In modern conditions of architecture and design, it is impossible to do without the use of heating batteries of various sizes and shapes. Along with standard batteries, narrow-shaped products began to be used. Their height usually varies from 200 to 350 mm. The height of some models can reach 450 mm. The minimum value is 150 mm. Products are available horizontal and vertical. In terms of cost, low-cost batteries are somewhat more expensive than their standard counterparts. The price mainly depends on the material of manufacture.
Areas and features of application, effectiveness
Model SOLIRA 2020/4 No. 12 with a height of 200 mm and a depth of 70 mm.
Narrow batteries have become an alternative to conventional batteries in the face of changing building standards. They are ideal for panoramic and stained glass windows. In addition, large radiators do not always fit into bathrooms, toilet rooms, and balconies. With their miniature size, low batteries are practically not inferior to standard analogues in terms of efficiency, if the installation is carried out without violating technology.
Low horizontal structures are used in narrow rooms where there are low walls, partitions or panoramic windows. They are also indispensable for small loggias and balconies, as they do not take up much space. Narrow horizontal radiators are also installed in long rooms and corridors.
The main feature of such radiators is not even the size and dimensions, but the specificity of heating the room: the lower and longer the heating device, the more even the temperature of the room and the better the entire volume of air is heated.
Heating systems as an interior element
Each model line of heating equipment has a segment where radiators of small height are presented. This group includes products in which this parameter does not exceed 450 millimeters. A low heating radiator under a window is indispensable for heating constantly wet and cold walls facing the street along their entire length.
Such devices are used in the following cases:
- the presence of large panoramic windows;
- location of the heat supply system in the baseboards.
When choosing heating equipment, you need to take into account a number of technical parameters of the products:
- material of manufacture;
- dimensions;
- power;
- resistance to corrosion processes;
- scope, etc.
The lowest heating radiators
The standard, most commonly used height of radiators is 500 mm, less often - 300-400 mm. At the same time, it is still important to raise the device at least 60 mm above the floor. The lowest heating radiators for 2022 have a height of 155 mm. For example, these are tubular steel Vogel&Noot Delta 155 or Purmo Delta 155. Slightly higher are steel tubular radiators of horizontal type in 4 sections, their height is 180 mm. For example, this is Loten Gray Z 2000 for 4 sections or GUARDO RETTA 6P 180.
Among steel panel, aluminum and bimetallic ones, the lowest are radiators with an interaxial distance of 150 mm, but be careful, the total height of the device is usually 200 mm. The choice of such devices is huge; they are produced by almost all well-known manufacturers. We will consider the best of these models in more detail later.
Heating convectors
The height of floor heating convectors can be 130 mm (KZTO Radiator Elegant Mini 130x130) and even 80 mm (SAVVA KN 80). These devices are often confused with heating radiators, but the principle of their operation is different. In convectors, the coolant circulates through pipes on which many metal plates are located. Due to this, the radiation area increases, heat exchange occurs faster, and the design creates air convection through the device. With much smaller dimensions, convectors have a large area of heating elements and high efficiency.
In general, convectors have a wide range of advantages:
- quick and uniform heating of rooms. Five minutes and the room is warm. The radiators will need one hour for this;
- long service life of some models (copper-aluminum);
- the ability to embed appliances into the floor;
- the heat transfer is already at 35° coolant. For most batteries this figure is 65°C.
However, due to the fact that heating in convectors occurs mainly due to convection, and not radiation, they transfer dust masses and dry the air to a greater extent. There are also other disadvantages compared to radiators:
- cool down faster;
- 1.5-2 times more expensive;
- soft materials of heat exchangers are more easily deformed.
The heat consumption of both is the same.
Cast iron
Long gone are the days when cast iron batteries were of only one type. The “Soviet” accordion is far from the only option; there are also modern, palace, and art nouveau styles. There are wall and floor models. Wall-mounted ones are basically the same “accordion” - MS-140, etc., as well as ordinary sectional ones, the style familiar today. Floor-standing ones are more often referred to as design radiators. And, unfortunately, they cost a lot. But they look stylish. Read about the types and types of radiators, their manufacturers and technical characteristics here.
