In accordance with the laws of physics, air rises when heated, so insulating the ceiling in a house with a cold roof is not a way to get rid of extra money, but a decision dictated by expediency. If you live in a private house, then you have directly encountered the problem of a cold ceiling in the room above which the attic is located. It is usually not heated, and its own thermal insulation is minimal to ensure normal temperatures during the cold season. As a result, there is a source of constant heat leakage above the living room.
You can insulate the ceiling in a private house from the inside or outside. Both options have their own advantages and disadvantages, the use of which is dictated by rationality, circumstances, technical nuances and other significant characteristics.
Insulation of the ceiling from the outside using rolled material Source buildfun.ru
Choice of insulation
Before purchasing thermal insulation material, it is necessary to take into account several quality characteristics, including:
- degree of vapor permeability;
- weight;
- strength;
- flammability;
- price.
There are two types of ceilings:
- Made from concrete slabs
. These products do not burn and have high load-bearing capacity. Concrete is considered to have partial vapor permeability. But for slabs this indicator is insignificant and therefore, when choosing which insulation is best for the ceiling, it is customary not to take it into account. - Wooden
. In private households, ceiling structures are often made of wood, which burns well and allows a little steam to pass through. If you block the air supply to the rafters, they will begin to rot over time. In addition, laying flammable insulation on a wooden surface is very dangerous.
One of the main parameters that influences which insulation to choose for the ceiling is where it is installed. This is explained by the fact that the ceiling can be thermally insulated both from the side of the unheated attic space and from the inside of the building.
For the home craftsman, the easiest way to do insulation is in the attic, because in this case there is no need to hem the ceiling from below. In addition, in the case of external installation, you will not have to decide what thickness of insulation is best to use, since there will be enough space in the attic. You can use both bulk material and in the form of slabs. You need to choose insulation for the attic based on your specific situation.
The situation is different with the installation of thermal insulation from inside the room. In private homes, you can’t always find really high ceilings, which means you will need to take every centimeter away from the living space.
As practice shows, property owners rarely decide to lower the ceiling surface by more than 15 centimeters. Accordingly, it is better to use insulation that is lightweight, but at the same time durable and with a low degree of thermal conductivity.
To find out which insulation is better for the ceiling under certain operating conditions, you should analyze information about the materials most often used in construction.
Video description
Which insulation divides heat better, watch the video:
Advice! When working with penoizol, it is recommended to wait until it hardens completely; it has a slight shrinkage that will have to be compensated to prevent the formation of voids.
The process of thermal insulation of the ceiling with foam insulation Source lestorg32.ru
Thermal insulation using foam plastic
In terms of popularity, this material occupies a leading position because it is lightweight, accessible and inexpensive. The strength of the foam will be sufficient for arranging insulation. Laying this material does not require special knowledge or high professionalism. But polystyrene foam also has disadvantages - low vapor permeability, and besides this, it burns well.
Is it possible to sew wooden floors with this material from the outside or inside? There is no clear answer to this question. It is undesirable to lay polystyrene foam in a continuous layer on top, because then warm and humid air will begin to accumulate in the wood, resulting in the appearance of fungus and mold.
If you install this insulation on wood from the inside, then air access will be provided from above to the ceiling, but there is no point in clogging the ceilings with waterproofing in a breathable and environmentally friendly house.
In some cases, some craftsmen lay foam plastic between the load-bearing ceiling beams, while others have a negative attitude towards this approach. The fact is that the beam has a minimum thickness of 15 centimeters and, if it is clamped on both sides with this material, it will not cope with the effects of moisture and will become damp.
Taking into account the above information, we can conclude that polystyrene foam is a good choice when you need to decide what kind of insulation to insulate the ceiling both outside and inside, if it is made of reinforced concrete slabs. When the floor is made of wood, the use of this material is undesirable.
Nowadays extruded polystyrene foam, a modern type of foam, is no less popular. It does not allow moisture to pass through and retains heat 30% better. Expanded polystyrene is a more effective analogue of polystyrene foam if it is necessary to insulate a concrete floor from the inside. In this case, you can use sheets of smaller thickness.
In the case of insulating a concrete floor with foam plastic from the inside, slabs with a thickness of 50 - 75 millimeters will be sufficient. If you plan to install external thermal insulation, the minimum thickness of the ceiling insulation in a private house should be 100 millimeters.
