None of the most modern building materials can displace natural wood from the market. Houses made of various types of timber are still very popular among developers. They are used to construct both residential buildings and outbuildings, baths, saunas, etc. The technology for constructing log houses requires the mandatory use of inter-crown insulation. Through their use, it is possible to improve the performance characteristics of wooden structures.
Inter-crown insulation for timber
- The heat saving indicators are significantly increased. This is a very important indicator given the high current fuel prices. In some cases, it makes it possible to do without the use of external insulation for the walls of wooden houses, which significantly reduces the estimated cost of construction.
- The service life of wooden buildings increases. Cold and humid air penetrates into the cracks between the crowns, and moisture condenses on the surfaces of the timber. The drying process is lengthy, resulting in accelerated destruction of the wood. It is affected by rot and mold, the strength of the wood is noticeably reduced, and in advanced cases, critical deformations of wooden houses can occur. It is necessary to make complex and expensive repairs, and in some cases they are ineffective.
Inter-crown insulation allows you to extend the life of a wooden house
- Modern inter-crown insulation compensates for annual fluctuations in the linear dimensions of the timber. They have plasticity; if the gaps increase, they expand and eliminate heat loss.
- The premises in the house are better protected from the penetration of street noise. Noise reduction characteristics are directly related to thermal conductivity.
Inter-crown insulation for timber improves the sound absorption properties of walls
The construction industry produces a wide range of inter-crown insulation materials, both in composition and in physical properties and linear parameters. This variety simplifies the choice of a specific type of insulation. But to make the best decision, you should briefly familiarize yourself with the types and characteristics of materials.
Types of inter-crown insulation for timber
What are the requirements for interventional insulation?
The main task for which a seal between the crowns of a log house is needed is to eliminate heat loss through the cracks. In addition, one should take into account the features of a log house, first of all, the mobility of the crowns. Even after shrinking, they do not remain completely static due to the fact that wood tends to “play” with changes in humidity. This changes the gaps a little.
To meet these conditions, the insulation requires the following set of qualities:
1. Sufficient density. Loose material will not be able to prevent air flow through it.
2. Low thermal conductivity. High heat transfer resistance of the material is achieved at a certain density, at which the air in it occupies a sufficiently large volume, but the occurrence of a noticeable flow is impossible. The thermal conductivity of the insulation should be at such a level that cold bridges do not form during the cold season.
3. Elasticity. Elasticity is necessary to compensate for seasonal fluctuations in the size of timber or logs. The material should be easily compressed and restore its volume again, avoiding the appearance of cracks.
4. Interaction with water. The seal is exposed to differences in temperature and humidity, which creates conditions for condensation to occur. A good inter-crown insulation should release moisture into the atmosphere, and not accumulate it inside. It must have good vapor permeability and not interfere with this process in the wood.
5. Durability and resistance to rotting. The insulation should not lose its useful qualities throughout its entire service life.
6. Eco-friendly. The insulation must be environmentally friendly material. It should not emit volatile substances and cause allergic reactions.
Performance characteristics
High-quality insulation, which is laid between the crowns of logs or beams, must meet high standards of quality and safety of use. Therefore, the main performance characteristics of the material include:
- High elasticity and density, maintaining properties throughout the entire period of operation. Thanks to its elasticity, the insulation is able to take the desired shape, and its density is able to fill existing gaps between the crowns.
- Low thermal conductivity for effective protection of walls from heat loss.
- High moisture and vapor permeability.
- Resistance to mold, fungi and harmful microorganisms that arise when exposed to increased moisture and heat.
- Resistant to ultraviolet exposure and adverse weather conditions.
What insulation materials are best suited for insulating the crowns of a log house?
Based on the above requirements, we can conclude that the best materials for inter-crown insulation of logs or beams are sealants made from natural materials.
Linen seals
There are two types of flax insulation suitable for inter-crown insulation - flax tow and felt.
Tow is a coarse fibrous waste from the primary processing of bast plants. Thanks to the uniformity of the fibers, it is easy to straighten and get rid of knots. But most often, tow is used for final caulking of inter-crown joints. Linen felt is used as the main material.
Linen tow.
