol-based coolant, you must completely remove the old liquid from the pipes and heating system. It is also necessary to clean the circuit from various deposits, scale, corrosion and check it for the presence of zinc-containing parts.
Refilling the heating system can be done manually or under pressure. The first type is suitable for open contours. To fill them, it is enough to gradually pour the coolant into the system using a ladle or other container.
With closed heating systems the situation is somewhat more complicated. To do this, it is necessary to insert a standard tee into the pipeline contour, the threaded connection of which is no more than half an inch. A shut-off valve with a fitting for connecting a hose is screwed onto this threaded connection.
The coolant is pumped into the system under pressure. For this, a manual or submersible electric pump of the “Kid” type is sufficient.
After filling with a new coolant, it is necessary to adapt the fluid to the new fluid:
- The first system startup is performed at low power
- The operating pressure in the system and the pump power increase gradually
It is also important to ensure that the system is completely sealed. As mentioned above, propylene glycol is very fluid, so where water does not leak, propylene glycol coolant can leak. When liquid leaks from the circuit, the efficiency of the entire heating system is reduced, so if they are detected, the system should be suspended until the fault is resolved.
What is propylene glycol
This substance is directly related to the class of dihydric alcohols. The reagent is a liquid substance with a barely pronounced odor and taste. In industry, it is obtained through the hydration of propylene oxide at a pressure of 16 megapascals and a temperature range of 160-200 degrees.
The chemical formula of propylene glycol is C3H6(OH)2. It is completely safe to use and does not contain toxic elements. For heating systems, aqueous solutions are used, which are based on this reagent.
Propylene glycol has a related composition to ethylene glycol - C2H4(OH)2. But the latter element is not used for heating residential buildings, as it has a fairly high level of toxicity. Moreover, the chemical formula of both substances has some similarity.
Questions and answers
Can all heating systems be filled with antifreeze?
It is not recommended to use antifreeze in open heating systems with natural circulation.
When can water be added to the heating system and when can antifreeze be added?
If the house is constantly heated and there is no threat of an emergency heating stop, then the system can be filled with distilled water. In other cases, only non-freezing liquid is poured. When releasing it, they are guided by the range of operating temperatures of the liquid and the technical characteristics of the heating system.
Is it possible to mix different antifreeze liquids?
It is strictly not recommended to mix coolants without checking compatibility. An unsuccessful composition can destroy the heating system and damage the heating boiler.
What kind of water can be used to dilute coolants?
Before pouring into the heating system, antifreeze is diluted with distilled water. This liquid is cleared of foreign impurities and desalted. In all other cases, scale will form on the inner walls of the heating system elements. Its quantity depends on the water hardness index.
Main characteristics
Propylene glycol is a hygroscopic substance that can dissolve in water, acetone, ethanol, chloroform and diethyl alcohol. This colorless liquid containing a carbon atom has a low degree of volatility. It is not capable of causing corrosion and is completely safe to use.
Among the characteristics of propylene glycol are:
- density – 1037 kg/m³, which is almost 4 percent more than that of water;
- a fairly high boiling point - 188 degrees above zero;
- thermal conductivity – 0.218 W/(m*K);
- the beginning of crystallization is at -60 degrees;
- specific capacity value – 2483 J/(kg*K).
What does propylene glycol look like?
The coolant propylene glycol is an aqueous solution that remains in liquid form at temperatures ranging from -40 to 100 degrees. The finished substance, in addition to the main component dissolved in distilled water, includes dyes, as well as no more than 5 percent of anti-corrosion, stabilizing, softening additives.
The density of propylene glycol coolant depends on the concentration of the main component. The higher its percentage, the higher its maximum boiling level. The density indicator also increases accordingly. Based on this, percentage markings are indicated on the coolants produced.
Why can’t water from a well be poured into a heated floor heating system?
Zheka888
I heard that the heating system cannot be filled with ordinary water from a well. This is true?
Regular FORUMHOUSE User
Why can't you fill it with water from a well? Does it have some kind of wrong chemical composition?
