Author: Site editors
Publication date: 25.04.2019
Issues discussed in the material:
- What is heat recovery ventilation?
- Ventilation scheme with recovery
- What are the advantages of a ventilation system with recovery?
- Types of recuperators for ventilation
- How to choose air handling units with heat recovery
- Tips on how to install supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery
Each person, of course, has his own idea of how comfortable housing should be arranged. For one, the appearance and interior of the premises will be of paramount importance, while the other will consider the various amenities most important. But no matter what we give preference to, in any case, the majority will agree that in order for housing to be called comfortable, it is necessary that it have an optimal temperature - warm in the cold season, and cool in hot weather.
Of course, no matter how we create such conditions, they are always associated with certain costs. We can use devices like air conditioners, fans, heaters. Someone will prefer to carry out repairs in such a way as to make the premises airtight. And such a move will really help preserve the internal temperature. But we must not forget that in such cases one serious trouble cannot be avoided - the housing will stop being ventilated, so there will be no talk of any comfort. The only solution is to ventilate to ensure air movement. Some may be concerned about whether this will result in additional energy costs. But they will even decrease if your choice is ventilation with heat recovery for a private house, apartment or industrial facility. What is it, how does it work? This article will tell you about this and much more.
What is heat recovery ventilation?
Home ventilation with heat recovery is one of the forced ventilation systems. It usually provides for air heating. This function is partially performed by a recuperator - a device designed to heat air, although the main heating is not provided by it, but by the air heater.
Of course, you may have never heard of supply or exhaust ventilation with heat recovery, but this does not mean that it is a new invention. Most likely, you are misled by the Latin word “recuperation,” which can be translated into Russian as “return of what was spent.” This reveals the whole point: a recuperator is a special heat exchanger, that is, a device that is quite common in ventilation systems, although in Russia it is not used as often as abroad. How does the ventilation of a private house or apartment recover? Let's take a closer look at it.
Heat recovery is the return of heat leaving a room. The point is that there is incoming and outgoing air flow. At the same time, the air that leaves the room heats the counter air due to heat exchange. This happens in the cold season, and on hot days, for example in summer, the outgoing air, on the contrary, cools the incoming air. But in such situations it is more correct to talk about cold recovery .
Obviously, such a procedure is necessary for the user to save available funds, because when the ventilation is not equipped with recovery, a lot of heat goes outside instead of being reused indoors. Accordingly, heating bills increase, since, in fact, we heat the street, spending an exorbitant amount of heat for nothing. It is precisely in order to avoid such waste and colossal bills that it is worth thinking about installing ventilation with heat recovery. After all, this way you return the air that you heated, do not allow the heat to leave the room, and save money.
It is not surprising that ventilation with recovery is becoming more and more popular and there is nothing to oppose to the classic versions of ventilation systems with such a design. This is logical, because forced ventilation with recovery is not much more expensive than conventional ventilation, and its maintenance is completely elementary. In this regard, many prefer to forget about climate control equipment, which was once positioned as the most effective in combination with ventilation systems. Recuperation is much more profitable both in terms of rational use of electricity and in terms of saving heating costs. Its cheapness is compared with the cost of lighting with energy-saving light bulbs.
What else attracts consumers to a supply and exhaust ventilation system with air recovery?
Firstly , such devices are small in size.
Secondly , they do not spoil the interior.
Thirdly , they have a low noise level.
Fourthly , with a minimum of costs we get maximum operating efficiency.
They are also in demand in public institutions, among which the following can be listed:
- Cinemas and theaters.
- Canteens, cafes, snack bars.
- Libraries.
- Hotels and inns.
- Stations.
- Offices and retail premises.
It is possible to design a ventilation system with recovery for a private house, multi-storey building, etc. The variety of such devices allows you to choose them for any occasion. The different capacities of such structures make it possible to find an option even for buildings that have a residential basement floor.
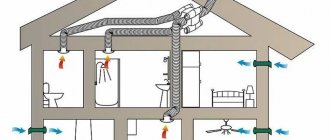
It is important to understand that supply ventilation with heat recovery for an apartment or house is a forced system. It is distinguished from natural by the presence of fans, which ensure the movement of air flows at any convenient time and do not depend on external factors, such as draft that appears due to differences in temperatures.
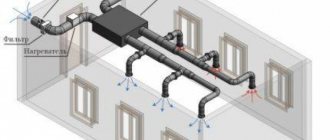
Ventilation scheme with recovery
Design and calculation examples
In order not to make a mistake when choosing a recuperator, you should calculate the efficiency and operating efficiency of the device. To calculate the efficiency, use the following formula: K = (Tp - Tn) / (Tv - Tn), where Tp denotes the temperature of the incoming flow, Tn is the street temperature, and Tv is the room temperature. Next, you need to compare your value with the maximum possible efficiency indicator of the purchased device. Typically this value is indicated in the model’s technical data sheet or other accompanying documentation. However, when comparing the desired efficiency and that indicated in the passport, you should remember that in fact this coefficient will be slightly lower than stated in the document.
