Sooner or later, everyone has to change the heating radiators in their apartment. Many people still have Soviet cast-iron batteries in their homes, which are rough in appearance and lack the ability to be adjusted. Others want to replace the construction one with something more elegant that matches the design of the room. Komsomolskaya Pravda studied the best heating radiators available for sale in 2022.
Please note that in our review we tried to select medium-sized radiators. At the same time, most manufacturers have a wide range of models. That is, you can find a similar device with fewer or more sections. This affects the price and degree of heat transfer.
The number of sections you need can be easily determined using the formula:
Number of sections = Room area * Ceiling height * Window coefficient (35 - euro windows, 40 - regular windows) / section heat transfer (indicated in the documentation for each battery).
Types of radiators
- Aluminum radiators are lightweight, durable, reliable and aesthetic heating devices. The aluminum radiator design has a well-developed surface. Coupled with excellent thermal conductivity, aluminum radiators are highly efficient and release 50% of the heat through radiation, and the other 50% through convection
- Bimetallic radiators are devices of double design and double advantages. These strong and durable devices successfully combine the advantages of aluminum and steel radiators, thus opening up new aspects of high-quality heating. Bimetallic radiators take high thermal conductivity and the ability to withstand high pressure from aluminum radiators, and strength and corrosion resistance from steel ones.
- Steel radiators are intended mainly for individual heating systems; they are characterized by low inertia and simplicity of design. Radiators of this type are made of two steel plates 1.25 mm thick, in which recesses are stamped, forming collectors and connecting channels. The advantage of this radiator is its immediate response to media temperature, i.e. rapid heating and cooling, which leads to maximum efficiency, especially when using modern thermostatic equipment such as thermostatic valves and thermal heads.
- Cast iron radiators are presented on the Russian market not only as Soviet classics. In modern design, they are the basis of the heating infrastructure of many countries. They are characterized by significant resistance to corrosion of materials, high pressure and various impurities.
What actually makes up the choice?
To begin with, we will provide a list of the main types of heating devices offered by modern stores. Some of them can only be installed in an autonomous heating system with clean water and low pressure. And others can easily withstand a brutal battle with water hammer and chemically active water in centralized heating systems. Let's see what and how.
Cast iron – we can’t live without it even today
Let's start with the cast iron radiators mentioned at the beginning of the article. Don't think anything bad about them - modern radiators made from this metal look quite nice. Budget models have flat, neat surfaces and compact (compared to Soviet batteries) sizes. And exquisite retro models with beautiful injection molding designs are the highlight of the interior. Standing on graceful legs near the window, they give the room a special charm and a touch of antiquity.
Retaining heat for a long time and not suffering from corrosion, cast iron products can last for several decades. The disadvantages of these devices can be considered their weight and the associated complexity of installation, inertia and large volume of coolant. In addition, the fragility of cast iron does not always allow it to withstand water hammer.
Cast iron radiators from domestic and foreign manufacturers.
Calculation of thermal power and number of radiators
Having decided on the type of radiator, you need to pay attention to the thermal power, the value of which depends on the specific room.
The amount of power consumed depends on a number of indicators:
- Room size;
- The number of external walls of the room and windows;
- Type of house (brick, panel);
- Window type (wooden, plastic).
Calculation of heat transfer is given for a room with a standard ceiling height of up to 3 meters and window sizes of up to 1.5 by 1.8 m.
In general, for ease of calculation, if the room is well insulated, you can take one radiator section per 1.5-2 square meters. m. area of the room.
Thermal power for all types of radiators is different:
- Cast iron radiator
- 80–150 W (for one section); - Steel radiator
- 450-5700 W (for the entire radiator); - Aluminum radiator
- 190 W (for one section); - Bimetallic radiator
- 200 W (for one section).
The power of the radiator, sectional or solid, is indicated in the technical specifications provided by the manufacturer. The optimal temperature of the coolant, water, under such conditions should be 70°C.