Linen felt is a non-woven material based on flax fiber. Its other names are eurolinen, flax wool. Actually, felt and linen are different materials. Felt is made using needle-punched technology; its threads are randomly woven throughout the thickness of the layer with special needles. The batting is held together by stitching through the fabric with cotton or synthetic thread. For inter-crown sealing, needle-punched material is usually used.
Linen felt is used in the form of strips 5-20 mm thick and up to 150 mm wide. The thickness and width of the tape is selected depending on the width and profile of the timber.
Linen felt has a density of about 700 g/m2, the fiber composition includes: 80% cellulose, 5% lignin, 3% each of pectin and wax. Thanks to the presence of lignin, it is able to breathe and release excess moisture to the outside. The flax seal does not accumulate large amounts of moisture even with prolonged exposure to humid air.
Linen felt.
Jute seals
Felt jute tape is similar to linen and is used in the same way. Jute is more resistant to rotting and birds are less interested in it. But it is tougher than flax and wrinkles worse, which must be taken into account when working. Jute fibers contain: 70% cellulose, 13% lignin, 0.2% pectin and 0.4% wax. Among the negative characteristics, it should be noted that jute has greater fragility and higher hygroscopicity. In addition, due to its foreign origin, this material is more expensive.
To improve the properties of the tape, from 30 to 50% flax fiber is added to jute. This is how jute-linen felt is obtained. In this case, the insulation combines the advantages of both materials.
To improve the quality and durability of insulation from non-woven tapes, lignin is added to them during production and antiseptic and fire-retardant treatment is carried out. Lignin is a natural polymer obtained from wood. It serves as an adhesive to hold the fibers together. Treatment with antiseptics and fire retardants compensates for the natural deficiencies of natural fibers.
Jute felt.
Seals in the form of a twisted cord made of jute fiber are used to seal joints from the inside after construction is completed. With their help, the joints are given a finished look and wood defects, which are especially visible at the edges of the crowns, are masked. Caulking with a cord performs mainly an aesthetic function. It is not used for timber frames due to narrow joints.
Jute cord for decorating inter-crown joints.
Moss
This is the oldest material used for sealing joints. Thin threads of moss create a dense, air-saturated mass with low thermal conductivity. Moss is valued for its ability to absorb and release moisture. In addition, it has antiseptic properties and is difficult to rot.
Currently, this material is not used because there are a number of sealants that are superior in their characteristics to moss. Moreover, the process of collecting and harvesting moss is very labor-intensive. It is very difficult to distribute in an even layer, and when completely dry, the moss becomes brittle, so it can only be used in a dried form. Previously, moss was indeed widely used to seal joints, but this happened only because there were no other materials.
Do I need to insulate the seams?
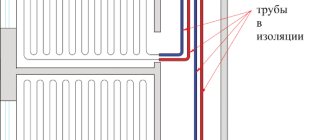
To ensure that a house made of laminated timber does not heat the surrounding air, it is necessary to carefully seal all the cracks and cracks. In particular, insulate inter-crown connections, or seams.
Fig.4. Seam insulation for different profiles
Laying thermal insulation tapes is required only for material with a “Finnish” profile. “German” timber has multiple teeth and grooves for them, which, when laid, form a tight connection. Therefore, the use of inter-crown insulation is not required; only the bowls are sealed. If laminated timber with a small number of teeth is used in the construction of a house, then insulation can also be used to reduce the ventilation of the joints.
Other materials used as inter-crown insulation
There are a number of materials intended for interventional insulation, in relation to which there are constant disputes regarding the suitability of their use for these purposes. These are mainly synthetic materials of various types. Compared to natural materials, they have both advantages and disadvantages.
Synthetic fiber seals
For inter-crown insulation, synthetic felt, which is made from polyester fibers (polyester), can be used.
Its main advantages:
- insensitivity to moisture;
- 100% biostability;
- elasticity, eliminating the appearance of cracks during operation.
If we leave aside the question of the environmental friendliness of polyester, one drawback remains - low hygroscopicity. The likelihood of condensation appearing in it is higher than in natural materials. Before using it, you need to accurately assess the temperature and humidity conditions of the room and the climate characteristics. You may need to vapor barrier the joints from inside the house.