Knowing the efficiency of a particular model, you can calculate its effectiveness. This can be done using the following formula: E (W) = 0.36xPxKx (Tv - Tn), where P will denote air flow and is measured in m3/h. After all the calculations have been made, you should compare the costs of purchasing a recuperator with its efficiency, converted into monetary equivalent. If the purchase justifies itself, you can safely purchase the device. Otherwise, it is worth considering alternative methods of heating the incoming air or installing a number of simpler devices.
When independently designing a device, it should be taken into account that counterflow devices have the maximum heat transfer efficiency. They are followed by cross-flow ducts, and in last place are unidirectional ducts. In addition, how intense the heat exchange will be directly depends on the quality of the material, the thickness of the dividing partitions, and also on how long the air masses will remain inside the device.
What are the advantages of a ventilation system with recovery?
As we have noted more than once, the main advantage of such a system is the ability to control the interaction of air inflow and outlet. Due to this, we significantly reduce ventilation heat loss, although we continue to saturate the room with fresh air.
Now let's talk in more detail about each of the advantages of ventilation systems with recovery.
Efficiency . Natural air removal is not always a convenient solution, because we become dependent on circumstances, environmental conditions, and temperature differences. In this regard, it is much easier to use a ventilation system with recovery, which can force air. A simple example of forced ventilation is a kitchen hood. More complex devices are capable, among other things, of getting rid of excess moisture. But this is simple exhaust equipment. In our case, we are talking about supply and exhaust systems that are capable of organizing the movement of air flows in both directions at once, mixing them and forming the necessary temperatures for a comfortable stay of a person in the room, that is, recuperating air.
Profitability. It should be noted that recuperation systems can recoup their cost through savings on heating and electricity. Costs are significantly reduced, sometimes by 5 times, that is, you are already paying 80% less than usual. Ask your friends how much it costs them to heat a country house if you don’t have one. The numbers will be impressive. Imagine how much money recovery ventilation can save. If inexpensive elements wear out, they can be replaced without negative consequences. During the warm season, you can save on climate control equipment, while simultaneously reducing emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere. Yes, even from an environmental point of view, you are causing significantly less damage to the environment, because, among other things, you are reducing the load on the network. And don’t let it seem to you that one person is too little. Firstly, these are quite serious amounts of energy. Secondly, more and more people are switching to ventilation with recovery over the years.
Practicality . Ventilation systems with recovery are usually small in size, which means they are easy to install. Such equipment can be located in the bathroom, in the closet, and built into the ceiling. Today there are a huge variety of models to suit all tastes. So you don't have to worry about the interior.
Plate type heat exchangers
The simplest designs for ventilation systems. The heat exchanger is made in the form of a chamber divided into separate channels located parallel to each other. Between them there is a thin plate partition, which has high thermal conductivity properties.
The principle of operation is based on the exchange of heat from air flows, that is, exhaust air, which is removed from the room and gives up its heat to the supply air, which enters the house already warm, thanks to this exchange.
The advantages of this technology include:
Heat exchange using a recuperator
- easy device setup;
- complete absence of any moving parts;
- high efficiency.
Well, one of the most significant drawbacks in the operation of such a recuperator is the formation of condensation on the plate itself. Typically, such heat exchangers require additional installation of special drop eliminators. This is a necessary parameter, since in winter the condensate can freeze and stop the device. That is why some devices of this type have built-in defrosting systems.
Types of recuperators for ventilation
A recuperator is a heat exchanger, albeit a special one. It is connected to ventilation channels that produce air exhaust and supply. Dirty air from the room gives off heat to incoming flows, that is, a recovery procedure is performed.
Plate recuperators differ from conventional ones in that they prevent air mixing. In them, recovery is performed somewhat differently. A number of plates are located close to each other, due to which the air can transfer heat without touching. The material in such ventilation systems is usually aluminum foil, known for its thermal conductivity. There are products made of plastic. They are more expensive, but more effective.
Ventilation with recovery, performed using plate heat exchangers, often suffers from ice. The fact is that the surfaces of the recuperator are covered with ice due to condensation. This does not have the most favorable effect on the quality of the device. And then the owner of ventilation with recovery has to work hard to make the ice melt. Accordingly, time, effort, and electricity are wasted.
However, some developers have foreseen how to protect ventilation with recovery from ice. For this purpose, a technology has been invented that heats the incoming air flow to the temperature at which the condensate simply cannot freeze.
By the way, this is not the only way out. Other developers have proposed equipping ventilation systems with recuperation with cassettes made of hygroscopic cellulose. We save on heating the air, since such cellulose itself absorbs moisture and then returns it at the outlet. But they can only be used in cases where there is no over-humidification of the air.