AlexMannFORUMHOUSE user
Due to its chemical composition, water from wells is not suitable for heating systems. Water for the heating system is prepared. Water preparation depends on the elements of the heating system. If you have aluminum radiators, then you need lower alkalinity of the water. If there is a steel heat exchanger, then iron in the water is especially dangerous.
Advantages and disadvantages
Propylene glycol is one of the most popular ready-made coolants for heating systems. Its main function is to protect heating equipment from ruptures, which occurs due to the ability to practically not change its volume at low temperatures. Therefore, in severe frosts when using it, there is no need to drain the system.
The advantages of using propylene glycol-based coolant include:
- Safety and environmental friendliness. The substance does not contain highly toxic components. The reagent does not have a negative effect when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of the eyes. Its vapors are quite harmless. When the floor finishing material gets on the surface, any chemical reactions are excluded.
- No corrosive activity. This property allows this coolant to be used for heating systems with various structural materials.
- High level of thermophysical characteristics. The use of an aqueous solution of propylene glycol for heating circuits promotes rapid and uniform heating of the room. At the same time, the heat is retained for a long time.
- No scale. When heated to high temperatures, this antifreeze does not form any solid deposits. At the same time, propylene glycol has bactericidal and cleaning properties. With its help, various deposits are removed from the internal areas of heating equipment.
The prepared propylene glycol solution is completely fireproof and its use eliminates the possibility of explosion.
This coolant also has some negative operational aspects:
- High turnover rate. Propylene glycol is able to penetrate through the smallest cracks. Its fluidity is somewhat higher from water, so sometimes leaks occur in places where they should not exist. But at the same time, this property can be considered a positive aspect, since it allows improving the assembly quality of a heat-conducting structure.
- The possibility of using propylene glycol as a coolant is excluded if there are parts containing zinc. If this precaution is not followed, the viscous antifreeze will eventually peel off the galvanizing, which will lead to clogging of the pipeline.
Also sometimes the negative aspects include the high cost of antifreeze based on propylene glycol. In this case, it must be replaced in the heating system at least every five seasons.
Heating with antifreeze or water
After reading this section, you will most likely refuse antifreeze in your heating system.
The main advantage of antifreeze - the safety of the system at subzero temperatures - is completely negated by its disadvantages. Low heat capacity of antifreeze. Increasing the size of radiators by 20-23% The heat capacity of antifreeze is significantly lower than the heat capacity of water. By diluting water with 35% antifreeze, we lose approximately 200 W per 1 kW of thermal energy. This means that the size of pipes, radiators and boiler must be increased by 20%. In terms of a country house of 300 m2, we lose approximately 60 thousand rubles by increasing the size of the system.
The service life of antifreeze is from 5 to 10 years. Over the years, antifreeze oxidizes and safely destroys brass connections. After 5 - 10 years, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol must be drained, disposed of and replaced with a new one. You will not only have to buy new antifreeze, but also pay to dispose of the old one. Unfortunately, in our country there is no service for recycling ethylene glycol in small volumes, so finding someone to hand over this chemical to will be difficult. I won’t consider the idea of dumping antifreeze on my neighbor’s property.
The use of sectional radiators in systems with antifreeze is unacceptable. Rubber sectional gaskets quickly oxidize, and the radiators leak. We use only steel panels. The use of galvanized pipes is also unacceptable. Antifreeze safely washes away the zinc, and the pipe remains bare.
Why is antifreeze useless for a country house? Antifreeze will successfully cope with the task - the heating system will not freeze in winter in your absence, but what to do with the water supply system? Water supply pipes at subzero temperatures will freeze faster and with worse consequences, because... laid not only in the floor, but also in the walls. You will have to remove the tiles, beat the screed and change the pipes in the bathrooms, showers, kitchen, and replace the entire water supply system of the boiler room. Of course, it will not be possible to pump antifreeze into the water supply system, nor will it be possible to lay all the pipes with heating cables.
Conclusion: Antifreezes are suitable either for heating small country houses for temporary residence, or large warehouses, workshops and enterprises. In the heating system of a full-fledged country house, antifreeze is useless.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house is needed if: you do not plan to live in the house in winter; the house has 1-2 bathrooms with a tee water supply system (without a collector), which can be drained before the onset of cold weather.