Calculation of heat transfer for an apartment
To roughly determine the required heat transfer for a home, you will need to make a simple calculation. We take the total area of all rooms and multiply it by 100 watts - the average heat loss coefficient of a house at a temperature of minus 30°C. For northern regions, this coefficient should be increased in proportion to the minimum winter temperature. As a result, we obtain the required minimum heat transfer from heating devices for winter. Heating engineers use more complex calculations that provide accurate estimates of a building's heat loss. But for installing heating batteries, an approximate calculation will do.
Determine the required dimensions
When buying a radiator, you need to know exactly the following points:
- What type of eyeliner do you have - hidden or open?
- How are the pipes connected to the radiator, from the floor, from the wall, from above, from the side, etc.;
- Diameter of heating pipes;
- Distance between pipes (center distance).
We also provide for placing the radiator in such a way that air can flow freely around it - otherwise the room will not receive 10 to 15% of heat.
The standards for placing radiators are as follows:
- The radiator distance from the floor is from 7 to 10 cm;
- distance from the wall – from 3 to 5 cm;
- distance from the window sill – from 10 to 15 cm.
Heating system type
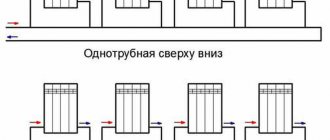
Single pipe systems can be routed vertically or horizontally. The latter option is most suitable for low-rise dwellings: usually we are talking about one- or two-story houses. Three-story buildings are rarely equipped with horizontal wiring. Vertical wiring is usually used in high-rise buildings. This scheme consists of a pipe coming out of the flow, going to the radiator, and then to the floor. This picture can be observed in all (or almost all) rooms. Sometimes there are cases where two radiators are powered from one riser at once. However, it is not at all necessary that they be in the same room.
The strengths of this scheme are the low installation costs and stability of operation (it is quite difficult to unbalance it). However, if significant changes in the parameters of batteries and pipes occur, this can significantly affect the hydraulic resistance. As a result, only the first two sections turn out to be warm, and the rest of the device remains cold.
Single-pipe wiring is characterized by a gradual decrease in the temperature of the coolant as it moves away from the boiler. The efficiency of heating the battery of the neighbor above (with top supply) is inversely proportional to the heating of the radiator on the floor below. To avoid such situations, a law on common ownership of the heating system was adopted. Now, in order to replace a pipe or heating device, you need to obtain the appropriate permits. High-rise buildings are not so often equipped with two-pipe wiring. This is explained by the large consumption of pipes for its organization. In addition, the large dimensions complicate the balancing of the circuit.
A two-pipe system in a multi-story building has the following diagram:
- Two pipes are brought into the room.
- The hotter part serves to supply coolant to the battery.
- The second removes the coolant that has cooled down after the radiator further.
Thanks to this scheme, the identical temperature of the coolant supplied to all heating devices is achieved
It is important to remember that if there is a change in hydraulic resistance in just one radiator, the entire system can be completely unbalanced. A very small resistance will provoke the passage of almost the entire volume of coolant through this section
Therefore, in the presence of such wiring, installation of control valves is mandatory. Most often these are manual control valves or thermostats.
We advise you to study - Which apartment is better to buy - a resale apartment or a new building?
Which radiators are more reliable and durable?
We will again provide in the form of a list the duration of uninterrupted operation guaranteed by the manufacturers.
- Cast iron radiators – more than 50 years.
- Aluminum radiators - from 15 to 20 years (provided that the pH of the water is not higher than 7-8).
- Steel radiators – up to 15-25 years
- Bimetallic radiators - up to 20-25 years.
- Convectors – 10-25 years.
So, if, when figuring out which heating radiator to choose, you set durability as the main criterion, then you don’t have to look far. Take cast iron - not a single newfangled radiator will last longer. Only choose a proven manufacturer who makes really high-quality batteries using excellent raw materials and components. Following this are bimetallic and steel radiators.
