Installation of an expansion tank in an open and closed heating system
In modern heating systems, to compensate for the thermal expansion of the coolant, expansion tanks of an open or closed type are installed, which have special requirements for installation, operating conditions and have various advantages and disadvantages.
In this article we will consider the main points of choosing and installing an expansion tank in a heating system with forced and natural circulation of coolant.
The main parameter of the tank is its useful volume, which must exceed the change in the volume of the system liquid as a result of the maximum change in its temperature.
The volume of liquid in the heating system is not constant, since the coolant can expand and contract during operation. Heating of the coolant, and accordingly an increase in its volume at a constant size of the internal space of the heating system, leads to an increase in pressure on the walls of pipelines and heating equipment, which can cause their destruction.
To compensate for changes in the volume of liquid and stabilize the pressure on the internal walls of the components of the heating system, an expansion tank (also known as an expansomat, from the English verb “expanse”, which means “to expand”) is introduced into its circuit. When the coolant expands, its quantity, exceeding the volume of the internal space of the system, enters the expander, and after the temperature drops, it returns back.
How many liters of water are in a pipe with a diameter of 50, 32, 20, 16 mm (1 meter long)?
The volume of coolant in various pipelines, such as low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE pipe), polypropylene pipes, metal-plastic pipes, steel pipes, must be known when selecting any equipment, in particular an expansion tank.
For example, in a metal-plastic pipe with a diameter of 16, a meter of pipe is 0.115 g. coolant.
Did you know? Most likely no. And why should you know this until you are faced with the selection of, for example, an expansion tank. Knowing the volume of coolant in the heating system is necessary not only for selecting an expansion tank, but also for purchasing antifreeze. Antifreeze is sold undiluted to -65 degrees and diluted to -30 degrees. Once you know the volume of coolant in the heating system, you can buy an even amount of antifreeze. For example, undiluted antifreeze must be diluted 50*50 (water*antifreeze), which means that with a coolant volume of 50 liters, you.
In order to find out how much liquid is in one meter of pipe, there are special tables, including those attached to the pipes. For example, in one meter of pipe with an internal diameter of thirteen point two millimeters, the liquid volume will be zero point one hundred thirty-seven thousandths of a liter. But for example, for a pipe with an internal diameter of about seventy millimeters, the volume of liquid will be about four liters. Thus, knowing the length of the pipeline, you can obtain the final value by multiplying the volume of liquid per meter of pipe by the entire length of the pipeline. It should also be taken into account that in addition to the pipeline, the liquid in the system is also contained in radiators, manifolds, and other units and fittings.
To find out the amount of water in a pipe, you can, of course, calculate the area, then the volume, and then calculate how much there is in total, but you can do it much simpler.
You need to know what kind of pipe you have and its.
Sometimes it is necessary to calculate the amount of water that is in a heating pipe or water supply pipe, or simply calculate the volume of the pipe. So the pipe is a geometric figure - a cylinder, but of great height, in the case of a pipe it is length. To calculate how much water is in the pipe, you need to use the formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder. The volume of the cylinder is calculated as follows.
The widespread use of metal-plastic pipes in domestic water supply and heating systems has become possible thanks to a unique design that combines the positive features of metal and plastic pipes at the same time.
Metal-plastic pipes - the technical characteristics of which, despite the popularity of the products, are not familiar to everyone, are distinguished by high anti-corrosion properties, flexibility and remain just as durable. In this article we will give a more detailed description of metal-plastic pipes, describe their structure and features of use.
Metal-plastic pipes and fittings for their connection
Construction of metal-plastic pipes
Composition of metal-plastic pipes
The base of a metal-plastic pipe is the inner layer of polyethylene, which gives the pipe strength and performs a load-bearing function.
A layer of aluminum foil is attached to it using an adhesive composition, which prevents diffusion.
Correctly determining the diameter of the pipes for the internal pipeline is no less important than choosing the material for the pipes. After all, the insufficient diameter of the pipes causes turbulence (tortuosity) of the water flow in them
As a result, the movement of water in the pipe will be accompanied by strong noise, and large quantities of lime deposits will be deposited on its inner surface.
You need to know that two meters per second is the maximum speed of fluid movement in the plumbing system. This is what you need to base your calculations on when choosing the diameter of the pipes for the water supply. Based on this, the following main dependencies are determined.
How does the length of the pipeline affect the choice of pipe diameter?
• If the length of the pipeline is less than ten meters, then a pipe diameter of 20 mm will be sufficient. • A pipeline length of more than thirty meters requires the use of pipes with a diameter of 32 mm. • For a pipeline whose length is from 10 to 30 meters, it is better to use.
Recommendations from experts
A closed expansion tank does not have to be installed at the highest point of the system.
The main advantage of membrane expansion joints lies precisely in the possibility of placing it in the place most convenient for installation and operation.
Small tanks with a volume of 20-25 liters are usually installed in systems with a circulation pump whose power is 1.2 kW. Increasing the capacity to 20-60 liters will lead to an increase in pump power to 2.0 kW.
There are compensating devices with a volume of 100-200 liters on sale. In addition to their direct purpose, they can play the role of a storage tank for warm water. True, they can be used in this way only if the main source of hot water is turned off for a short period of time.
The standard sizes of expansion tanks cover a fairly wide range. Among them there are models with dimensions so large that standard doorways do not allow them to be brought inside the room. In such a situation, it is better to replace one huge container with several small ones. The main thing is that their total volume is equal to the calculated one.
Installation work
Strict adherence to installation rules when equipping an open or closed heating system with an expander will ensure the safety and efficiency of the equipment.