Cast iron radiators are now available in a modern style
“Accordion” is also being produced today, and it is in good demand. Called MS-140, MS-110 and MS-90. There are also low models: with an interaxal distance of 300 mm, and a mounting height of 382-388 mm (the height varies slightly among different manufacturers).
Cast iron radiators are available in a modern style: they look very similar to aluminum and bimetallic ones. In this group, the smallest radiators will also be slightly less than 400 mm.
Retro style cast iron radiators are often small
And the third group of cast iron batteries is design radiators. They are mostly floor-mounted - on legs. And their sizes are also about the same: around 40 cm (with legs). But some companies have very compact ones:
- model BOLTON 220 with installation height 330 mm;
- The Hellas 270 from Viadrus has a height of only 340 mm.
There may be other low cast iron radiators: there are so many different offers, it’s impossible to track everything.
Advantages, disadvantages
The undoubted advantages are a long service life, low price (except for design radiators) and the ability to work with any coolant. Disadvantages - large mass and fragility, difficult to process, cannot be repaired, low operating pressure - 9-10 bar.
There are also properties that in one case are an advantage, and in another - a disadvantage:
- Great inertia. Thick walls take a long time to heat up when the system is overclocked. But they also take a long time to cool down. This feature allows them to smooth out temperature fluctuations when using a conventional coal boiler.
- Large cross-section of sections. A lot of water is placed in them, which again leads to increased inertia of the system and the use of a more powerful pump in systems with forced circulation. But for systems with natural circulation, the low hydraulic resistance of wide collectors is a definite plus.
Application area
All these properties determine the scope of use of cast iron radiators, including low ones: they are optimally suited for individual heating systems (houses, dachas, cottages). They work well in small high-rise buildings: where the operating pressure in the system does not exceed 9-10 bar. They make no other demands on the coolant: they don’t care whether there is oxygen, how many suspended particles are contained, or what its acidity is. With periodic washing they will last a long time.
Read how to clean the battery here.
Reviews of low heating devices: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Small dimensions allowing installation of devices under any windows, as well as in rooms with insufficient free space | Greater cost compared to standard products. For one narrow battery you have to pay 2-3 times more |
| More comfortable heating, the lower and longer the heating device, the more even the room temperature and the better the entire volume of air is heated | Less efficient, since with the same width they have a smaller heat exchange area, and it is not always possible to install extremely wide radiators |
| Models with a height of 200 mm have a wide selection (any material, almost any manufacturer, various colors) | More demanding on the quality of the coolant. According to owner reviews, some models with complex designs clog quickly. This leads to air pockets |
| Stylish and modern appearance, most models do not need to be hidden from view | Shorter service life |
| The small volume of coolant (with the exception of tubular steel) makes the system more inert and functional | Slightly more complex installation |
Problems with large windows - why do they occur?
A French window is, by and large, a glass wall.
Its main advantage - a large glazing area - from the point of view of heating engineering becomes a disadvantage. This is why such windows often “cry”: at the slightest drop in temperature, condensation forms on the inner surface of the glass, which flows down and can form large puddles. If the temperature outside the window has gone into the “deep minus”, then the condensation at the bottom of the window will freeze, forming a layer of ice. In addition, freezing can occur along the perimeter of the structure, so heat loss will be enormous.
And the point is not that you bought low-quality windows - you just can’t argue with physics:
- The thermal conductivity of the window (even if you have chosen an energy-saving double-glazed window) will in any case be higher than that of the walls surrounding it. Thus, the glass becomes the coldest area in the room, and it is on it that moisture from the air will condense.
- Warm air rises and cold air sinks. This is why the lower part of the window, adjacent to the floor, will suffer: it is in this zone that the temperature will be the lowest. So freezing will start from here.
In the case of ordinary windows, the problem is solved by heating with radiators installed under the window sills. They already do a good job, but if you cut a special grill into the window sill board, condensation, if it appears, will only last for a few minutes.
This solution is not suitable for French windows: they do not have a window sill as such, and placing the radiator in front of the glass means significantly worsening the appearance of the entire structure. That is why to solve the problem of condensation and freezing you need to use special heating devices.
