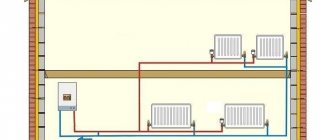
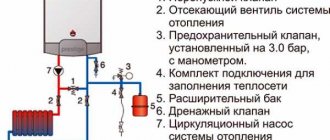
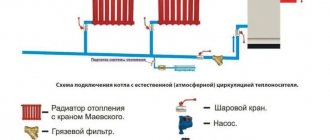
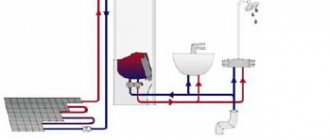
Due to systematic changes in temperature conditions in the heating system, the volume of coolant takes on different values. Which often leads to emergency situations. To avoid such problems, it is necessary to establish stable operation of the installation, maintaining the required characteristics within normal limits. To do this, you need to study in detail the structure and operating principle of a membrane expansion tank for heating.
Purpose
Most substances used to transfer thermal energy are a neutral, slightly compressible liquid medium. That is why when using it, the presence of stabilization devices is required - expansion tanks with a membrane. Such units accept part of the liquid when it increases in volume when heated, and also return it back to the circuit when the temperature decreases.
When the temperature of the coolant increases, the water pressure in the system increases. Due to the inability of the heat carrier to compress and the tightness of the installation as a whole, pipes and boilers often fail.
In this situation, it is a mistake to think that the problem can be solved solely by installing a special valve that allows you to displace excess filling material during the heating period. As the liquid cools, it will decrease in volume and air will take its place. The air gap will begin to impede the circulation of the liquid medium. In order to eliminate this nuisance, you will have to systematically drain the excess and supplement the circuit with new coolant, as well as heat it. Which, in itself, will not be cheap.
To avoid such difficulties, you should install a membrane expansion tank, which is a special tank connected to the system through a pipe. Excess pressure in it will be neutralized due to the dynamics of volume indicators and the network will be able to operate stably.
Tank pressure
In some boilers (usually gas ones), the passport indicates what pressure must be set on the expander. If there is no such record, for normal operation of the system, the pressure in the tank should be 0.2-0.3 atm lower than the working one.
The heating system of a low-rise private house usually operates at 1.5-1.8 atm. Accordingly, there should be 1.2-1.6 atm in the tank. The pressure is measured with a conventional pressure gauge, which is connected to a nipple located in the upper part of the container. The nipple is hidden under a plastic cover; unscrew it and gain access to the spool. You can also relieve excess pressure through it. The principle of operation is the same as that of a car spool - you bend the plate with something thin, bleeding the air to the required levels.
Where is the inflation nipple located?
You can also increase the pressure in the expansion tank. To do this, you will need a car pump with a pressure gauge. Connect it to the nipple and pump it up to the required readings.
All of the above procedures are carried out with the tank disconnected from the system. If it is already installed, there is no need to remove it. You can check the pressure in the expansion tank of the heating system on site. Just be careful! It is necessary to check and adjust the pressure in the expansion tank for heating when the system is not working and the coolant has been drained from the boiler. For the accuracy of measurements and tank settings, it is important that the pressure on the boiler is zero. That’s why we drain the water carefully. Then we connect the pump with a pressure gauge and adjust the parameters.
Advantages and disadvantages
The expansion tank absorbs a certain amount of water as its volume increases, then returns it. The pronounced advantages of such devices should be noted:
- possibility of use for any liquid circulating in water supply and heating complexes, even with excessive calcium content;
- no need to pump in a large amount of air (when compared with tanks operating without a membrane);
- simplicity and comparative cheapness of installation of structures;
- significant savings during operation.
We cannot remain silent about the existing disadvantages of expansion tanks. These include:
- increased likelihood of rust occurring in units;
- increased heat loss due to heat transfer to the hydraulic accumulator;
- Impressive dimensions requiring enough space for installation.
Design features
In residential and industrial premises, heating networks are installed according to open and closed schemes. The first option is more suitable for centralized systems, which allows the liquid to be collected directly for hot supply. In this case, the tank is installed in the upper zone of the circuit. The container makes it possible to control the process of pressure surges by removing air pockets from the pipes.
The second type of installation involves the use of tanks with a membrane. They are distinguished by their comparative simplicity of design. They consist of an expansion tank and a membrane-plate, which, in turn, can be:
- Balloon. This means that the heat carrier is placed inside a rubber cylinder, and on the outside there is nitrogen or air. If this element breaks down, it’s easy to replace; you don’t have to buy a whole new device.
- Diaphragm. Made in the form of a permanent partition made of metal or polymer material. This part has a compact capacity and can neutralize only small pressure surges in the network. If it fails, it is impossible to replace it, as a result of which you will have to purchase another tank. Of course, the cost of this membrane is slightly lower than the above option.
Types of household heating systems with liquid coolant
There are many different heating options for individual homes. The premises can be heated with electric convectors, heat pumps, electric heating cables, stoves, films, and receive thermal energy using solar panels.