Synthetic fiber seal.
Pre-compressed tape (PSUL)
This material was developed to seal assembly joints when installing windows, and has interesting properties.
- Thermal conductivity is 50% higher than that of fiber insulation.
- Vapor permeability is 15% lower than that of felts.
- Does not absorb water: water absorption – 4% (measured after 12 hours of exposure under water).
- Waterproof: the tape does not allow water to pass under pressure from 200 to 600 Pa, depending on the brand and manufacturer.
- At 20°C after installation, it expands 5 times within 15-30 minutes, filling all the irregularities.
- When the thickness of the seam fluctuates, it changes its volume without leaving any gaps.
- Easy to install thanks to the adhesive layer.
- Service life - at least 20 years.
The comparison with fibrous materials given at the beginning of the list is conditional, since the real parameters of both felt and PSUL depend on the degree of compression.
Pre-compressed sealing tape can be used both as the main insulation and as an additional one - on the outside of the joint. The external seal reliably protects the joint from water, but does not prevent water vapor from escaping. During operation, the tape does not require updating or additional caulking of joints.
Despite their advantages, foam tapes are rarely mentioned in the list of materials for building a log house. Apparently, their use does not correspond to the philosophy of wooden construction.
PSUL.
Sheep wool felt
This material is superior in its thermal insulation qualities to insulation made from plant fibers. It wrinkles easily and regains its shape after the load is removed. It has high vapor permeability, is able to accumulate and easily release moisture. Doesn't shrink over time.
The biological resistance of wool insulation is ensured by antiseptic treatment. Among the disadvantages, it is necessary to note the high cost and allergenicity.
Sealants
This class includes special pastes that fill the joint and harden in it, creating an insulating layer. For log houses, special sealants are used that have sufficient elasticity. Typically, sealants are applied from the inside. They not only seal cracks, but also form joints. Most of them are easy to paint, and some already have a specific shade that can be matched to the interior.
Sealing joints with sealant.
When using synthetic materials and sealants, it is better to consult a specialist. An unsuccessful selection or the wrong combination can ruin the house in a few years.
Do-it-yourself finishing caulk
After the log house has been subjected to shrinkage, finishing caulking is carried out at home. During the shrinkage process, the previously laid layer of insulation is deformed, voids can form in the inter-crown cracks, and vertical cracks can form in the corners of the frame. The operation is performed from the outside and inside. Caulking is a labor-intensive process that requires diligence and attention; the main tool is a wide wooden chisel or rubber mallet. To avoid damaging the integrity of the fibers, it is better to blunt the chisel. The operation begins with the lower crown along the entire perimeter, after caulking of the first crown is completed, they move on to the second, etc.
Advantages of jute
Safety
The insulation must be safe for human health. In the bath we enjoy the smell of natural wood and get healthier, so the materials used should not contain any harmful components.
Fire resistance
The insulation for a bath should not flare up from every little spark. Experts recommend using materials no higher than the second flammability group.
Biological resistance
The insulation should not attract the interest of birds and allow the emergence and proliferation of various fungi and bacteria.
Vapor permeability
In a steam room, humidity and temperature constantly fluctuate, and condensation of water in the inter-crown space can only be avoided by using materials with a good ability to transmit moisture without rotting the wood
Therefore, pay attention to the coefficient of vapor and air permeability of the material
Country bathhouse
Durability
Good insulation lasts as long as the structure itself, and at the same time maintains its integrity and elasticity throughout the entire period of use.
Step-by-step instructions for laying inter-crown insulation
Typically, installation is carried out in two stages: initial insulation, which is performed during the construction phase of the building, and the so-called caulk, that is, secondary insulation. It is necessary to caulk the walls at least twice: immediately after completion of construction and about a year later, after the building has completely settled.
Primary and secondary caulking of a log house
Stage one. Preparing tools
To install inter-crown insulation, a set of special tools is used, which can be purchased at any store. The main requirement is that they should not be too sharp or rough so that the blades do not cut the material or pull it out of the seams.
Caulking tools
- Flat blade. Used for sealing joints and cracks in a log house.
