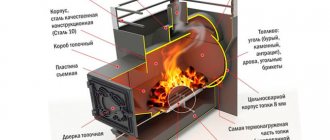
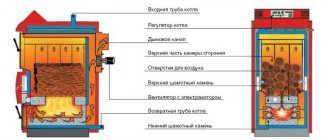
The theoretical combustion temperature of coal lies in the range of 1000...2300 °C and depends on a number of factors - combustion conditions, specific calorific value, moisture content, and so on. The actual heating at the center of the flame burning in the firebox of a boiler or stove rarely exceeds 1200 degrees. But the owner of the home is not at all faced with the task of heating the unit and pipes white-hot. The main goal is to efficiently use the energy of a valuable fossil, obtaining the required amount of heat over a long period.
Features of different types of fuel
Let's consider the two main, most common types of solid fuel raw materials - firewood and coal.
Firewood contains a significant amount of moisture, so the moisture first evaporates, which will require a certain amount of energy. After the moisture evaporates, intense combustion of the wood begins, but, unfortunately, the process does not last long.
Therefore, to maintain it, regular addition of firewood to the firebox is required. The ignition temperature of wood is about 300°C.
In terms of the amount of heat generated and the duration of combustion, coal is superior to wood . Depending on the age of the fossil material, the mineral is divided into types:
- brown;
- stone;
- anthracite.
Specifics of a coal-fired furnace
Such a device has design features that imply a coal pyrolysis reaction. Coke is not a mineral; it is a product of human activity.
The combustion temperature of coal is 900 degrees, which is accompanied by the release of the required amount of heat energy. What is the technique for creating such an amazing product? The role lies in the established woodworking, due to which a significant change in its structure occurs and a very large amount of moisture is released from it. A similar process is performed in specialized ovens. The working principle of such devices is based on the pyrolysis process. A coke furnace consists of four basic elements:
- fireboxes;
- reinforced foundation;
- chimney;
- recycling compartment.
Composition of different types of fuel
Brown coal is a young deposit, so it contains the largest amount of moisture (from 20% to 40%), volatile substances (up to 50%) and a small amount of carbon (from 50% to 70%).
Its combustion temperature is higher than wood and is 350°C. Heat of combustion - 3500 kcal/kg. The most common type of fuel is coal. It contains a small amount of moisture (13-15%), and the content of the combustible element carbon exceeds 75%, depending on the variety.
The average combustion temperature is 470°C. Volatile gases in coal are 40%. When burned, 7000 kcal/kg is released.
The oldest solid fuel deposits include anthracite, which occurs at considerable depth. It contains virtually no volatile gases (5-10%), and the amount of carbon varies between 93-97%. The heat of combustion ranges from 8100 to 8350 kcal/kg.
Special mention should be made of charcoal. It is obtained from wood by pyrolysis - combustion at high temperatures without oxygen. The finished product has a high carbon content (from 70% to 90%). When burning wood fuel, about 7000 kcal/kg is released.
You can read about the features of using peat briquettes in this article:
Temperature detection option
During winter, the issue of heating living spaces is very important. Due to the systematic increase in the cost of thermal media, people need to look for other options for generating heat energy.
The best way to solve this problem is to select solid fuel boilers that have good production characteristics and excellent heat conservation.
The specific heat of combustion of coal is a physical quantity that shows how much heat can be released during the complete combustion of a kilogram of fuel. In order for the boiler to work for a long time, the main thing is to choose the right fuel for it. The specific calorific value of coal is high (22 MJ/kg), due to which this type of fuel is considered good for good boiler operation.
Combustion process
Depending on the type and grade, fuel is divided into short-flame and long-flame.
Short-flame coals include anthracite and coke, and charcoal. When burned, anthracite produces a lot of heat, but to ignite it it is necessary to provide a high temperature with a more easily flammable fuel, such as wood. Anthracite does not emit smoke, burns odorless, and has a low flame.
Long-flame fuels burn in two stages. First, volatile gases are released, which burn above the coal layer in the furnace space.
After the gases burn out, the remaining fuel begins to burn, which has meanwhile turned into coke. The coke burns on the grates with a short flame. After carbon burns out, ash and slag remain.
Heating with coal - practical advice
Complete combustion of coal fuel requires a special approach to the issue. The task is to achieve maximum efficiency of the heat source, not to overheat the coolant and not start a fire due to too high a temperature.
Anthracite is the highest calorific coking coal
We suggest taking into account our recommendations for choosing equipment:
- It is not advisable to heat purely wood-burning boilers and factory-made steel stoves with high-calorie coals - stone and anthracite. Powerful heat transfer and strong heating can deform the walls of the firebox (usually they are made 3 mm thick).
