When building any heating system, different types of radiators are used. Any heating system must be designed taking into account the number of radiators and their internal volume. Each radiator section has a certain volume, and when installing a heating system, you need to know for sure the number of sections in the battery. The efficiency and proper operation of the heating system depends on the correct calculation of the number of sections.
What types of heating radiators are there?
Today the following types of radiators are most often used:
- cast iron radiators;
- aluminum alloy radiators;
- bimetallic radiators.
Types of heating batteries
Standard
These units are available in a range of heights, typically from 300mm to 750mm, with the largest range of lengths and height configurations ranging from 450mm to 600mm high. Lengths vary from 200mm to 3m or more, with the largest range being 450mm to 2m in length.
Panels and convectors
Such radiators usually consist of one or two panels, but sometimes 3-panel ones are found. Modern single panel radiators have a corrugated panel forming a series of fins (called "convectors") attached to the rear (wall-facing) side of the panel, which increases the convection power of the battery. They are commonly known as "single convector" (SC). Radiators consisting of two panels with fins stacked on top of each other (with fins in the middle) are known as "dual convector" (DC). There are also double radiators, consisting of one finned panel and one without fins. Older design radiators consisted of one or two panels without any convection fins.
A traditional standard radiator has seams on the top, sides and bottom of each panel (where the pressed sheets of steel are joined together). Nowadays, most seamed batteries are sold with decorative panels installed on the top and sides (the top ones have vents for air circulation) and are known as "compact" batteries. An alternative to the top seam radiator design uses a single sheet of pressed steel and this sheet is joined in a "roll" fashion at the top of the radiator.
Low surface temperature batteries
Most of these radiators are designed so that their radiating surfaces have relatively low temperatures at normal heating system temperatures. They are used where there may be a risk of burns - most often in children's institutions, nursing homes, hospitals and hospitals.
Designer batteries
There is a huge selection of radiator designs available that can be more pleasing to the eye than their conventional counterparts. Some designer radiators are available in tall, narrow configurations which may be suitable for rooms with, for example, narrow walls near doors where conventional radiators cannot provide sufficient power with limited wall space available.
Skirting radiators
These devices are usually disguised as baseboards. The operation of these radiators is similar to the effect of a “warm floor”, since the user’s eye does not notice any radiator sections on the walls. Installing skirting boards allows you to save interior space.
Heated towel rails
Such radiators are specially designed for drying towels, as well as for drying bathtubs and showers. However, the thermal output of heated towel rails is significantly reduced when covered with towels, and even if they are not covered with towels, heated towel rails are able to dissipate much less heat than conventional radiators of similar size. Heated towel rails are usually not enough to heat rooms. They are used only in relatively small and well-insulated bathrooms. Some heated towel rail designs contain a regular radiator with towel racks above and sometimes on the sides of the radiator. Such devices have better thermal power.
Storage and wear processes
In order to reduce the risk of deterioration of battery performance during long-term storage, you must adhere to the following rules:
- do not allow complete discharge;
- storage temperature is not lower than -20 °C and not higher than +30 °C;
- charge annually for 48 hours;
- The battery surface must be clean to avoid self-discharge.
The main processes that destroy a lead-acid battery:
- Sulfation is the formation of crystals of lead salts. They are deposited on the plates and prevent the normal passage of current.
- Corrosion is an oxidative process that destroys the lead electrodes of a battery.
- Shedding - the active mass in the cells of the positive electrodes loses normal adhesion to the base and falls off.
- Adhesion defects also lead to the sliding of the powdery contents of the conductive plates.
Failed batteries cannot be repaired and must be recycled. Vapors of heavy metals can cause serious harm to humans and the environment, so artisanal smelting of lead from batteries is life-threatening.
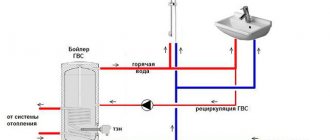
The amount of coolant in the heating battery
The correctly selected volume of coolant in the section allows the heating radiator to operate most optimally. The amount of water in the radiator affects not only the operation of the boiler, but also the efficiency of all elements of the heating system. The most rational selection of other equipment included in the heating system also depends on the correct calculation of the volume of water or antifreeze.
The volume of coolant in the system also needs to be known in order to select the correct expansion tank. For houses with a central heating system, the volume of radiators is not so important, but for autonomous heating systems, the volume of water in the radiator sections needs to be known for certain. You also need to take into account the volume of the heating system pipelines so that the heating boiler operates in the correct mode. There are special tables for calculating the internal volume of heating system pipelines. You just need to correctly measure the length of the heating circuit pipes.