However, in everyday reality, for a number of reasons, most consumers use water heating boilers, the coolant from which is directed to underfloor heating circuits or to radiator heat exchangers. In this case, the following two main types of hydraulic heating systems are distinguished.
Rice. 2 Scheme of the gravitational system
Gravity
In gravity (gravity) systems, as the name suggests, the circulation of heating fluid along the circuit occurs naturally.
This is due to a simple physical law, according to which heated water has a lower density than cold water. As a result, after heating in the boiler, it is pushed out by cold water masses and rises upward.
The heated coolant fills the expansion tank and spreads down the circuit with the heat exchange radiators. The gravity system has the following features:
- The storage tank to support pressure is made with an open lid. As a result, there is constant evaporation of the liquid and it has to be regularly replenished, which creates significant operational inconveniences.
- In an open heating system, you cannot use the inexpensive toxic antifreeze liquid ethylene glycol. As an anti-freeze agent, you will have to use propylene glycol, which costs twice as much, or make do with ordinary distilled water.
- The working pressure in gravity systems rarely exceeds 1 bar and requires a hydraulic tank raised to a height of 10 m from the boiler to obtain it. This is clearly not enough for long heating circuits with radiator heat exchangers, and especially for underfloor heating. As a result, an additional circulation electric pump is often installed in a gravity heating system.
- The speed of movement of the coolant in gravity circuits is low, therefore, to ensure good heat transfer, the use of large diameter pipelines of 32 or 40 mm is required.
Rice. 3 Gravity tanks
Article on the topic:
Heating in a private house from polypropylene pipes - nuances, calculations. It may be interesting to read in more detail about organizing a heating system made of polypropylene pipes in a private house.
- The pipeline in gravity systems goes to the heat exchange devices from above along the walls, which does not contribute to improving the aesthetic appearance of the premises.
- If the expansion tank in an open-type heating system is located in the attic and it is not heated, it will have to be well insulated to reduce heat losses.
- Also, the process of heating water is accompanied by some noise, which worsens the comfort of living in living rooms.
- Since the coolant comes into contact with air, it is saturated with oxygen. This leads to accelerated corrosion of the metal elements of the boiler and triggers the processes of decomposition of non-freezing liquids.
- A significant advantage of the gravity system can be considered the ability to operate in the absence of electricity, however, this statement is not entirely correct, since most heating boilers cannot function normally in the absence of electricity.
- A more important advantage is the upper location of the expansion tank in an open system. Thanks to this, the problem of air exhaust is effectively solved and you can do without a number of air vents. This allows you to save some money.
Rice. 4 Closed circuit
Closed type
When considering an open heating system, quite a few disadvantages were cited that such a connection scheme has. This led to the widespread use of another scheme with a closed hydraulic tank and forced supply of the working fluid.
How does a membrane expansion tank work?
For any system, the coolant parameters are set in accordance with the recommendations specified in the operating instructions for the unit. The type of membrane-plate does not directly affect the functional features of the device. However, if it belongs to the balloon variety, the reservoir is able to accommodate a larger amount of heat-carrying liquid medium.
1.5 m3/h For process water
1.5 m3/h For process water
MBFT-75 Membrane for 75GPD
The principle of operation of the expansion tank does not differ between different designs. When the number of atmospheres increases due to the increase in liquid volume when heated, the membrane stretches. Next, the gas located outside is compressed, which allows the remnants of the liquid medium to penetrate inside. Well, after the pressure decreases due to a decrease in temperature, the reverse process is activated.
Stability of operation is ensured in automatic mode. In order for it to function correctly, it is necessary to select a suitable container and perform preliminary calculations before installation. The required parameters cannot be achieved if the tank is larger or smaller than the required volume. Such a discrepancy can lead to an emergency.
Where and how to install the tank
The coolant in individual heating systems can move by gravity, or due to the pressure created by the pump. But in any case, it requires a capacity that will compensate for the expansion. This is not necessary only if the water is heated by a gas boiler, since it has a built-in tank.
Expansion tank inside a gas boiler
A system based on a solid fuel boiler requires the installation of an expansion tank
Electric boiler circuit
Prices for popular models of indirect heating heaters
Indirect Heaters
When choosing a location to install the tank, you need to consider the following requirements:
- It must be located in the same room as the boiler.
- Unobstructed access to the tank must be provided.
- It can be installed on the floor or hung on a bracket. In this case, the inlet pipe must be at the bottom, although in some models it is located on the side. In any case, the air chamber should be higher than the water chamber - this way air will not enter the chamber with water and provoke the occurrence of cavitation phenomena.
- If the container is hung on the wall, then the pipeline supplying it must be secured independently so as not to create a load with its weight.
- Only tanks with a small capacity can be attached to the wall, and only when there is confidence in its sufficient load-bearing capacity.
- There must be a gap sufficient between the tank body and the wall to allow a visual inspection.
- The pipe route should approach the connection point in the shortest possible way.