Installation of an open type expansion tank
It has already been said above that the expansion tank for an open system is mounted at the highest point. This requirement is due to two factors:
- The coolant rises into the expander and drains it back into the heating system by gravity, because there is usually no circulation pump in such systems.
- This arrangement of the expansion tank allows it to effectively carry out its additional function - air removal. Bubbles always rise to the top.
Connection diagram for a membrane tank in an open type heating system
A special feature of installing an expander in an open system is that there is no need to equip the tank with shut-off valves. As a rule, the tank is supplied with only two pipes, through one of which the coolant enters the container, and through the other it returns to the system. Even the presence of a lid on the tank is not essential, although its absence can lead to an increase in the loss of water volume from evaporation, as well as the entry of debris and dust into the system.
Installation of a closed tank
Installing an expansion tank for heating in closed systems is somewhat more complicated, since it is a completely sealed device. Unlike open expanders, which users often make on their own, such units are created only in the factory, so you will have to buy an expansion tank for the heating system if you have this type.
The photo shows an expander in a closed heating system
There are several rules by following which you can install a heating expansion tank correctly.
- In most cases, expanders of closed systems are installed on the return line in front of the circulation pump, if we consider the sequence of elements along the flow of the coolant. If for some reason such an installation is impossible, select a section where the flow parameters are close to laminar flow. The main and mandatory requirement is the horizontal location and straightness of the strapping section.
- The best option would be to purchase and install a tank with a safety valve. This additional device is designed to relieve pressure if its value exceeds the maximum permissible value. This increases the safety of equipment operation, however, you should be aware that if there is an error in the calculations (to a lesser extent) of the volume of the expansion tank, the safety valve will operate too often. A solution to the problem may be replacing the expander with a more capacious one or parallel installation of an additional tank.
- For ease of monitoring the operation of the system, it is best to equip the expansion tank with a pressure gauge during installation.
Selection of volume
Let's consider separately how to calculate an expansion tank for heating of sealed and open types.
Since the design and principle of operation of such tanks are completely different, although both perform the same function. Open tank
The dimensions of the expansion tank for an open heating system, by and large, determine its volume, since the design of such a tank is quite simple. It is made from sheet metal. There is a hole in it through which the coolant enters and goes back into the pipes. They can also be equipped with an overflow hole through which excess water is discharged into the sewer.
It happens that automatic recharge is supplied to the tank. But the main thing is how the expansion tank in the heating system is designed, or rather, its volume. Let’s take the same system with one hundred liters of water. After heating, the liquid will increase by five percent, maybe more, depending on the temperature in the circuit. It turns out that the volume of the expansion tank for this open heating system should be at least five liters, preferably more. And the calculation of the expansion tank for the heating system comes down to the following algorithm:
- five liters is the expansion of water;
- a couple of liters should always be in the tank - this is to prevent air from entering the circuit;
- We need to make three liters in reserve.
Based on the results of calculating the volume of the expansion tank for heating, ten liters are obtained. By the way, this is the simplest and most common method of selection - ten percent of the amount of water in the circuit.
For closed systems, in addition to the simple, folk method of calculating the volume of the expansion tank of a heating system, there are more accurate methods. To use them, you need to know several meanings. These include:
- How much does the volume of water (W) increase when heated? Answer: five percent. The value is rounded to the nearest whole number without fractions for convenience. If a non-freezing liquid, antifreeze, circulates in your circuit, then this value will be greater;
- how much water is in the circuit (VC). Such data should already be available from the design stage. Since the selection of the heater is carried out based on this value. If it happens that you don’t know how many liters there are, all you have to do is measure. The first thing that comes to mind is to completely drain all the liquid from the circuit and fill it again. The number of liters can be measured in buckets, or you can use a special counter that is installed on the stream;
- What is the maximum pressure the circuit and boiler (DC) are designed for? This value can be read in the heater documents, or on the heater itself. It is unlikely that there will be no documents or information on the boiler body. But if this happens, then the Internet will help you;
- what is the pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank (DB). This is also indicated in the technical documentation.
To calculate how much expansion tank volume is needed for heating, you should perform a simple mathematical calculation:
OB x VK x (DK + 1) / DK – DB
Based on the results of calculating the capacity of the expansion tank for heating, you will receive the exact value. The question of the appropriateness of such complex calculations remains open. Undoubtedly, according to the results of this formula for calculating the expansion tank of the heating system, the result will be a smaller value than according to the results of the “folk” method. But an error on the larger side is not an error. If the tank is larger than necessary, it’s okay, you just need to configure it correctly.
Useful tips
It should be remembered that installing an expansion tank in a heating system involves selecting, purchasing and installing a model with a red body. Models painted blue are designed for cold water supply. Structurally, the expanders do not differ from each other, but the red ones are designed for prolonged high-temperature exposure. Despite the generally accepted practice of using a circulation pump only for closed systems, the presence of a pumping unit does not change the state of the system. That is, if you install a circulation pump on a heating system with an open tank, it will not become closed. It’s just that in open systems there is most often no need for such units. The boiling of the coolant in the heating system has nothing to do with the operation of the expander
Most likely, you should reconsider the slope of horizontal pipelines and the diameters of the pipes used. It is not recommended to install the expander in close proximity to the pump due to possible pressure drop. During installation, only special heat-resistant sealants should be used. When installing the expander, take into account the need for its maintenance and possible repairs and ensure free access to the unit. Some boiler models are already equipped with expansion tanks and then there is no need to purchase one additionally.
Rules for selecting an expanzomat
Most developers, especially those who are faced with the creation of autonomous heating systems for the first time, are interested in the question: “How to choose an expansion tank for a heating system?”
