Home / Solid fuel boilers
Back
Published: 05/14/2019
Reading time: 5 min
0
4051
Boiler manufacturers offer a wide range of boilers, differing in characteristics, purpose, type of fuel and quality. Industrial boilers can be gas, electric, solid fuel, gas-oil, combined, water-heating and steam.
Industrial solid fuel boilers are used by enterprises for heating and hot water supply needs. Such equipment is used in industrial, administrative, commercial, and agricultural buildings. Since such premises are usually large in area, they use powerful equipment that runs on solid fuel (pellets, briquettes, coal), with a power of 100 kW and above.
- 1 Pros and cons of industrial solid fuel boilers
- 2 Types of industrial solid fuel boilers 2.1 Steam boilers
- 2.2 Hot water
- 4.1 Requirements for TT boiler houses
Automation and Security
Solid fuel water-water boilers are equipped with a control and automatic safety unit. Of course, the peculiarities of the solid fuel combustion process do not allow the boiler to provide a level of automation similar to gas or electric boilers; however, installing a thermostat in the heating circuit allows you to control the temperature in the room.
The automation system works on the principle of regulating the air supply through a fan or by opening the damper, which is performed by the actuator, receiving a signal from the temperature sensor and from the electronic unit.
The second level of automation can be implemented by changing the coolant circulation speed set by a centrifugal pump, which is connected to an electronic control unit.
This starts or stops the circulation of water through the pipes, for which the system must have a circulation pump connected to the control electronics:
And the third, higher-quality level of automation of solid fuel boilers is achieved by regulating the fuel supply to the firebox and can only be implemented in pellet boilers.
Pros and cons of industrial solid fuel boilers
Industrial solid fuel water heating boilers are a good alternative to gas installations, especially when the gas main runs too far.
Most of these enterprises, having completed an economic calculation of the costs of design estimates, purchase and installation of gas equipment, confidently choose solid fuel boilers. Such thermal installations have both advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages include:
- autonomy;
- automatic control system;
- high heat output and efficiency (except for coal furnaces);
- variability in the choice of solid fuel;
- simple operation and maintenance;
- quick and easy installation of heating systems;
- combustion control system;
- availability of security systems.
However, it is worth highlighting the disadvantages:
- creating conditions for storing fuel reserves;
- more frequent equipment maintenance (cleaning of the firebox, chimney);
- regular monitoring of combustion processes and fuel supply;
- lack of a reliable temperature control system.
How does a typical steam heating boiler work?
Heat is generated in the combustion chamber. Subsequently, it arrives at the heating surfaces. There are 2 types of heating surfaces: convective and radiation.
The composition of convective surfaces includes the following elements:
- air heaters;
- economizers;
- heat exchange devices.
The listed additional equipment is needed to increase the efficiency of the boiler, rationalize fuel consumption and reduce the level of heat losses.
It is important that the water used to operate the boiler is extremely clean - impurities are unacceptable. Therefore, before being fed into the boiler, the liquid must be cleared of gases and various impurities, ultimately becoming nutritious. The purified liquid is sent to the economizer
A special pump helps her with this. The economizer heats the coolant liquid under the influence of gases. Next, the liquid passes into the upper compartment of the drum compartment. Here the boiler water is mixed with the nutrient liquid
The purified liquid is sent to the economizer. A special pump helps her with this. The economizer heats the coolant liquid under the influence of gases. Next, the liquid passes into the upper compartment of the drum compartment. Here the boiler water is mixed with the nutrient liquid.
A certain amount of water passes from the upper compartment of the drum compartment to its lower compartment. The movement of water occurs through boiling tubes.
At the top of the steam boiler, the gases have a lower temperature, which gradually increases as they approach the lower compartment of the unit.
The water is heated and, together with a mixture of steam and water, is sent to the upper chamber of the drum.
The second part of the liquid from the upper drum compartment goes for redistribution. The boiler water is heated. The resulting steam bubbles go to the upper compartment of the drum compartment.
In the upper chamber of the drum, due to the separator, the mixture of liquid and steam is almost completely separated. As a result, saturated steam is created, which further increases the efficiency of the boiler. It is this saturated steam that is used by the end consumer.
In order to increase the efficiency of boilers, their operation is organized in such a way that in the upper chamber of the drum compartment the level of “lower” and “higher” water fluctuates. Between the mentioned liquid levels there is a reserve supply of water designed to maintain the operation of the heating unit in the event of a loss of liquid flow into the system.
The permissible “highest” liquid level in the drum compartment is determined with the expectation that water does not enter the superheater.
The maximum permissible “lowest” liquid level in the drum is calculated so as to prevent overheating of the upper compartment of the drum, as well as the boiler bundle
It is important that water enters the downpipes in a stable volume
To further increase efficiency, the design is equipped with an air heater.
The liquid in the system can circulate forcibly and naturally. Natural movement is based on the difference in density between the liquid and the vapor being created. The mixture of water and steam in the rising tubes has a lower density than the same composition in the descending tubes. However, the pressure and temperature remain the same throughout the tube. As a result, the steam, which is a gas in nature, rushes upward.
Forced circulation is provided by special pumping equipment.