Rotary recuperators. In recovery ventilation systems using these devices, the air is mixed. The operating principle is as follows: a metal rotor rotates, allowing air to move outward and inward. The rotation speed is usually adjustable.
As is clear, recovery in this case has a number of disadvantages, for example, it is much more expensive due to the presence of elements that fail over time. But high efficiency rates, reaching 90%, contribute to the popularity of such products.
In essence, the feasibility of purchasing such a device largely depends on the efficiency of organizing air recovery. A quality product can usually pay for itself.
Recuperators with intermediate coolant . This device has two compartments separated by a container of liquid capable of transferring heat from the outgoing to the incoming air.
Of course, recovery in this case is very safe, because contaminants are not transferred between streams. Speed adjustment is provided. Wear is unlikely. But the disadvantage is the low efficiency, ranging from 45 to 60%.
Chamber recuperators . The flap divides the compartment into two halves. Rotating, it changes places of air flows. The temperature change occurs from the chamber walls.
Although air recovery in this case has a high efficiency rate of 70 to 80%, and wear is unlikely, there is a tendency for the transmission of dirt and unpleasant odors.
Heat pipes . This recovery device is made of hermetically connected tubes. They contain a substance that contributes to changes in air temperature. Most often it is some kind of freon.
Closedness avoids leakage of substances. It simply flows to different sides of the tube. The efficiency of such equipment is in the region of 50 – 70%.
Heat pipes
It is worth highlighting one more type of recuperator. Heat recovery in a home using heat pipes is quite effective. Such devices are sealed tubes made of metal that has high heat-conducting properties. Inside such a tube there is a liquid that has a very low boiling point (freon is usually used here).
Such a heat exchanger is always installed in a vertical position, with one of its ends located in the exhaust duct and the other in the supply duct.
The principle of operation is simple. The drawn out warm air, washing the pipe, transfers heat to the freon, which, boiling, moves upward with a large amount of heat. And the supply air washing the top of the tube takes this heat with it.
The advantages include high efficiency, quiet operation and high efficiency. So today you can save a lot on heating your home, paying some of it back.
How to choose air handling units with heat recovery
What should you remember when choosing ventilation with recovery? You need to buy such equipment so as not to regret it, so ask the seller about the following nuances:
First of all, ask the seller the following questions:
- Who is the manufacturer of this air recovery ventilation? How long has this company been in business, what reputation does it have, what else does it produce?
- How productive is this ventilation with air recovery?
- What will be the resistance of the system to air flows after installing this equipment?
- How expensive will it be to maintain ventilation with this recuperator? What is its energy class? What are the savings when using this device?
- What are the Efficiency Coefficients of this recuperator for ventilation?
Here you will need a specialist who can make a detailed calculation based on the characteristics of your premises. It is clear that buying supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery for an apartment and a three-story house is not the same thing.
Here again you will need specialist advice. It is important not to just limit yourself to some general characteristics indicated in the table from the Internet, but to make a detailed calculation, for example, taking into account the number of bends in the air duct and many other nuances. The ratio of air flow to system resistance is one of the most important selection factors.
Note that we say “coefficients” and not “coefficient”. Why? Is he really not alone? Not really. There is a declared one - this is some average value. And there is real efficiency, which is an objective indicator. What does it depend on? There are many factors. Here is the humidity and air, and how the system is organized, and the temperatures inside and outside.
Here are some recommendations for calculating the efficiency of a recuperator:
- If there is a paper heat exchanger, the efficiency will be from 60 to 70 percent. What does this mean for us? Is it good or bad? This means that ventilation with air recovery is resistant to freezing, although not one hundred percent.
- If there is an aluminum heat exchanger, the efficiency will be no more than 63%, while the efficiency of the air recuperator will be from 42 to 45% percent. Thus, you will have to use a significant amount of electricity to get rid of the frost.
- A rotary air recuperator has excellent efficiency indicators, but provided that it is controlled automatically, based on the readings of special sensors. However, these recuperators can freeze in the same way as aluminum ones, which reduces efficiency.
What else should you consider when choosing a recuperator for ventilation?
- You are unlikely to find a supply and exhaust air recuperator that can effectively cope with work at temperatures below minus ten degrees Celsius. Don't trust the promises on labels and the assurances of sellers. The best option is a metal recuperator for ventilation, capable of coping with its task at that same -10 ºС. At lower temperatures, the recuperator simply stops working effectively. And if advertising promises you that this device is capable of functioning at -50 ºС, then, quite possibly, it is so, but with one caveat - this is more of an appearance of activity than real recovery. In any case, the efficiency will decrease, the air recuperator will freeze, so do not believe the promises of 100% efficiency and efficiency up to 99% - this is all just an advertising gimmick and deception that has nothing to do with reality.