Competent selection of this device can be divided into four stages. The algorithm is as follows:
Determine the required type of expansion tank
Everything is simple here: for open COs - an open tank; for closed ones - a membrane (balloon) tank. Calculate the required tank volume.
Pay attention to the quality of the product. Important points are: the quality of the metal case and paint, which should protect the device from corrosion; presence of an adjustable blast valve; membrane characteristics and availability of an international quality certificate. Tip: Today, a wide range of tanks with a replaceable membrane are available
If funds allow, we recommend choosing just such a model.
Decide on the design, size and shape of the device.
On the Russian market of climate control equipment there are containers of various volumes, horizontal or vertical orientations, designed for different operating and maximum pressures
Pay attention to the color of the device: blue – for the water system; red – for CO
And one last thing. Selecting an expansion tank for heating is a rather important process, on which the stability of the CO operation depends. Entrust the choice to professionals.
Open type containers
These tanks are used for an open heating system (otherwise known as gravity, gravity) and are a metal tank with an open top of any shape. A pipe for connecting a hose or overflow pipe is welded to the upper part of the side wall; the coolant is supplied to the tank from below. The element is installed above the entire system on the supply pipeline, usually in the attic of the house.
Any expansion tank for open type heating performs 2 functions:
- serves to compensate for the expansion of the coolant;
- removes air from the system, since its top communicates with the atmosphere.
This is its advantage, but it is not the only one. An open container can also successfully and durablely serve in systems with forced circulation, since the design of the tank is very simple, there is nothing to break. However, it also has many disadvantages:
- a tank installed in the attic requires good insulation;
- During the season, it is necessary to constantly monitor the water level in the tank and replenish it in a timely manner;
- the coolant is constantly saturated with oxygen from the atmosphere, which is why the metal parts of the boiler corrode faster;
- additional consumption of materials and difficulties during installation.
General calculations
It is necessary to determine the total heating capacity so that the power of the heating boiler is sufficient for high-quality heating of all rooms. Exceeding the permissible volume can lead to increased wear of the heating device, as well as significant energy consumption.
The required amount of coolant is calculated according to the following formula: Total volume = V boiler + V radiators + V pipes + V expansion tank
Boiler
Calculating the power of the heating unit allows you to determine the boiler capacity indicator. To do this, it is enough to take as a basis the ratio in which 1 kW of thermal energy is enough to effectively heat 10 m2 of living space. This ratio is fair in the presence of ceilings whose height is no more than 3 meters.
As soon as the boiler power indicator becomes known, it is enough to find a suitable unit in a specialized store. Each manufacturer indicates the volume of equipment in the passport data.
Therefore, if the correct power calculation is performed, there will be no problems with determining the required volume.
Pipes
To determine the sufficient volume of water in the pipes, it is necessary to calculate the cross-section of the pipeline according to the formula - S = π × R2, where:
- S – cross section;
- π is a constant equal to 3.14;
- R is the inner radius of the pipes.
Having calculated the cross-sectional area of the pipes, it is enough to multiply it by the total length of the entire pipeline in the heating system.
Expansion tank
You can determine what capacity the expansion tank should have by having data on the coefficient of thermal expansion of the coolant. For water this indicator is 0.034 when heated to 85 °C.
When performing the calculation, it is enough to use the formula: V-tank = (V system × K) / D, where:
- V-tank - the required volume of the expansion tank;
- V-syst - the total volume of liquid in the remaining elements of the heating system;
- K – expansion coefficient;
- D – efficiency of the expansion tank (indicated in the technical documentation).
Radiators
Currently, there is a wide variety of individual types of radiators for heating systems. In addition to functional differences, they all have different heights.
To calculate the volume of working fluid in radiators, you must first count their number. Then multiply this amount by the volume of one section.
You can find out the volume of one radiator using the data from the product technical data sheet. In the absence of such information, you can navigate according to average parameters:
- cast iron - 1.5 liters per section;
- bimetallic - 0.2-0.3 l per section;
- aluminum - 0.4 l per section.
The following example will help you understand how to correctly calculate the value. Let's say there are 5 radiators made of aluminum. Each heating element contains 6 sections. We make the calculation: 5 × 6 × 0.4 = 12 liters.
Types of expansion tanks
As you know, for heating private housing, different principles of coolant supply can be used - natural and forced circulation. For each type of system, its own modifications of the expansion tank are used:
- Open. In a natural circulation infrastructure, additional capacity is installed at the highest point and takes the form of an open tank. The pressure in the pipes is equal to atmospheric pressure, and air bubbles are released through the tank and, if necessary, water is added.
- Closed. If a pump is installed in the heating line to circulate the coolant, a sealed metal cylinder with compressed air acts as an expansion tank. When heated, excess coolant is supplied to the tank, and when the temperature drops, air pressure displaces the liquid back.
A closed expansion tank provides significant advantages over an open one. Its installation can be done in any convenient place; the lack of contact with the atmosphere protects the internal space of pipes and heating radiators from corrosion and the penetration of dirt and small debris. However, the final decision on choosing the type of expansion tank is usually dictated by the design of the heating system as a whole, and not by these important, but not decisive, advantages.
Installation
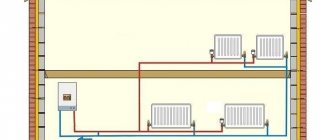
Installation diagram of a tank in a private house system
If you are confident in the calculations and your own abilities, the tank and all materials have been purchased, then you can install the container yourself.
Tools you will need:
- Step and adjustable wrenches;
- Soldering device for plastic pipes;
- Wrench for installing plastic pipes;
- In some cases, a welding machine and an angle grinder are needed.
Before installation, you need to turn off the power to the boiler, turn off the valves and drain the coolant if it is already in the pipes.