Steam boiler structure
The design of a PC can be simplified in the form of a container where water is converted into steam. It is made of pipes of different diameters. In addition to the pipe system, the PC has a combustion chamber in which natural fuel is burned.
The design of a steam boiler and its design features are determined by the type of fuel. For example, coal fireboxes are equipped with grates on which a burning fuel layer is placed, through which oxygen enters the firebox.
A chimney is installed at the top of the firebox, which creates draft in the steam-gas path of the unit, thereby maintaining normal operation. Gas-fired steam boilers have gas or oil burners.
I heat the hot exhaust gases produced during the combustion of fuel to boiling water, after which steam begins to be released from the evaporation surface and supplied to the consumer, and the flue gases escape through the pipe into the atmosphere.
The main structural elements of steam boiler houses are connected into one complete boiler system using fittings, fittings, circulation pumps, instrumentation and control of smoke exhausters and fans.
Coolant: water, antifreeze, propylene glycol
The equipment may also differ in the method of loading the energy carrier - manually, or mechanically from a special bunker. Some models may have movable grates, while others may have stationary ones. Others are equipped with pre-furnace chambers. What kind of coolant will be chosen for such a boiler room does not make much difference. The boiler can heat:
- water;
- antifreeze;
- propylene glycol.
Of all the options, water is the cheapest. But it must be drained from the system if it is not used in winter, and it also creates a deposit of scale that can clog pipes and radiators. Antifreeze and propylene glycol do not freeze during winter downtime and do not clog pipes with scale.
Steam separator.
The steam separator removes the liquid phase from the wet steam passing through the pipe, so that only dry steam enters the steam consuming apparatus. Moisture may be contained in the steam stream as it enters the pipe, but even if dry steam is supplied, it partially condenses in the pipe itself, giving it some of its heat. The liquid phase in a steam flow is undesirable because it reduces the efficiency of heat transfer in the steam consuming apparatus. In addition, sudden braking or acceleration of condensate accumulated in any cavity in the steam line can result in water hammer, which can cause damage to valves and other equipment. Two typical steam separator designs are shown schematically in Fig. 6.
License for gas boiler house
In accordance with the Federal Law “On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities” dated July 21, 1997 N 116-FZ, it is required to obtain a license to operate certain types of boiler houses.
Necessity of boiler room licensing
Factors determining the need for boiler room licensing are the presence of equipment operating under excess pressure and the presence/handling of a hazardous substance.
- The boiler room uses equipment (steam boilers) operating under excess pressure of more than 1.6 MPa or at a working environment temperature of more than 115ºС. With the exception of the equipment specified in paragraph 4 of the Federal Rules and Regulations “Industrial Safety Rules for HPFs that use equipment operating under excess pressure”;
- The boiler house runs on natural gas (gas boiler house). In the event that the hazardous production facility contains gas pipelines with a pressure above 0.005 MPa;
- The boiler house supplies heat to the population and socially significant categories of consumers;
- The boiler room has reserve fuel, which belongs to the category of flammable liquids in a volume of more than 20,000 tons or more.
If the boiler room is assigned hazard class 4, then licensing is not required.
Obtaining a license to operate a boiler room
Obtaining a License for a gas boiler house
In cases where a boiler room is assigned hazard class 2 or 3, it is subject to mandatory licensing. Obtaining a License is regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 492 of 06/10/2013 “Regulations on licensing the operation of hazardous production facilities of I, II and III hazard classes” and Federal Law No. 99-FZ of 04/22/2011 “On licensing of certain types of activities”.
License for servicing a gas boiler house
The activity of servicing a gas boiler house is not a licensed activity and is not required to obtain a license. The organization servicing boiler houses must have SRO approval and certified personnel in accordance with the relevant industrial safety rules.
Answers to frequently asked questions
1. Question: I am an individual entrepreneur, do I need a license to operate a gas boiler with a capacity of up to 100 kW?
Answer: The operating organization, regardless of the form of ownership (LLC, individual entrepreneur, CJSC) must obtain a license to operate this facility. It is not the gas boiler house itself that is subject to licensing, but a hazardous production facility (gas consumption network) consisting of: external and internal gas pipelines, gas distribution system (if any) and gas consuming equipment (boilers, regardless of their power). It is necessary to obtain a Rostechnadzor License, regardless of the power of the gas-consuming equipment (boiler). A sign of danger is not the power of the boiler, but the presence of a dangerous substance - natural gas. If the hazardous production facility does not contain gas pipelines with a pressure higher than 0.005 MPa, this facility does not fall under the definition of a hazardous production facility - only in this case, licensing of a gas boiler house is not required.
2. Question: If the boiler room is not actually functioning, can a fine be imposed for the absence or non-renewal of a license?
Answer: In short, yes, you can be fined for violating industrial safety requirements. After all, legally you are operating this facility. If the facility is not in operation, then it must be mothballed or liquidated.
3. Question: Can our organization, having received a license to operate hazardous production facilities, operate other boiler houses?
Answer: No, it does not. Because The licenses for the operation of gas boiler houses indicate the addresses of specific boiler houses. If you plan to operate boiler houses at new addresses, you need to enter the new addresses of the places where the licensed type of activity is carried out in the existing License.
