A circulation pump for heating systems, its technical characteristics, design, principle of operation - this is what you will learn in this article. Such a device makes forced circulation of water in the coolant. Thanks to it, the diameter of the pipelines is reduced, it allows you to heat the room faster and correctly distribute a comfortable temperature.
Also, using a circulation pump allows you to save money, since as a result of circulation, thermal energy is evenly used. This allows you to reduce electricity or gas costs by up to 30%. Next we will talk about other advantages of this device.
Why is a circulation pump needed in a heating system?
In general, the purpose of the pump is indicated by the very name “circulation”: it is needed to create circulation (movement) of the coolant in the heating system. Water circulation in heating systems can be natural or forced. For systems of the first type, pumping equipment is not needed; it is used only for the second type. Pumps ensure faster circulation of coolant through pipes, which results in resource savings. Owners of houses with such systems pay 20-30% less for heating. This happens because the temperature of the coolant entering the heating boiler remains high. It has to be heated less, which reduces resource consumption and the load on heating equipment.
Boiler with two outlets
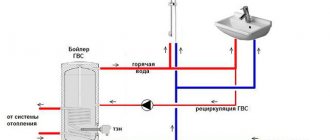
Circulation pump for hot water supply - from an indirect heating boiler without outlet for recirculation
To obtain a stable temperature in the DHW circulation circuit, a three-way thermostatic mixer is used here. To lower the temperature of the water from the primary circuit (at the boiler outlet), he mixes water from the cold water supply into it; it also feeds the boiler, compensating for the consumption of hot water.
Mixing unit with thermostatic head
It’s interesting: the high temperature in the boiler tank is useful because it disinfects it, preventing the growth of bacteria and the appearance of a specific unpleasant odor in the water.
The optimal temperature for heating water with a boiler is 55-75 degrees
Circulation pump device for heating
The design of the circulation pump is an implementation of the standard design of a centrifugal machine.
- The main structural components include:
- frame;
- a rotor that transmits rotation from the engine shaft to the turbine block;
- turbine impeller with inclined blades, which is also called an impeller;
- means of sealing, insulation from water or coolant;
- the main electrical circuit that switches operating modes and monitors engine parameters.
Circulation pumps can have different body shapes and locations of outlet and inlet pipes. This is done so that the device can be easily installed and maintained under the operating conditions for which it was designed. In particular, selection can be made according to the type of connection: with flange, threaded connection, nut.
The circulation pump has small dimensions. It is often built directly into the internal cavity of the housing of domestic gas heating boilers. Security devices can be installed with it.
The small size of the blower is easy to understand if you consider the purpose of circulation pumps. They do not require record liquid supply power. In fact, they literally move water horizontally.
The task of circulation pumps is to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipelines. If a collector group of a warm floor is considered, the blower is busy creating a flow of very small volume as such, since no significant gravitational forces exist in a heating circuit of this type.
Types of circulation pumps
As a result of pump operation, a certain vacuum is obtained at the inlet and the required pressure (compression) is obtained at the outlet.
- All circulation pumps, depending on their design features, are classified into two types (types):
- “dry” type (with a dry rotor);
- “wet” type (with a wet rotor).
“Dry” type pumps are characterized by the fact that their rotor does not itself come into contact with the working fluid of the heating circuit during operation. It is reliably isolated from it by a sliding seal - a ring.
Such pumps have a fairly high efficiency - up to 75-85%, but operate with a certain noise level. They are larger in size than their “wet” counterparts and require special piping of the circuit.
In addition, they usually require periodic maintenance. As a rule, these pumps are used in individual boiler houses that provide heat to several buildings or an industrial enterprise.
In “wet” type pumps, the rotating rotor itself is in contact with the pumped coolant fluid, and the stationary part of the electric motor, the stator, is isolated from it.
Interaction with the liquid ensures the necessary lubrication of the rotor parts and quiet operation of the entire pump as a whole. Typically pumps have a built-in step speed controller. Wet-type circulation pumps can operate for years, and sometimes decades, without requiring any maintenance.
But they have low efficiency - only 50-65%. Pumps of this type are most widespread in private household heating systems precisely because of their small size and quiet operation. These aspects are among a number of others when choosing a circulation pump for the heating circuit of your home. But there are other aspects of choice.
Boost pump for heating
The main difference between a circulation pump and a booster pump is its function. Ensuring the movement of fluid through the water supply/heating system and creating increased pressure in certain areas are different tasks.