The installation is carried out taking into account certain rules.
- The tank must be mounted and installed so that it can be easily approached for adjustment and maintenance.
- The room temperature should not be below 0.
- A pre-shut-off valve must be installed on the supply pipe, which will allow the expander to be removed for maintenance and repair.
After installing the tank, you need to start the entire heating system. If boiling is detected in it, then the reason lies in the incorrectly selected pipe diameter. It's not about the tank. The installation of the expansion tank is described in the following video:
Volume calculation
You can calculate the volume of the tank yourself using several online calculators, or using a fairly simple formula:
Vtank=(Vsystem * k)/(1-Pmin /Pmax), where
Vtank – tank volume;
Vsyst – the total volume of the heating system, including all radiators, heated floors, boiler, etc.;
k is the expansion coefficient of the liquid; for water, its values, depending on heating from 10° to the maximum temperature of the coolant, are indicated in the table below;
Pmin – initial pressure in the container;
Pmax is the maximum possible pressure in the tank, which is calculated from the settings of the safety valve, taking into account the difference in the heights of the tank insert and the valve.
Table. The coefficient of expansion of water depending on heating at an initial temperature of 10 o C.
| Temperature from 10 | k value, % |
| Up to 40 | 0,8 |
| Up to 50 | 1,2 |
| Up to 60 | 1,7 |
| Up to 70 | 2,3 |
| Up to 80 | 2,9 |
| Up to 90 | 3,6 |
| Up to 100 | 4,3 |
| Up to 110 | 5,2 |
Since the quality of operation of the entire heating system depends on the correctness of the calculations, you should not spare money and contact a special organization that will take into account all the parameters, which will allow you to purchase the most suitable tank. Here you can be given advice on choosing and installing a tank.
How to correctly calculate the volume of a tank for heating systems?
To correctly calculate the volume of the expansion tank, several factors are taken into account that influence this indicator:
- The capacity of the expansion machine directly depends on the amount of water in the heating system.
- The higher the permissible pressure in the system, the smaller the tank you will need.
- The higher the temperature to which the coolant is heated, the larger the volume of the device should be.
Reference. If you choose an expansion tank that is too large, it will not provide the required pressure in the system. A small tank will not be able to contain all the excess coolant.
Calculation formula
Vb=(Vс * Z)/N, in which:
Vc is the volume of water in the heating system. To calculate this indicator, multiply the boiler power by 15. For example, if the boiler unit power is 30 kW, then the amount of coolant will be 12*15 = 450 liters. For systems where heat accumulators are used, the capacity of each of them in liters must be added to the resulting figure.
Z is the coolant expansion index. This coefficient for water is 4%, so when calculating we take the number 0.04.
Attention! If another substance is used as a coolant, then the corresponding expansion coefficient is taken. For example, for 10% ethylene glycol it is 4.4%
N is an indicator of the efficiency of tank expansion. Since the walls of the device are made of metal, it can slightly increase or decrease in volume under pressure. To calculate N, you will need the following formula:
N= (Nmax—N)/(Nmax+1), where:
Nmax is the maximum pressure in the system. This number is from 2.5 to 3 atmospheres; to find out the exact figure, look at what threshold value the safety valve is set to in the safety group.
N is the initial pressure in the expansion tank. This value is 0.5 atm. for every 5 m height of the heating system.
Continuing the example with a 30 kW boiler, let’s assume that Nmax is 3 atm., the height of the system does not exceed 5 m. Then:
N=(3—0.5)/(3+1)=0.625;
Vb = (450*0.04)/0.625 = 28.8 l.
Important! The volumes of expansion tanks available on the market meet certain standards. Therefore, it is not always possible to buy a tank with a capacity that exactly matches the calculated value
In such a situation, purchase a device that is rounded up, since if the volume is slightly less than necessary, it may harm the system.
Types of expansion tanks
Depending on what type of heating system the tanks are used in, they are divided into 2 types.
Open type
Such a tank is used for open heating without the use of forced circulation. It is a container without a top. There is a hole at the bottom of the tank; a heating pipeline is connected to it using a thread.
In some houses you can still find a container; it copes with its function, but is quite outdated and has a number of disadvantages:
- the need to place the tank at a height;
- evaporation of liquid from the container;
- acceleration of corrosion processes in different parts of the heating system due to contact of the coolant with air;
- large tank sizes.
Due to these disadvantages, closed expansion tanks are now becoming increasingly popular.
Closed type or membrane
Such tanks are used for heating systems with forced circulation. The container compensates for the pressure surge not only when the coolant heats up, but also when the circulation pump is turned on.
It is also called a membrane-type tank due to the peculiarities of its internal structure. This is a spherical or flat tank, which inside is divided into two cavities by a rubber membrane:
- one is filled with coolant through a threaded pipe;
- the other - with inert gas or air.
The second container has a nipple that regulates the gas pressure. The compartments do not connect to each other.
The operating principle of a closed tank is simple:
- excess hot coolant enters one of the chambers, the volume of which increases;
- the pressure in the gas compartment increases, which makes it possible to compensate for the voltage in the heating system.
When the coolant cools down, the process in the tank follows the reverse path.
There are 2 types of closed containers depending on the membrane:
- In some, the membrane is made in the form of a diaphragm that cannot be changed. Such containers are cheaper.
- In the second type of closed devices, the membrane is removable and has the shape of a pear.
The choice depends on the capabilities of the buyer. It should be taken into account that damage to this rubber element occurs quite rarely.
Before purchasing a tank, you need to decide on its volume.
How to calculate the volume of an expansion tank for closed heating
The heating system of a private home must be equipped with all the elements necessary for proper operation.