Obtaining a license to operate a boiler room
Best Industrial Boiler Brands
Leading developers and manufacturers of heating systems include:
- Russian “Teplodar”, offering a line of “Kupper” units;
- domestic “Trayan”, which supplies equipment for household and industrial purposes and produces fuel briquettes from pressed sawdust;
- Czech Viadrus, specializing in the assembly of small-sized installations;
- Russian Zota, offering 9 types of water heating units using solid fuel;
- domestic Protherm, which produces equipment with a power of up to 48 kW and is characterized by high maintainability.
Brands of solid fuel boilers made in Russia
Analysis of technical characteristics will help to get a general idea of long-burning solid fuel boilers. Consumer reviews on independent forums provide an objective assessment of domestic developments.
Table 1. Solid fuel boilers Zota Mix and Pellet produced by the heating equipment and automation plant (Krasnoyarsk):
Table 1. Solid fuel boilers Zota Mix and Pellet produced by the heating equipment and automation plant (Krasnoyarsk)
- The efficiency of boilers of the Zota Mix model range is 80%, Pellet – 90%;
- Zota Mix combined steel solid fuel boilers operate on any type of fuel (liquefied or natural gas, electricity, liquid fuel);
- the combustion chamber and ash box are located inside the water jacket;
- an adjustable chimney damper, a mechanical draft regulator and air suction by an ejector installed in the combustion door ensure complete combustion of fuel with minimal draft;
- the outer surface of the body is coated with an anti-corrosion polymer composition;
- a removable door behind the front panel provides access for cleaning the flue;
- possibility of repair.
Zota Mix boiler design
- you need a supply of fuel and a place to store it;
- costs for delivery, unloading and storage of firewood, coal, briquettes;
- reduction in the productivity of Zota Mix boilers when using low-quality fuel (brown coal by 10÷20%, raw firewood by 60÷70%);
- for Zota Mix - manual loading of fuel, cleaning of the ash pan, firebox walls, flue ducts and smoke pipe;
- mandatory preparation of boiler water (hardness up to 2 mEq/l);
- installation in a separate room;
- For boilers of the Zota Mix line, it is necessary to install a heat accumulator, a smoke exhauster, and a boiler.
Table 2. Combined solid fuel devices with a water circuit (AKTV). (Novosibirsk city):
Table 2. Combined solid fuel devices with a water circuit (AKTV). (Novosibirsk city)
- budget option for solid fuel boilers with a water circuit for the home (price 11,000÷25,000 rubles);
- compact size;
- the water heat exchanger covers the firebox from all sides (except the front);
- retractable ash drawer;
- mounting socket for draft regulator;
- the ability to connect to a chimney of any configuration;
- the steel heat exchanger allows for simplified connection to the heating system (without mixing);
- The design is adapted to operate on gas and electricity.
Boilers "Karakan" from
- outdated design, primitive automation of low quality;
- The technical characteristics declared by the manufacturer (power, heated area and efficiency) according to consumer reviews do not correspond to actual indicators.
Table 3. Solid fuel pyrolysis boilers Bourgeois & K from NPO TES LLC (Kostroma):
Table 3. Solid fuel pyrolysis boilers Bourgeois & K from NPO TES LLC (Kostroma)
- ensures stable combustion of fuel of any grade and degree of humidity;
- efficient operation of the boiler from one fill for 8 hours;
- economical fuel consumption;
- compatibility of the generator with natural or forced circulation systems;
- an environmentally friendly unit, the fuel undergoes a complete combustion cycle without producing harmful emissions into the atmosphere;
- The design of the firebox ensures reaching an effective operating mode in 40 minutes.
Solid fuel pyrolysis boilers "Bourgeois & K"
- complex installation: the connection must be made by employees of specialized enterprises that have a license for this type of activity (otherwise the manufacturer’s warranty does not apply to the unit);
- manual fuel filling and combustion chamber cleaning;
- heavy weight.
Installation and operation of solid fuel boilers must be carried out in accordance with fire safety rules
For heating a country house. In a garage or greenhouse, it is possible to make long-burning solid fuel boilers with your own hands. Videos with materials on this topic can be found on the Internet. But remember that the main condition for using heating equipment is fire safety. And only a certified manufacturer can guarantee the fulfillment of this condition under proper operating and installation conditions of the equipment.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3sfw2qpCMrY
https://youtube.com/watch?v=1z6OOs3WdH4
The best solid fuel direct combustion boilers
Viadrus Hercules U22
The lineup
The model range of this series of Vidarus boilers is represented by seven solid fuel boilers with a capacity from 20 to 49 kW. The most productive of them is capable of heating a building with an area of up to 370 sq.m. All equipment is designed for a maximum pressure in the heating circuit of 4 atm. The operating temperature range in the coolant circulation system is from 60 to 90o C. The manufacturer claims the efficiency of each product at 78%.
Watch the product video
Design features
All models in the presented line are designed for floor installation. They have an open combustion chamber with air supplied due to natural draft. Large doors with a square configuration easily open wide, which is convenient when loading fuel, removing ash and inspecting the condition of internal elements.
The built-in heat exchanger made of high-quality cast iron is adapted to work in a single-circuit heating system. The boilers do not have devices powered from an external electrical network and operate in a completely autonomous mode. All settings are mechanical.