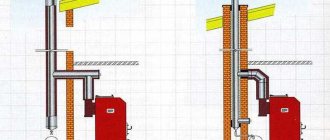
The age-old question - to insulate from the inside or outside
Any external fence separating a living space from the street should be sheathed with thermal insulation on the outside. Accordingly, the insulation of the ceiling on the top floor of a private house is done from the attic side. Causes:
- Installation is physically simplified, which is important when doing the work yourself. There is no need to make a suspended frame or attach insulation from below to the ceiling.
- A layer of insulation 10-20 cm thick (depending on the region of residence) will not reduce the height of the rooms. This is an important plus for old buildings and “Khrushchev” buildings with low ceilings.
- In a lived-in house or apartment, you won’t have to redo the renovations.
- If you do not follow the internal thermal insulation technology, the surface under the insulation will get wet and fungus will appear. Moisture condensation inside the “pie” is promoted by 2 factors: the penetration of water vapor and the formation of a dew point at the junction of dissimilar materials.
When the outer fence is sewn up from the inside, the point of moisture condensation is located near the junction of 2 different building materials
. About the notorious dew point, which is used to scare ordinary homeowners. To avoid condensation inside the structure, it is worth meeting 2 conditions: do not allow water vapor from the room to enter there and use an insulator of sufficient thickness. Then the dew point will be inside the insulation, where there is nothing to condense. The second way is to organize moisture removal using ventilation (read below).
Reference. Dew point is the phenomenon of condensation of water vapor from the air at a certain humidity and temperature. The lower the air temperature, the sooner the degree of extreme saturation with moisture is reached and condensation begins to form.
There are exceptions to the rules; not every room can be insulated from the outside. Examples:
- ceiling of the upper apartment of a multi-story building;
- attic;
- balcony, loggia;
- concrete garage floor above the basement, cellar;
- the need to save money, etc.
For obvious reasons, it will not be possible to insulate a garage basement from above.
In the listed cases, internal thermal insulation of ceilings is arranged with strict adherence to technology. We will describe the work procedure in the form of step-by-step instructions, but first you need to find out...
Mineral wool for ceiling insulation
The range of this type of thermal insulation materials is wider than that of foam plastic. Both soft elastic mats and high-density slabs are available for sale.
Previously, only one type of such thermal insulation material was produced - glass wool. Despite the fact that it is of dubious quality, it is still used due to its low cost. But after contact with glass wool, if you do not wear thick work clothes, your body will itch for about 3 days.
The inexpensive segment includes soft mats that do not cause as many problems. True, many experts prefer dense basalt wool products, since they are a universal insulation material that can be laid on any surface.
In terms of weight, mineral wool is no different from polystyrene foam, but its advantage is that it has a significant level of vapor permeability and is a non-flammable material. But it has a big disadvantage. With high vapor permeability, mineral wool for ceiling insulation strongly accumulates moisture.
At the same time, if dense slabs can be dried, then soft mats after drying lose their original volume, and, accordingly, their thermal insulation qualities. The thermal conductivity coefficient of mineral wool is in the range of 0.3 – 0.4 W/mºK, which is similar to the same characteristic of foam plastic.
But these are laboratory results. In fact, due to the ability to absorb moisture in residential premises, this coefficient for this insulation is several times higher.
When installing mineral wool on the ceiling, its thickness should exceed this parameter compared to polystyrene foam by at least 30%. When it is necessary to thermally insulate the ceiling of a cold attic, then the thickness of the slab for insulating the ceiling cannot be less than 150 millimeters - the more, the better.
It is very convenient to work with mineral wool, and most importantly, the result will be effective. It can be laid on different types of ceilings, both inside and outside. When installing this material, you must strictly follow the relevant instructions of the product manufacturer and only in this case will a positive effect be achieved.
Video description
Insulating the ceiling from the inside, watch the video:
The process of insulating the ceiling from the inside with polystyrene foam Source nl.decorexpro.com
Thermal insulation of the ceiling from the inside with polystyrene foam boards Source barmanlive.ru
Bulk types of insulation
Such thermal insulation materials are used only for insulating attic floors from above. Expanded clay is the most popular among them.
The granules of this bulk material come in three fractions:
- The smallest of them is called sand, since expanded clay does not exceed 5 millimeters in diameter.
- The larger and most popular granules have a diameter of up to 20 millimeters. They are also called gravel.
- Expanded clay crushed stone has a diameter from 20 to 40 millimeters.