It is impossible to leave a full-fledged country house in winter without heating on duty. In winter, it is necessary to maintain constant standby heating +10-12°C. Heating a full-fledged country house for permanent residence with antifreeze is the same losing option as heating a house with warm floors, which is applicable only in the southern regions of our country.
This way your engineering systems will be truly protected without antifreeze.
If you liked my article and are looking for reliable design specialists, call or email me.
Scope of application
Propylene glycol is quite in demand in modern industry. Coolants made on its basis are widely used not only for heating systems, but also as antifreeze for ventilation and air conditioning equipment.
The scope of application of propylene glycol in the industry is quite extensive:
- pharmaceuticals;
- tobacco production;
- production of food products;
- automotive and aviation industry;
- Oil and gas industry;
- cosmetology, perfumery;
- medicine.
Uses of propylene glycol include livestock and agriculture. It is practiced to improve the quality of feed, as well as to extend the shelf life of vegetable crops. In chemical production, a viscous substance is used in the production of polyurethanes, paint solvents, plastics or polymers.
Harm
According to ongoing research, propylene glycol can cause harm to health in two cases:
- when consumed in large doses;
- when used by persons belonging to a particularly vulnerable group.
Large amounts of the substance can cause heart rhythm disturbances and changes in blood pressure, thereby increasing the likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases.
People at particular risk include children under 3 years of age and pregnant women. Their bodies practically do not produce the enzyme necessary to process propylene glycol, which means the substance will accumulate in the body, which can cause intoxication.
Allergic reactions
Scientists estimate from medical research that 1 to 4% of people are allergic to propylene glycol. In most cases, the reaction manifests itself in the form of a rash, localized on the face or scattered throughout the body.
For the body of people with hypersensitivity, propylene glycol is harmful even in small quantities. For example, contact dermatitis appears from skin contact with cosmetics (cream or shampoo) containing propylene glycol - rashes accompanied by dry skin and severe itching. Inflammatory skin lesions can also be caused by taking medications or products containing the substance.
Toxicity level
The toxicity of the substance is very low. No studies have shown that propylene glycol causes cancer, damages genes, or is fatal. Approximately half of the substance that enters the body is excreted by the kidneys in its original form, the second half is processed, resulting in the formation of lactic acid.
In people with liver or kidney pathologies, the elimination of propylene glycol and lactic acid is not as effective as in healthy people. In this case, a negative effect of propylene glycol on the body is possible, since both the substance itself and its decomposition product - lactic acid - accumulate, leading to toxic poisoning, acidosis, renal failure, depression of central nervous system functions (slow breathing, loss of consciousness, decreased heart rate ).
Inhalation
Considering the fact that propylene glycol is contained in most e-cigarette liquids, it would be useful for fans of this gadget to be aware of its effect on the body when inhaled. During the vaping process, substances contained in the steam (including propylene glycol) affect the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, as well as the organs of vision and respiratory tract.
Liquid for electronic cigarettes
Regular inhalation of vapors can provoke dry mucous membranes, inflammatory processes, and allergic manifestations. The risk of respiratory and allergic diseases increases. The same effect can be obtained by inhaling fumes from certain types of paints and household chemicals.
Criterias of choice
The main point that should be taken into account when choosing a coolant for space heating systems is the manufacturer’s recommendation for heating equipment. The instructions for the boiler often indicate the requirements for the liquid that fills the water circuit, and sometimes the brand of antifreeze.
The main factors to consider when choosing a propylene glycol solution for heating systems are:
- Climatic conditions of use. Different brands of products indicate the maximum freezing temperature level. This indicator depends on the concentration of the solution, the percentage of which is also indicated in the name of the coolant.
- Manufacturer. The efficiency of the heating system depends on the quality of antifreeze. You can purchase good products from trusted manufacturers. High-quality products do not contain toxic substances and are completely safe for use.
- Characteristics of additives. Propylene glycol-based products included in ready-made coolants can have anti-corrosion characteristics, while providing protection against metal destruction. Softening components are often added to the composition, which protect rubber elements from deformation. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze, the technical and design features of heating equipment are taken into account.