Fuel used. The design of the spacious firebox is designed to use wood as the main fuel, but coal, peat and briquettes can be used.
Zota Topol-M
The lineup
The line of six Zota Topol-M solid fuel boilers begins with a compact 14 kW model, designed to heat a home for an average family, and ends with an 80 kW unit capable of heating a large cottage or industrial workshop. The boilers are designed for operation in systems with pressures up to 3 bar. The efficiency of thermal energy use is 75%.
Watch the product video
Design features
Their distinctive feature is their slightly raised design, which makes it more convenient to open the ash pan door and empty it. The combustion chamber is open type with a chimney connection from the rear wall. There is a built-in temperature sensor. All adjustments are made manually.
A heat exchanger for a single-circuit heating system is mounted inside, connected to 1.5 or 2” pipelines. The boilers operate in autonomous mode. Products of this brand are easy to install and reliable in operation.
Fuel used. The fuel used is wood or coal, for which a special grate is provided.
Bosch Solid 2000 B-2 SFU
The lineup
Solid fuel boilers Bosch Solid 2000 B-2 SFU are presented in a number of models with power from 13.5 to 32 kW. They are capable of heating buildings with a usable area of up to 240 sq.m. Circuit operating parameters: pressure up to 2 bar, heating temperature from 65 to 95o C. Efficiency according to the passport is 76%.
Watch the product video
Design features
The units have a built-in single-section heat exchanger made of cast iron. It is connected to a single-circuit heating system through standard 1 ½” fittings. The boilers are equipped with an open combustion chamber with a chimney with a diameter of 145 mm. For normal operation, a connection to a 220 volt electrical network is required.
There is a temperature regulator and protection against water overheating. The ash pan has a small volume, so it requires regular cleaning. Manufacturer's warranty 2 years. The design is simple, safe and highly reliable.
Fuel used. The boiler is designed to use hard coal. Using this type of fuel it demonstrates high efficiency. When working with wood or briquettes, efficiency decreases noticeably.
Protherm Bober
The lineup
The Protherm Bober series of solid fuel boilers is represented by five models with power from 18 to 45 kW. This range completely covers any private home. The unit is designed to operate as part of a single-circuit heating circuit with a maximum pressure of 3 bar and a coolant temperature of up to 90 ° C. For the correct operation of the control system and activation of the circulation pump, a connection to a household electrical network is required.
Watch the product video
Design features
Boilers of this series are equipped with reliable cast iron heat exchangers. The original design of the combustion chamber increases the efficiency of heat transfer. Exhaust gases are discharged through a chimney with a diameter of 150 mm. For connection to the heating circuit there are 2" pipes. Such boilers are designed for long-term operation.
Fuel used. The declared power is designed to burn wood with a humidity of up to 20%. The manufacturer has provided for the possibility of using coal. In this case, work efficiency increases by several percent.
From theory to practice
More often, those who want to make equipment with their own hands opt for a vertical solid fuel boiler. The manufacturing process will be considered using the example of a solid fuel boiler for heating a house with an area of 100 m2. This system consists of seven radiators and a plumbing system.
So, let's make a heat exchanger:
- We manufacture vertical bases for the heat exchanger. To do this, we take four profile pipes, each 30 cm long, which will be located on the side of the combustion chamber;
- We make four holes in them with a diameter of 5 cm using a gas cutter. We remove irregularities with an angle grinder (grinder). There should be eight holes;
- in the pipes that will be located at the back of the equipment, we make four holes with a diameter of 40 mm and four with a diameter of 50 mm. All of them should be located on the side connected to the front pillars. The result should be eight holes;
- in a profile pipe 500 mm long, we cut out a hole for attaching a pipe through which waste water will be discharged;
- We make a hole in the upper part of the rear pillar to supply water to the system.
Then we proceed to assembling the heat exchanger. The vertical bases are connected by a profile pipe. To do this, we place it on bases installed perpendicular to the surface. We weld the joints. We connect this entire structure on the reverse side with a profile pipe with holes for water drainage. As a result, we get the front wall of the heat exchanger.
Next, we install the vertical bases perpendicularly and weld them with four round pipes. This turns out to be the rear wall of the heat exchanger. We connect the front and back walls together. To do this, you need to bring the longitudinal pipes to the holes and weld them, and then weld the pipes for supplying and discharging water to the structure. We weld the joints using pieces of metal and check the strength of the heat generator.
After checking the strength of the weld, close the water drainage pipe with a plug, and pour water into the inlet hole. We check the tightness of welding joints for visible leaks.
Making the case will also require effort. To do this, we cut out eight walls from sheets of heat-resistant steel - 2 front, 2 rear and 4 side. The area of each of them should be 850 x 300 mm. We take all measurements using a meter ruler and cut the material with a grinder. Then we cut out two plates measuring 450 x 450 mm: one for the bottom, the other for the top plate of the boiler.
We make two holes for the doors in the front wall: the first - at the level of the grate for igniting the fuel and cleaning the combustion chamber, and the second - a little higher level for loading fuel. In our work we use a drill and a grinder. From the sheet we cut stiffening ribs 80 cm long.