With this arrangement of the tank, air can enter the water
Pipe connection from below is more correct
Option to install the tank on the wall
The best place to install a compensation tank is the return pipeline, between the circulation pump and the boiler. Here the temperature of the water (or other coolant) is minimal, which is a gentle operating mode for the rubber membrane. Although, the tank can also be installed on the supply side. There will be no error in this case - however, the membrane will have to be changed more often.
Where there is no centralized supply of heated water and gas is not supplied, water heating equipment powered by electricity is the only chance for a comfortable home life. How to choose an electric storage water heater for an apartment? In a special article we will consider what their features and differences are, what are the principles of operation, placement and installation.
Product selection rules
When deciding on a model, you should pay attention not only to the volumetric characteristics. It is equally important that the device meets a number of other requirements:
- the membrane-plate must withstand high temperatures and changes in atmospheric parameters;
- the unit must not deviate from established sanitary and hygienic standards;
- installation features also need to be taken into account when purchasing.
When choosing a device (membrane-type expansion tank), it is easy to notice that today there are many types of tanks on the market, manufactured both in Russia and abroad. The main differences lie in the price range of the products.
Sticking with the cheapest model is definitely not the best decision. After all, a minimum of purchase costs can subsequently result in many problems due to the low quality characteristics of the materials used in production. In this regard, it is worth giving preference to domestic manufacturing companies. The products they produce are in no way inferior in quality to expensive imported products, and are much less affordable. Do not forget that a famous brand does not guarantee the reliability and long service life of the device.
The leading parameter that you should rely on when choosing a tank is its volume. Many experts advise buying an expander with a capacity of 10% of the total amount of coolant in the heating network. The expansion coefficient at maximum temperature conditions must remain within 0.8. Therefore, all required calculations must be carried out with utmost accuracy. And it is necessary to take into account:
- system pressure limit;
- volumetric characteristics of the coolant;
- the initial number of atmospheres in the tank;
- corresponding thermal coefficient.
When deciding on the dimensions of the device, be sure to check the availability of all components. To do this, just carefully review the project documents. If the necessary documentation is missing (lost), the required parameters should be calculated approximately. Just know that 1 kW provides 15 liters of liquid. In high-rise buildings, the coefficient is usually calculated by taking into account the composition of the liquid medium, which often includes glycols, which have a beneficial effect on its quality.
In addition, it is quite possible to determine this value based on the temperature of the coolant. The maximum network pressure is determined using the limit set for the nodes. This is done by setting up special locking elements. The initial number of atmospheres must be minimal. On a number of models it is adjusted by pumping or deflating air. Directly in the tank, control is carried out using a pressure gauge.
The use of an expansion tank with a membrane has its own limitations. The possibility of its use in a given situation is mainly influenced by the production methods used by the manufacturer, as well as the materials. In some situations, special requirements are imposed on the composition of the coolant. Thus, a mandatory reduction in the amount of ethylene glycol or antifreeze may be indicated.
When choosing a suitable product, pay attention to the Russian company -. The products manufactured by the organization meet the highest quality characteristics and are able to serve their owners for a long time. The reliability and high quality of the products are confirmed by the company's many years of experience and many positive reviews from grateful customers.
Expansion tank for closed heating: installation
When planning to create a water heating system in your own home, the owner is faced with a choice of several options. The list of the most important questions includes the type of system (will it be open or closed), and what principle will be used to transfer coolant through pipes (natural circulation due to gravitational forces, or forced, requiring the installation of a special pump).
Expansion tank for heating closed type installation
Each of the schemes has its own advantages and disadvantages. But still, nowadays preference is increasingly given to a closed system with forced circulation. This scheme is more compact, easier and faster to install, and has a number of other operational advantages. One of the main distinctive features is a completely sealed expansion tank for closed-type heating, the installation of which will be discussed in this publication.
But before purchasing an expansion tank and proceeding with its installation, you need to at least become familiar with its structure, operating principle, as well as which model will be optimal for a particular heating system.
What are the advantages of a closed heating system
Despite the fact that many modern devices and systems for space heating have appeared recently, the principle of heat transfer through a liquid with high heat capacity circulating through pipes undoubtedly remains the most common. Water is most often used as a carrier of thermal energy, although in some circumstances it is necessary to use other liquids with a low freezing point (antifreeze).
Water heating is the leader in prevalence
The coolant receives heat from the boiler (furnace with a water circuit) and transfers heat to heating devices (radiators, convectors, “warm floor” circuits) installed in the premises in the required quantity.
How to decide on the type and number of heating radiators?
Even the most powerful boiler will not be able to create a comfortable atmosphere in the premises if the parameters of the heat exchange points do not correspond to the conditions of a particular room. How to correctly calculate the required number of heating radiators is in a special publication on our portal.
But any liquid has general physical properties. Firstly, when heated, it increases significantly in volume. And secondly, unlike gases, this is an incompressible substance; its thermal expansion must be compensated in some way by providing free volume for this. And at the same time, it is necessary to ensure that as it cools and decreases in volume, air does not enter the pipe contours from the outside, which will create a “plug” that prevents the normal circulation of the coolant.
These are the functions that the expansion tank performs.