The task of a booster (pressure) pump is to increase pressure in a certain area. This is narrow-profile equipment, which is why manufacturers cannot boast of a huge number of models. However, the range is sufficient
Types by type of accommodation
According to the method of placement, water supply hydraulic pumps are divided into two classes:
- Surface type. Located away from the water source, they ensure its suction through a pipe lowered into a well or borehole.
- Submersible. They sink completely into the water to a certain depth.
Sometimes pumping stations are classified into a separate class, which are essentially a compact, self-sufficient water-pressure complex consisting of a surface pump, a diaphragm accumulator tank, a water pressure switch and a control circuit.
Source: https://nasos-kitai.ru/czirkulyaczionnye-nasosy/czirkulyaczionnyj-nasos-kak-vybrat-pod
How does a circulation pump work in a heating system?
The task that circulation pumps are designed to perform for heating private houses is relatively simple. By creating excess pressure in the pipes with the coolant, the unit forces it to circulate, thereby ensuring the delivery of the required amount of thermal energy to all rooms of the house.
The presence of such a supercharger allows not only to reduce the diameters of the heating circuit pipes, but also to lay them in the most convenient way and even taking into account the features of the interior.
- The principle of operation of the circulation pump can be illustrated by several points:
- The coolant enters the inlet pipe.
- When the engine is turned on, the rotational torque is transmitted through the rotor to the turbine wheel.
- Rotating, the wheel moves water with inclined blades, which moves to the edge of the disk under the influence of mechanics (distribution of forces along an inclined plane), as well as due to centrifugal force.
- As you approach the edge of the disk, the speed of the water flow increases, as does its pressure.
- The liquid is discharged into the outlet pipe.
As water or coolant moves to the edge of the turbine wheel, a vacuum arises in the inlet pipe; it captures a new portion of the working fluid for transportation.
The circulation pump of a gas or solid fuel boiler is capable of effectively servicing a certain length of pipelines, pumping the volume of coolant stated in the characteristics. If greater performance and pressure are required, it is not necessary to buy a separate, external supercharger.
An additional pump can be installed in the system, which will create the necessary flow or help raise water to the second floor. The same is done when building a distributed, zoned floor heating system.
Both a conventional home heating system and a dual pump heating system can use different types of blowers. The main difference between the models offered on the market is the engineering solution of the rotor-turbine zone.
A dry rotor pump is a conventional electric motor with an impeller mounted on its shaft, housed in a sealed housing. That is, in this unit the pumping unit and the drive are located separately and, of course, the electric motor rotor does not come into contact with the coolant in any way.
Due to their characteristics, these blowers are used where significant circulation pump power is needed - in heating networks of industrial enterprises or centralized boiler houses of various institutions and organizations.
Powerful circulation pumps for heating systems with a separate drive are distinguished by their impressive dimensions and high noise level, which makes their use in private housing construction impossible. In individual systems, units with a wet rotor are installed, which are very small in size and make virtually no noise during operation.
In these pumping devices for home heating, the drive and impeller are combined in one housing. To seal, the rotor is encased in a stainless steel shell and placed inside a sleeve made of the same material. The sleeve protects the stator of the unit from moisture, the entire structure is shown in the figure:
Structurally, circulation pumps for heated floors are no different from those installed in the main heating circuits and they are selected according to the same principle, as will be discussed below.
One of the most popular brands is German WILO circulation pumps. Over the years of operation, they have proven themselves to be the best. The manufacturer offers several lines of units of varying power and set of functions.
So when choosing a brand of pumps, you should first pay attention to this brand. Devices from GRUNDFOS are also widespread, but their quality is a little worse.
External factors influencing pump operation
And, of course, external conditions affect the operation of the pump. The ambient temperature has a greater influence on the amount of heat needed to heat the room, and therefore on its operation. In some rare cases, it also affects the operation of the pump itself - a “frozen” one does not work as well as a “warmed-up” one.
By the way, the pump will begin to overheat if it is chosen incorrectly - it may not cope with excessive load. Therefore, when purchasing it, you should know the parameters of your heating system and boiler. The larger the diameter of the pipes, the more water in the system, the more powerful the pump is needed.
In addition, the coolant made from non-freezing liquid has a viscosity that is different from the viscosity of water, so a pump should be chosen that is more efficient and reliable. Fortunately, the choice of circulators is quite large - you can choose the right circulator for almost every heating system.
If your pump operates in tandem with a natural circulation circuit, then the load on it may be high. In this case, the greater its productivity and pressure, the better.
If the wrong choice is made, the pump may simply not cope with the task assigned to it - it will not “push” the system well, as a result the batteries will be barely warm. And it itself can overheat and burn out. Also, do not install the device 1 inch into 1.25 inch pipes through adapters. In some cases, it will not be able to provide the required pressure.