In terms of their qualitative characteristics, the fractions are identical, and their difference lies only in size. The cost of expanded clay is affordable. Compared to other types of bulk materials, there is much less dust from expanded clay. The big advantage of this ceiling insulation is that rodents are indifferent to it. But, like any bulk heat insulator, expanded clay is afraid of high levels of humidity, since it is capable of absorbing moisture.
Sawdust is also considered a fairly effective insulation material, given that its price is more than affordable. But there is an important nuance here - they are not used when they are fresh or in their pure form.
To prevent rodents from living in this loose fill, you need to keep it in a dry room for about a year. Then it is mixed with “fluff” - this is what slaked lime powder is called, observing the proportion of 8 parts sawdust and 2 parts lime. From already seasoned sawdust, you can make insulation slabs that are quite highly efficient.
The manufacturing technology of such a heat insulator is simple:
- Sawdust, lime and cement must be mixed in a ratio of 9:1:1.
- The resulting mass is moistened and then poured into pre-prepared molds and compacted a little.
- After about 7 days at room temperature they dry and are ready for use.
Polyethylene foam films
Most often used as a vapor barrier. They retain heat to a small extent, so they are practically not used as the main insulation. The metallized coating increases the amount of infrared rays reflected into the room. But during installation you need to follow some rules:
- the foil layer should be directed downwards;
- the distance from it to the nearest surface is at least 20-25 mm.
If these conditions are met, the foil will actually work. Otherwise, the reflection effect is practically absent.
Important. Multilayer thermal insulation effectively retains heat. The main thing is that it is safe to use.
Application of new technologies
Among modern materials used for thermal insulation of ceilings, the following are most in demand:
- Polyurethane foam
. Refers to new and quite expensive thermal insulation materials. Its characteristics have much in common with extruded polystyrene foam. This insulation is not afraid of moisture, it has a long service life - manufacturers provide a 50-year warranty on it. But polyurethane foam, similar to extruded polystyrene foam, is a waterproofing material, and since it is applied in a continuous layer, it is not suitable for wooden floors. - Penoizol
. It is a widely advertised material. But in reality it is ordinary foam plastic, but in a liquid state. In addition to all the previously described advantages of this insulation, penoizol is applied without gaps, which means that the material is recommended to be used only for thermal insulation of concrete floors. - Ecowool
. It is considered the most suitable choice of insulation for the ceiling. For its production, natural cellulose is used, adding a binder, antiseptics and fire retardants. Ecowool absorbs water, but its level of water absorption is lower than, for example, mineral wool. At the same time, their vapor permeability and thermal conductivity are almost the same.
An important feature of using foam insulation is that their application requires the use of expensive compressor equipment, and with the participation of professionals. An exception is the installation of glass wool, which in a dry state can be poured independently onto the floor of an unheated attic. If it is necessary to carry out insulation from the inside, a compressor will also be required for ecowool.
Spray polyurethane foam
The advantage of this type of insulation is the creation of a seamless coating and high installation speed. PPU is sprayed using a compressor unit or a hand-held spray can with a gun. The polymer hardens very quickly, and the surface shape can be any.
The vapor permeability of polyurethane foam is close to that of wood. Unlike the foam shell, which does not allow the wood to breathe, polyurethane foam does not retain moisture, so it freely migrates between layers and evaporates into the atmosphere.
Spraying is done in one layer. One can is enough for 1.2 square meters with a coating thickness of 50 mm. But this is not enough for the middle zone. According to the standards, floors under a cold roof in a temperate climate zone must be insulated to a thickness of at least 81 mm, that is, the cylinder will be consumed for 0.74 sq.m.
Polyurethane foam, like any polymer, is afraid of ultraviolet radiation, so leaving it unprotected in direct sunlight is not recommended. It is also necessary to take into account that polyurethane foam is low-flammable, so it is advisable to spray it on a non-flammable substrate.
Option No. 1 – foam insulation
The work of laying this heat insulator is not difficult:
- Concrete slabs generally have a flat surface, so surface leveling problems rarely occur. All you have to do is putty the joints between the plates, or better yet fill the cracks with polyurethane foam.
- The next step is to apply a deep penetration primer to the ceiling twice. Since smooth concrete has low adhesion, without this treatment the required effect will not be achieved.
- Next, they take pre-prepared sheets of insulation, spread them with adhesive and apply them to the ceiling surface. Many craftsmen place them without gaps, as densely as possible. But there will still be gaps between the sheets, so they are initially glued with a gap of 5 - 7 millimeters. Then the gaps are filled with foam, the coating is continuous.
- But polystyrene foam should not be left in this state, since it is a flammable material and the ceiling looks ugly. Its surface needs to be plastered. To do this, apply a layer of Ceresit CT83 3–4 millimeters thick with a spatula and immediately embed a reinforcing fiberglass mesh in it.
- Next, to be on the safe side, the foam plastic is additionally secured with umbrella dowels, which requires a hammer drill. A hole is drilled in the concrete through the thickness of the ceiling insulation, a plastic dowel is placed in it and the central rod is driven in. For one square meter of such fasteners you will need 5 pieces.
When everything is dry, begin applying the decorative finish. If you don’t want to use Ceresit CT8, you can use any starting plaster, but before doing this, the foam should be primed.
If the ceiling is to be insulated with this material in a wooden building, then the insulation is laid between the load-bearing beams to their entire depth and the gaps are foamed. The ceiling is hemmed from below, and it is better to fill the subfloor on top, since you will have to move around the attic. In this case, installation of a vapor barrier is not required, since moisture is not dangerous to the foam.
Despite the fact that there is a large selection of adhesive compositions on the construction market, experts most often use the following three options:
- "Liquid Nails"
. High-quality glue, but the process of applying it is not easy and therefore when using it you need to follow the instructions. - Polyurethane foam
. A pattern of it is applied to a sheet of foam plastic. Then they apply insulation to the ceiling. Next, the sheet is pressed against the surface several times over the course of an hour, since the foam expands and until this process is completed, the material will move away a little. - Dry mix Ceresit CT83
. It is simply diluted according to the instructions, applied to the sheet using a notched spatula and glued. If such a tool is not at hand, it is necessary to lay “buns” at several points and attach the insulation.
Materials for interior work: what is better to use
Content
Most often, it is impossible to insulate the ceiling from the attic due to the low slope of the roof or too thin beams. Often the reason is a simple lack of access. In this case, you need to install insulation inside the room. This complicates the work and increases its cost. We have to think about the presence of a vapor barrier and make a new “finishing” ceiling. The impossibility of using the most common, cheap, easy-to-use thermal insulation materials, such as expanded clay and sawdust.
Not every material is suitable for interior work. The main condition is compliance with the following requirements:
- high fire resistance;
- environmentally friendly, at room temperature the material should not emit substances harmful to humans;
- durability, resistance to fungus;
- adequate price;
- sufficient efficiency with minimal thickness, which is especially critical for low ceilings;
- low specific gravity so as not to load the structures of wooden floors.
Of course, there is no insulation that would fit the listed conditions without restrictions, but there are materials that have a good average balance of parameters, which allows them to be used for insulating the ceiling in a house with a cold roof.
First of all, this:
- Styrofoam;
- expanded polystyrene;
- polyethylene foam;
- mineral wool.
The quality of the materials used directly determines how effective and durable the insulation will be. Accordingly, this issue requires detailed consideration.
Option No. 2 - installation of mineral wool from the inside
It can be done in two ways. The first of these is similar to gluing and plastering foam. The second option, no less common, is internal installation, carried out under a suspended sheathing, which is installed on concrete or wooden ceilings.
The frame for the sheathing can be made from wooden blocks or from two types - UD and CD profiles. Experts recommend using metal products, since they will not move in the event of a temperature change.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- First of all, a horizontal line is struck along the perimeter of the room at the level of the future ceiling plane. The easiest way to do this is with a laser level, but if you don’t have one, you can use a hydraulic level, which is a long soft tube with graduated tips that operates using the communicating vessels method.
- Then, according to the applied markings, two UD profiles are fixed on two opposite, longer walls.
- Perpendicular to them, the location of CD profiles is marked on the ceiling, usually observing an installation step of about 50 centimeters.
- In accordance with the markings, the perforated suspensions are secured with dowels at intervals of one meter, their wings are bent downwards.
- Next, they begin to glue the mineral wool slabs to the ceiling. The insulation under the wings of the suspension is cut with a knife.
- To complete the work, CD profiles are inserted into the UD profiles and fastened to each other and to the hangers using self-tapping screws. Now you can begin covering the frame with plasterboard or other finishing material.
Worker skills and tools
Popular insulation methods do not require expensive equipment or high qualifications. For insulation, a home craftsman will only need general construction skills and ordinary tools:
- knife
- hammer
- screwdriver
- hacksaw
- stepladders
- roulette
When installing the guides, it is best to call an assistant. Help with cutting and laying rolled materials would also be helpful.
Before starting work and purchasing materials, it is necessary to make a sketch drawing. This will help you avoid making mistakes with dimensions and correctly calculate the amount of materials purchased.
Option No. 3 – thermal insulation of the ceiling from above
It is considered the simplest way. If the ceiling made of concrete slabs or load-bearing wooden beams have been previously covered and there is no desire to touch them, then lathing is installed in the attic. For its construction, a wooden beam with a thickness of 50 millimeters or more is usually taken.
The width of the beam, which is also the depth of the sheathing, is calculated taking into account what layer of insulation is needed on the ceiling. 30 millimeters are added to this value to create a ventilation gap.
Next, the entire attic space is covered with a vapor barrier over the sheathing. We should not forget that the membrane of this material allows steam to pass in only one direction and it should only move upward. These products always contain markings indicating which side is vapor-permeable. The membrane is secured to the sheathing using a furniture stapler.
Then you can fill or lay the insulation. If bulk materials are used, they are poured out, leveled and everything is ready. As for laying a heat insulator in slabs, for example, mineral wool, then you have to work hard.
To obtain the required density of insulation for the ceiling, it is necessary that the mats or slabs be 20 - 30 millimeters wider than the gap. Then they will fit between the wooden guides as tightly as possible. In order to prevent the formation of cold bridges at the joints of the plates, the insulation is usually installed in two layers.
When laying mineral wool, slabs with a thickness of 100 mm are usually used. They are mounted in one layer. Next, another row of insulation is placed on top. In this case, the joints of the lower and upper layers should not coincide with each other. The result is monolithic thermal insulation. At the final stage, a rough flooring is made on top of the sheathing.
Expanded clay, vermiculite, perlite
These bulk insulation materials are made from mineral raw materials - clay, shale, volcanic rocks. High-temperature swelling results in the formation of porous granules with low thermal conductivity.
Mineral materials do not burn, tolerate waterlogging well, and shrink little. But there is a significant drawback - it is quite heavy in comparison with fibrous or polymer heat insulators.
A higher load may not be critical for load-bearing structures if they are calculated with a margin. But bringing, pouring out and leveling several dozen cubes of expanded clay in the attic is not such an easy task. For comparison, the weight of 1 cubic meter of mineral wool weighs 50 kg, foam plastic - 35 kg, and expanded clay of fractions 5-40 mm - 300-400 kg. In terms of an attic area of 100 sq.m and a layer height of 25 cm, the result is 7.5-10 tons.
The second drawback is that a fairly thick layer is required. Its thickness should be determined by calculation. On average, it is 25-30 cm. In the southern regions, it is allowed to reduce the thickness of the insulation to 15-20 cm. In the northern regions, it should be increased to 35 and even 40 cm.
Bulk materials must be protected from moisture from steam. To do this, a vapor barrier made of dense film is spread on the base under the insulation layer. There is no need to cover the top with anything; moisture evaporation should occur naturally.
Calculation of the thickness of the thermal insulation layer
The efficiency of thermal insulation depends on the accuracy of determining the thickness of the insulation, which is part of the thermal engineering calculation. In addition, the indicator allows you to calculate the loads placed on the ceiling structure. When calculating, the values of the permissible weight and the required thermal protection are compared.
The thickness of the insulation is determined by the formula
q = R * k,
Where:
- q – thickness of heat-insulating material, m;
- R – thermal resistance, m2°С/W;
- k – thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation, W/(m°C).
The R value is determined from tabular data - the indicator is calculated for each region, taking into account the climate characteristics.
For example, the standardized thermal resistance of floors for Nizhny Novgorod is 4.26 m2°C/W. If you use penoplex to insulate the ceiling, you will need a layer of thermal insulation 12 cm thick
To calculate, it is enough to multiply the indicators 4.26 and 0.038. The last value is the thermal conductivity coefficient of extruded polystyrene foam. The weight of the ceiling is calculated based on the volume of insulation and its density. The first indicator is determined by the product of the area and thickness of the thermal insulation, the second - the table value.
The minimum load on the ceiling is exerted by polyurethane foam and ecowool, their density is in the range of 25-60 kg/cu. m. One of the heaviest insulation materials is expanded clay - 180-330 kg/cu.m. m.