Not yet in private construction, there was no particular alternative - an open expansion tank was installed at the highest point of the system, which completely coped with the tasks.
Schematic diagram of an open type system
1 – heating boiler;
2 – supply riser;
3 – open expansion tank;
4 – heating radiator;
5 – optional – circulation pump. In this case, a pumping unit with a bypass loop and a valve system is shown. If desired or if the need arises, you can switch forced circulation to natural circulation, and vice versa.
You may be interested in information about how to properly install heating radiators
Prices for circulation pumps
circulation pumps
A closed system is completely isolated from the atmosphere. A certain pressure is maintained in it, and the thermal expansion of the liquid is compensated by installing a sealed tank of a special design.
Differences between a closed heating system
The tank in the diagram is shown pos. 6, embedded in the return pipe (item 7).
It would seem - why “fence the garden”? A regular open expansion tank, if it fully copes with its functions, seems to be a simpler and less expensive solution. It probably doesn’t cost much, and besides, with certain skills, it’s easy to make it yourself - weld it from steel sheets, use an unnecessary metal container, for example, an old can, etc. Moreover, you can find examples of using old plastic canisters.
Open expansion tank
Does it make sense to spend money on purchasing a sealed expansion tank? It turns out that there is, since a closed heating system has many advantages:
- Complete tightness absolutely eliminates the process of evaporation of the coolant. This opens up the possibility of using, in addition to water, special antifreezes. The measure is more than necessary if the country house is not used constantly in the winter, but only occasionally, from time to time.
- In an open heating system, the expansion tank, as already mentioned, must be mounted at the highest point. Very often, an unheated attic becomes such a place. And this entails additional efforts to thermally insulate the container so that even in the most severe frosts the coolant in it does not freeze.
The expansion tank can be placed in an inconspicuous corner
And in a closed system, the expansion tank can be installed in almost any area. The most appropriate installation location is the return pipe directly in front of the boiler entrance - here the tank parts will be less exposed to temperature effects from the heated coolant. But this is by no means a dogma, and it can be mounted in such a way that it does not create interference or disharmonize its appearance with the interior of the room, if, say, the system uses a wall-mounted boiler installed in the hallway or in the kitchen.
- In an open expansion tank, the coolant is always in contact with the atmosphere. This leads to constant saturation of the liquid with dissolved air, which causes increased corrosion in the circuit pipes and radiators, and increased gas formation during the heating process. Aluminum radiators are especially intolerant of this.
- A closed heating system with forced circulation is less inert - it warms up much faster when starting up, and is much more sensitive to adjustments. Completely unjustified losses in the area of the open expansion tank are eliminated.
- The temperature difference in the supply and return pipes in the connection currents with the boiler is less than in an open system. This is important for the safety and longevity of heating equipment.
- A closed circuit with forced circulation to create circuits will require pipes of a smaller diameter - there is a benefit both in the cost of materials and in simplifying installation work.
- An open-type expansion tank requires control to prevent overflow when filling, and to prevent the liquid level in it from falling below a critical level during operation. Of course, all this can be solved by installing additional devices, for example, float valves, overflow pipes, etc., but these are unnecessary complications. In a closed heating system, such problems do not arise.
- And finally, such a system is the most universal, as it is suitable for any type of battery and allows you to connect underfloor heating circuits, convectors, and heat curtains. In addition, if desired, you can organize hot heat supply by installing an indirect heating boiler into the system.
Of the serious shortcomings, only one can be mentioned. This is a requirement of the “safety group”, which includes control and measuring instruments (pressure gauge, thermometer), a safety valve and an automatic air vent. However, this is most likely not a disadvantage, but a technological cost that ensures the safe operation of the heating system.
In a word, the advantages of a closed system clearly outweigh, and spending on a special sealed expansion tank looks completely justified.
How does an expansion tank for closed heating work and how does it work?
The design of an expansion tank for a closed type system is not very complicated:
Diagram of the device and operation of a sealed expansion tank
Usually the entire structure is housed in a stamped steel body (item 1) of a cylindrical shape (there are tanks in the shape of a “tablet”). For production, high-quality metal with an anti-corrosion coating is used. The outside of the tank is covered with enamel. Products with a red body are used for heating. (There are blue tanks - but these are water batteries for the water supply system. They are not designed for elevated temperatures, and all their parts are subject to increased sanitary and hygienic requirements).
On one side of the tank there is a threaded pipe (item 2) for insertion into the heating system. Sometimes fittings are included in the package to facilitate installation work.
On the opposite side there is a nipple valve (item 3), which serves to pre-create the required pressure in the air chamber.
Inside, the entire cavity of the tank is divided by a membrane (item 6) into two chambers. On the side of the pipe there is a chamber for coolant (item 4), on the opposite side there is an air chamber (item 5)
The membrane is made of elastic material with a low diffusion rate. It is given a special shape, which ensures “orderly” deformation when the pressure in the chambers changes.
The principle of operation is simple.
- In the initial position, when the tank is connected to the system and filled with coolant, a certain volume of liquid enters the water chamber through the pipe. The pressure in the chambers is equalized, and this closed system acquires a static position.