Today, radiators made of bimetal and aluminum alloy are most in demand. A bimetallic radiator section with a height of 300 millimeters has an internal volume of 0.3 l/m, and a section with a height of 500 millimeters has a volume of 0.39 l/m. The radiator section made of aluminum alloy has the same indicators.
Radiators made of cast iron are also still in use. An imported cast iron section with a height of 300 millimeters has an internal volume of 0.5 l/m, and the same section with a height of 500 mm already has an internal volume of 0.6 l/m. Domestic cast iron batteries with a height of 300 mm have an internal volume of 3 l/m, and a section with a height of 500 mm has a volume of 4 l/m.
Water or antifreeze
Ordinary water is most often used as a coolant, but antifreeze and distillate are also used. Antifreeze is used only if the residence in the house is not permanent. Antifreeze is needed when the heating system does not work in winter. Using antifreeze as a coolant is much more expensive than using ordinary water. In order not to spend extra money when using antifreeze as a coolant, you need to know exactly the volume of the heating system. You should count the number of radiator sections and calculate the volume of heating batteries using the above parameters. The volume of the pipeline is determined using a special table. But to do this, you first need to measure the length of the pipes with a regular tape measure.
At the end of the calculations, the volume of pipelines and the volume of heating radiators are added together, and based on these data, the required amount of antifreeze is purchased. This data will also be useful for determining the amount of water to be used in the heating system. This information will allow you to configure the heating boiler, as well as other elements of the heating circuit, in the most flexible way.
How can you tell if there is not enough water in the heating system?
To do this, carefully unscrew the tap with a screwdriver or wrench. It is necessary to place a special container under the radiator to prevent water
on the floor.
water
will immediately flow out of it . If there is air, there will be a hissing sound.
Interesting materials:
How did the word Russian come about? How to perform a morphological analysis of a word? How is an unstressed vowel at the root of a word checked? How to check the unstressed vowel in the word forty? How to check for an unstressed vowel in the word water? How to check if the root of a word is unstressed? How to check the vowel at the root of a word? How to check the spelling of an unstressed vowel at the root of a word and prove it using an example? How to check the spelling of an unstressed vowel sound at the root of a word, examples? How to check the spelling of paired consonants in the middle of a word and at the end?
Average data
If for some reason the user cannot determine the exact volume of water or antifreeze in heating radiators, then average data that is applicable to heating radiators of certain types can be used. If, say, we take a panel radiator of the 22nd or 11th type, then for every 10 cm of this heating device there will be 0.5-0.25 liters of coolant.
If you need to determine “by eye” the volume of a cast iron radiator section, then for Soviet models the volume will range from 1.11 to 1.45 liters of water or antifreeze. If the heating system uses imported cast iron sections, then such a section has a capacity of 0.12 to 0.15 liters of water or antifreeze.
There is another way to determine the internal volume of the radiator section - close the lower necks, and through the upper ones, pour water or antifreeze into the section to the top. But this does not always work, since aluminum alloy radiators have a rather complex internal structure. In such a design, it is not so easy to remove air from all internal cavities, so this method of measuring internal volume for aluminum radiators cannot be considered accurate.
Heater Rado
Panel heaters from this German company are the best option for cost-quality ratio.
Steel radiator type 22, 500x1000 mm Rado, has a power of 1826 W when the media is heated to +110 degrees and a permissible pressure of up to 9 Bar (test 14).
This is truly a panel radiator of the highest quality, as it is made from environmentally friendly steel produced in Europe.
The steel heating radiator type 22 (500x1000) has a low weight with high heat transfer and two convectors, which allows you to heat the room in a short time, saving energy costs.
Correct calculation
You also need to take into account the fact that the heat exchanger of the heating boiler also holds a certain amount of coolant. The heat exchanger of a wall-mounted heating boiler can hold from 3 to 6 liters of water, and floor heating devices can hold from 9 to 30 liters.
Having determined for certain the internal volume of all heating radiators, pipelines and heat exchanger, you can proceed to selecting an expansion tank. This element of the heating system is very important, since maintaining optimal pressure in the heating circuit depends on it.
Dimensions
The size of the bimetallic radiator sections is determined by the distance from the middle of the inlet to the middle of the outlet. Today batteries are manufactured with the distance between the specified holes
:
- 200 mm;
- 350 mm;
- 500 mm.