Another pump parameter is its electrical power consumption. As a rule, it is small - from 50 to 200 watts. It is only of great importance when the pump is constantly on.
Design differences
Hydraulic pumps come in the following design types:
- Piston. Now they are practically not used for small pumping stations due to their bulkiness, low efficiency, and low lifespan.
- Centrifugal. One of the most popular and in demand due to its simplicity of design, efficiency and high reliability.
- Turbine. Similar to centrifugal ones, but with axial rather than lateral blades. More powerful and productive. They are mainly used in industrial hydraulic structures.
- Rotary or so-called screw pumps. They are distinguished by their small diameter dimensions, therefore they are most suitable for lifting water from wells.
- Vibrating or membrane. Cheap, but low-performance. The “Rucheek” and “Baby” models, which have been produced for summer residents for a long time, are known.
How to choose a circulation pump for heating
In order to select a circulation pump for the heating system, it is necessary to determine the selection parameters. And although there are few of them, each of them requires serious calculations; in simple words, it is necessary to make a hydraulic calculation of the system.
It should be noted that such calculations are quite complex and if you set out to determine the characteristics in this way, you will have to be patient. We will try to simplify this process as much as possible.
- In fact, for the correct selection of a pumping unit, it is necessary to calculate 2 main parameters:
- performance;
- developed working pressure (pressure).
The operating performance of the pump stems from the thermal output of the entire heating system. In simple words, the unit must pump such a volume of coolant in order to deliver with it a sufficient amount of thermal energy to the radiators in all rooms.
To do this, you need to know the thermal power required to heat the building. If we take it in aggregate by quadrature, then for a house with an area of 100 m2 the power value will be 10 kW. Then the performance calculation is performed using the formula:
G = 3600Q/(c∆t), where: G – required coolant flow, kg/h; Q – thermal power of the system, kW; с – specific heat capacity of water, equal to 4.187 kJ/kg ºС; Δt is the temperature difference in the supply and return lines; in calculations it is usually taken equal to 20 ºС.
The circulation pump for the boiler in our example with a 100 m2 building should have the following performance:
3600 x 10 x 4.187 x 20 = 429.9 kg/h or 0.43 t/h. When choosing a circulation pump, you may notice that its performance in the passport or operating instructions is indicated not in mass flow units, but in volume units. Then you just need to convert the mass of water into volume through density, which at a temperature of +60 ºС is 0.983 t/m3: 0.43 /0.983 = 0.44 m3/h - this is the required operating capacity of the unit.
Important. For the operation of the circulation pump to be reliable and durable, it must operate in a comfortable power range. When choosing, you need to make sure that the performance you need lies in this range.
Recommendations from an expert
The pump must be installed in accordance with the following rules:
- It is mandatory to install a bypass, which will ensure the movement of energy through the system during a power outage;
- the check can only be carried out if the system is completely filled;
- It is imperative to install a coarse filter.
Important!
- Bypass is a small section of pipe built into bypassing the circulation pump.
- It is advisable to install a filter for fine cleaning.
If you carefully look at the photographs with installed circulation pumps, you will certainly notice that devices with a wet rotor are always mounted vertically!
Calculation of a circulation pump for a heating system
The next stage of calculating the circulation pump is more complex and consists of determining its operating pressure.
- It should be enough to overcome:
- resistance to friction of water against pipeline walls;
- local resistances that change the flow structure (turns, tees, fittings, equipment, and so on).
In mathematical terms, the formula for calculating the pump power, that is, the required pressure, is as follows:
P = Rl + Z, where: P – total pressure loss in the system that must be overcome by the pump, Pa; R – specific friction losses, Pa/m; l – length of a pipeline of the same diameter, m; Z – pressure drop in local resistances, Pa. This is where the jungle begins, which is sometimes very difficult for an ordinary homeowner to understand. We propose to calculate the pump pressure in a simpler way.
- To do this you need to follow the algorithm:
- follow the link https://dwg.ru/dnl/11875 and download “Tables for hydraulic calculation of the Shevelevs” in one click. Starting on page 31 (Table 1) the 1000i values are shown for different flow rates and pipe diameters;
- Convert the previously calculated flow rate for the water pump from m3/h to l/sec. In our example, it will be 0.12 l/sec;
- we find this value in the left column of the table and take the optimal pipe diameter according to the columns on the right. The speed of movement should be within 0.7-1 m/s. For our example and steel pipes, the speed will be 0.71 m/s and the diameter will be 15 mm.