- As the temperature rises, the volume of coolant in the heating system expands, accompanied by an increase in pressure. Excess fluid enters the expansion tank (red arrow), and its pressure bends the membrane (yellow arrow). In this case, the volume of the coolant chamber increases, and the air chamber correspondingly decreases, and the air pressure in it increases.
- As the temperature decreases and the total volume of the coolant decreases, excess pressure in the air chamber causes the membrane to move backward (green arrow), and the coolant moves back into the pipes of the heating system (blue arrow).
If the pressure in the heating system reaches a critical threshold, then the valve in the “safety group” should operate, which will release excess liquid. Some expansion tank models have their own safety valve.
Expansion tank on a special bracket
Different tank models may have their own design features. So, they can be non-separable or with the ability to replace the membrane (a special flange is provided for this). The kit may include brackets or clamps for mounting the tank on the wall, or it can be provided with stands - legs for placing it on the floor.
In addition, they may differ in the design of the membrane itself.
Differences in the design of expansion tanks with diaphragm (left) and balloon type membranes
On the left is an expansion tank with a membrane diaphragm (it has already been discussed above). As a rule, these are non-separable models. A balloon-type membrane (picture on the right), made of elastic material, is often used. In fact, it itself is a water chamber. As pressure increases, such a membrane stretches, increasing in volume. It is these tanks that are equipped with a collapsible flange, which allows you to independently replace the membrane in the event of its failure. But this does not change the basic principle of operation.
Video: installation of expansion tanks brand "Flexcon FLAMCO"
Prices for expansion tanks Flexcon FLAMCO
Flexcon expansion tanks
How to calculate the required parameters of the expansion tank?
When choosing an expansion tank for a specific heating system, the fundamental point should be its working volume.
Calculation using formulas
You can find recommendations to install a tank, the volume of which is approximately 10% of the total volume of coolant circulating through the system circuits. However, a more accurate calculation can be made - there is a special formula for this:
V b = V c × k / D
The symbols in the formula indicate:
Vb – required working volume of the expansion tank;
Vс – total volume of coolant in the heating system;
k – coefficient taking into account the volumetric expansion of the coolant during heating;
D is the efficiency coefficient of the expansion tank.
Where to get the initial values? Let's look at it in order:
- The total volume of the system ( V s ) can be determined in several ways:
- You can use a water meter to determine how much total volume will fit when filling the system with water.
- The most accurate method used when calculating a heating system is the summation of the total volume of pipes of all circuits, the capacity of the heat exchanger of the existing boiler (it is indicated in the passport data), and the volume of all heat exchange devices in the premises - radiators, convectors, etc.
- The simplest method gives a completely acceptable error. It is based on the fact that to provide 1 kW of heating power, 15 liters of coolant are required. Thus, the rated power of the boiler is simply multiplied by 15.
2. The value of the coefficient of thermal expansion ( k ) is a tabular value. It varies nonlinearly depending on the heating temperature of the liquid and the percentage of antifreeze ethylene glycol additives in it. The values are shown in the table below. The heating value line is taken from the calculation of the planned operating temperature of the heating system. For water, the percentage value of ethylene glycol is taken as 0. For antifreeze - based on the specific concentration.
| Coolant heating temperature, °C | Glycol content, % of total volume | |||||||
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 70 | 90 | |
| 0 | 0.00013 | 0.0032 | 0.0064 | 0.0096 | 0.0128 | 0.016 | 0.0224 | 0.0288 |
| 10 | 0.00027 | 0.0034 | 0.0066 | 0.0098 | 0.013 | 0.0162 | 0.0226 | 0.029 |
| 20 | 0.00177 | 0.0048 | 0.008 | 0.0112 | 0.0144 | 0.0176 | 0.024 | 0.0304 |
| 30 | 0.00435 | 0.0074 | 0.0106 | 0.0138 | 0.017 | 0.0202 | 0.0266 | 0.033 |
| 40 | 0.0078 | 0.0109 | 0.0141 | 0.0173 | 0.0205 | 0.0237 | 0.0301 | 0.0365 |
| 50 | 0.0121 | 0.0151 | 0.0183 | 0.0215 | 0.0247 | 0.0279 | 0.0343 | 0.0407 |
| 60 | 0.0171 | 0.0201 | 0.0232 | 0.0263 | 0.0294 | 0.0325 | 0.0387 | 0.0449 |
| 70 | 0.0227 | 0.0258 | 0.0288 | 0.0318 | 0.0348 | 0.0378 | 0.0438 | 0.0498 |
| 80 | 0.029 | 0.032 | 0.0349 | 0.0378 | 0.0407 | 0.0436 | 0.0494 | 0.0552 |
| 90 | 0.0359 | 0.0389 | 0.0417 | 0.0445 | 0.0473 | 0.0501 | 0.0557 | 0.0613 |
| 100 | 0.0434 | 0.0465 | 0.0491 | 0.0517 | 0.0543 | 0.0569 | 0.0621 | 0.0729 |
3. The value of the expansion tank efficiency coefficient ( D ) will have to be calculated using a separate formula:
D = ( Qm – Q b) / ( Qm + 1)
Where:
Qm is the maximum permissible pressure in the heating system. It will be determined by the response threshold of the safety valve in the “safety group”, which must be indicated in the product passport.