When choosing a coolant based on propylene glycol, take into account the characteristics of the additives
Antifreeze with carboxylate-type additives is especially popular. Such a coolant can be used for almost any material included in the design of a thermal device.
Propylene glycol intended for heating systems must meet all technical requirements and comply with the characteristics of the heating equipment used.
Choosing an “anti-freeze” for heating
Tip number one: buy and fill in antifreeze only in extreme cases - for periodic heating of remote country houses, garages or buildings under construction. Try to use water - regular and distilled, this is the least troublesome option.
When choosing a frost-resistant coolant, follow the following recommendations:
- If your budget is limited, take ethylene glycol from any well-known brand - “Teply Dom”, Dixis, Spektrogen Teplo Coolant, Bautherm, Termo Tactic or “Thermagent”. The cost of the concentrate -65 °C from Dixis is only 1.3 USD. e. (90 rubles) per 1 kg.
- If there is a danger of antifreeze getting into household water (for example, through an indirect heating boiler, double-circuit boiler), or you are very concerned about the environment and safety, buy harmless propylene glycol. But keep in mind: the price of the chemical is higher; a ready-made Dixis solution (minus 30 degrees) will cost 100 rubles (1.45 USD) per kilogram.
- For large heating systems, we recommend using premium class HNT coolant. The liquid is made on the basis of propylene glycol, but it has an increased service life of 15 years.
- Do not buy glycerin solutions at all. Reasons: sedimentation in the system, too high viscosity, tendency to foam, a large number of low-quality products made from technical glycerin.
In the light of the flashlight, tiny white flakes are visible - a sediment of technical glycerin - Electrode boilers require a special liquid, for example, HNT-35. Before use, be sure to consult with a representative of the manufacturer.
- Do not confuse automobile antifreezes with chemicals used in heating systems. Yes, both formulations are glycol-based, but the additive packages are completely different. Engine coolant is not compatible with residential water heating.
- For open and gravity-flow heating systems, it is better to use water, or, in extreme cases, propylene glycol diluted at minus 20 °C.
- If the heating distribution is made with galvanized pipes, there is no point in purchasing glycol mixtures. The substance will deal with zinc, lose the package of additives and quickly degrade.
Clarification. It is not profitable to use frost-resistant liquid for an open heating system. Hot antifreeze will evaporate into the atmosphere through the expansion tank, the antifreeze will have to be constantly topped up, and money will be spent. It is unacceptable to pump in ethylene glycol, since its vapors are toxic.
There is a lot of debate about the harmfulness of ethylene glycol compounds, including on the pages of construction forums. Without denying the harmful effects of the chemical on human health, let us draw attention to a convincing fact.
Homeowners whose closed systems are installed well have been using inexpensive glycol for years without any problems. Let's listen to the expert's opinion in the video:
Features of use for heating
The coolant propylene glycol is poured into the system in accordance with the technical specifications. Before using antifreeze, a number of preparatory steps should be carried out:
- drain the liquid from the system, flush all circuits with caustic soda, remove all deposits and rust;
- perform sealing of all connections, including tappings and bends;
- remove and replace all zinc-containing parts.
After this, you can fill the system with propylene glycol solution. In this case, it is recommended to keep the drain valve open at the lowest point. This action will allow you to immediately see when the thermal contours are completely filled. After filling, the system is checked for leaks and a test run of the heating equipment is carried out.
What happens if you pour water from a well into a heated floor?
Kardinale FORUMHOUSE user
Hi all! Help me solve the problem. I have a heated floor installed. Filled with water from the well. Look what happened after the summer heat. The water bloomed. There's some mucus inside. The system works, but I want to flush it. And most importantly, how to avoid this in the future?
MycraftUser FORUMHOUSE
I advise you:
- Flush the system.
- Remove all ferrous metal components and replace them with copper, stainless steel, etc.
- Fill the closed system with water purified by reverse osmosis.
- Additionally, install a sludge separator.
If you think that rust in a heated floor will lead to nothing, look at the photos taken by Mycraft.
This is what pipes clogged with rust look like.
TP combs.
System elements and branches.