- Flat chisel. Necessary for sealing seams in corners and shaped elements of a building.
- Triangular caulking with a groove. With its help, rollers are formed from insulation.
- Narrow thick wedge. With this tool, narrow cracks are enlarged to make caulking more convenient.
- Wooden mallet. Needed to tightly drive the sealant into the gaps.
- Construction stapler. Fastening strip materials to logs.
- Sharp scissors.
Basic list of caulking tools
The material that will be used for insulation must be dry and packaged in airtight packaging. The exception is moss, which should be slightly moistened before work.
Stage two. Primary installation of insulation
Primary caulking of seams
The initial installation of insulation is carried out at the construction stage of the building, and the algorithm of actions is as follows.
Step 1. If tape or roll insulation is used to insulate the log house, it must be cut into strips (they should be about 10 cm wider than the logs).
Step 2. Lay moss or tow in an even layer along the entire length of the log so that the material hangs down on both sides by about 5 cm. When using tape insulation, it must be laid on the log with the same margin and secured with a stapler. The second tape is laid overlapping on top, so that there are no gaps at the joints.
Laying insulation
Step 3. After the entire row around the perimeter is covered with material, the second crown is laid on top.
Step 4. Once the entire frame is completed, you can move on to caulking. Twist a roller from the insulation and push it into the gap with caulk - it is important that it is not interrupted and is continuous along the entire length of the frame.
The principle of caulking is simple - tightly fill the inter-crown gap with a sealant
Stage three. Caulking seams
After completion of construction work and shrinkage of the building, caulking of the seams is carried out - additional insulation, for which several technologies can be used.
Caulking technique
Caulk with tape insulation
| Step, no. | Description |
| Step 1 | Stand near one of the ends of the building, place the end of the tape on the ground and move to the other end, gradually unwinding it. The tape should run smoothly, not twist or stretch, but sag slightly |
| Step 2 | Return to the beginning, lift the tape and tuck it between the crowns with a chisel or other tool (do not caulk the gaps, but lightly tuck the material). As soon as the entire wall has been passed, you should cut off the tape with sharp scissors, leaving a margin of 10-20 cm |
| Step 3 | At this stage it is necessary to caulk the wall, but do it very carefully so that the tape does not go into waves. This is done until the entire tape, along with the reserve, disappears into the gaps |
| Step 4 | Repeat all the processes described above, starting from the first stage between the same crowns (you can freely lay several more tapes there, regardless of their thickness and density). Typically, caulking walls only on the outside requires four times more material than is used for primary insulation during the construction process |
Insert insulation into the seam
After the insulation laid in the grooves becomes very dense (almost like wood), the work can be considered complete.
Log baths
Brick is an environmentally friendly material, but only in addition to being decorative, because various additives are used in its manufacture. Of all the existing bricks, choose lightweight varieties with existing voids inside; baths made of such material will last a long time. The main advantage of brick buildings is their fire resistance and resistance to biological damage. You can build a brick bathhouse on several floors; it will be stable and can be erected easily and quickly.
Log baths were built by our grandfathers back in the last century. Now they are no less popular. A sauna built from logs is environmentally friendly. External and internal decoration of the walls can be done at will, although they already look good. It is advisable to build a columnar or strip foundation for a log bathhouse, you need to look at its dimensions and the weight of the wooden material.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Gas boilers for steam baths
The disadvantages of building a bathhouse from logs include the fact that it will be necessary to insulate the walls and caulk. And also the fact that it will be impossible to cope with heavy logs alone; you will need to use special equipment. And cutting out corner joints is not easy.
A bathhouse built from timber is also environmentally friendly, but only in addition to laminated timber. Walls made of profiled and laminated timber do not require additional processing. And interior and exterior finishing must be done for baths from edged and unplaned timber. The foundation for the construction of a timber bathhouse can be built lightweight, because
the material itself and the structure made from it are light in weight. You can assemble a bathhouse from timber in a short time. Caulking and insulation work must be carried out for the walls of the bathhouse made of edged timber. But planed, edged and profiled structures do not need additional insulation. It is better not to use laminated veneer lumber for the construction of a bathhouse, because... it may not withstand high temperatures or temperature changes and may crack.
It is advisable to build baths from wooden materials, not brick. After all, wood breathes, thereby constantly circulating air and regulating the microclimate in the room. They mainly use coniferous trees, and when heated, they release substances into the air that are beneficial for the respiratory system and the entire body as a whole. Of all the materials, the most profitable construction of a bathhouse is carried out using rounded logs and profiled timber.
A real Russian bathhouse is a home “center” where you can improve your health. However, everyone knows that a sauna requires high temperatures, to achieve which a lot of fuel is spent, and, therefore, your money. Therefore, even at the time of construction, the issue of insulating a wooden structure should be carefully considered.
As for the process of insulating a bathhouse, its beginning must necessarily be based on the choice of inter-crown insulation, the best options for which are moss and jute tow. Actually, we will talk about which of the listed materials is better for us to choose in this article.
For a bathhouse, it is recommended to use inter-crown insulation for timber made of natural fibers. This seal does not accumulate moisture, provides good air exchange, and is resistant to rotting and destruction.
We suggest you read: Make a door from boards with your own hands
The best representatives are insulation materials made of moss, jute and flax, as well as their derivatives. They are successfully used for caulking wooden houses and baths.
To understand which is the best insulation for a bathhouse, you should pay attention to the main characteristic of the material – density. For timber structures, insulation with a thickness of 4 mm and a density of 350–450 g/sq.m is used.
For timber structures, insulation with a thickness of 4 mm and a density of 350–450 g/sq.m. is used.
For houses with 2–3 floors combined with a bathhouse, material with a thickness of 9–11 mm and a density of up to 750 g/sq.m is used.
To choose a quality sealant, you need to know what type of wood is used to build the log house.
For bathhouses made of timber and rounded logs, you can choose materials up to 10 mm thick - jute felt, flax felt, a combined version with jute and flax.
For a chopped-type bathhouse, it is better to choose insulation up to 15 mm thick - felt made of jute and flax, tow in ribbons and bales made of flax or jute, moss.
Final Recommendation
By the way, recently (on the eve of the New Year) a fellow colleague of mine bought flax-jute fabric at. He liked the conversation with the consultant (in his words, he understands issues of wooden house construction very well) and the price of the product was quite reasonable. This is not an advertisement - just a consultation, which is always useful. I recommend this company for residents of Moscow and the Moscow region. Moreover, the company is specialized and has been on the construction market for several years.
Well, perhaps he said everything he wanted. If it was informative, then do not miss the release of new information. Do you have friends who are building a bathhouse or a house? Recommend the article to them.
Good luck and warm, well-caulked walls. Bye!
Quote of wisdom: This is how men are made: they can resist the smartest arguments and cannot resist a single glance (Bazzak).
Lnovatin
Depending on the manufacturing technology, it may be called differently. Refers to quilted fabric (made using the needle-stitching method).
- Good hygroscopicity;
- Easy to install;
- Prevents fungal activity;
- Good sound insulator;
- Environmental friendliness;
- Cost-effective;
- Almost no re-caulking is required.
- The moth "chicks".
Carefully! When purchasing this product, pay attention to the structure. If you notice very short fibers, trimmings of thread, twine and inclusions of other colors, you know that the material contains recycled products. For example, recycled bags, rags, etc. This is not entirely good. Such insulation will be fragile. And besides, it is unknown under what conditions the processed products were used.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any construction technique, interventional insulation has its pros and cons. The disadvantages include:
- Violation of the wood structure. The use of synthetic insulation leads to disruption of the structure of wood fibers. This can ruin the environmental friendliness of the structure and affect the tree’s ability to breathe. This means that synthetic materials impair the air permeability of the enclosing structure, which leads to stagnation of air inside the room.
- On the other hand, natural insulation materials can lead to the formation of rot and mold. Natural fibers contribute to the accumulation of moisture and swelling of logs. Ultimately, this leads to damage to the enclosing structure.
- Any insulation is at risk of pests. To one degree or another, this problem occurs in both synthetic and natural materials. Most pests have adapted absolutely any building material into their homes. Ants are able to gnaw passages even in brick and concrete, let alone soft and pliable insulation.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=MKyOb_xzlJw