We take the value 1000i from the same column (ours is 139.9) and calculate the friction resistance of the entire pipe. If we take its length to be 20 m in the example given, then the resistance will be:
139.9 / 1000 x 20 = 2.8 m water column or 0.28 bar. Since the heating system consists of pipes of different diameters, it is necessary to calculate the resistance of each of them in the same way. After this, all the results are summed up and we obtain the total pressure loss due to friction (the Rl value in the formula).
To make the final selection of the pump according to its parameters, it remains to find out the amount of pressure loss in local resistances (Z value in the formula).
As for the boiler, shut-off valves and radiators, their resistances are indicated in the technical data sheet; they must be summed up and added to the previous figure for friction losses.
The pressure drop at turns, tees and other local resistances should simply be taken as 20% of the total friction losses and added to the previously obtained amount. This completes the calculation.
general information
The autonomous water supply system of a private house consists of several components:
- A well is an artificial excavation-mine dug to collect underground groundwater in the surface aquifer to a depth of 10-15 m and reinforced against crumbling.
- Wells. They are performed by drilling and come in several types:
- Non-pressure: “on sand” - up to 50 m, “on limestone” - up to 150 m.
- Artesian - over 150 m.
- Abyssinian and others.
- Artificial reservoirs. Tanks for collecting melt and rain water. If there is a spring or spring nearby, you can organize an in-depth diversion of its bed.
- Natural bodies of water. Streams, rivers, lakes.
- Water consumers on site and in the house: sinks, sinks, baths, saunas, swimming pools, irrigation.
- Supply and distribution system: pumps, storage tanks, pipelines.
When designing an autonomous system, the first question that arises is the selection of a pump for the water supply of a private home, as one of the most important and, if we talk about the quality of work and durability, the most expensive part of the hydraulic equipment.
And its choice is determined, first of all, by the type of water source on the site, and then by the selected water supply scheme.
Circulation pump for heating price
To answer the question “Which circulation pump is best for heating?” We have collected the best models of pumps for heating systems in one rating.
Prices for some models:
| Rating | Model | Price |
| 1 | GILEX Compasses 25-40 | RUR 2,466 |
| 2 | Wester WCP 25-40G | RUB 1,875 |
| 3 | VORTEX CN-25-4 | RUB 1,980 |
| 4 | Grundfos UPS 32-80 180 | RUB 12,500 |
| 5 | Grundfos ALPHA2 25-40 180 | RUR 9,399 |
| 6 | DAB A 80/180 XM | RUB 11,300 |
| 7 | GILEKS Compasses 32-80 | RUR 5,640 |
| 8 | Wilo Star-RS 25/4 | RUR 4,560 |
Circulation pumps made in Russia
Now let's take a short review of each of them. Why are we considering Russian-made models? — our factories have long learned to produce reliable circulation pumps, even if they are made from imported components.
GILEX Compasses 25-40
High-quality pump with three speeds and low noise level for single-story houses. In this unit you will not find oil seals - the electric motor is cooled by the fluid being moved and lubricated with it.
The throughput capacity is decent - 3 cubic meters per hour, which is quite enough to transfer the coolant in the system of a small and medium-sized cottage.
You will find it easy to install this pump as it is compact and lightweight. Nuts are protected from corrosion. Please note: you should buy this model if the pressure in the heating system is at least 0.9 bar and no more than 10 bar.
- Advantages:
- Good build quality
- Decent Bandwidth
- Easy installation (nuts included)
- Three operating speeds
- Quiet operation
- Minuses:
- Sensitive to water quality
Wester WCP 25-40G
A good, almost silent pump for heating systems, underfloor heating and air conditioning.
Winner in the class: “Small circulation pump”, but due to its compactness, its throughput capacity is small - 2.5 cubic meters per hour. However, there are three operating speeds, and water, antifreeze, and ethylene glycol can be used as a liquid.
The pump is capable of pumping moisture at temperatures up to 110 degrees. Power consumption – 65 W at maximum speed. You need to be careful: the pump cannot run dry!
- Advantages:
- Quiet operation
- Low price
- Simple design
- Ability to work with different types of liquid
- Three operating speeds
- Minuses:
- Not the highest throughput
VORTEX CN-25-4
You can use this simple and inexpensive pump in classic heating systems, heated floors, and air conditioning systems. The design of the drive operates according to the wet rotor scheme: a sealed sleeve isolates the drive from the starter.
The maximum pump capacity is 3 cubic meters per hour. The unit can be installed both horizontally and vertically.
The aluminum motor housing and cast iron cover ensure reliability. You can use both water and antifreeze as a liquid.