And this is an experiment that Mycraft conducted. Two cans of water. On the left is plain water, on the right is desalted water. Samples of metals commonly used to make heating system components - copper, brass, steel and aluminum - were added to the jars. The water was periodically heated and cooled.
Start of the experiment:
11 months later:
In 2 years.
As they say, comments are unnecessary.
Do not pour water from a well or distilled water into the heated floor, because... The pH value of distilled water decreases after contact with air when filling the system. As a result: the acidity level of distilled water increases and acid corrosion can occur. Pour into warm, specially prepared coolant or demineralized water.
Operational moments
A ready-made solution of propylene glycol for heating devices has lower thermal conductivity and heat capacity than water. Therefore, when using a substance, it often becomes necessary to add the number of batteries in the room. Heating equipment may also need to be replaced.
To productively use polypropylene-based antifreeze for a heating system, you should consider some operational recommendations:
- due to the high viscosity of this coolant, it is necessary to install a pipeline with a diameter of at least 25 millimeters, and also select a sufficiently powerful circulation pump;
- for metal pipes, antifreeze with additives that prevent the formation of corrosion should be used;
- use an aerometer annually to check the concentration of the main reagent;
- use an expansion tank of at least 10 liters;
- provide free access to all connections of heating equipment in case of leaks;
- replace propylene glycol coolant every five operating seasons;
- use and regularly monitor strainers for heating systems.
- When replacing antifreeze, thoroughly flush the heating equipment.
Replacement of propylene glycol-based coolant should be done every 5 seasons
If it is necessary to mix this coolant, it must be taken into account that the solution combines well with liquid based on glycerin, propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. In this case, the type of additive included in the composition is taken into account, since incorrect combination of different additives can cause a decrease in the technical characteristics of antifreeze.
Due to its many advantages, propylene glycol is considered one of the best coolants for heating equipment. But in order to ensure the efficient operation of the heating system for several years in a row, all technical and operational requirements must be observed when using it.
One of the most common coolants today is propylene glycol for heating systems, which carries out the heat exchange process and is considered the safest and non-toxic substance.
A special solution is made from equal parts of propylene glycol and water, that is, in a proportion of approximately one to one. It contains a small amount of carboxylate additives - within 5% of the total volume.
Thanks to this composition, the liquid can withstand temperatures from +100 to -40 degrees, which makes it the most reliable coolant in such a changeable climate.
Alternative sources of home heating
Alternative sources of heating for the home are economical and safe.
When using alternative or renewable energy sources, such as the sun or earth's energy, the owner of the premises is also independent of external communications. In this case, collectors are used to collect the collected energy or heat pumps to supply it continuously. Such systems are completely safe for nature and save money for owners who do not have to pay for the supply of gas or electricity.
Most often, home owners who want to protect themselves as much as possible from economic crises and the lawlessness of public utilities install autonomous heating. For this system, specialists select the installation methods and format individually, adapting it to the characteristics of the room. Autonomous heating can be electric or gas, if it is possible or necessary to connect to fuel communications. For complete independence from external suppliers, boilers running on solid or liquid fuel are used. In addition, autonomous heating allows you to combine different energy sources, creating the most adaptable and convenient option for most buildings.
Characteristics of propylene glycol
When choosing propylene glycol as the main coolant, it is necessary to take into account its technical characteristics, chemical composition and other parameters, which differ markedly from water familiar to humans.
Propylene glycol-based coolant is more chemically active and quickly reacts with surfaces and other substances.
That is why the mixture always contains special additives that neutralize the oxidation process, as well as functional additives:
- anti-corrosion;
- stabilizing;
- antiscale;
- etc.
Propylene glycol solution should not be used in a heating system containing zinc-based materials. These precautions are necessary to avoid material peeling off.
It does not react as aggressively to other types of surfaces (plastic, textiles, etc.).
Density of propylene glycol
The higher the concentration of the starting substance in the solution, the denser the coolant becomes and the higher the maximum boiling and crystallization temperatures.
This parameter varies from 30 to 55%, which is often indicated in the name of the coolant: propylene glycol 30, propylene glycol 40, etc.