Requirements for the premises for boiler room equipment
Basic standards regulated by standard SP 89.13330.2016:
- The area of the boiler room is selected depending on the thermal power of the equipment. For example, for a 30-kilowatt unit, 13.5 m² is enough. The ceiling height is at least 2 m, regardless of the characteristics of the water heating units.
- Wall and door materials must have a fire resistance rating of 45 minutes or more. To increase security, vertical surfaces are covered with fire-resistant plaster, and a steel sheet is provided under the equipment.
- The exit from the boiler room should lead to the street and not to adjacent buildings. Installation of boilers in workshops or warehouses is not allowed. There should be no flammable materials in the same room as the equipment.
- When using coal, a dust collection system is provided, which forms explosive mixtures with air.
SUPERHEATER
A superheater is a heat exchanger designed to raise the temperature of steam above its normal boiling point. High-temperature superheated steam makes it possible to increase the efficiency of steam engines and turbines, since their steam consumption decreases by approximately 1% with an increase in superheat by 5° C. The upper temperature limit is determined only by the heat resistance of mechanical equipment and materials. Large power plants operate with superheated steam temperatures of up to 500°C.
The superheater is made of steel pipes that form a heating surface for the steam passing through them. Saturated steam from the boiler enters one end of the pipe and is heated to the desired outlet temperature by the heat of the flue gases supplied to its outer surface. The heating surface area of steam superheaters is approximately half the heating surface area of the boiler at moderate steam temperatures and twice as large at high steam temperatures. Although the superheater can be designed as a separate unit connected to the boiler with its own firebox, as a rule, superheaters are built into the steam generator system. Built-in superheaters come in two types: radiation and convection. The surface of a radiation superheater, located so that it receives radiant heat from the combustion zone in the steam generator furnace, transfers 2–3 times more heat to the steam than the same surface of a convection superheater. Convection superheaters are located in high-temperature areas of the gas passages of boilers.
Steam boiler structure
Equipment generating steam is divided into the following types:
- steam boilers for energy purposes (used at power plants to drive turbines that generate electricity);
- industrial-type steam boilers (steam production for technological operations in production);
- steam boiler equipment intended for heating, laundries, operation of disinfection units;
- recovery boilers that produce steam by extracting heat from superheated flue gases generated as a result of production in the metallurgy and chemical industries.
Industrial steam boiler
The most powerful devices are used in the energy sector, producing up to 5000 tons of steam per hour at a pressure of about 280 kgf/cm2. The steam is obtained superheated to a temperature of 500 C, after which it enters turbine units, where thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy.
Steam boilers for heating systems produce low pressure steam, most often in a saturated state. It is advisable to use this type of heating in very cold climatic zones to prevent freezing of the heating system, in particular its circulation cycle.
Some establishments benefit from operating a steam boiler, which heats the building and supplies steam to the laundry rooms. Sometimes steam generators are installed where it is possible to utilize high-temperature gases; this solution allows you to save significant amounts during the heating season.
Steam boilers and their operating principles differ significantly from water heating systems. The operation of steam generating units is based on heating water and its subsequent transformation into steam. Heating is carried out using the release of heat from the combustion of combustible materials, most often natural gas or coal is used. The boiler always produces steam under excess pressure and, depending on the purpose, its value varies widely and can vary from 1 kgf/cm2 to several hundred kgf/cm2.
Steam boiler operation diagram
The operation of such devices is associated with some danger, since steam is a compressible medium and in boilers of a certain type it is in large volumes in a compressed state, and therefore the reliability of the equipment is regulated by special GOSTs. The main reliability factor is due to the absence of depressurization and the release of a large mass of heated steam into the nearby space.
What applies to solid fuels
Fuel of this type are substances of natural origin, consisting mainly of carbon. They may also contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur compounds. Depending on the ratio of components and humidity, the calorific value (the amount of energy released during the complete oxidation of 1 kg of fuel) differs. Solid fuels include coal or brown coal, wood, shale and peat. Some types of substances are used in the chemical industry to produce synthetic gasoline or kerosene.
Solid fuels include peat and coal.
Design of TGU 100-200 kW on gaseous fuel
TGUs are small-sized boiler houses of a modular type. The modules are made in the form of block boxes - metal containers with fixed sandwich panels 80 mm thick. Sandwich panels are installed from the outside as wall and roof panels. The color is selected in accordance with the wishes of the Customer.
The modules are equipped with a supply and exhaust ventilation system, which is carried out through easily removable ventilation grilles. Air is supplied in sufficient quantities, ensuring the necessary air exchange in the room and stable operation of gas burners.
Equipment and pipelines are coated with an anti-corrosion compound, which increases their strength and resistance to negative chemical influences. Heating surfaces with temperatures above 45°C are additionally thermally insulated.
What is the working principle of a steam boiler
- First of all, the water needs to be purified. This happens using an electric pump. The liquid is first sent to a reservoir located at the top of the boiler.
- Then it moves from top to bottom through the pipes into the collector.
- Directly from it, water flows back in the direction, however, through the heating zone. This is where fuel combustion actually occurs.
- Then it is converted into steam, which eventually comes out upward. This is due to the pressure difference between gas and liquid.
- There is a separator in the upper section. It is designed to separate steam from water (the latter of which is sent to the steam line to consumers). The excess that remains after this manipulation is returned to the tank.
- As for the steam generator, all the listed steps are repeated to achieve the desired result.
Features of the design of industrial boilers
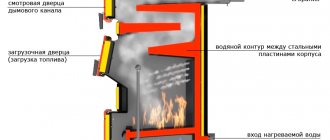
The equipment is characterized by increased dimensions and weight, which requires installation on a foundation. To burn fuel, a firebox with a grate is used, on top of which a boiler with heat exchangers is located. The flow of hot gases flows around the radiator pipes and ensures the heating of water or steam. The number and location of lines depends on the model and manufacturer. To increase operational efficiency, pipe packages are arranged in a staggered sequence with the installation of partitions between the risers.
Gases passing through the heat exchangers are collected at the rear of the housing and discharged into the atmosphere through the chimney. The height of the pipe provides natural draft and supports combustion. The boiler design includes inspection and technological hatches.
On hard and brown coal
The equipment is equipped with a forced gas exhaust system, but is not equipped with a fan to supply additional air to the firebox.
Hard coal and brown coal equipment is not equipped with a fan.
Boilers can operate on coal or brown coal; performance depends on the characteristics and moisture content of the fuel. A system for collecting ash generated during the combustion of solid fuel may be located in front of the smoke exhauster. Water is supplied using an electric circulation pump, supplemented by a make-up pump.
The chimney is installed on each boiler or on a group of devices connected in cascade into one module.
Wood burning
Such boilers are equipped with heat exchangers with constant circulation of liquid, which prevents local overheating and the formation of a layer of scale on the internal walls. To reduce energy losses, heat-resistant insulation of the housing and partitions of the combustion chamber is provided. The absence of cracks ensures stabilization of the oxidation process. There are sealed doors for loading fuel. The capacity of the firebox promotes complete combustion of firewood and prevents the release of residues with the flow of gases into the chimney and atmosphere.
The equipment is distinguished by a developed heating surface, which ensures a reduction in the temperature of combustion products to +200°C and an increase in efficiency. The ash is collected in a separate niche under the firebox and is periodically disposed of (for example, during routine maintenance). Boilers can reduce heating costs due to ease of use and increased efficiency of burning dry wood.
On pellets and sawdust
The equipment is equipped with automatic fuel supply mechanisms; the conveyor speed depends on the boiler settings. The raw material burns in a vortex chamber, the primary air flow enters the furnace under increased pressure created by the fan. The secondary vortex has a reduced pressure and ensures afterburning of sawdust or pellets. Fresh fuel is supplied by an air-cooled auger, which prevents fire in the bunker.
Pellets and sawdust burn in a vortex chamber.
Hot water and steam
Equipment is usually divided into categories according to the type of coolant. In classic water-heating boilers, liquid circulates in tubes, while in steam boilers, steam is heated. The temperature of the latter reaches +500°C at a pressure of 25 MPa and higher. Superheated steam can be used to drive turbine rotors (until the 50s of the last century it was used for double or triple expansion piston machines), and saturated steam, characterized by reduced parameters, can be supplied to the heating circuits of residential buildings or factory premises.
By material and type of heat exchanger
Heat exchangers can be:
- cast iron;
- copper;
- aluminum-silicon;
- made of carbon or stainless steel.
The design of the heat exchanger may also vary.
The most popular are separate heat exchangers. Heating water flows separately, and water for residents’ household needs passes separately. They are a little more expensive, but more reliable.
A bithermic heat exchanger looks like a pipe within a pipe. In the inner pipe there is DHW water, which needs to be heated, and in the outer pipe the heating coolant circulates.
The third type is a heat exchanger in which a coil is built in. The container with water is heated by the coolant flowing in the coil. An indirect heating system is good for everyone, but in the summer you will either have to heat the boiler or live without hot water.
The bithermic option is not recommended for use where there is hard water. And be prepared that every time scalding water will flow out of the tap first, and only then at the temperature you need.
Advantages and disadvantages
Boilers with a fire tube design have the following advantages:
- high efficiency, reaching 92-93% due to efficient heat distribution and complete power take-off from the generated heat flow during fuel combustion;
- no heating of the outer surface of the housing due to the use of a water jacket;
- high heat capacity of the boiler and minimal heating inertia during operation;
- stable temperature parameters due to complete control of the fuel combustion process;
- safety during operation: the risk of explosion due to high pressure growth is minimal;
- the ability to make modifications to change technical characteristics;
- simplicity of design, allowing maintenance and repairs without the involvement of specialists;
- compact dimensions compared to other types of boilers with similar characteristics;
- reliability and durability due to the use of heat-resistant steel and a minimum number of welds;
- Possibility of use for heating objects operated in harsh climatic conditions;
- average service life from 20 to 50 years;
- excellent maintainability;
- availability of structures for the use of various types of fuel.
Fire tube boilers have high efficiency, reaching 92-93% due to efficient heat distribution
The disadvantages of the fire tube design include:
- if hard water is used, uneven scale forms on the internal surfaces, which can only be removed after disassembly, which is very labor-intensive;
- high water consumption;
- the appearance of stagnant zones of the coolant due to the low speed of its circulation;
- the need for constant condition monitoring and periodic maintenance to prevent emergency situations;
- the difficulty of cleaning passages to remove combustion products from the combustion chamber;
- the presence of unheated areas inside the heat exchangers due to the low circulation rate of the heat flow.
All classifications of boilers for industrial premises
Industrial water heating equipment is divided into categories according to:
- design features;
- method of supplying fuel to the working chamber;
- type and calorific value of fuel.
By design and operating principle
Equipment is usually divided into categories according to heating method:
- Fire- or fire-tube. In them, combustion products pass through a heat exchanger located in a water tank. The fire tube is the firebox. The concept was widely used in compact water heaters called “Titan”. The flow of hot gases passed through the chimney inside the coolant tank, ensuring the liquid was heated to the required temperature. Fire tube boilers are not used in industry due to low productivity.
- Water-tube, equipped with a radiator with coolant, the outer walls of which are washed by a flow of hot gases. Installations are usually divided into direct-flow and drum. The first type is equipped with a heat exchanger in the form of a coil; a superheater can be installed at the end of the radiator. Drum units provide fluid supply to the lines. Due to the temperature difference, steam is separated from the water, which enters the unit for additional heating and increasing pressure.
By fuel loading method
Basic boiler models are equipped with a grate firebox with a door. Fuel is supplied manually or with a shovel. The operator independently determines the moment of loading a fresh portion of fuel, focusing on the temperature and pressure of the liquid or steam in the circuit. Periodic shutdown of the boiler is required to clean the ash pan and remove deposits from pipes, risers and walls of the combustion chamber. The design is simple, but does not provide stable operation.
The operator determines the moment of fuel loading.
Improved high-power water heating boilers have automatic fuel supply; slag is removed from the furnace by a screw mechanism for subsequent disposal. The equipment reduces the consumption of firewood or coal. It is possible to install electronic controls that allow you to automate the processes of loading raw materials and regulate productivity by adjusting the combustion intensity.
By type of fuel consumed
Solid fuel boilers are divided into categories according to the type of fuel:
- on crushed brown or coal;
- on pre-dried firewood (the size of the log is regulated by the equipment manufacturer);
- on shavings or waste from woodworking industries;
- on pressed briquettes made of sawdust, peat or husks;
- on fuel granules (pellets), which simplify the automation of supply and ensure long-term combustion.
Types of devices and their structure
A gas boiler of any modification has three required elements:
- fittings through which fuel (gas) is supplied;
- gas-burner;
- heat exchanger
It should be noted that the most common material for creating a heat exchanger is copper. However, quite often there are models of gas boilers in which this element is made of cast iron or steel.
Schematic diagram of a gas boiler
Each modern wall-mounted gas boiler is equipped with a circulation pump designed to move the coolant, a special safety valve, an expansion tank, and an electronic control system. In addition, the device of gas heating boilers is also equipped with monitoring and self-diagnosis systems. Such an abundance of special and auxiliary equipment makes gas boilers quite close to mini-boiler rooms. And the calculation of the power of a gas heating boiler, made before installing the system, shows that some of these additions can increase efficiency.
Next, the gas fittings are automatically started - fuel is supplied to the system. At the same time, a spark ignites in the combustion chamber, and it ignites the fuel. The heat exchanger heats the coolant to the required level. Using a circulation pump, heated water moves through the system to the radiators - where it gives off its heat. This is how we can briefly describe the operating principle of a gas heating boiler with one circuit.
The principle of operation of a gas boiler
However, in some cases, the boiler can serve not only for heating, but also for supplying hot water. In order to organize the operation of two systems at once in the house, a double-circuit gas boiler is needed. Its main difference is the presence of a second circuit, which may well satisfy the need for hot water.
It should be noted that the circuits of this type of boiler cannot operate simultaneously. That is, if you need to warm up the room, then at this moment the heating of water for hot water supply will be suspended or will be produced more weakly. However, according to the owners of double-circuit boilers, such equipment operating conditions and design do not cause any inconvenience.
Diagram of a heating and hot water supply system from a gas double-circuit boiler
Fuel: firewood, pellets, coal
Previously, boilers were designed exclusively to use solid fuels such as coal. Their design was such that the energy carrier thrown into the firebox burned out too quickly. This led to a large consumption of both material and money spent on it over the entire heating season. But today technologies provide different types of fuel with a solid component , which are organically integrated into the system, burn longer, and give off more heat. Modern boilers can now operate on:
- brown or black coal;
- coking substances;
- wood logs;
- remnants of furniture production;
- pellets – peat briquettes;
- pressed shavings, sawdust;
- combined versions.
In terms of benefits, the least expensive materials for starting a technical boiler are firewood and industrial waste, shavings , if it is possible for the boiler room to receive them. In some cases, enterprises have the opportunity to receive industrial waste as combustible material free of charge. The next most expensive item is coal. And the most expensive heating materials are pellets. In addition, it should be mentioned that these briquettes are not so available on the market; not every store has them in stock.
For solid energy, you always need a separate warehouse , because you need to store coal or firewood somewhere throughout the winter. In this regard, even greater savings occur when the building for storage belongs to the company whose buildings are heated. But if you have to rent space for storing flammable materials, then this in itself is an additional expense.