- TT boilers with water-filled grates are not suitable for coal heating. Due to the temperature difference, the hot sintered layer tightly sticks to the water pipes, making air passage and further cleaning of the unit very difficult.
- If you have calibrated coal with a fraction size of 25-50 mm (classified as walnut), the best choice would be a boiler with automatic fuel supply. The unit is equipped with a retort burner and a fan that precisely meteres the air injection at the command of the electronics. Duration of continuous operation – up to 7 days.
- The ideal option is to buy a mine or traditional boiler designed to use coal. The heat generator is equipped with movable grate bars, rotated by an external handle. The device helps to dump ash from the firebox into the lower chamber.
- Heaters equipped with a fan or smoke exhauster are more convenient and safer than boilers with mechanical regulators on a chain. If the temperature rises critically, the automation will turn off the air supply and the channel will be closed by a damper. The usual blower cover does not fit tightly, oxygen seeps into the chamber, and slow combustion continues.
- Heating an open fireplace with coal is a futile exercise. You won’t get much heat, you’ll just spread dirt in the room and an unpleasant smell will appear.
- To increase safety, it is highly advisable to install an additional thermal relief valve on the boiler. In case of overheating and boiling, the element discharges part of the coolant from the boiler jacket and simultaneously fills it with cold tap water.
You need to get used to each type of coal. It is better to add unfamiliar fuel in small portions, adjusting the draft with a damper and watching the temperature rise. When you have calculated all the combustion nuances of a given brand, fill the firebox 2/3 full.
An important point regarding the operation of a brick oven with a stove. Never open the burners after loading a new portion of coal; use the side door. If there is a lack of oxygen, the fuel releases pyrolysis gas, which will come out through the moved burner.
Burning
Let's consider the process of fuel combustion in a conventional stove, which is used for heating private houses. It consists of main parts:
- fireboxes;
- blower;
- chimney with pipe.
The firebox is connected to the blower through a special grate (grids) located at the bottom of the firebox . Fuel is placed on the grate, and air enters the firebox from the ash pan through the grate.
What coal to choose for the fire?
What is coal? This is a product of plant origin, which contains carbons and non-flammable impurities. It is they who form ash and slag-like substances after burning. The ratio of the two components is different everywhere. It is this, as well as the “age” of natural fuel, that determines the grade of coal. Experts distinguish several varieties.
The “youngest” type of coal is lingite. It has a rather loose structure. If you pick up a lump of lingite, it will quickly crumble and lose its shape. This type of coal is most often used in thermal power plants, but lingite is not suitable for heating a home.
In addition to lingite, brown coal, hard coal, and anthracite are also mined - the most ancient carbon deposits. All varieties have different humidity levels. In brown coal, for example, humidity is 50%; in anthracite its threshold does not exceed 7%. Therefore, anthracite has the highest specific heat. Its indicators are 9 thousand kcal/kg.
Material for coal-fired stoves is the main criterion for choosing fuel and stove. Let's look at these qualities in more detail.
When the heating of the stove is successfully completed and the firewood is happily blazing in the firebox, all that remains is to monitor the thermal operating conditions and add new logs in time. As for the mode, it is recommended to maintain it constantly at the same level, avoiding overheating
This is important because alternating intense heating and cooling often causes the furnace body to expand and contract, causing cracks to occur.
Maintaining optimal thermal conditions and timely adding logs is the best way to properly heat a stove with wood, although it is not very convenient at night. No one wants to get up in the middle of the night, although if there is severe frost outside, this cannot be avoided, otherwise the house will be cold by morning. During continuous burning for several days, the ash pan has to be cleaned
Combustion formulas
Ignition temperatures of different types of fuel (click to enlarge)
When fuel (wood, coal) ignites, a chemical reaction occurs and heat is released.
Carbon dioxide reacts with the carbon in the fuel in the upper layers to form carbon monoxide.
The combustion process does not end there, because rising up in the combustion space, carbon monoxide reacts with oxygen from the air, the influx of which occurs through the vent or the open firebox door.
Its combustion is accompanied by a blue flame and the release of heat. The resulting carbon monoxide (carbon dioxide) enters the chimney and escapes through the pipe.
Smoldering with minimal oxygen will produce non-poisonous carbon monoxide, producing even heat.
Wood: properties and characteristics
Solid fuel heating boilers are replacing installations based on the principle of gas combustion. Some have been using them for a long time, others are just starting to use them to heat their homes. But everyone knows that the creation of cozy conditions in the house depends entirely on the quality of the fuel. A common material used in similar devices is wood. In fact, it is used quite widely. However, it is very difficult to heat a home using this material throughout the winter. Namely, this becomes clear during the worst cold weather, when the boiler does not stop working almost at the maximum of its capabilities.
At the same time, the use of firewood is associated with some inconveniences. First of all, it is a fairly low temperature and rapid combustion. During the combustion of wood, the temperature rises to only 200-400°C, and heat transfer rates can reach significant values. However, due to the rate of combustion, this type of fuel poses specific challenges, requiring strict control of the presence in the combustion chamber. This fact is the most important drawback, because it requires a very large supply of firewood for the winter.
Application
The main use of fuel is to burn it to produce heat.
Heat is used not only for heating a private home and cooking, but also in industry to support technological processes that occur at high temperatures. Unlike a conventional stove, where the process of oxygen supply and combustion intensity is poorly regulated, in industrial stoves special attention is paid to controlling the supply of oxygen and maintaining a uniform combustion temperature.
Let's consider the basic scheme of coal combustion.
- The fuel heats up and moisture evaporates.
- As the temperature rises, the coking process begins with the release of volatile coke gases. When burned, it provides the main heat.
- Coal turns into coke.
- The coke combustion process is accompanied by the release of heat sufficient to initiate coking of the next portion of the fuel.
In industrial boilers, the combustion of coke is separated into different chambers from the combustion of coke oven gas. This allows the flow of oxygen for coke and gas at different intensities, achieving the required combustion rate and maintaining the required temperature.
Characteristics and properties of wood
Nowadays there is a tendency to switch from installations, which were based on the process of gas combustion, to solid fuel home heating systems.
Not everyone knows that creating a comfortable climate in the house depends on the quality of the selected fuel. As a classic material used in such heating boilers, we note wood.
In harsh climate conditions, characterized by very long and cold winters, it is very difficult to heat a home with wood for the entire heating period. With a sharp drop in ambient temperature, the boiler owner is forced to use it to the limit of its greatest capabilities.
When choosing wood as a solid fuel, big problems and inconveniences arise. First of all, let us remind you that the combustion temperature of coal is much higher in comparison with wood. One of the disadvantages is the high rate of combustion of firewood, which makes it very difficult to operate the heating boiler. Its owner is forced to regularly check the availability of firewood in the combustion chamber; a very large amount of it will be needed for the heating period.
Using Charcoal
In everyday life, charcoal is used to cook meat on the grill.
Thanks to the high combustion temperature (about 700°C) and the absence of flame, uniform heat is provided, sufficient for cooking meat without charring.
It is also used as fuel for fireplaces and cooking on small stoves.
In industry, it is used as a reducing agent in metal production. Charcoal is indispensable in the production of glass, plastics, and aluminum.
It is possible to make charcoal yourself. Details:
Combustion temperature of wood and coal in a variety of devices
The primary parameter that makes it possible not to make a mistake in your choice of fuel and heating units is the combustion temperature of coal, because its value determines the reliable operation of the boiler and its productivity.
The issue of heating your home during winter is especially acute. In conditions of continuous rise in price of energy sources, people are forced to look for alternative ways to generate heat. An excellent way out of this situation is the use of solid fuel boilers that have good production and heat saving parameters.
However, for their full operation, the preparation of solid fuel is necessary. Its best variation is considered to be coal, which provides good stove performance. A balanced choice of this fuel is considered the key to good boiler operation.
Birch
It can also be said about birch firewood that it is second in power after oak. In terms of their heat characteristics, they are actually not inferior to larch trees. However, they cut and saw noticeably better, and they flare up much easier. In addition, they have birch bark, which is one of the best natural kindlings. Well, of course, birch is found much more often in our area than oaks and larches, and in some places it even grows en masse. By the way, even when fresh (“green” and damp) it burns quite well, because it contains a relatively small amount of moisture, although it produces less heat than dry wood. This often comes to the rescue in damp areas, where dried or littered birch trees quickly rot, and high-quality dry birch firewood is a rarity. By the way, even in dry forests birch birch birch can be difficult to find, because this tree does not shed its bark after drying out, and almost always becomes rotten.
- Fire power: 0.80 de.
- Calorific value: 3016 kWh/m³.
- Combustion temperature: 816 °C.
- Burning time: long.
- Flame: even, with a slight crackle; in the case of damp wood, it hisses and can sometimes “shoot.” It smokes at the very beginning (while the bark is burning).
- Coals: “thermonuclear” (smolder for a long time and give off intense heat).
- Difficulty of lighting: medium or easy - depends on whether the birch is wet or dry. The first one flares up very tediously, sometimes you have to have a decent amount of good kindling. Dry birch is a completely different matter. She is able to quickly work from her own wood chips and birch bark.
How to store coal
When purchasing a large amount of fuel at once, you need to know how to store it. If you follow storage rules, coal will not lose its original properties.
Shelf life
It is beneficial to purchase solid fuel in large quantities at once. But, like any other combustible material, coal has a shelf life that depends on the deposit and brand.
It is interesting that coal can remain in the bowels of the earth for millions of years without losing its quality. However, once mined, it immediately begins to interact with the environment. The most dangerous thing for it is a meeting with oxygen - that is, oxidation. It destroys the structure of the raw material and renders it unusable.
The larger the coal pieces, the longer it will take to oxidize. For example, coal with a fraction above 100 mm can be stored without loss of quality characteristics for up to 3 years, with pieces with a size of up to 100 mm - about 1 year, and fuel with a fine fraction - less than 24 months. The 20-40 mm fraction, which you can purchase from our company, retains its quality for one season. That is, it makes no sense to store such coal for several winters.
Premises requirements
The ideal storage location is dark, covered and well ventilated. The material can be packaged in bags or wooden boxes. Coal can be placed in the yard. To do this, use a platform into which coal is poured and compacted to reduce the air gap. To extend shelf life, it is advisable to cover the fuel with a lid or polyethylene.
Let's look at a specific example. For the heating season we need 3.5 tons of coal (about 4.5 cubic meters). This means you need a room of 4 m2 and another area for passage. It is advisable that the premises have a reserve area (at least 5% of the area). It will be needed to refresh coal during long-term storage and cooling if it is hot.
It is best if the coal storage room is next to the boiler room. This way you won't have to carry heavy buckets over long distances. It must be equipped with drainage structures to drain melt, rain and groundwater.
The warehouse cannot be equipped with various communications - gas pipelines, heat sources, electrical lines. In addition, it should not be located where underground communications pass - electrical cables, pipelines, and so on.
You should always remember that coal can ignite. That is why this factor must be taken into account during storage. You need to place the fuel, compacting the small pieces well. After all, spontaneous combustion, which occurs due to the penetration of air into the layers of coal, can cause a fire. Spontaneous combustion can occur in places where different types of fuel or different grades of coal come into contact. Also, fresh coal should not be unloaded onto a site that is poorly cleared of old fuel residues.
Storing coal indoors or under a canopy helps preserve the quality characteristics of the fuel for a longer period. But it is not always possible to store it in closed conditions.
Outdoor coal storage
It is best if you find a dry and dark place to store the fuel. This could be a barn, shed or other outbuildings. You can purchase a special bunker - a metal box with a closing hatch. Canvas bags are also suitable (it will be more convenient to transport coal to the boiler in them).
It’s not scary if the coal is stored in the open air. As for precipitation, it is not harmful to fuel. But in order for coal not to lose its properties, you need to follow several recommendations for storing the material.
So, if you are forced to store coal outside:
- Choose a flat, debris-free area for the material. It must be located in a non-flooded, somewhat elevated place (so that during spring floods or rainy times the water does not wet the coal from below). The soil under the material must be dry or frozen.
- It is desirable that the base under the coal be solid. You can lay it out with bricks, tiles, and finally lay down boards or lay wooden pallets.
- When choosing a site, make sure that there are no open sources of fire nearby or expected. Also make sure that there is no equipment that operates at high temperatures (for example, welding) near the coal.
- Before adding material to the site, place a tarp underneath it. This way the coal will be dry, without snow and leaves.
- Periodically pour and stir the material (especially during frosts). This is necessary to ensure that the coal does not freeze in the open air.
As you can see, this material is quite demanding in terms of storage conditions. However, this is compensated by its high efficiency.
When to place food on the grill
When the charcoal briquettes are covered with a thin layer of ash (and the charcoal is hot around the edges), the heat from the coals will be very intense. For most grilled foods, this temperature is too high.
Distribute the coals as desired, position the grill and close the grill lid
It is important that the grill warms up for 10-15 minutes, then the grate will become hot and you can quickly fry food on it. Plus, once the grate is warm, it's easy to clean.
The heat will warm up any remaining food stuck to the grate so that you can easily remove it with a special brush.
Briefly about the main thing
To summarize, in order to achieve maximum heat transfer from burned wood, you need to:
- Select wood with the highest density.
- Prepare firewood in advance by sawing trunks and cutting logs.
- Reduce the moisture content of wood by storing it in piles under cover for at least one year.
- When burning in a furnace, provide the required amount of oxygen to the fire, trying not to exceed the required threshold.
Compliance with all specified conditions will guarantee that the combustion temperature of the wood will reach its maximum value, but will not disappear in the chimney. With a reasonable approach, all heat transfer will remain in the living space and optimally heat it.
Source