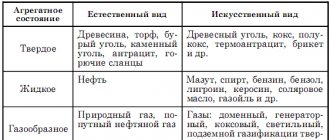
The tables present the mass specific heat of combustion of fuel (liquid, solid and gaseous) and some other combustible materials.
The following fuels are considered: coal, firewood, coke, peat, kerosene, oil, alcohol, gasoline, natural gas, etc. List of tables:
- Specific heat of combustion of solid fuel
- Specific heat of combustion of liquid fuel
- Specific heat of combustion of gaseous fuel
- Specific heat of combustion of some combustible materials
During the exothermic reaction of fuel oxidation, its chemical energy is converted into thermal energy with the release of a certain amount of heat. The resulting thermal energy is usually called the heat of combustion of the fuel. It depends on its chemical composition, humidity and is the main indicator of fuel. The heat of combustion of fuel per 1 kg of mass or 1 m3 of volume forms the mass or volumetric specific heat of combustion.
The specific heat of combustion of a fuel is the amount of heat released during the complete combustion of a unit mass or volume of solid, liquid or gaseous fuel. In the International System of Units, this value is measured in J/kg or J/m3.
The specific heat of combustion of a fuel can be determined experimentally or calculated analytically. Experimental methods for determining calorific value are based on practical measurement of the amount of heat released when a fuel burns, for example in a calorimeter with a thermostat and a combustion bomb. For fuel with a known chemical composition, the specific heat of combustion can be determined using the periodic formula.
There are higher and lower specific heats of combustion. The higher calorific value is equal to the maximum amount of heat released during complete combustion of the fuel, taking into account the heat expended on the evaporation of moisture contained in the fuel. The lowest heat of combustion is less than the highest value by the amount of heat of condensation of water vapor, which is formed from the moisture of the fuel and hydrogen of the organic mass, which turns into water during combustion.
To determine fuel quality indicators, as well as in thermal calculations, the lowest specific calorific value is usually used , which is the most important thermal and operational characteristic of the fuel and is shown in the tables below.
Specific heat of combustion of solid fuels (coal, firewood, peat, coke)
The table presents the values of the specific heat of combustion of dry solid fuel in the dimension MJ/kg. Fuel in the table is arranged by name in alphabetical order.
Of the solid fuels considered, coking coal has the highest calorific value - its specific heat of combustion is 36.3 MJ/kg (or in SI units 36.3·106 J/kg). In addition, high calorific value is characteristic of hard coal, anthracite, charcoal and brown coal.
Fuels with low energy efficiency include wood, firewood, gunpowder, milling peat, and oil shale.
For example, the specific heat of combustion of firewood is 8.4...12.5, and that of gunpowder is only 3.8 MJ/kg. Specific heat of combustion of solid fuels (coal, firewood, peat, coke)
| Fuel | Specific heat of combustion, MJ/kg |
| Anthracite | 26,8…34,8 |
| Wood pellets (pellets) | 18,5 |
| Dry firewood | 8,4…11 |
| Dry birch firewood | 12,5 |
| Gas coke | 26,9 |
| Blast coke | 30,4 |
| Semi-coke | 27,3 |
| Powder | 3,8 |
| Slate | 4,6…9 |
| Oil shale | 5,9…15 |
| Solid rocket fuel | 4,2…10,5 |
| Peat | 16,3 |
| Fibrous peat | 21,8 |
| Milled peat | 8,1…10,5 |
| Peat crumb | 10,8 |
| Brown coal | 13…25 |
| Brown coal (briquettes) | 20,2 |
| Brown coal (dust) | 25 |
| Donetsk coal | 19,7…24 |
| Charcoal | 31,5…34,4 |
| Coal | 27 |
| Coking coal | 36,3 |
| Kuznetsk coal | 22,8…25,1 |
| Chelyabinsk coal | 12,8 |
| Ekibastuz coal | 16,7 |
| Frestorf | 8,1 |
| Slag | 27,5 |
Firewood
These are sawn or chopped pieces of wood, which, when burned in furnaces, boilers and other devices, generate thermal energy.
For ease of loading into the firebox, wood material is cut into individual elements up to 30 cm long. To increase the efficiency of their use, the firewood must be as dry as possible and the combustion process must be relatively slow. In many respects, wood from hardwoods such as oak and birch, hazel and ash, and hawthorn are suitable for heating premises. Due to the high resin content, increased burning rate and low calorific value, coniferous trees are significantly inferior in this regard.
Specific heat of combustion of liquid fuels (alcohol, gasoline, kerosene, oil)
A table is given of the specific heat of combustion of liquid fuel and some other organic liquids. It should be noted that fuels such as gasoline, aviation kerosene, diesel fuel and oil have a high heat release during combustion.
The specific heat of combustion of alcohol and acetone is significantly lower than traditional motor fuels.
In addition, liquid rocket fuel and ethylene glycol have a relatively low calorific value - with complete combustion of 1 kg of these hydrocarbons, an amount of heat will be released equal to 9.2 and 13.3 MJ, respectively. Specific heat of combustion of liquid fuels (alcohol, gasoline, kerosene, oil)
| Fuel | Specific heat of combustion, MJ/kg |
| Acetone | 31,4 |
| Gasoline A-72 (GOST 2084-67) | 44,2 |
| Aviation gasoline B-70 (GOST 1012-72) | 44,1 |
| Gasoline AI-93 (GOST 2084-67) | 43,6 |
| Benzene | 40,6 |
| Winter diesel fuel (GOST 305-73) | 43,6 |
| Summer diesel fuel (GOST 305-73) | 43,4 |
| Liquid rocket fuel (kerosene + liquid oxygen) | 9,2 |
| Aviation kerosene | 42,9 |
| Kerosene for lighting (GOST 4753-68) | 43,7 |
| Xylene | 43,2 |
| High sulfur fuel oil | 39 |
| Low sulfur fuel oil | 40,5 |
| Low-sulfur fuel oil | 41,7 |
| Sulphurous fuel oil | 39,6 |
| Methyl alcohol (methanol) | 21,1 |
| n-Butyl alcohol | 36,8 |
| Oil | 43,5…46 |
| Methane oil | 21,5 |
| Toluene | 40,9 |
| White spirit (GOST 313452) | 44 |
| Ethylene glycol | 13,3 |
| Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) | 30,6 |
What is combustion
During the combustion process, the temperature rises sharply and a large amount of thermal energy (heat) is released. Therefore, combustion is an exothermic process.
Fuel contains atoms of a chemical element called carbon. When fuel burns, each carbon atom combines with two oxygen atoms and energy is released.
When a substance burns, we see a flame (Fig. 2).
A flame is a stream of hot gases, a part of the space in which fuel and oxygen are converted into combustion products.
Rice.
2. Combustion is a chemical reaction of fuel oxidation with the formation of combustion products, the flame releasing heat . Combustion is a complex process because during its occurrence a chain of chemical transformations occurs. Basically, these are oxidation reactions between burning fuel and oxygen;
Note: The surrounding air contains oxygen. Oxygen is a strong oxidizing agent.
What is needed for combustion to occur?
The mere presence of fuel and oxygen in the surrounding air is not enough for this fuel to ignite. We must first heat the fuel to a temperature at which it will ignite. For preheating we use an ignition source. For example, matches, lighter, etc.
Note: For combustion to occur, the fuel must first be heated to a temperature at which combustion will occur.
For example, paper heated to 233 degrees Celsius or wood heated to 300 degrees Celsius can ignite on its own.
Therefore, thoughtlessly heating flammable substances is dangerous. Since a heated flammable substance can ignite on its own, sometimes with an explosion.
Autoignition temperature of some substances
- paper: 233 (C);
- wood: 300 (C);
- gasoline: 250 - 300 (C);
- ethyl alcohol: 400 (C);
The combustion temperature of certain substances
- dry firewood: from 800 to 1000 (C);
- match flame: from 750 to 1400 (C);
- coal in a furnace or boiler: from 1000 to 2300 degrees Celsius (depending on air supply);
- gasoline: 1300 - 1400 (C);
The temperature of the flame parts varies
The gases released during fuel combustion, heated to a high temperature, glow. They form a light halo around burning fuel. This halo is called a flame. The flame can be roughly divided into layers. The temperature of these flame layers varies. The brighter the flame, the closer its color to white, the higher its temperature.
Rice. 3. Hot gases released during combustion glow and form a flame, which can be divided into layers according to the degree of heating
Specific heat of combustion of gaseous fuels and combustible gases
A table is presented of the specific heat of combustion of gaseous fuel and some other combustible gases in the dimension MJ/kg.
Of the gases considered, hydrogen has the highest mass specific heat of combustion. The complete combustion of one kilogram of this gas will release 119.83 MJ of heat. Also, fuel such as natural gas has a high calorific value - the specific heat of combustion of natural gas is 41...49 MJ/kg (for pure methane it is 50 MJ/kg). Specific heat of combustion of gaseous fuel and combustible gases (hydrogen, natural gas, methane)
| Fuel | Specific heat of combustion, MJ/kg |
| 1-Butene | 45,3 |
| Ammonia | 18,6 |
| Acetylene | 48,3 |
| Hydrogen | 119,83 |
| Hydrogen, mixture with methane (50% H2 and 50% CH4 by mass) | 85 |
| Hydrogen, mixture with methane and carbon monoxide (33-33-33% by weight) | 60 |
| Hydrogen, mixture with carbon monoxide (50% H2 50% CO2 by mass) | 65 |
| Blast furnace gas | 3 |
| Coke Oven Gas | 38,5 |
| Liquefied hydrocarbon gas LPG (propane-butane) | 43,8 |
| Isobutane | 45,6 |
| Methane | 50 |
| n-Butane | 45,7 |
| n-Hexane | 45,1 |
| n-Pentane | 45,4 |
| Associated gas | 40,6…43 |
| Natural gas | 41…49 |
| Propadiene | 46,3 |
| Propane | 46,3 |
| Propylene | 45,8 |
| Propylene, mixture with hydrogen and carbon monoxide (90%-9%-1% by weight) | 52 |
| Ethane | 47,5 |
| Ethylene | 47,2 |
Burning rules
When a consumer becomes familiar with the combustion temperature of a particular coal, he needs to take into account that manufacturers indicate only those figures that are relevant for ideal conditions. Of course, it is simply impossible to recreate the necessary parameters in an ordinary household boiler or oven. Modern heat generators made of metal or brick are simply not designed for such high temperatures, since the main coolant in the system can quickly boil. That is why the combustion parameters of a particular fuel are determined by its combustion mode.
In other words, it all depends on the intensity of the air supply. Both fossil and charcoal heat a room well if the oxygen supply level reaches 100%. To restrict the air flow, you can use a special damper/gate. This approach makes it possible to create the most favorable combustion conditions for filled fuel (up to 950˚C).
If coal is used in a solid fuel boiler, then boiling of the coolant must not be allowed. The main danger is that the safety valve may simply not work, which can lead to a large explosion. In addition, a mixture of water and hot steam has a bad effect on the functionality of the circulation pump. Experts have developed two most effective methods that allow you to control the combustion process:
- Crushed or powdered fuel must enter the boiler exclusively in a dosed volume (the same scheme applies as in pellet devices).
- The main energy carrier is loaded into the firebox, after which the intensity of the air supply is adjusted.
Specific heat of combustion of some combustible materials
A table is provided of the specific heat of combustion of some combustible materials (building materials, wood, paper, plastic, straw, rubber, etc.).
Materials with high heat release during combustion should be noted. Such materials include: rubber of various types, expanded polystyrene (foam), polypropylene and polyethylene. Specific heat of combustion of some combustible materials
| Fuel | Specific heat of combustion, MJ/kg |
| Paper | 17,6 |
| Leatherette | 21,5 |
| Wood (bars with 14% moisture content) | 13,8 |
| Wood in stacks | 16,6 |
| Oak wood | 19,9 |
| Spruce wood | 20,3 |
| Wood green | 6,3 |
| Pine wood | 20,9 |
| Capron | 31,1 |
| Carbolite products | 26,9 |
| Cardboard | 16,5 |
| Styrene butadiene rubber SKS-30AR | 43,9 |
| Natural rubber | 44,8 |
| Synthetic rubber | 40,2 |
| Rubber SKS | 43,9 |
| Chloroprene rubber | 28 |
| Polyvinyl chloride linoleum | 14,3 |
| Double-layer polyvinyl chloride linoleum | 17,9 |
| Polyvinyl chloride linoleum on a felt basis | 16,6 |
| Warm-based polyvinyl chloride linoleum | 17,6 |
| Fabric-based polyvinyl chloride linoleum | 20,3 |
| Rubber linoleum (Relin) | 27,2 |
| Paraffin paraffin | 11,2 |
| Polystyrene foam PVC-1 | 19,5 |
| Foam plastic FS-7 | 24,4 |
| Foam plastic FF | 31,4 |
| Expanded polystyrene PSB-S | 41,6 |
| Polyurethane foam | 24,3 |
| Fiberboard | 20,9 |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | 20,7 |
| Polycarbonate | 31 |
| Polypropylene | 45,7 |
| Polystyrene | 39 |
| High pressure polyethylene | 47 |
| Low-pressure polyethylene | 46,7 |
| Rubber | 33,5 |
| Ruberoid | 29,5 |
| Channel soot | 28,3 |
| Hay | 16,7 |
| Straw | 17 |
| Organic glass (plexiglass) | 27,7 |
| Textolite | 20,9 |
| Tol | 16 |
| TNT | 15 |
| Cotton | 17,5 |
| Cellulose | 16,4 |
| Wool and wool fibers | 23,1 |
Sources:
- Abryutin A. A. et al. Thermal calculation of boilers. Normative method.
- GOST 147-2013 Solid mineral fuel. Determination of the higher calorific value and calculation of the lower calorific value.
- GOST 21261-91 Petroleum products. Method for determining the higher calorific value and calculating the lower calorific value.
- GOST 22667-82 Natural flammable gases. Calculation method for determining the calorific value, relative density and Wobbe number.
- GOST 31369-2008 Natural gas. Calculation of calorific value, density, relative density and Wobbe number based on component composition.
- Zemsky G. T. Flammable properties of inorganic and organic materials: reference book M.: VNIIPO, 2016 - 970 p.
Charcoal how to use
You need to light charcoal without using any chemicals: the unpleasant smell from it will remain as long as the fuel burns. Therefore, we take a piece of paper, crumple it, build a few thin dry splinters around the paper in a “hut”, set the paper on fire, wait for the splinters to burn, put some dry firewood on top. When they burn well, you can add charcoal. Moreover, it needs to be folded in a slide. This way it flares up better. If we are talking about barbecue and cooking, then so that the charcoal flares up evenly, we put those pieces that are on the edges of the hill on top. Those that were closer to the center end up on the edge. So we wait until all the pieces are covered with a white coating and flames stop appearing above them. Now you can barbecue.
How to light charcoal? Using paper and thin wood chips or...a hair dryer
There is a way to light charcoal without paper, matches or wood. All you need is a hair dryer and an electrical outlet. All. No paper, no matches. Take a hairdryer, turn it on to maximum, direct the air flow onto the piled charcoal. The first ember will flare up in about half a minute, then the rest will take over, and in about five minutes everything will be burning.
How much wood is required to heat a house?
We always look at the quality of the firewood we buy. Soft wood burns quickly, but does not produce much heat. Preference is given to hard rocks, which, although they burn slowly, provide a lot of heat to the project. Rotten firewood very often comes across on sale. When you prepare firewood yourself, this will never happen. And most often they sell raw wood.
It turns out that for a private house or cottage it is best to find about 10 cubic meters of firewood for the season. In order not to spend money on buying chopped firewood, you can start harvesting it yourself. Moreover, near the summer cottage there will always be a forest where there is a fallen old tree. An excellent option for preparing firewood is to take advantage of the moment when someone is dismantling an old wooden house.
Equipment for preparing firewood for the winter
You cannot prepare a lot of firewood with a hacksaw or an ax. In addition, you need to put in a lot of effort.
In order to carry out preparation work, you need to buy special tools, of which there are not so many.
In order to cut a tree trunk in the forest, you need to choose a good chainsaw. The best option is a device with a power of up to two kilowatts. If the work will be carried out near the house, then there is an option to use an electric saw. There are types of saws on sale that are equipped with batteries. If the work will be carried out very often, it is recommended to buy semi-professional saws. Their power is higher than two kilowatts, and their price is higher.
Then, to chop firewood, you need to buy a high-quality horizontal type wood splitter. For the home, this is the best device that works safely. Working with a wood splitter is simple: you need to turn on the device, which runs on electricity, then put in a log, and then wait for the knife to split it.
There will be trash after the work. And here you will need a shredder that can be used to process the waste. Wood chips, shavings, and leaves can be quickly turned into fertilizer for the garden.
If you want to purchase high-quality equipment, you will have to shell out a lot of money. However, the tools will last a long time. After a while they will fully pay for themselves. For those who think that buying ready-made firewood is cheaper, they are deeply mistaken. For example, what does it cost just to deliver ready-made firewood, and then you also need to store it. Firewood is stored under special sheds or in woodpiles.
Do-it-yourself firewood shed at the dacha, photo
Sheds for storing firewood in winter at the dacha
shed for storing firewood in winter
Experts have proven that self-harvesting wood is much cheaper for the owner, even if he has spent significant amounts of money on purchasing garden equipment.
Where can you find q values
Information on the values of the specific heat of combustion for specific types of fuel can be found in technical reference books or in their electronic versions on Internet resources. They are usually presented in the following table:
Specific heat of combustion, q
| Substance | MJ/kg | Substance | MJ/kg |
| Peat | 8,1 | Diesel fuel | 42,7 |
| Firewood | 10,2 | Kerosene | 44,0 |
| Brown coal | 15,0 | Petrol | 48,0 |
| Coal | 29,3 | Propane | 47,5 |
| Oil | 41,3 | Methane | 50,11 |
Resources of proven, modern fuels are limited. Therefore, in the future they will be replaced by other energy sources:
- atomic, using the energy of nuclear reactions;
- solar, converting the energy of sunlight into heat and electricity;
- wind;
- geothermal, using the heat of natural hot springs.
Advantages and disadvantages of pellet boilers
The equipment has a wide list of advantages:
- high efficiency up to 97%
- automation of the process, which explains the high safety indicators for using the units;
- boilers are considered long-burning equipment;
- unpretentiousness of service;
- the ability to equip the system with remote sensors to control the heating temperature of the coolant.
Combined heating boilers for a private home
Installation of pellet boilers does not require permits; installation and commissioning are simple and therefore do not pose any difficulties for the home craftsman. In addition, if additionally equipped with a control module, the device can be controlled remotely via a mobile application.
But there are a number of disadvantages:
- High price per unit of heat received. To maintain normal heating in regions with harsh winters, about 1000 kg of pellets are consumed per month; it is not difficult to calculate how much the entire heating season will cost.
- Boilers require connection to a power supply or generator and additional technical equipment. The generator will allow the equipment to function autonomously, for example, during power outages.
Comparison of energy intensity of different types of fuel
When comparing the energy value of the main types of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels, it can be established that one liter of gasoline or diesel fuel corresponds to 1.3 m³ of natural gas, one kilogram of coal - 0.8 m³ of gas, one kg of firewood - 0.4 m³ of gas.
The heat of combustion of a fuel is the most important indicator of efficiency, but the breadth of its distribution in areas of human activity depends on the technical capabilities and economic indicators of use.
Briquettes
Briquettes are solid fuels that are in many ways similar to pellets. For their manufacture, identical materials are used: wood chips, shavings, peat, husks and straw. During the production process, raw materials are crushed and formed into briquettes by compression. This material is also an environmentally friendly fuel. It is convenient to store even outdoors. Smooth, uniform and slow combustion of this fuel can be observed both in fireplaces and stoves, and in heating boilers.
The types of environmentally friendly solid fuel discussed above are a good alternative for generating heat. Compared to fossil sources of thermal energy, which have a negative impact on the environment when burned and are, moreover, non-renewable, alternative fuels have clear advantages and a relatively low cost, which is important for certain categories of consumers.
At the same time, the fire hazard of such fuels is much higher. Therefore, it is necessary to take some safety measures regarding their storage and the use of fire-resistant materials for walls.
Pellets
Pellets (fuel granules) are solid fuels created industrially from wood and plant waste: shavings, bark, cardboard, straw.
The raw material, crushed to dust, is dried and poured into a granulator, from where it comes out in the form of granules of a certain shape. To add viscosity to the mass, a plant polymer, lignin, is used. The complexity of the production process and high demand determine the cost of pellets. The material is used in specially equipped boilers.
Types of fuel are determined depending on the material from which they are processed:
- round timber of trees of any species;
- straw;
- peat;
- sunflower husk.
Among the advantages that fuel pellets have, it is worth noting the following qualities:
- environmental friendliness;
- inability to deform and resistance to fungus;
- easy storage even outdoors;
- uniformity and duration of combustion;
- relatively low cost;
- Possibility of use for various heating devices;
- suitable granule size for automatic loading into a specially equipped boiler.
| Type of fuel | Thermal capacity, kcal/kg |
| Pellets | 4500 |
| Firewood | 2500 |
| Charcoal | 7500 |
| Coal | 7400 |
| Fuel oil | 9800 |
| DT | 10200 |
| Natural gas | 8300 |