Boiler and pipes for steam heating
For efficient operation of a steam heating system, the type and power of the steam boiler (steam generator) must be correctly selected. There are several types of steam boilers that can operate on different fuels:
- gas;
- solid fuel;
- liquid fuel;
- universal or combined, which can operate on several types of fuel.
As with water heating, the most economically advantageous are steam boilers running on natural gas. In the same case, if the house is not gasified, you will have to use solid or liquid fuel boilers.
In addition to the type of boiler, it is also necessary to choose the right power. It must correspond to the total area of the premises that will need to be heated. On average, it is believed that for a 10 m2 room with a height of up to 3 m, 1-1.2 kW of thermal power is sufficient:
- for a house with an area of 100 m2, a boiler with a capacity of 10-15 kW will be sufficient;
- for a house with an area of up to 200 m2 - 20-25 kW;
- up to 300 m2 – up to 30-35 kW.
In this case, a lot depends on how insulated the house is. High-quality insulation of a house with modern materials can reduce its heat loss, and therefore reduce the amount of heat required for heating it, and therefore the boiler power, by 30-50%.
What pipes are used for steam heating
As already mentioned, in the pipes of steam heating systems the temperature of the coolant (steam) is quite high - 100 ° C or even more. Therefore, only metal pipes of different types are suitable for such heating:
- steel - ordinary, galvanized or stainless steel;
- copper.
Using conventional steel pipes for wiring is the most economical option.
They are quite reliable and durable, but are susceptible to corrosion. But it usually involves welding work. Pipes, galvanized or made of stainless steel, are corrosion resistant, but are more expensive and are used less frequently for installation. Date: September 25, 2022
The best pyrolysis solid fuel boilers
Buderus Logano S171
The lineup
Floor-standing pyrolysis boilers made in Germany, Buderus Logano S171, are available in four modifications with a power of 20, 30, 40 and 50 kW. They operate automatically and do not require constant human supervision. Their performance is sufficient to heat low-rise buildings of various sizes. Equipment efficiency reaches 87%. For normal operation, a connection to a 220 volt electrical network is required. Electricity consumption does not exceed 80 W. The unit is reliable and easy to use. Manufacturer's warranty 2 years.
Watch the product video
Design features
The boiler has a spacious open-type combustion chamber with a two-stage air supply circuit. Exhaust gases are discharged through a chimney with a diameter of 180 mm. Wide doors facilitate the process of loading fuel and inspecting internal devices. The design pressure in the heating circuit is 3 bar. The coolant temperature is 55-85o C. Overheating protection is provided.
Fuel used. The main source of energy is dry firewood up to 50 cm long. The burning time of one bookmark is 3 hours.
Ecosystem ProBurn Lambda
The lineup
Bulgarian single-circuit pyrolysis boilers are available in two versions with a capacity of 25 and 30 kW. Their performance is sufficient to heat a medium-sized private house. To operate the automatic control system, a connection to a standard electrical network is required.
The unit is designed to heat circulating water up to 90o C. The maximum pressure in the circuit is 3 atmospheres. There is protection against overheating of the coolant. The boiler is easy to maintain and highly efficient. A 12 month warranty is provided.
Watch the product video
Design features
There is a pipe with a diameter of 150 mm for connecting the chimney and 1 ½” fittings for the circulation circuit. In the area where the flue gases exit the furnace, a probe is installed that measures the oxygen concentration. It gives control signals to the damper that regulates the air supply.
Fuel used. Regular wood is used as fuel.
Atmos DC 18S, 22S, 25S, 32S, 50S, 70S
The lineup
The line of elegant pyrolysis boilers of this brand includes a number of models with a power from 20 to 70 kW. They are intended for floor installation in residential, industrial and warehouse premises. The equipment is highly efficient and reliable. For correct operation of the automatic control system, the unit requires power from a 220 volt network. Maximum power consumption is 50 W.
The intelligent control system for air flow entering the combustion chamber ensures the efficiency of each model at 91%.
Watch the product video
Design features
The devices are distinguished by spacious fireboxes of a special configuration, wide doors and a convenient control panel. The heat exchanger is designed for a maximum pressure of 2.5 bar. Maximum heating of the coolant is 90o C. When overheating, a protective lock is triggered. The exhaust gas outlet pipe is adapted for connecting chimneys of various diameters.
Fuel used. To load the firebox, use firewood with a relative humidity of no more than 20%.
Kiturami KRH-35A
The lineup
This floor-standing boiler of the Korean brand is designed for heating residential and industrial premises with an area of up to 280 sq.m. It has two heat exchange circuits that work for heating and heating hot water for household needs. They are designed for operating pressures of 2 and 3.5 bar respectively. For correct operation of the equipment, a connection to an electrical network is required.
This model has a remote control unit with the ability to select several operating modes. Automation protects equipment from overheating and freezing of the coolant. Unit efficiency is 91%.
Watch the product video
Fuel used. The main difference of the presented brand is its versatility. The boiler can operate not only on solid fuel, but also on diesel fuel. When loading coal, its power reaches 35 kW. With the liquid fuel version it decreases to 24.4 kW.