As for reliability, there are two aspects here - the ability to withstand pressure and how demanding a particular type of radiator is on the coolant. If we talk about pressure, then the undisputed leader will be bimetallic radiators, followed by aluminum, cast iron and steel radiators.
But radiators treat coolant differently. The most durable in this regard are cast iron radiators, followed by bimetallic ones. For steel radiators, it is important that water is not drained from the system for a long period, otherwise corrosion may occur when oxygen enters the system. Well, the most “delicate” are aluminum radiators, which require Ph in the range of 7 - 8 units.
Convectors
Recently, floor-to-ceiling glazing has become increasingly popular. It’s really beautiful, but what about the heating….question. You can put low radiators on legs, but then all the chic will be lost. That's when in-floor convectors are used. A niche is made in the floor under them and the device itself is installed in the floor, covering it with a grate. In order to increase heat transfer (necessary during cold periods), fans are built inside. The solution is aesthetic, but such systems cost a lot. There is also a nuance - fans, even the quietest ones, are noisy. This noise does not bother some people, but it bothers others very much. In any case, there are more and less noisy models.
In-floor convector - an outlet for heating French windows and glass doors from floor to ceiling
So, if you need to heat a floor-to-ceiling French window, the best option is an in-floor convector.
Appearance and finishing
Cast iron radiators are models from domestic manufacturers, although they have become smaller in size and have undergone changes in design (their façade has become flat), but they cannot boast of finishing. They are coated only with an anti-corrosion primer, which requires subsequent painting. But the models from European manufacturers and the coating are beautiful and durable, and the design is quite modern.
Separately, it is worth mentioning retro-style radiators; they are expensive, but their appearance is simply delightful.
Aluminum radiators are distinguished by a variety of designs. Many manufacturers produce multi-colored radiators that look very elegant and attractive. Models of aluminum radiators are distinguished by a wide range of center distances and standard sizes. This allows them to fit perfectly into any corner of the house.
Steel panel-type radiators can fit into almost any apartment interior. Smooth panels are not very noticeable, blending harmoniously with the surroundings. And tubular steel radiators are often distinguished by their unconventional shape. For example, they can be angular or made in the form of a trapezoid. They are also used to protect staircase steps and fit into niches and attic spaces. And everywhere such radiators look fresh and modern, shining with multi-colored paints.
Bimetallic radiators are very sophisticated in design. There are many models that have curved rather than straight surfaces. This allows them to fit perfectly into rooms with smooth angles.
Rules for the location of batteries in the house
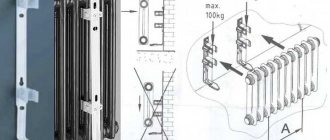
In order for the system to work properly, installation rules must be strictly followed. Although the installation technology is not complicated, it has its own nuances, so the work must be carried out by specialists.
Important! If radiators are installed incorrectly, they are not covered by the warranty.
In order to avoid heat loss and uneven heating of the room, when installing devices it is necessary to observe indentations and choose the correct location:
- The most suitable option for the battery is considered to be a place under the window, i.e. where the heat loss is the most significant. The radiator width must be at least 70% of the window width. Mounted clearly in the middle.
- Leave at least 10 cm from the battery to the windowsill, as well as to the floor. The optimal distance between the floor and the radiator is 12 cm. It is not recommended to leave more than 15 cm.
- The battery is fixed at a distance of 5 cm from the wall.
- You can stick heat-reflecting material behind the radiator - then some of the heat will not go into the wall, but will return to the room.
- If the radiator is planned to be placed not under the window sill, but on the wall, then the distance between them should be at least 20 mm.
Price categories
- Cast iron radiators (except for retro models) - from 300 rubles per section.
- Cast iron “retro” radiators - from 2000 rubles per section.
- Aluminum radiators - from 300 rubles per section.
- Steel radiators (price for a whole radiator) - from 1,500 to 10,000 rubles.