- Advantages:
- Low price
- Simple design
- Good throughput
- Possibility to use antifreeze
- Minuses:
- Build quality is not the highest
Grundfos UPS 32-80 180
A powerful and high-quality pump that is suitable for a heating system not only in a large cottage, but even in a large industrial premises. A wet rotor engine can pump up to 11 cubic meters of liquid per hour. You can install the pump either horizontally or vertically.
Energy consumption for such a performance model is not too high - 135 Wh. The impeller is corrosion resistant and the graphite axial bearing is very reliable. The price is high, but this is the price to pay for quality.
- Advantages:
- High power
- Excellent Productivity
- Reliability
- Optimal energy consumption
- Easy installation
- Minuses:
- High price
Grundfos ALPHA2 25-40 180
The price of this pump should not alarm you: it will pay for itself quite quickly.
ALPHA2 is one of the most energy efficient models on the market, consuming only 22 W. The pump with a stainless steel body is capable of operating with liquid temperatures from +2 degrees. The stainless steel housing provides excellent corrosion protection.
In AUTOADAPT mode, the unit itself will analyze the heating system, set the optimal parameters, and then monitor changes. You can also adjust the pump manually. The maximum productivity of ALPHA2 is 2.4 cubic meters of coolant per hour.
- Advantages:
- Automated operation
- High energy efficiency
- Reliability
- Compactness
- Dry running protection
- Minuses:
- Not the highest throughput
DAB A 80/180 XM
A powerful pump for heating, air conditioning and underfloor heating systems, capable of pumping up to 9 cubic meters of water per hour.
The pump body is made of cast iron, the impeller is made of technopolymer, and the motor is made of extruded aluminum. A very reliable unit that will serve you for many years. It has three operating speeds. It is very convenient to have a special plug for removing air from the system. There is protection against overheating.
Installation is possible in both horizontal and vertical planes. Energy consumption in maximum mode is high, but with such productivity this is not surprising.
- Advantages:
- High power
- Excellent Productivity
- Reliability
- Three operating speeds
- Quiet operation
- Easy installation
- Minuses:
- High power consumption
GILEKS Compasses 32-80
One of the most powerful circulation pumps for heating systems. Pumps up to 8 cubic meters of water per hour, while consuming 245 W in maximum mode.
The cast iron body ensures durability and at the same time makes the model unsuitable for use in food water supply systems, do not forget about this.
GILEKS Compass 32-80 has three operating modes, allowing you to save on energy costs if necessary. Installing the pump is not difficult. It works almost silently.
- Advantages:
- High power
- Excellent Productivity
- Reliability
- Three operating speeds
- Quiet operation
- Easy installation
- Minuses:
- Decent power consumption
Wilo Star-RS 25/4
An excellent option for a heating system in a small private house. These circulation pumps are specially designed for heating installations with constantly varying outputs.
The unit can distill up to 3 cubic meters per hour. Please note: the installation is strictly horizontal; Wilo Star-RS 25/4 will not work in any other plane.
The operating speed switch is traditionally three-position. But even at maximum the pump is quiet. The temperature of the coolant does not matter much - even boiling water - but poor water quality quickly wears out the engine.
- Advantages:
- Good build quality
- Decent Bandwidth
- Easy installation
- Three operating speeds
- Insensitive to coolant temperature
- Minuses:
- Horizontal installation only
- Doesn't like too hard water
Let's look at how a circulation pump is built into a heated floor connection diagram. And how to choose the right wall-mounted double-circuit gas boiler for your heating system.
Author: Sergey Vladimirovich, electrical engineer. More about the author.
Frequently asked questions from consumers
- Will the pipes make noise when the pump is running? The pipes may make noise if the pump is selected incorrectly or if air has accumulated.
- Is it permissible to use a high pressure pump in a water supply system? This type of pump cannot be used. The pumps are similar in appearance, but in a water supply system, pumps are used only to maintain a small pressure if there is not enough pressure.
- What are pumps made of? Many pump parts are made from ceramics, which ensures low noise operation and increases service life.
- Are there hot water pumps? Such pumps are commercially available. Their use will increase water consumption, as well as electrical energy consumption.
- How much electricity do pumps use? Many circulation pumps are economical devices. They consume energy like a simple light bulb. Pump manufacturers have adopted a convention to give pumps labels that show their electricity consumption, just like household appliances. There is a special classification.
- How often do circulation pumps need to be replaced? If the pump is of high quality, it will work for many years. But this depends on the manufacturer. In order for the pump to work longer, you need to follow the recommendations of specialists: select and install the pump correctly, prevent air from entering the system, use clean water.