Types depending on material of manufacture
Cast iron
Model RetroStyle Bolton 330/330.
Radiators made of this material are deservedly popular. Now they are performed in both standard and modern styles. Exclusive decorative floor samples are also produced.
Cast iron products have some advantages:
- high resistance of cast iron to the adverse effects of coolant and corrosion;
- huge service life of 30 years or more;
- The batteries take a long time to heat up, but cool down slowly.
However, there are many more disadvantages than advantages:
- low resistance to hydraulic shocks, they can withstand up to 10-12 atm (which is not always the limit in apartments of tall apartment buildings);
- low heat transfer;
- a large volume of coolant, which further reduces the efficiency of the heating system;
- heavy weight.
- specific and, despite all the attempts of manufacturers, relatively monotonous design.
However, due to their low cost and durability, cast iron radiators are in great demand.
Steel
Heating radiators made of steel are divided into two categories: tubular and panel.
Panel radiators are available in heights from 300 mm. For European manufacturers, this parameter starts from 200 mm, with an interaxle height of 150 mm. This is the optimal option both in terms of heat transfer and cost.
Advantages of steel panel batteries:
- optimal heat transfer;
- still low cost;
- small volume of coolant;
- a huge selection of models with any connection method;
- aesthetic appearance.
Flaws:
- instability to corrosion;
- narrow channels that easily become clogged with poor-quality contaminated coolant;
- intended only for closed heating systems;
- wall thickness is only 1.25 or 1.4 mm;
- vulnerability to water hammer of the central heating system (over 10-12 atm.).
Tubular steel batteries can have an even more compact design with a height of 155 mm and a more stylish appearance. Depth varies from 50 to 250 mm. Along with wall-mounted analogues, low water floor heating radiators are used.
Advantages of low tubular batteries:
- wide choice of width and depth;
- higher limit of permissible operating pressure, often up to 15-25 atm.
- large cross-section of pipes;
- attractive design;
- large selection of decorative models;
- low hydraulic resistance.
Flaws:
- susceptibility to corrosion;
- large volume of coolant;
- less heat transfer than panel analogues;
- high production costs and, accordingly, price.
- Designed for closed heating systems.
Aluminum
Model TIANRUN RONDO 150 with center distance 150 mm and height 237 mm.
Aluminum radiators come in heights from 200 mm. Such devices have high thermal power - from 89 to 98 W per section, but there are many nuances in their use.
Advantages of aluminum batteries:
- extremely good efficiency;
- light weight;
- low thermal inertia;
- small internal volume.
The devices are sensitive to the quality of the coolant. For stable operation, a pH value of 7-8 is required. They are also incompatible with copper pipes, boiler heat exchangers and other system elements, since aluminum reacts with them. Working pressure is directly dependent on the manufacturing technology of the product. Extrusion models have 5-6 bar, for cast models this figure reaches 10-12 bar. For this reason, such batteries are better suited for autonomous systems. Their use in apartment buildings with centralized heating systems is contraindicated.
Bimetallic
Model TENRAD 150/120 with center distance 150 mm and height 250 mm.
The name of the radiators indicates that they are made of two metals. The coolant collectors are made of high-strength steel. The aluminum casing fused on top increases heat transfer. Bimetallic radiators do not differ in center distance from their aluminum counterparts. In general, this is a more advanced design of aluminum radiators, while maintaining all their advantages.
Advantages:
- high threshold of permissible operating pressure (30-35 atm.), possibility of use in centralized and autonomous systems;
- the highest heat output, from 140 W to the maximum power on the market of 280 W per 1 section (Sira RS 800 model);
- ability to work with any coolant;
- long service life, at least 20 years.
Bimetallic batteries have almost no weak points. Except that in terms of inertia they are slightly inferior to aluminum radiators, and they cost quite a lot.
For autonomous heating systems with operating pressure up to 3 atm. Any radiators will do. For an apartment where the system may have 10 atm, 12 atm batteries are needed. In heating systems in which the coolant flows by gravity, aluminum or cast iron batteries are suitable.