To calculate the full dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators, you need to add 8 centimeters to this indicator. The resulting sizes are 28, 43 and 58 centimeters.
Dimensions of bimetallic heating batteries
Before choosing the required dimensions of the heating radiators, you should remember that from the floor to the bottom of the radiator there should be at least 12 cm, and from its top to the protruding part of the window sill - at least 10 cm. Otherwise, there will not be sufficient air circulation, which will reduce the heat transfer efficiency of the device.
The section width ranges from 80 to 90 mm. Thickness – from 80 to 120 mm. Height, width and thickness affect the energy output of the battery.
Conclusion
The correct operation and efficiency of the heating system, as well as the optimal operation of other elements of the system, depend on the accurate determination of the full volume of the heating system. The most important thing in correctly determining the volume of the heating circuit is that each heating boiler is designed for a certain volume of coolant. If the volume of the heating system is excessive, the boiler will work constantly. This will significantly reduce the service life of the heating device and entail unplanned costs. The volume of the heating circuit must be calculated correctly.
Main types of steel radiators
Steel is ideal for the manufacture of radiators due to its flexibility, strength, ductility, and wear resistance. These devices may differ in their shape and design. Based on the principle of their design, they can be divided into tubular and panel.
As for tubular steel radiators, they consist of rectangular or round pipes, and panel ones - of 1-2-3 panels. To make a decision on choosing the optimal type of heating device, you need to fully understand the technical and design features of each of them.
Forced initiative
In a panel house with central heating, you don’t have to worry about issues such as filling the system with coolant; this is the diocese of housing and communal services. But taking care of your estate or dacha is a huge responsibility that rests entirely on your shoulders. The opportunity to save time and money forces owners to maintain thermal communications themselves, sometimes using non-standard methods.
In the photo - checking the battery operation
Summarizing
The principle is better to underfill than the opposite; it is not applicable in heating systems, since airing the system will mean cold radiators. By calculating the quantity of each structural element of the heating system using tables or a skillful method, heat consumption will become more meaningful and enjoyable. And the repair or replacement of a separate fragment will no longer be a sealed secret.
The video in this article demonstrates the process of pouring coolant into the heating system.
Section capacity
The specific design of radiators determines their rather low capacity. This is both good and bad.
A small container does not require a large amount of coolant (hot water), which means it saves water and fuel to heat it. But the less coolant, the faster the radiator cools. Here, rapid cooling does not occur, since between the water and the aluminum surface there is also a steel shell that does not cool down for a long time.
Joining two metals
A small container contributes to rapid contamination and clogging of channels when using low-quality water. To solve this problem, a cleaning system is installed in a private house. The minimum requirement is to install two filters: fine and coarse.
The volume of one section depends on its size
:
- with a distance between the inlet and outlet openings of 500 mm, the section capacity will be 0.2–0.3 liters;
- with a distance of 350 mm, the capacity will be 0.15–0.2 liters;
- a distance of 200 mm guarantees a volume of 0.1–0.16 liters.
Calculation of the volume of a heat accumulator
In some heating systems, auxiliary elements are installed, which can also be partially filled with coolant. The most capacious of them is the thermal accumulator.
The problem in calculating the total volume of water in the heating system along with this component lies in the configuration of the heat exchanger. In fact, the heat accumulator is not filled with hot water from the system - it serves to heat it from the liquid in it. For correct calculations, you need to know the design of the internal pipeline. Alas, manufacturers do not always indicate this parameter. Therefore, you can use an approximate calculation method.
Before installing the heat accumulator, its internal pipeline is filled with water. Its quantity is calculated independently and taken into account when calculating the total heating volume.
If the heating system is modernized, new radiators or pipes are installed, it is necessary to perform an additional recalculation of its total volume. To do this, you can take the characteristics of new devices and calculate their capacity using the methods described above.
As an example, you can familiarize yourself with the method for calculating an expansion tank:
Easy way
There is another way to determine the volume of coolant, which does not require the possession of any information. Everything is extremely simple. Close all the caps on the battery and fill it with water using a measuring container. At the same time, naturally, you count how much liquid got in.
At the end of the procedure, drain everything accumulated from the radiator. Of course, all these operations must be performed either in the bathroom or in the yard so as not to flood the house. Based on the obtained indicator, you can easily navigate the total volume of coolant for your heating system. Good luck!