Attempts to do without some “unimportant” devices lead to emergency situations requiring serious repairs and restoration.
Moreover, even the complete presence of the necessary parts of the circuit will not ensure normal operation if they are selected incorrectly and do not match the characteristics.
All components must be carefully calculated and selected according to the data obtained.
The expansion tank is an element that protects the system from rupture if the permissible pressure is exceeded.
Being left without heating in the winter is a serious problem (read about repairs and diagnostics of plumbing problems in the bathroom here).
Therefore, reliable and correct operation of the expansion tank is a vitally important task.
Volume calculation
Still, the basis of choice is volume. Let's look at the dependence of the volumetric parameter of the device and those indicators that affect its changes:
- The greater the volume of coolant in a closed heating system. the larger the expansion tank you need to purchase.
- The higher the temperature of the coolant, the greater the capacity of the device.
- The higher the coolant pressure (the permissible value of the indicator is taken), the smaller the container can be purchased.
Three main dependencies. Now you can proceed directly to the calculation. Let's face it, this is not an easy matter, but it's worth dealing with. Because a small deviation can lead to unpleasant consequences. For example, a safety valve will continually reset.
So, the formula by which the calculation is carried out:
Vb=(Vc * K)/D, where
Vb is the capacity of the device.
Vc is the volume of coolant in the heating system.
K is the expansion coefficient of the coolant. For water, this figure is 4%, so the formula uses 1.04.
Table with formulas
D is the expansion efficiency of the tank itself. Made of metal and under the influence of temperature changes, it can slightly change its dimensional parameters. To accurately determine “D” you can use the following formula:
D = (Pmax - Pstart)/ (Pmax + 1), where Pmax is the maximum pressure inside the heating system, Pstart is the pressure inside the tank, planned by factory parameters (usually 1.5 atm.). By the way, it is planned to adjust the safety valve according to the maximum indicator.
It turns out that the volume of the expansion tank depends on the strength and temperature characteristics of the device itself. Please note that all these indicators and characteristics should not exceed acceptable standards. The volume of the expansion device should be equal to or slightly larger than the results obtained.
Calculation methods
Each installation is selected in accordance with the size of the expected load, which will require preliminary calculations.
Knowing how to calculate the volume, the owner will be able to choose the right tank. To choose the right expander, you will need to know:
- heating boiler volume;
- additional devices;
- all pipes included in this heating system.
Next, let’s designate the required indicators with any letters, for example, A is the desired value, B is the efficiency of the membrane equipment, C is the constant expansion rate of the coolant water, and AO is the total volume of the heating system. Next, we calculate using the following formula: A = (AO * C) / B.
Sizing
The final value is rarely absolutely accurate, so approximate calculations are made, and the resulting number will be a guideline for choosing a unit, which should be taken with a margin to the obtained number, leaving at least 3% for the increase in volume during heating.
If a membrane type has been selected, the operating potential of the membrane may be indicated by the manufacturer, but you can make your own calculation. To do this, take the most permitted indicator of pressure inside the system (AB), data on the pressure of the initial filling of the expander (BC) and calculate the desired value (T). Use the following formula: T = (AB – BC) / (AB + 1).
If you do not make calculations and take the equipment “at random,” you may encounter some problems during operation of the device. The main purpose of the expander is to pump out excess liquid with a strong increase in pressure (moisture expands, requiring the excess to be removed from the pipeline). After everything has stabilized, the liquid is compressed back, it must be returned to the pipes, otherwise there will not be enough of it to maintain the temperature. Therefore, identifying differences in the internal pressure of the heating system indicates an imminent breakdown.
Tank too small
If the volume of the installed expander is insufficient, the pressure will increase too much and the automatic valve will operate. It will remove excess moisture, stabilizing the operation of the system. But then everything will return to normal, and the water will no longer be enough to continue proper heating. Additional refueling will be required. A lack of heating fluid will lead to the boiler shutting down, since at low levels the device cannot continue to function. Because of this, pipes may freeze in winter. Breakdowns will occur again and again until the optimal size expander is installed.
Excessively large tank
Installing a tank that is too large is also dangerous. When taking part of the moisture from the pipes, the expander must maintain the optimal permissible operating pressure, which is simply impossible if the dimensions are too large. The unit will constantly show the maximum permissible load without crossing the very line when the valve should operate. This means that the device operates at its maximum potential level, which will quickly lead to breakdown.
Types of tanks
Expansion tanks can be of two types - open and closed. For the first type of tank, no calculations are required; in fact, it is a bucket half filled with coolant, installed in the highest part of the heating system, with a hole through which excess air escapes when the coolant expands. Open tanks are considered obsolete and have a number of disadvantages, so it is more advisable to take on the calculation and installation of a closed type expansion tank.
A closed expansion tank is installed in systems equipped with a pump, which is responsible for circulating water in the heating system. A closed tank is a container divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. At the bottom of the tank there is coolant, and at the top there is air.
When the heating system heats up, the coolant expands and its excess rises into the lower compartment of the expansion tank. Next, the membrane rises upward, compressing the air chamber and thereby maintaining the system pressure level at normal. When the temperature of the coolant decreases, the pressure in the system also decreases, which entails a decrease in the level of coolant in the tank.
After installing the tank, its upper chamber is filled with air using a pump; the pressure in the air chamber must be equal to the initial pressure in the entire system.
How to choose the right device?
The main characteristic on the basis of which equipment is selected is its volume. In this case, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Number of people using the water supply system.
- The number of water intake points, which include not only showers and taps, but also household appliances, for example, a washing machine and dishwasher.
- The likelihood that water will be consumed by several consumers at the same time.