Heat transfer from heating radiators Comparison of indicators and calculation methods
Bimetallic
Bimetallic radiators are usually called heating devices in which the collectors through which water flows are made of steel (sometimes stainless, sometimes black). An aluminum “jacket” of ribs is then fused onto this frame (to increase heat transfer).
Bimetallic radiators do not have very small radiators
Such batteries have a high operating pressure - up to 20-24 Bar, can work with almost any coolant (stainless steel manifolds work with any), and have a fairly high heat transfer. Their disadvantage: often a small cross-section of vertical ducts, as well as a high price.
The situation here is almost the same as in aluminum ones: some manufacturers have very small radiators with a height of 245-265 mm (the same Sira and Rifar have them), and almost all of them have a height from 350 mm to 450 mm.
Advantages, disadvantages
Advantages - high working pressure, compatibility with any metals (aluminum does not come into contact with the coolant or supply pipelines). Works with coolant in a wide range - Ph 6.5-9 in models with steel collectors and Ph from 5 to 10-11 in models with stainless steel (Royal Thermo, Calidor, Nova Florida, Radena). Another good quality is the high heat transfer of the section, as well as low inertia (allows you to accurately regulate the temperature in the room using an automatic boiler or a temperature regulator for the radiator).
Disadvantages: high price, which is due to the high complexity of the technology. And one more drawback: some companies make vertical collectors of small diameter, and if there is a high content of suspended particles in the coolant, they can become clogged. Therefore, it is advisable to install filters at the inlet (and they need to be cleaned regularly).
Application area
This type of radiator was developed specifically for the conditions of our central heating. That’s why they need to be installed in high-rise apartments. They will work great in individual heating, but why pay a lot of money for an unnecessary safety margin (almost tenfold)?
Minimum required thermal power
Typically, thermal calculations of houses are done infrequently, so calculations have to be done room by room. The power of all radiators should be 20% higher than the power of the boiler. For a house insulated according to GOST, heat loss is 10 kW per 100 sq. m. with a ceiling height of up to 2.7 m.
Determining the number of radiators in each room by area is not always reasonable. Heat loss depends on walls, windows, doors. You shouldn't hang too many batteries either. But there should be enough of them so that the system is not hot (>70°C).
Here is an example of power distribution:
- The inner room is heated by the neighboring ones and can be equipped with a minimum number of radiators.
- External wall and window – 1 kW per 10 m2.
- A long outer wall and two windows - multiply the previous figure by 1.2.
- Two external walls and a window - multiply by 1.3.
- Two external walls and two windows - we multiply the primary data by 1.4 or 1.5.
This definition of power is relative. Much depends on other characteristics of the house: layout, size of external walls and windows. But for more than 90% of standard Russian houses, such a simple calculation is quite enough.
What should the dimensions be?
In order for the heating radiator to give off maximum heat (in this case we are not talking about its thermal power, but about the efficiency of its operation), the dimensions must be as follows:
- The length should be more than 70-75% of the width of the window opening.
- The height should be such that there is 8-12 cm between the floor and the battery, and 6-12 cm between the window sill and it.
If the recommendations are not followed, the operation of the aluminum radiator will be accompanied by heat loss. Therefore, even if he can provide the necessary for a room with an area of 20 square meters. m 200 watts of heat, then due to incorrect dimensions there will be insufficient heat in the room. After all, part of it may be lost under the windowsill or used to heat the floor.
When the length is less than 70% of the width of the window opening, the battery will not be able to create a thermal curtain capable of blocking the movement of cold air entering through the window. The consequence of this situation will be the appearance of cold and warm zones in the room. Also, the windows will be constantly covered with steam. And even the power of the heating radiator, which is greater than the need, cannot become a “magic wand”.
Therefore, if the window is 2 m wide, then the length of the battery should be at least 1.4 m
Of course, in order to select a device with such a length, you will need to take into account sections of different heights and their heat transfer. The calculation may take a long time, but it is worth it
What else to look for when choosing
Before you buy low and narrow batteries, you should pay attention to some nuances in choosing products. The efficiency of the heating system will depend on this. To spend your money wisely, it is recommended to consider the following conditions:
- It is better to heat rooms equipped with panoramic windows using aluminum or bimetallic batteries;
- It is better to heat your own houses with an autonomous heating system with radiators made of steel or aluminum;
- the length of the radiator under the window must exceed the width of the window. This will create an effective thermal curtain over the entire window area;
- it is necessary to clarify the operating pressure in the system;
- determine the battery connection side.