- Bimetallic radiators - from 500-600 rubles per section.
The cheapest radiators are steel panel and cast iron, especially those made domestically. After them will come aluminum injection molded radiators; extrusion models will be slightly cheaper. But the most expensive ones will be bimetallic radiators, retro-style cast iron radiators and steel tubular radiator models.
Air vents
The standard installation kit includes a manual air vent (Maevsky valve). The place where it is installed is the free upper manifold. The presence of an air bleeder is mandatory when connecting a bimetallic radiator. The fact is that the contact of the coolant with the materials of the collector provokes chemical reactions, as a result of which gases are formed.
Thanks to this small device, it is possible to remove air and gases accumulated inside the radiator. If this is neglected, excess pressure will appear in the system, causing circulation problems and uneven heating of the batteries. To release gases, you need to open and close the valve with a key.
Quantitative characteristics
Quantitative characteristics must be confirmed during tests, the results of which serve as the basis for obtaining a certificate of conformity. The list of confirmed characteristics, as well as test methods and conditions are specified in regulatory documentation - Russian (GOST) and European (EN 442-2) standards, or specially issued and approved technical specifications (TU).
Number of sections
The vast majority of aluminum radiator models consist of separate sections. Division into sections allows you to select a device of the required power depending on the area of the heated room.
Five-section aluminum radiator.
The buyer can purchase both individual radiator sections and a ready-made factory-assembled heating device. As a rule, factory-assembled radiators include from 4 to 12 sections. When assembling sections together, a nipple connection is used.
The number of sections required to heat the room is determined by the approximate formula:
N =100*(S/P);
where S is the area of the room, m2;
P – thermal power of one section, W.
The Italian company Global produces twin models of the GL/D series, which have 2 rows located symmetrically relative to the plane of the rear wall of the sections. Double radiators are used if they need to be installed at a distance from the wall.
Thermal power (nominal heat flux)
This parameter (measured in W) allows you to determine how many sections a radiator should have to heat a certain area.
Separate sections of aluminum heating radiators.
According to GOST 31311-2005 “Heating devices. General technical conditions", thermal power is determined under the following conditions:
- temperature difference (difference between the temperatures of the coolant and the air in the room) ΔT= 70°C;
- atmospheric pressure B = 760 mmHg;
- The coolant moves through the heating device from top to bottom.
Some manufacturers additionally indicate thermal power measured at a temperature difference of 30°C and 50°C.
External heating surface area
This value includes the area of all surfaces of the radiator section that are in contact with the air in the room, including the area of the fins. The outer surface area is usually:
- for sections with an interaxial distance of 350 mm – 0.3…0.4 m2;
- for sections with an interaxial distance of 500 mm - 0.4...0.5 m2.
Geometric characteristics
Overall and installation (connection) dimensions determine the possibility of installing a heating radiator under specific placement conditions. Also, the dimensions of the heating device affect its thermal output.
Dimensions.
Center distance
Center-to-center is the distance between the axes of the upper and lower collector. Among mass-produced radiators, models with center distances of 200, 300, 350, 500, 600, 800 mm predominate. A center distance of 500 mm is the most common, and radiators of this size are present in the model range of all manufacturers. Global produces Oscar series models with center distances from 900 to 2000 mm.
Installation dimensions.
Section width
The vast majority of aluminum radiator models have a section width of 80 mm. Sections with a width of 70 mm, 100 mm and other values are less commonly produced.
Depth
This value determines the installation distance from the axis of the collector to the adjacent wall of the room. The most common products are 80 mm deep, but to increase thermal power, manufacturers in some models increase the radiator depth to 100 mm.
Section internal volume
One of the parameters that determines the power of the heating device. The internal volume of the section (measured in liters) depends on the height of the radiator, as well as the shape and cross-sectional area of the vertical channel. To increase the internal volume, some manufacturers produce models with an oval channel section (Royal Thermo radiators).
Vertical channel of oval cross-section.