Q b - pre-pumping pressure of the air chamber of the expansion tank. It may also be indicated on the packaging and in the product documentation. It is possible to change it - pumping it up using a car pump or, conversely, bleeding it through a nipple. It is usually recommended to set this pressure within 1.0 – 1.5 atmospheres.
Calculator for calculating the required volume of the expansion tank
To simplify the calculation procedure for the reader, the article contains a special calculator in which the indicated dependencies are included. Enter the requested values, and after pressing the “CALCULATE” button you will receive the required volume of the expansion tank.
Go to calculations
The obtained value is minimal - a model with the closest indicators is selected based on it. In this case, rounding is carried out only upward - additional volume will not be superfluous.
And finally, from the model range of calculated volumes presented for sale, it will be possible to choose the most optimal option, based on the intended location of the expansion tank - wall-mounted or placed on the floor.
There is one more nuance. Some heating boilers have their own built-in expansion tank. This does not mean that there is no need to carry out calculations - it happens that the volume of the built-in tank is clearly not enough. In this case, you will have to purchase and install an additional one, with a working volume equal to the difference between the calculated indicators for the entire system and the parameters of the built-in capacity.
Prices for expansion tanks Gilex
Expansion tank Gileks
And one more note. If the heating system operates on the principle of forced circulation, then, even with small volumes of coolant, an expansion tank with a capacity of at least 15 liters should be installed.
You may be interested in information on how to choose an electric boiler for heating a private home
Expansion tank for closed heating: do-it-yourself installation
For a person who has skills in plumbing work, installing an expansion tank yourself will not be difficult. The principle of its insertion into the system is shown in the diagram:
Recommended scheme for inserting an expansion tank into a closed heating system
On the return pipe (item 1), in the area as close as possible to the entrance to the heating boiler (item 2), but usually in front of the circulation pump (item 3), a cut is made into which the tee (item 4) is packed. The installation method may be different - it all depends on the type of pipes used - metal, polypropylene or metal-plastic.
A ball valve (pos. 7) is packed onto the branch pipe (pos. 6) of the expansion tank itself (pos. 5). It is necessary to ensure the possibility of turning off the expansion tank in case of need for repair or maintenance work. For the same purposes, it makes sense to place a connection with a union nut - “American” (pos. 8) between the tap and the tank. In the operating position, the valve must be constantly open.
From the tap there is a connecting section of the pipe (item 9) to the tee. Its length and configuration (number of bends or turns) do not matter much - but it is usually done along the shortest and most convenient path from the location of the tank to the return pipe.
Now let's see what needs to be done on the tank itself.
| Illustration | Brief description of the operation performed |
| The tank was taken out of its original packaging and the necessary tools and accessories were prepared for work. | |
| If necessary, an adapter is packed onto the threaded pipe of the expansion tank. It is important to achieve extremely reliable sealing of the connections. It is best to pack tow using Unipack paste or using a special thread-sealing thread (cord) impregnated with a sealing compound (as shown in the figure).. | |
| The adapter is tightened, and you can proceed to installing the tap. It is worth noting right away that in the example shown there was a flaw - the master did not install a detachable connection - “American” between the tap and the tank. That is, if it is necessary to dismantle the tank with the tap closed, this will be very difficult to do. A recommendation to all installers is not to forget about this point. | |
| The thread is wound to wrap the tap,... | |
| ... the tap is put in place and tightened tightly. You should immediately ensure that the “lamb” is in a position convenient for use after placing the tank on the wall. | |
| A transition is mounted from the tap to a pipe of the required configuration, in accordance with the drawn up diagram of the general installation of the expansion tank. Essentially, this part of the work is finished. | |
| Now you can check the pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank. On its opposite side there is a nipple - almost exactly the same as on car wheels. In many models it is covered with a special plastic cap, which, if necessary, access to the valve is simply unscrewed. | |
| You can check the pressure with a car pressure gauge. If it exceeds the values that were used when calculating the system, then it can be released to the required level by pressing the valve stem. If there is insufficient supply, you will have to pump it up - a car pump is quite suitable for this. | |
| In the variant under consideration, the tank already has devices for its placement, even in two versions - legs for installation on a horizontal surface (blue arrows) and a mounting panel for hanging on the wall (yellow arrow). The tank is mounted in the chosen location, and then connected by a section of pipe to a tee embedded in the return line. At this point the installation can be considered complete. | |
| Another version of the tank, on the body of which there are no structural elements for fastening at the installation site. But they are usually included as separate parts in the delivery kit. | |
| Usually this is a bracket - a mounting pad for fastening to the wall, and a long screw band clamp. | |
| The collar of the clamp is straightened and threaded through the slots of the mounting area. | |
| All this is done in such a way that the protruding side of the tank falls into a special groove in the mounting platform (shown by arrows), and the clamp is higher than the side. | |
| After installing the tank in the mounting area, the ends of the clamp are connected, first tightened by hand... | |
| .. and then - all the way, using a screwdriver or wrench. | |
| In this form, the tank will be ready to hang on the wall. | |
| Installation of plumbing fittings to the cistern pipe is carried out in the same order as mentioned above. | |
| The nipple can be located openly, only with a dustproof plastic cap. Checking the pressure and pumping, if necessary, is no different from the previously considered option. | |
| By the way, tanks usually come from the factory with a preset pressure in the air chamber, and you can immediately select the required parameter. It is indicated on the packaging and in the technical documentation of the product. Further installation of the tank is carried out in the already known order - installation on the wall in the selected location and connection with a pipe with a tee. |
After final installation, be sure to open the tap and fill the system with coolant. If no leaks are detected in the connecting nodes, the installation of the expansion tank can be considered complete.