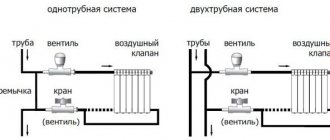
Specifics of connecting and installing different systems
Redevelopment of old houses or simple renovation of an apartment with the replacement of old heating radiators is always associated with the need to study the peculiarities of laying pipelines and methods of connecting batteries. With the open installation method, it is enough to select the correct parameters of the device and shut-off valves, calculate the mounting locations for the brackets and install the battery.
When installing hidden, work is carried out on laying communications, equipping the installation site, and adjusting the decorative grille. It must be remembered that hidden installation requires more space than the size of the convector. For air movement, it is necessary that there is at least 3-5 cm of free space around the radiator around the perimeter and the same amount below it.
In addition, the decorative grille should have an inclined arrangement of the blinds. This element plays an important role in shaping the direction of the flow of warm air. If the sashes are turned towards the frames, then a heat shield will be created effectively. And if the blinds are turned in the opposite direction, then the flow of heated air will be used ineffectively.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Buderus Logatrend K-Profil 11 300
The German company Bosch produces radiators under the Buderus brand in Russia in the city of Engels. The products fully comply with GOST. Owners note in reviews a wide selection of products in sizes. The good thing about batteries from this company is that they have no division into front and rear. The configuration without a backplate allows the battery to be mounted on either side.
The height of the device is not a record, but quite small - 300 mm, length - 400-3,000 mm. Thermal power depends on the size of the battery and the temperature of the coolant. These figures range from 136-15,083 W. Radiators are designed for forced circulation. Also among the advantages are good and reliable coverage, affordable prices, lower than those of foreign, non-localized suppliers.
Among the shortcomings, one can note only the absence of even lower models with a height of 200 mm, rather weak brackets and difficulties in cleaning from dust.
Kermi FKO 22 200
This Swiss company with production in Germany produces a wide range of radiators that are used in various places. Owners in reviews note the wide possibilities of using batteries in design projects. They also like the wide range of lengths available. Kermi FKO 22 200 is one of the best radiators from the manufacturer, as they combine optimal efficiency and time-tested quality.
It is also worth noting the durable and high-quality coating technology (KEF) - the most effective and environmentally friendly today. Available in lengths from 600 to 2,600 mm, power 510-2,210 W. Working pressure – 10 bar. The only downside is the high prices.
Purmo Ventil Compact 200
The Finnish brand has been producing steel radiators since the 50s of the last century. Radiators have a height of 200 mm, a length of 600-3,000 mm. A special feature is the universal connection type; the radiators have two bottom and four side connection holes with internal threads. Already in the basic package there is a thermostat. Available to order in any color. In general, the devices are known to be reliable and trouble-free.
Thermal power, depending on the length, ranges from 589 to 2,942 W. The maximum permissible operating pressure is 10 bar. The steel thickness complies with EN-442, i.e. equal to 1.2 mm, which is sufficient, but inferior to some models with a thickness of 1.4 mm. The only disadvantage is the high prices of the devices.
Radena CS 150
Bimetallic heating radiators with a center distance of 150 mm, but a total height of 250 mm. They are distinguished by the well-thought-out shape of the vertical and horizontal collectors, which are a wide ellipse, this allows to greatly reduce hydraulic resistance. Another feature worth noting is the wall thickness – 1.9 mm. The volume of coolant in the radiator is extremely small (0.13 liters per section).
Maximum operating pressure – 25 atm., heat transfer per section – 120 W. There can be from 6 to 16 sections in total, the length of the device is up to 1,184 mm. Please note that the diameter of the threaded connection on the radiator is non-standard – 1″.