- Limit number of start-stop cycles in one hour for installed pumping equipment.
Experts recommend using the following indicators as a guideline when choosing an expansion tank:
- If the number of consumers does not exceed three people, and the installed pump has a capacity of up to 2 cubic meters. m per hour, a tank with a volume of 20 to 24 liters is selected.
- If the number of consumers is from four to eight people and the pump capacity is within 3.5 cubic meters. m per hour, a tank with a volume of 50 liters is installed.
- If the number of consumers is more than ten people and the productivity of the pumping equipment is 5 cubic meters. m per hour, choose an expansion tank of 100 liters.
When selecting the desired device model, it is worth considering that the smaller the tank volume, the more often the pump will turn on. And also the fact that the smaller the volume, the greater the likelihood of pressure surges in the system. In addition, the equipment is also a reservoir for storing a certain supply of water. Based on this, the volume of the expansion tank is adjusted. You should know that the design of the device allows the installation of an additional tank. Moreover, this can be done during the operation of the main equipment without labor-intensive dismantling work. After installing the new device, the volume of the tank will be determined by the total volume of the containers installed in the system.
In addition to technical characteristics, when choosing an expansion tank, special attention should be paid to its manufacturer. The pursuit of cheapness can result in much more significant expenses. Most often, to produce models that are attractive for their cost, the cheapest materials are used, and, as practice shows, they are not always of high quality. The quality of the rubber from which the membrane is made is especially important. Not only the service life of the tank, but also the safety of the water that comes from it directly depends on this.
When purchasing a tank with a replaceable membrane, be sure to check the cost of the consumable element. Very often, in the pursuit of profit, not always conscientious manufacturers significantly increase the price of a replacement membrane. In this case, it will be more appropriate to choose a model from another company. Most often, a large manufacturer is ready to be responsible for the quality of its products because it values its reputation. Thus, it is worth considering models from these brands first. These are Gilex and Elbi (Russia) and Reflex, Zilmet, Aquasystem (Germany).
The volume of the expansion tank for water supply may vary; it is selected based on the needs of the users. If a larger volume is subsequently required, an additional device can be installed
Why do you need an expansion tank?
As we know, water tends to expand when heated. Just like any other liquid in general. The coolant in the heating system is no exception. When a liquid expands, its excess needs to go somewhere. For these heating purposes, expansion tanks were invented.
First of all, let us remember the basic law of physics: when bodies are heated, they increase, and when they cool, they shrink. When heated, the circulating coolant (water) in the system increases in volume by an average of 3-5%. To prevent accidents and maintain the functionality of heating equipment, you need a container that will smooth out the temperature difference and, as a result, the pressure and volume of water. That is, when heated, the tank will absorb excess liquid, and when cooled, it will release it back into the system. Thus, the pressure in the boiler remains within acceptable limits. Otherwise, the automatic protection is triggered and the system stops. Which can be unsafe in severe frosts.
Principle of operation
From the physics course we know that fluid is incompressible.
In the heating circuit, water is used as a coolant.
In the temperature range from 20 to 90 degrees, it changes volume, expanding as it heats up.
If we imagine a heating network as a vessel of complex configuration, then heating the contents will cause the walls to rupture due to expansion of the liquid.
To compensate for this phenomenon, an expansion tank is used, which serves as an additional volume for storing excess coolant.
Having expanded, the water enters the tank, and when cooled (approximate prices for a heating cable for water supply) it goes back into the system.
It is simply impossible to remove excess water, since when it cools, air will fill the void and the circuit will cease to function.
Do you know what to do if water flows from the tank into the toilet. Read this useful article for tips and recommendations from master plumbers on troubleshooting.
The scope of application of asbestos-cement pipes measuring 150 mm is written on this page.
Thus, the expansion tank protects the heating system from both excess and shortage of coolant, compensating for all movements of its volume.
Types of tanks
The heating system can be equipped with one of the types of expansion tanks.
How to choose the right element of the heating system in each individual case? This will be discussed further.
Open type
As the name suggests, an open-type tank is a container with an open top into which coolant can be added. It does not require locking parts, a membrane partition or a lid. But due to the fact that water evaporates in such a container, and its quantity must be constantly monitored (topped up), open-type tanks are gradually being abandoned.
In addition, such heating is characterized by low pressure, and the tank itself is often subject to corrosion. Therefore, today more modern closed-type containers are installed.
Closed type
Closed expansion tanks (diaphragms) are installed in lines with a circulation pump. The highest quality samples are produced in the form of a sealed red container with a rubber membrane inside. Their membrane is made of more durable technical rubber.
Products for hot water supply, the body of which is painted blue, have a lower quality rubber (it is food grade). Such models can withstand pressure less well and wear out faster.
In addition to the main function - compensation of the coolant volume when the temperature drops and its intake during expansion from heating, the membrane controls the liquid level in the heating line, removes air from the system, drains water into the sewer when there is an excess volume and acts as a buffer zone during a pressure surge.
Types of coolants
- Water. The simplest and most accessible resource. Can be used in any heating systems. In combination with polypropylene pipes - an almost eternal coolant.
- Antifreeze. Used to fill systems of irregularly heated buildings.
- Liquids containing alcohol. An expensive option for filling the heating system. High-quality preparations contain at least 60% alcohol, about 30% water, and part of the volume is occupied by other additives. Mixtures of water with ethyl alcohol with different percentages. Non-freezing liquid (down to -30°C with an alcohol content of at least 45%), but dangerous: it can burn, ethyl itself is poisonous for humans.
- Oil. As a coolant today it is used in individual heating devices, but in heating systems it is abandoned: it is expensive and difficult to operate the system, technologically dangerous (long heating of the coolant to a temperature of 120°C and above is required). The advantage is that it really takes a long time to cool down, maintaining the temperature in the room, but the main disadvantage is the high cost of the coolant.
Useful tips when choosing
When purchasing and installing an expander, there are several nuances to consider.
- When choosing a location for installing the tank, it is necessary to take into account that it cannot be installed immediately behind the circulation pump.
- Commercially available tanks come in two colors: red and blue. In the first, the membrane is stronger, but made of technical rubber. Blue tanks are used for water supply; they contain food-grade rubber, but it is less strong and durable.
- When installing, you need to use a special sealant.
- If you decide to go with an open system, then the tank must be placed at the highest point, and when installing the pipeline, the recommended slope must be observed.
- The size of the tank should not be less than the calculated value; a slightly larger volume is allowed. When using forced circulation, the capacity cannot be less than 15 liters.
- Antifreeze can act as a coolant. For a glycol mixture, it is better to choose an expansion tank whose volume is twice as large as the calculated one.
The main advice is to contact professionals, because installing a tank only seems simple. In addition, you cannot do without a special tool.
Selection of device according to calculation
Before you start calculating the membrane, you need to know that the larger the volume of the heating system and the higher the maximum temperature index of the coolant, the larger the volume of the tank itself should be.
There are several ways to carry out the calculation: contacting specialists at a design office, performing the calculations yourself using a special formula, or calculating using an online calculator.
Formula
The calculation formula looks like this: V = (VL x E) / D, where:
- VL – volume of all main parts, including the boiler and other heating devices;
- E – coefficient of expansion of the coolant (in percent);
- D – membrane efficiency indicator.
Determination of volume
The easiest way to determine the average volume of a heating system is by the power of the heating boiler at the rate of 15 l/kW. That is, with a boiler power of 44 kW, the volume of all system lines will be equal to 660 l (15x44).
If antifreeze is poured into the pipes, then they resort to the following calculation:
- 10% - 4% x 1.1 = 4.4%;
- 20% - 4% x 1.1 = 4.8%, etc.
The efficiency rating (D) is based on the initial and maximum pressure in the system, as well as the starting air pressure in the chamber. The safety valve is always set to maximum pressure. To find the value of the efficiency indicator, you need to carry out the following calculation: D = (PV - PS)/(PV+1), where:
- PV is the maximum pressure mark in the system, for individual heating the indicator is 2.5 bar;
- PS – the charging pressure of the membrane is usually 0.5 bar.
Now it remains to collect all the indicators into the formula and get the final calculation:
- VL = 15x44=660 l;
- D = (2.5 – 0.5) / (2.5+1) = 0.58;
- E = 4% = 0.04;
- V = (660×0.04) / 0.58 = 45.5 l.
You can round up the resulting number and choose an expansion tank model starting from 46 liters. If water is used as a coolant, the volume of the tank will be at least 15% of the capacity of the entire system. For antifreeze this figure is 20%. It is worth noting that the volume of the device may be slightly larger than the calculated number, but in no case less.
Operating principle of the expansion tank
The principle of operation of the compensating device is simple; it does not contain any complex technical solutions. However, the slightest error in the calculation can lead to failure of the heating system as a whole.
The internal space of the tank is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. The upper cavity is called the air cavity - air is pumped into it. The purpose of this operation is to create an initial pressure in the container. Water from the system is supplied to the lower cavity. As soon as the membrane takes a stable position - it lies on the surface of the liquid, the system can be considered ready for operation.
Operating principle of a closed expansion tank
The heated coolant expands, and its excess enters the tank, displacing the membrane towards the air chamber. As soon as the water begins to cool, the membrane returns to its original position under air pressure, thereby maintaining the set pressure in the heating system.
An expansion tank that is too large is not able to create the required pressure in the system. The insufficient capacity of the compensating device will not allow it to accept all the excess expanded water.
Therefore, it is so important to correctly calculate the optimal volume of this important element of an autonomous heating system
Tanks with a balloon type membrane.
In this case, the air chamber is located around the perimeter of the entire tank and surrounds the rubber chamber for the coolant. When it arrives, the latter begins to expand like an inflated balloon. Thanks to this tank design, it is possible to more accurately control the pressure in the system.
I would like to note that balloon membranes can be replaced as they wear out, but diaphragm membranes cannot be replaced. The material from which the membrane is made is very important. It must have heat resistance and at the same time high elasticity. When choosing a tank, you should familiarize yourself with such membrane characteristics as durability, operating temperature, water resistance and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards.
Expansion tank operation diagram
How to install the tank correctly
When installing an open tank in the attic, a number of rules must be followed:
- The container should stand directly above the boiler and be connected to it by a vertical riser of the supply line.
- The body of the product must be carefully insulated so as not to waste heat heating a cold attic.
- It is imperative to organize an emergency overflow so that in an emergency situation hot water does not flood the ceiling.
- To simplify level control and make-up, it is recommended to install 2 additional pipelines into the boiler room, as shown in the tank connection diagram:
Note. It is customary to direct the emergency overflow pipe to the sewer network. But some homeowners, in order to simplify the task, bring it through the roof straight to the street.
Installing a membrane-type expansion tank also has its own characteristics. Considering how this product works, it can be placed vertically or horizontally in any position. Small containers are usually attached to the wall with a clamp or suspended from a special bracket, large containers are simply placed on the floor. There is one point here: the performance of a membrane tank does not depend on its orientation in space, which cannot be said about its service life.
A closed-type vessel will last longer if it is mounted vertically with the air chamber upward. The fact is that sooner or later the membrane will exhaust its resource, causing cracks to appear in it. The internal structure of the tank is such that when positioned horizontally, air from its half will quickly penetrate through the cracks into the coolant, which will take its place. We will have to urgently install a new expansion tank for heating. The same result will quickly appear when the container is hanging upside down on the bracket.
In a normal vertical position, air from the upper part will not rush to penetrate through the cracks into the lower part, just as the coolant will reluctantly go up. As long as the size and number of cracks do not increase to a critical level, the heating will work properly. This process sometimes takes a long time, and you will not notice the problem right away. But no matter how you place the vessel, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- The product must be located in the boiler room in such a way that it is convenient to service. Do not install floor-standing units close to a wall.
- When wall-mounting the expansion tank of the heating system, do not place it too high so that during maintenance you do not have to reach the shut-off valve or air valve.
- The load from the supply pipelines and shut-off valves should not fall on the tank pipe. Attach the pipes and taps separately, this will make it easier to replace the tank in the event of a breakdown.
- It is not allowed to lay the supply pipe along the floor through a passage or hang it at head height.
How to beautifully place equipment in a boiler room
Equipment and principle of operation
The expansion tank, in addition to the housing, includes a membrane (cylinder or diaphragm), the upper part of which is filled with inert gas or air. The lower compartment of the sealed container is intended for coolant.
Along with an increase in temperature, the water expands, and the excess mass of the coolant enters the membrane. The volume of the chamber with air decreases, and the pressure in this part of the closed system increases, compensating for the pressure in the line. When the coolant temperature decreases, the reverse process is observed.
The expansion tank can be equipped with a replaceable (flange) or permanent membrane. The second type of product is cheaper.
The membrane in the tank is pressed tightly against the inner wall, since its entire volume is filled with gas.
When water gets inside, the pressure increases. At the moment the heating starts, there is a risk of damage to the diaphragm from a pressure surge, and then the pressure gauge gradually changes the readings and the integrity of the part is out of danger.
To avoid damage to the membrane, it is necessary to install a pressure gauge safety valve that reacts to increased pressure (for private houses the norm is from 3.5 to 4 bar).
Advantages of the flange model
The advantages of flanged devices include the following characteristics:
- withstands greater pressure inside the system than a device with a constant diaphragm;
- it is possible to replace the membrane if it is damaged;
- horizontal and vertical installation of the device.
Online calculator
The third way to perform calculations is an online calculator. On the Internet you can find several different programs that simplify the question of how to choose the volume of the expansion tank. Information about coefficients and the dependence of the desired value on temperatures or pressure in communications is already included here.
Our website provides a program for determining the capacity of a closed tank. Here, the adjusted gas pressure refers to the minimum limit that is typical for a heating boiler. For example, if it is 1.5 Atm, then there should be the same amount in the tank. The safety valve is often set to the maximum pressure in the line or equipment. The third thing you need to know is the volume of the coolant.
There are two advantages to working with online calculators, and they are significant:
- immediate results;
- accounting for tabular data that the user does not need to search for.
However, there are also disadvantages. Here it is impossible to track what exactly was taken into account by the developers to produce a particular result. The result can also be considered as close to the exact one.
What is an expansion tank for?
Depending on the weather conditions and the climate in the room, the coolant that circulates through the heating pipes heats up to a greater or lesser extent. When intensely heated, it expands and forms excess volume, which can create a pressure that exceeds the maximum allowable for system operation. Installing an expansion tank in the heating line is precisely what is needed to temporarily remove these excess liquids.
Closed heating system with installed expander
A double-circuit boiler usually has its own capacity for coolant removal, the capacity of which is quite sufficient for average operating conditions.
But if your house has a lot of heated rooms, and at least some of them use metal pipes as batteries, then much more liquid is required in normal mode, which means the increase in volume during expansion will be more noticeable. Therefore, the built-in expansion tank may not be enough, and then the installation of an additional tank will be required.
FAQ
http-equiv=”Content-Type” content=”text/html;″>class=”reviewsblock”>
How does the size of the house affect the amount of storage needed? The volume of the house does not affect in any way, the efficiency of the heating system and the power of the boiler do. After all, variables such as the required heat for heating per hour and the difference between supply and return are precisely indicators of the quality of your system.
The better the heat accumulator is insulated, the more efficiently it will work? According to installation requirements, such a container should only be located in a room with a positive temperature. In this case, standard insulation 10 cm thick will be sufficient. There are cases when such containers are buried in the ground to store more energy, but further maintenance of the system becomes very difficult.
Is this container only suitable for heating? It can be used in several ways. To provide a heating system or hot water. A solid fuel boiler or an electric boiler can be used as a source (an example operating at night with a two-zone meter installed and a preferential tariff). When using a solar collector, solar panels or a wind generator. View all construction myths
Why do you need an expansion tank for heating?
For the normal functioning of the heating system and stable circulation of coolant through all its elements, stable pressure is required. Its sharp jumps lead to disruption of the hydraulic regime and incorrect operation of individual components. To avoid this, the system includes an expansion tank. Its task is to compensate for changes in the volume of coolant (water or antifreeze) caused by changes in its temperature, and to reduce the possibility of water hammer. The change in the volume of the coolant is also affected by its composition and, accordingly, the temperature coefficient. When using water, the average value of this coefficient is 4%, in the case of antifreeze, such as ethylene glycol, from 4.4 to 4.8% (depending on the concentration of glycol in the antifreeze). It is the expansion tank that is the very container into which excess coolant is discharged in order to maintain the required pressure in the network.
Depending on the type of heating system (open or closed), different expansion tanks are used. Let us immediately note that the open system (it is also called a system with natural circulation - gravity) is rarely used in new houses; it can be found mainly in old buildings.
(no votes yet)