Video: inserting an expansion tank into the contour of polypropylene pipes
At the end of the article, it is necessary to emphasize once again that a closed heating system with a sealed expansion tank must necessarily have a reliable “safety group”. If it is located in a place that is not entirely convenient for regular visual monitoring, it makes sense to install an additional pressure gauge in the immediate vicinity of the expansion tank - this will make it much easier to monitor the condition of the entire system. You can find out the expansion tank for heating at the link.
You may be interested in information about what a bimetallic radiator is
Types of membrane expanders
To compensate for the volume of coolant in the network at the time of temperature changes, two types of containers are used: open and closed. The first type is very popular among consumers, but has a number of disadvantages:
- installation requires significant costs, since such devices are installed in the upper zone of the system in order to set the required atmospheric parameters;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of the liquid medium;
- there is a possibility of rust due to prolonged contact of water with air.
The second type of expansion tanks is devoid of such disadvantages. Their design provides for the presence of a special membrane (balloon or diaphragm).
SF-mix Clack up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix Runxin up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix manual up to 0.8 m3/h
Volume calculation
There is a very simple method for determining the volume of an expansion tank for heating: 10% of the volume of coolant in the system is calculated. You should have calculated it when developing the project. If this data is not available, you can determine the volume experimentally - drain the coolant, and then fill in a new one, measuring it at the same time (put it through a meter). The second way is to calculate. Determine the volume of pipes in the system, add the volume of radiators. This will be the volume of the heating system. From this figure we find 10%.
Shape may vary
The second way to determine the volume of an expansion tank for heating is to calculate it using the formula. Here you will also need the system volume (indicated by the letter C), but other data will also be needed:
- the maximum pressure Pmax at which the system can operate (usually the maximum boiler pressure is taken);
- initial pressure Pmin - from which the system begins operation (this is the pressure in the expansion tank, indicated in the passport);
- coolant expansion coefficient E (for water 0.04 or 0.05, for antifreeze it is indicated on the label, but usually in the range of 0.1-0.13);
Having all these values, we calculate the exact volume of the expansion tank for the heating system using the formula:
Formula for calculating the volume of an expansion tank for heating
The calculations are not very complicated, but is it worth bothering with them? If the system is open, the answer is clear - no. The cost of the container does not depend very much on the volume, plus you can make it yourself.
Expansion tanks for closed type heating are worth counting. Their price depends greatly on volume. But, in this case, it is better to take it with a reserve, since insufficient volume leads to rapid wear of the system or even its failure.
If the boiler has an expansion tank, but its capacity is not enough for your system, install a second one. In total, they should give the required volume (the installation is no different).
What will result from insufficient expansion tank volume?
When heated, the coolant expands, its excess ends up in the expansion tank for heating. If all the excess does not fit, it is released through the emergency pressure relief valve. That is, the coolant goes into the sewer.
Working principle in graphical representation
Then, when the temperature drops, the volume of coolant decreases. But since there is already less of it in the system than there was, the pressure in the system drops. If the lack of volume is insignificant, such a decrease may not be critical, but if it is too small, the boiler may not work. This equipment has a lower pressure limit at which it is operational. When the lower limit is reached, the equipment is locked. If you are at home at this time, you can correct the situation by adding coolant. If you are not there, the system may unfreeze. By the way, working at the limit also does not lead to anything good - the equipment quickly breaks down. Therefore, it is better to play it safe and take a slightly larger volume.
Installation Requirements
It is quite possible to install the unit even with your own hands. It is absolutely not necessary to call a specialist for this. The main thing is to strictly follow the installation rules and carry out everything according to the design of the expansion membrane tank.
An expander with a volume of 30 liters or more should not be attached to load-bearing walls. As a rule, large tanks are installed directly on the floor on special steps. During installation, you must ensure that:
- the circumference of the adapter was ¾, and the return had a corresponding thread;
- during the installation process, the structural elements did not interfere with the work;
- no excessive load was placed on the tank;
- you had paronite heat-resistant gaskets at your disposal;
- the container was equipped with a special locking mechanism that allowed the gas pressure to be adjusted.