Section weight
The mass of the section includes the weight of the paint and varnish coating, as well as the average mass of gaskets and nipples. Sometimes the specific mass value (material intensity), which is measured in kg/kW, is indicated in the product passport.
Pressure
Most aluminum radiators are designed for a working pressure of 16 atm (1.6 MPa). Some models require operation in systems with operating pressures of 20 and 25 atm (for example, Rovall manufactured by Sira Group).
The test (pressure testing) pressure, at which the radiator should not be destroyed, should be 1.5 times higher than the working one. Manufacturers also indicate the maximum (destructive) pressure, which is usually 40-60 atm, but not less than 2 times higher than the working one.
Coolant temperature
Heating devices of this type are designed for a coolant temperature of 110°C. Some models (for example, Rifar Alum series) allow operation at 135°C.
Tables 1 and 2 show the technical characteristics of models with center distances of 350 and 500 mm. The comparative tables indicate the weight and size parameters, coolant volume and nominal heat flow of sections produced by 7 different companies.
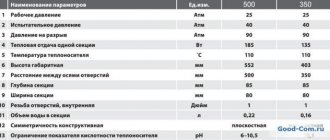
Table 1 - Technical characteristics of aluminum radiators (center distance 350 mm)
| Manufacturer and model | Overall dimensions, mm | Section volume, l | Section weight, kg | Thermal power, W | ||
| height | width | depth | ||||
| Rifar Alum 350 | 415 | 80 | 90 | 0,19 | 1,20 | 139 |
| Royal Thermo Indigo 350 | 435 | 80 | 100 | 0,29 | 1,30 | 155 |
| Conner LUX 80/350 | 430 | 80 | 80 | 0,28 | 1,05 | 145 |
| Ferroli POL 350 | 431,5 | 80 | 98 | 0,31 | 1,10 | 155 |
| General Hydraulic Lietax B 350-80 | 420 | 80 | 80 | 0,22 | 0,80 | 135 |
| Global VOX R 350 | 440 | 80 | 95 | 0,35 | 1,12 | 145 |
| Varmega Almega 350/80 | 426 | 80 | 80 | 0,30 | 1,10 | 147 |
Table 2 - Technical characteristics of aluminum radiators (center distance 500 mm)
| Manufacturer and model | Overall dimensions, mm | Section volume, l | Section weight, kg | Thermal power, W | ||
| height | width | depth | ||||
| Rifar Alum 500 | 565 | 80 | 90 | 0,27 | 1,45 | 183 |
| Royal Thermo Indigo 500 | 585 | 80 | 100 | 0,37 | 1,65 | 205 |
| Conner LUX 80/500 | 582 | 80 | 80 | 0,43 | 1,25 | 190 |
| Ferroli POL 500 | 581,5 | 80 | 98 | 0,38 | 1,40 | 180 |
| General Hydraulic Lietax B 500-80 | 582 | 80 | 80 | 0,36 | 1,03 | 180 |
| Global VOX R 500 | 590 | 80 | 95 | 0,46 | 1,45 | 195 |
| Varmega Almega 500/80 | 576 | 80 | 80 | 0,38 | 1,20 | 191 |
Models with a center distance of 200 mm are the smallest in height among aluminum sectional radiators. Products of this standard size are used for installation under window openings with increased glazing area. Comparative characteristics of devices of this standard size are given in Table 3 and include data on products from three manufacturers.
Table 3 - Technical characteristics of aluminum radiators (center distance 200 mm)
| Manufacturer and model | Overall dimensions, mm | Section volume, l | Section weight, kg | Thermal power, W | ||
| height | width | depth | ||||
| Varmega Almega 200/80 | 275 | 80 | 80 | 0,20 | 0,64 | 101 |
| Sira Heatline 200 | 245 | 80 | 80 | 0,16 | 0,56 | 89 |
| Conner LUX 80/200 | 275 | 80 | 80 | 0,26 | 0,62 | 123 |