- Look at the thickness of the case and the material. The fact is that thin cases freeze very quickly. For example, 3 centimeters is an insignificant obstacle to the cold. It's more about the name of the case than any effectiveness. It's the same with the material. The same aluminum - the coating is useless unless an additional layer of insulation is applied on top of it, or better yet, more than one. Otherwise, you just get an effective conductor for cold, which will very quickly freeze the equipment, and ventilation with recovery will stop working or begin to demonstrate very low efficiency.
- Pay attention to such an indicator as the free pressure of the fans. The fact is that the characteristic “500 m³” means nothing when “0 Pa” is indicated next to it. You may be deceived by large figures, which are actually incredible under the operating conditions that are typical for an ordinary residential building in Russia. In other words, they are writing to you about how ventilation with recovery can work in some ideal circumstances that you will never physically be able to provide for it. Thus, we are talking about a hypothetical ability, and not the real capabilities of the system.
- Switching modes and options is a useful thing, because it allows you to achieve significant savings in energy resources. Of course, you can monitor the temperatures yourself and quickly adjust the equipment to suit them, but sensitive sensors and automation will do this much better.
- The main parameter when choosing equipment for ventilation with recovery is the volume of air that enters the room in one hour. The optimal amount is at least 60 cubic meters per person. If there are two of you in the apartment - there are no less than 120, etc. Make sure that the equipment you are thinking of purchasing can actually provide this amount of air flow. If not, then don’t waste your money or time on purchasing it and find something suitable for your conditions. In addition to the performance itself, it is worth paying attention to the pressure that the fans have.
Cost estimates
The cost of natural ventilation in the house Murator M93a – Air ducts made of concrete blocks – 2615 rubles – Chimney insulation and facade – 2255 rubles – Chimney caps – 130 rubles – Grilles (blinds) in the chimney (8 items) – 700 rubles – Adjustable window air fans * (11 pcs.) – 715 rub. – PVC exhaust ventilation grilles (7 pcs.) – 245 rub. TOTAL: 6,660 rub.
* humidity-sensitive diffusers - with automatic performance control depending on air humidity - will cost 2090 rubles.
The cost of ventilation with a recuperator in the house Murator EM93a – Air ducts made of concrete blocks ** – 710 rubles – Expedition to insulate chimneys and facades – 1740 rubles – Chimney caps – 95 rubles – Ventilation grilles in the chimney (4 pcs.) – 350 rubles .– PVC exhaust grilles (2 pcs.) – 70 rub.– Air ducts and fittings made of galvanized sheet – 2000 rub.– Insulation – 1000 rub.– Supply and exhaust diffusers (14 pcs.) – 210 rub.– Ground heat exchanger made of plastic pipes with a diameter of 200 mm and a length of 40 m – 3300 rubles – Outside air intake – 700 rubles, exhaust – 150 rubles – Roof launcher – 200 rubles – Recuperator with an air volume of 240 m3 / h, compression 205 Pa and efficiency 85% – 7,000 rubles. TOTAL: 17,525 rubles.
** gravity ventilation was used in the garage and boiler room
Technical characteristics that you should pay attention to when choosing
- Metal devices are effective in operation down to -10ºС. At low temperatures, performance decreases noticeably. As a result, electric pre-heating elements are used;
- When choosing, you should study the thickness of the case and the material of the cold bridges. The thickness of 3 cm is subject to additional insulation when the outside temperature drops below -5ºС. You will have to doubly use insulating material if the frame is made of aluminum;
- Particular attention should be paid to the free pressure indicators of the fans. It may happen that at 500 m3 the pressure may be completely absent. Consumers usually find out about this when the recuperator fails;
- It’s a big plus when additional functions can be connected to the automatic system. Thanks to improved automation, operating costs are reduced and the performance of the entire device is improved;
- The main indicator for deciding which recuperator to choose is ventilation pressure and power. A preliminary calculation is made of how much air should enter the house in one hour.
Water
Water recuperators are rarely used due to insufficient efficiency and energy dependence. The basis of the design is a metal heat exchanger, the cavity of which is filled with water. Antifreeze is used instead. The heat exchanger is adjacent to two ventilation channels: supply and exhaust. When the masses come out, they give up some of the heat to the coolant inside the battery. When the supply air comes inside, it picks up this energy and takes it with it.
Advantages: the ability to return a portion of the heat when the supply and exhaust units are separated from each other, since the heat exchanger can have any shape and length, like the pipes of a heating system. But then, to circulate the coolant inside the pipeline, you will need to install a heat pump. It is powered by electricity and requires additional costs.
Disadvantages: low efficiency, efficiency usually does not exceed 50-65%. The design of these devices is very complex, and it does not provide for moisture return. The last disadvantage of the design is its energy dependence, since the pump is powered from the mains.