Loten Gray Z 750 180 mm
Russian tubular steel batteries under this brand have a horizontal position of heat-conducting profiles. The latest technologies and high-quality materials are used in production. Therefore, the products are highly durable and durable. It is worth noting the extremely attractive design; the radiators can be made in any RAL color. The company does not skimp on the amount of materials. The thickness of the pipe walls is 2.5 mm.
The width of the battery is 750 mm, in this low version there are only 4 sections with a total heat transfer of 366 W. The design is designed for operating pressure up to 16 atm, which allows radiators to be installed in any closed system. Depending on the design variation, both bottom and side connections are possible. Despite all the advantages, these are one of the most inexpensive tubular heating devices; the disadvantages are quite difficult to detect.
Rettig Column H-2x200x700
Another tubular steel model with horizontal sections from a Finnish concern, but with production in Germany. Attractive in design, can be painted in any color, do not raise questions regarding reliability, but in terms of technical characteristics they are somewhat inferior to the previous Gray Z. With a width of 700 mm, the heat transfer is 319 W, which is less in terms of kW/m. The permissible operating pressure is also lower - 10 atm, so radiators are not suitable for all heating systems of apartment buildings.
Both bottom and side connections are possible. Aside from the lower specifications, the downsides are hard to find and the prices are even lower than the Loten Gray Z.
Cost: 7,800 rub.
Types of panoramic windows
Panoramic windows come in two types: cold and warm. Cold glazing is used on unheated balconies, loggias, and terraces. They are framed or frameless. Frameless ones are simply thick glasses of a certain size that fit tightly one to the other. Panoramic glazing with frames is what we are used to. A wooden or plastic frame into which glass is inserted. But cold glazing is rarely installed; much more often they use windows that can protect against cold and heat.
An example of cold frameless glazing
Most often today, plastic or metal-plastic windows are installed. Depending on the climate, you can select the required number of cameras, the type of glass (tinted, mirror-coated, energy-saving, reinforced and even armored). As a result, with proper installation, you can get windows that, in terms of their thermal characteristics, are no worse than the adjacent walls.
A house with panoramic windows can have windows with different types of opening:
- Deaf. These are the ones that don't open at all.
- With ventilation and micro-ventilation. Open windows are necessary to provide fresh air. Such modes are not needed if there is supply and exhaust ventilation.
- Swing. The usual form of opening. Such windows can be used to access a balcony or terrace, veranda, or simply to the street.
Hinged windows - the ones we are used to
Sliding. They differ in that the doors move to the sides. They are more convenient because they do not require free space in front of them to open. In modern versions they have no worse heat and sound insulation characteristics than traditional swing doors.
Sliding systems are convenient because they do not require space in front of the door
Foldable. Panoramic windows can be folded like a book. 5-6 valves can be involved. When installing such windows/doors, you can turn the room into an open terrace.
The doors were folded and the room turned into part of the terrace
Using doors of various opening methods, you can achieve the functionality that you need. Wooden houses with panoramic windows are rare. The fact is that wood constantly changes size and ordinary windows are placed in special casing boxes that compensate for this movement. If the window area is very large, this may be problematic. If a solution has been found, you can install wooden or plastic windows. And so that white plastic does not look alien, they install frames laminated with a film that imitates wood.
Prices: summary table
| Model | Height, mm | Working pressure, atm. | price, rub. |
| Buderus Logatrend K-Profil 11 300 2000 | 300 | 10 | 6 930 |
| Kermi FKO 22 200 2000 | 200 | 10 | 8 599 |
| Purmo Ventil Compact 200 2000 | 200 | 10 | 11 400 |
| Radena CS 150 16 sections | 150 | 25 | 10 100 |
| Loten Gray Z 750 180 mm | 180 | 16 | 9 189 |
| Rettig Column H-2×200×700 | 200 | 10 | 7 800 |
Advantages
In addition to various design solutions, tall radiators have several more advantages:
- at low media temperatures, they provide the highest possible heat transfer;
- Due to their light weight and the use of small volumes of water, the devices reduce energy costs;
- radiators are equipped with regulators that allow you to independently set the temperature;
- When installing devices with lower communication lines, the aesthetic appearance of the room is preserved.
The advantages of these models include the fact that while saving space, you can install several heating devices in one room at once.