Temperature also affects the density of a liquid:
| Freezing temperature t°С | -40 | -30 | -20 | -10 | |
| Density of the substance kg/m3. | 1040 | 1037 | 1031 | 1019 | 999,3 |
Certain types of propylene glycol-based coolants are capable of not freezing in weather conditions down to -60 degrees and not destroying pipes down to -80 degrees.
Why choose propylene glycol for heating systems?
The substance serves as an additive in most types of coolants and has a number of unique properties:
- It dissolves quickly in water and mixes well with other types of substances.
- Reduces the freezing point of the starting substance several times.
- Perfectly absorbs moisture from the surface and from the air.
This substance has a low crystallization temperature, is fireproof and non-toxic.
It is harmless to the human body and the environment, as it is easily subject to decomposition. Propylene glycol without impurities is used in cosmetology, food industry and pharmaceuticals.
Using glycerin as a coolant
To obtain a glycerin-based coolant, the pure substance is mixed with various impurities that allow it to remain liquid when used in cold conditions. The resulting composition is chemically inert, and no chemical processes occur inside that can have a detrimental effect on the elements of the entire system.
The ability to maintain a liquid state at sub-zero temperatures and absolute safety for humans allows the coolant to be used for heating systems in residential buildings, including floor heating.
The operation of this heating system is based on one principle: there is a heater, heating elements and coolant. In this case, the main characteristics of the coolant will affect the overall heating efficiency.
Advantages of glycerin coolant
Compared to propylene glycol or ethylene glycol compounds, this antifreeze has the following advantages:
Can be used in a wide temperature range from -30 to +105 °C. Even when the substance is completely frozen, it does not expand and does not cause damage to the pipes. After thawing, all its original properties are restored. The coolant is sold ready-made and does not require additional dilution with water.
Glycol formulations must be diluted; Antifreeze does not cause corrosion or other damage to heated floor elements, including galvanized pipes and rubber gaskets; The substance is absolutely safe for human health and the environment, which is very important in case of leaks or damage to the system as a whole; At a relatively high price, the composition has a long service life of up to 8 years. Another type of antifreeze has been used for about 5 years; The coolant can be poured into the pipes after any other type of antifreeze; no flushing is required; Antifreeze is produced only from high-quality raw materials, which are also used in the food and cosmetic industries; Belongs to the class of non-flammable substances.
Disadvantages of glycerin composition
Glycerin-based coolant has its disadvantages, which must be taken into account when designing a heated floor:
- When freezing, the density and viscosity of the glycerin composition increases, which leads to a decrease in its heat capacity. In the heating system project, you will have to use pipes of a larger diameter than when using ordinary water;
- The high viscosity of the composition will require the installation of a more powerful circulation pump in the heating system;
- Glycerin-based antifreeze requires the use of reliable and expensive gaskets and seals during heating installation. Teflon or paronite gaskets are recommended;
- Antifreeze has a tendency to foam, which can cause the heated floor to become airy. Special additives help to partially reduce foaming;
- A glycerin-based composition has a density and mass greater than a glycol-based one. The use of a glycerin composition in a heated floor system will increase the load on the floors and foundation of the building.
Harm and effects on the body
Currently, there is no official confirmation of the harm of propylene glycol to the body. If it comes into contact with the skin, there is no irritation; simply rinse the area with cool water.
Propylene glycol is a food additive whose use is officially approved. It was found safe and did not cause side effects. However, when consuming an increased amount of the substance, harmful consequences may occur. When the concentration of the compound in the blood increases to 1 g per liter, an acute form of poisoning develops.
Causes:
- Use of medications containing propylene glycol,
- Intravenous administration according to the wrong scheme,
- Ingestion of a large volume of a substance.
If ingested, the product has a negative effect on the body. The vapors of the compound cause unpleasant symptoms, irritation of the respiratory tract and visual organs. In case of contact with the skin, redness is possible in people with allergic reactions.
Constantly increased concentrations indoors lead to the development of immune diseases and disruption of the respiratory organs. It is possible for a person to develop asthma, eczematous skin lesions, and severe allergic reactions. Has the second class of danger.
The substance is used in many fields. The properties of propylene glycol allow it to be used in medicine, cosmetology, and the food industry. What is the connection used for? Where is a similar product used?