Membrane tank design
The expansion membrane tank for heating is a sealed cylindrical steel body coated with red epoxy varnish (there are also tanks coated with blue varnish, but they are intended for cold water). The housing contains 2 chambers: gas and water, which are separated from each other by a movable gas-tight membrane (diaphragm) made of butyl rubber. Thanks to this material, the membrane is able to function stably at various temperatures (from -10 to +100°C) and perform up to 100,000 cycles.
Design of a membrane expansion tank.
The membrane almost completely eliminates the interaction of coolant and gas. The absence of such interaction allows the pre-pressure in the gas chamber to be maintained longer, which has a positive effect on the service life of the tank.
Note! Modern high-quality membranes do not simply stretch under the pressure of the expanding coolant, but seem to “stick” to the walls of the tank. This operating principle allows you to increase the service life of the membrane.
Reflex tank in section.
Both chambers have the same pressure, which allows you to maintain the tightness of this section of the heating system. The air chamber is filled with a nitrogen-containing mixture. As the coolant expands, nitrogen is “compressed,” allowing the coolant to “enter” the water chamber.
Most modern membrane heating tanks have a nipple built into the body (similar to a regular car nipple), with which you can “pump up” the air chamber, increasing the pressure in it. You can do this yourself at home using a pump or compressor. However, it should be remembered that it is recommended to pump in nitrogen, not air. The fact is that the oxygen contained in the air will cause accelerated corrosion of the walls of the tank body, which will inevitably shorten the service life of the device. Nitrogen is neutral and does not contribute to corrosion.
Beam for tank and safety group. , Saint Petersburg.
Imera membrane type expansion tank.
The tank body has an outlet with an external threaded connection, which simplifies the installation process. Depending on the model, the thread may be:
- For low pressure tanks (from 0.5 to 1.5 bar) - 3/4″ or 1″;
- For medium pressure tanks (1.5 bar) – 1″;
- For high-pressure tanks (from 3 bar and above) - from 1″ to flange connection DN 100;
Use as a hydraulic accumulator
Thus, the expander is used in water supply systems. Thanks to the unit, it is possible to accumulate a certain amount of liquid and then use it for its intended purpose. It is noteworthy that to organize the supply, the accumulated liquid medium under pressure is used without taking into account the operation of the pumping station. The pump does not have to be turned on too often, which significantly extends its service life.
In addition, the membrane cistern replenishes the expansion of H2O in the hot water supply.
For protection against water hammer
Such a load represents a sharp jump in the speed of water flow, which occurs when the pipeline is unexpectedly blocked. A change in the number of atmospheres, in turn, can cause damage to pipes. In such a situation, the expansion tank acts as a damper: the membrane-partition stretches, which leads to an increase in the volume of the corresponding compartment of the tank, and the pressure decreases.
Installation instructions
When planning to install the device yourself, we must not forget about the need to first study the installation manual in detail. If you do not have the necessary documentation, you should definitely contact the retail outlet where you purchased the product. Otherwise, understanding the nuances of the equipment will be much more difficult. And every mistake will subsequently only result in additional costs.
According to the advisory document included with the device, design changes are not permitted. Repair or installation work may only be carried out by persons who have access to perform a specific activity.
When replacing a failed tank part, you should replace it with only the original. After all, according to the instructions, it is prohibited to use elements of inadequate quality. The installation manual also contains a detailed description of safety precautions that must be strictly adhered to during installation of the unit.
AMETHYST - 02 M up to 2 cubic meters/day.
Aeration unit AS-1054 VO-90
Main table dispenser AquaPro 919H/RO (hot and cold water)
The difference between a tank and a hydraulic accumulator
Despite the similarity in design characteristics, the purpose of the devices is still not the same. The expansion tank compensates for the increase in liquid volume due to heating. A similar device accumulates a liquid medium under pressure, minimizing the number of starts of the pumping station, thereby prolonging its performance.
Also inside the hydraulic accumulator structure there is a special rubber bulb container, thanks to which it is possible to avoid contact of H2O with the walls of the tank. The expander, in contrast, is manufactured together with a membrane designed to divide the body into two compartments. In this case, there is interaction of the coolant with the tank.
Recommendations for selection
When choosing a tank, special attention should be paid to its design. If critical pressure drops are not expected, then it is better to choose an inexpensive fixed tank. Otherwise, you will need to install a collapsible expansion tank, since replacing the membrane will cost much less than replacing the entire structure completely.
Additional factors to consider when choosing:
- wall thickness: must be at least 1 mm;
- type of external and internal coating: the body made of metal should not be subject to corrosion;
- volume of the liquid compartment: should not be too large to avoid reducing the temperature of the coolant in the pipes;
- container design: it can be horizontal or vertical; in other positions its installation is prohibited.
Expansion tank in the room
Despite the apparent simplicity of such an element of the heating system as a water tank, its selection and installation require a lot of attention and scrupulousness, even in small things. A serious attitude will help you avoid any troubles and make heating a private home effective and safe.
Video on the topic: