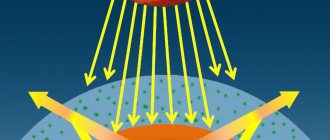
In everyday life we encounter various sources of infrared radiation. They can be either a natural phenomenon or the result of human activity. Half of solar radiation is infrared radiation. This type of ray is invisible to the human eye. But there are various species of animals whose vision is susceptible to such radiation, which allows them to navigate in the dark. A person can feel it with his skin in the form of heat.
These electromagnetic waves are also called thermal waves. This is because this radiation generates heat. It is on the basis of this phenomenon that various meters work, including a thermal imager. It measures the difference in radiation, which also corresponds to the temperature difference between different objects.
Such radiation can be divided into:
- Long wave;
- Medium wave;
- Shortwave.
In this case, the wavelength depends on what temperature the source itself emits. The higher the temperature, the shorter the radiation wave will be, but at the same time it will be more intense. Short-wave radiation is considered the most dangerous for the human body. The temperature of such radiation exceeds 800 degrees Celsius.
Solids are the source of this type of radiation and produce long-wave infrared radiation. The higher the temperature, the lighter the object will appear. So, at temperatures above 5 thousand Kelvin, the color of the object becomes completely white, and at lower temperatures it can reach dark red. This phenomenon can be noticed when heating various objects. For example, when a metal wire is heated, it changes color, indicating an increase in temperature. But as much as possible at home, you can only get a rich red color, because there are no suitable conditions for a subsequent increase in temperature.
People often use infrared radiation for their needs. You need to know what it is, in what doses it is safe for humans and what consequences it can cause. Also, IR rays can be natural. Sunlight is such radiation. Depending on the dose, it can be both beneficial to a person and cause many problems, a common one being sunburn.
First aid for heatstroke
If complications cannot be avoided, it is necessary to take a set of certain measures.
When providing first aid for heatstroke, the following steps should be taken.
- Call an ambulance.
- Move the victim to a cool place, preferably in the shade, where there is access to fresh air.
- Make it easier for him to breathe by removing or unbuttoning his clothes. Give validol.
- Place the victim in a horizontal position, raising his legs.
- Give the victim 1 liter of water with a little salt.
- Cool the person by wrapping him in a cold wet towel and applying ice to his forehead.
- In case of loss of consciousness, it is necessary to give the victim a sniff of ammonia.
The benefits of infrared radiation for humans, application in medicine
Medical research has proven that long-range infrared rays are not only safe for humans, but also very useful. They activate blood flow and improve metabolic processes, suppress the development of bacteria and promote rapid healing of wounds after surgical interventions. They promote the development of immunity against toxic chemicals and gamma radiation, stimulate the elimination of toxins and waste through sweat and urine and lower cholesterol.
Particularly effective are rays with a length of 9.6 microns, which promote regeneration (restoration) and healing of organs and systems of the human body.
From time immemorial, folk medicine has used treatment with heated clay, sand or salt - these are vivid examples of the beneficial effects of thermal infrared rays on humans.
Modern medicine has learned to use beneficial properties to treat a number of diseases:
• using infrared radiation, you can treat bone fractures, pathological changes in joints, and relieve muscle pain;
• IR rays have a positive effect in the treatment of paralyzed patients;
• quickly heal wounds (postoperative and other), relieve pain;
• by stimulating blood circulation they help normalize blood pressure;
• improve blood circulation in the brain and memory;
• remove heavy metal salts from the body;
• have a pronounced antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effect;
• strengthen the immune system.
Bronchial asthma, pneumonia, osteochondrosis, arthritis, urolithiasis, bedsores, ulcers, radiculitis, frostbite, diseases of the digestive system - this is not a complete list of pathologies for the treatment of which the positive effects of infrared radiation are used.
Heating residential premises using infrared radiation devices promotes air ionization, fights allergies, destroys bacteria, mold fungi, and improves the condition of the skin by activating blood circulation. When purchasing a heater, it is imperative to choose long-wave devices.
Where is infrared light used?
Medicine
Infrared physiotherapy has been successfully used in the treatment of various diseases, as well as post-operative rehabilitation. Its effectiveness has been proven to combat burns and frostbite of various stages. After sessions of dosed irradiation, activation of redox processes, stimulation of the functions of the endocrine glands, rapid restoration of capillaries in damaged tissue and improvement of collateral circulation are observed.
The thrombolytic effect of therapy prevents the development of necrosis due to thrombosis of small vessels. There is a pronounced analgesic and sedative effect. In clinical practice, low-frequency IR radiation is widely used for bactericidal and bacteriostatic treatment of open wounds.
Based on research results, it has been established that infrared light improves regional blood flow in the pathological focus, enhances the chemotaxis of leukocytes, and activates the production of proteolytic enzymes. IR irradiation is indicated for the treatment of:
- furunculosis;
- abscess;
- festering cyst;
- panaritium;
- trophic ulcer;
- acute superficial thrombophlebitis;
- herpes;
- fractures and injuries.
Industry
- control of automatic lines and automation systems (IR sensors, remote controls);
- drying wood and paintwork;
- spectroscopy – determination of the structure and composition of samples;
- sterilization and pasteurization of food products;
- heating systems.
Agriculture
- heating of young animals and birds;
- drying and dehydration of fruits;
- drying grain in an elevator with simultaneous disinfection from pests.
Other Applications
- thermography – creating an image of objects by converting their thermal radiation into the visible part of the spectrum. These are night vision devices, sights and thermal imagers;
- photography – taking a photo displaying the landscape according to the level of heat transfer;
- optical communications based on laser devices;
- security alarm;
- heating of residential and non-residential premises;
- remote controls for controlling various equipment.
Devices
Today it is possible to take light therapy procedures both in medical institutions and at home. There is a large selection of stationary and portable devices for this purpose. For treatment at home, portable devices are used that do not require special conditions of use.
Despite this, before starting self-medication, it is necessary to consult with a physiotherapist to determine the possible risks of prescribing the treatment method in question, as well as choosing a specific technique for each specific case. The doctor will describe the treatment method, which will indicate which area needs to be treated, what gap between the device and the skin needs to be maintained, the intensity of the effect, the time of the treatment session and the number of procedures per course of physiotherapy.
What should you consider when using the device?
However, it is necessary to take into account some factors that can reduce the effectiveness of infrared therapy or provoke a negative reaction of the body to infrared radiation. Thus, the use of the device is prohibited when:
- Oncological diseases;
- Open bleeding;
- Active stage of tuberculosis;
- Pregnancy;
- Severe forms of pulmonary and heart failure, arterial hypertension;
- Taking certain medications, such as immunomodulators and hormonal drugs.
For hypertension, coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis, it is recommended to use infrared lamps to improve the condition of blood vessels and normalize pressure. However, the device should be used with caution, only after consultation with a doctor, and never direct the light stream to the heart area.
In any case, before using an infrared lamp, you must consult your doctor and follow his recommendations exactly. If discomfort or pain occurs during the procedure, the session must be stopped immediately and then reported to the doctor. The lamp should be located at a distance of 20-30 cm from the surface of the skin, otherwise there is a risk of burns.
Benefits and harms
Infrared rays affect living organisms in different ways. For example, long waves have a healing effect on human health, so they are often used for medicinal purposes. It is on this principle that the operation of equipment for physiotherapeutic procedures is based.
Infrared devices can be both beneficial and harmful
Long-wave infrared rays have the following positive effects on humans:
- improve cerebral circulation and memory;
- strengthen the immune system;
- normalize water-salt balance;
- improve hormonal levels;
- normalize blood pressure;
- cleanse the body of toxins and heavy metal salts;
- prevent the proliferation of bacteria, fungi and pathogens.
Thus, long-wave infrared radiation is not only useful for humans, but also necessary for them. With a lack of such rays, the immune system suffers and the process of accelerated aging begins.
In this video you will learn what infrared heat is:
Heaters based on infrared rays eliminate various harmful and dangerous bacteria, and special IR lamps help with:
- radiculitis;
- disruption of ovarian function;
- bronchial asthma;
- osteochondrosis;
- disruption of the mucous membrane.
Also, using such an irradiator, you can cure pneumonia, prostatitis in the acute stage, rhinitis, tonsillitis and otitis media without purulent formations.
Despite the large number of useful and medicinal properties, this device has contraindications. Infrared radiation is harmful to humans if they have acute inflammatory diseases.
Infrared rays may cause side effects
Short waves also cause great harm to infrared radiation on the human body. The following symptoms may appear under their influence:
- nausea;
- severe dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- fainting;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- cardiopalmus.
Usually, under the influence of such rays, the skin begins to turn red, burns and convulsions may appear. Prolonged exposure to short waves leads to disruption of the water-salt balance or heat stroke. Such radiation also poses a great danger to the mucous membrane of the eyes, as it can lead to the development of photophobia, cataracts and other vision problems.
More details about the infrared heater:
Treatment of bruises with an infrared lamp
In the treatment of soft tissue bruises, the main goals are to relieve swelling and hematoma, since these are the manifestations that can lead to complications. For such injuries, the benefit of an infrared lamp is explained by its ability to:
- Relieve pain;
- Activate local immunity;
- Prevent inflammation;
- Launch the process of natural tissue healing;
- Stimulate blood circulation and metabolism;
- Reduce muscle hypertonicity.
Thanks to infrared radiation, the healing process is significantly accelerated, the consumption of painkillers is reduced, and their negative impact on the body is reduced.
For bruises, the lamp can be used not immediately after the injury, but from 2-3 days. IR rays should be directed to the affected area for 10-15 minutes, and the full course should include 10-15 procedures. Pain during the first session is associated with vasospasm, but this symptom should pass fairly quickly. If pain persists, you should consult your doctor.
Applications of infrared radiation
Infrared energy is used in various fields, positively affecting humans:
- Thermography. Using infrared radiation, the temperature of objects located at a distance is determined. Heat waves are mainly used in military and industrial applications. Heated objects with such a device can be seen without lighting.
- Heating. Infrared rays contribute to an increase in temperature, having a beneficial effect on human health. In addition to being useful infrared saunas, they are used for welding, annealing plastic objects, and curing surfaces in the industrial and medical fields.
- Tracking. This method of using thermal energy is to passively guide missiles. These flying elements have a mechanism inside them called a “heat seeker.” Cars, planes and other vehicles, as well as people, emit heat to help rockets find the right direction to fly.
- Meteorology. Radiation helps satellites determine the distance at which clouds are located, determines their temperature and type. Warm clouds are shown in gray, and cold clouds are shown in white. Data is studied without interference both day and night. The Earth's hot plane will be indicated in gray or black.
- Astronomy. Astronomers are equipped with unique instruments - infrared telescopes, which allow them to observe various objects in the sky. Thanks to them, scientists are able to find protostars before they begin to emit light visible to the human eye. Such a telescope will easily identify cold objects, but planets cannot be seen in the infrared spectrum being viewed due to the muting light from the stars. The device is also used to observe galactic nuclei that are obscured by gas and dust.
- Art. Reflectograms, which work on the basis of infrared radiation, help specialists in this field examine in more detail the lower layers of an object or an artist’s sketches. This method allows you to compare the drawings of the drawing and its visible part to determine the authenticity of the painting and whether it was restored. Previously, the device was adapted for studying old written documents and making ink.
These are only the basic methods of using thermal energy in science, but new equipment operating on its basis appears every year.
The benefits of infrared rays
The benefits of using infrared rays in medicine have been scientifically proven. General improvement of human health, treatment of bacterial infections, lowering blood pressure and muscle relaxation - this is an incomplete list of the positive aspects of this amazing discovery.
Man, thanks to his perseverance, managed to find useful application for this amazing phenomenon in the most diverse and sometimes even unrelated areas of his activity. Of course, behind all this there is a careful study of the properties of rays.
Ceramic infrared heaters
These are ordinary heating elements, “sharpened” into a shell made of ceramic material, which acts as a body base. Heat from the heating element is transferred to the ceramic, and from it heat rays are emitted into the external environment. The ceramic shell has an area several times larger than the area of the heating element, so the temperature is transferred more actively. These heaters are often called panel infrared heaters. The shape of heating panels can be very diverse. Ceramic IR emitters can be flat, concave or, conversely, convex.
Appearance of a ceramic emitter
The configuration of the heating element is often visible on the front surface, and wires with insulation in the form of ceramic beads are on the back surface. The operating temperature of ceramic heaters is 700 ... 750 degrees, specific surface - up to 64 kW / m2. The power of ceramic heaters can vary from several tens of watts to several kilowatts. What is called for all occasions.
Some types of ceramic heaters have an open, visible coil, such as the HSR type. The operating temperature of the heater is 900 °C, it is designed for fast heating.
Ceramic infrared heaters come in three types: volumetric (solid), hollow, and heaters with a built-in thermocouple. Volumetric elements are inertial, take a long time to heat up and cool down slowly. In cases where periodic switching on/off of the heater is necessary, hollow heaters are used.
They are not so inertial, which allows them to be used in various technological processes where it is necessary to maintain the exact temperature of the working fluid by periodically turning on / off the emitting device. Due to the reduced mass, the heating rate of hollow heaters is 40% higher than that of volumetric heaters.
Unlike volumetric emitters, most of the radiation from hollow devices is directed forward. Reverse radiation is prevented by a hollow thermal barrier on the rear side, which provides mild temperature conditions for the chassis components and also improves efficiency. Compared to volumetric heaters of the same power, the reduction in electricity consumption reaches 15%.
When using a volumetric radiator, such heat distribution can only be achieved with a reflector. Some types of infrared panel heaters have a built-in K or J type thermocouple, which allows precise temperature control and regulation, which is very convenient for various processes.
There are many technological processes that use IR emitters. Here are just a few of them:
Infrared ceramic Edison lamps
They are a type of hollow ceramic heaters, produced with an E27 base, like a regular incandescent lamp. This base was invented long ago by the great scientist T. Edison. It is the letter “E” in the name of the cap that perpetuates the name of the inventor, and 27 indicates the diameter of the cap in millimeters. The design is very convenient: you simply screw in the socket instead of an incandescent lamp, and it immediately becomes warm!
Why can’t you hang such a heater, if not at home, then at least at your workplace? After all, it’s no secret that our employers do not particularly care about creating normal conditions in the workplace: in the summer there is not enough air conditioning, and in the fall, when the heating is not turned on, you have to put on a padded jacket in the workshop or design department.
Metal reflectors are available for Edison metal heaters, which increases heat transfer in the desired direction and reduces thermal effects on walls and ceilings. Naturally, such “lamps” should be screwed into a high-temperature ceramic socket.
The more expensive electronics are, the safer they are?
In theory, high-quality household appliances will be more harmless, since the larger and more “renowned” the manufacturer, the more he will care about his image and, accordingly, certify all his products as responsibly as possible. But this, of course, also affects the cost of the equipment.
However, it is worth considering that this only applies to new equipment that has not been subjected to physical impact, repairs, with proper operation, location, etc. If at least something has been disturbed, then the intensity of the radiation can change significantly.
Discovery history and general characteristics
Herschel's experiment
Infrared radiation was discovered in 1800 by the English astronomer W. Herschel. While studying the Sun, Herschel was looking for a way to reduce the heating of the instrument with which the observations were made. Using thermometers to determine the effects of different parts of the visible spectrum, Herschel discovered that the “maximum of heat” lies behind the saturated red color and, possibly, “beyond visible refraction.” This study marked the beginning of the study of infrared radiation.
Previously, laboratory sources of infrared radiation were exclusively hot bodies or electrical discharges in gases. Nowadays, modern sources of infrared radiation with adjustable or fixed frequency have been created based on solid-state and molecular gas lasers. To record radiation in the near-infrared region (up to ~1.3 μm), special photographic plates are used. Photoelectric detectors and photoresistors have a wider sensitivity range (up to approximately 25 microns). Radiation in the far infrared region is recorded by bolometers - detectors that are sensitive to heating by infrared radiation.
IR equipment is widely used in both military technology (for example, for missile guidance) and civilian technology (for example, in fiber-optic communication systems). IR spectrometers use either lenses and prisms or diffraction gratings and mirrors as optical elements. To eliminate the absorption of radiation in air, spectrometers for the far IR region are manufactured in a vacuum version.
Since infrared spectra are associated with rotational and vibrational movements in the molecule, as well as with electronic transitions in atoms and molecules, IR spectroscopy allows one to obtain important information about the structure of atoms and molecules, as well as the band structure of crystals.
What is infrared light?
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation, occupying a portion of the spectrum in the frequency band from 3 to 380 Terahertz, with wavelengths of 0.78-1000 micrometers. It is adjacent to the region of visible light and the radio wave range.
The Earth's biosphere receives maximum natural infrared light from the Sun. But there are many other, completely earthly sources.
All warm-blooded living beings, including humans, emit infrared waves. Any physical bodies in a heated state also glow in the infrared range. For example, a red-hot forge billet, an electric welding arc, or molten metal flowing from a blast furnace. And for the lamps that illuminate our apartments, the share of IR glow is 60-70% of the total luminous flux.
Here is the division into subranges in accordance with the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) methodology:
| Name | Wavelengths, microns | Frequencies, THz | Peculiarities |
| Far (long wave) | 50-1000 | 6-3 | Borders on the microwave subrange. Exhibits the characteristic properties of radio waves (passing through obstacles, absorption by certain materials). Beneficial for all living organisms |
| Medium (medium wave) | 3-50 | 100-6 | Combines the features of the long-wave and, to a greater extent, short-wave subranges |
| Near (short wave) | 0,78-3 | 384-100 | Borders the visible spectral region, exhibiting its properties (linear propagation, reflection, refraction) |
Infrared radiation can heat surrounding objects because the emitted photons are absorbed by atoms and transfer their energy to them. There is a transition of electromagnetic radiation into thermal energy.
Human vision does not perceive infrared light, but there are small exceptions. Scientists from the USA (St. Louis University), conducting research using IR lasers, discovered an interesting effect. During the operation of laser emitters at wavelengths of 800-900 nm, light flashes were periodically observed. The experiments carried out allowed us to draw a conclusion about the ability of the eye to perceive IR light of the high-frequency subrange in the pulsed mode of a powerful laser.
Subcategories of IR waves
The IR portion of the electromagnetic spectrum occupies the range from 300 GHz (1 mm) to 400 THz (750 nm). There are three types of infrared waves:
- Far IR: 300 GHz (1 mm) to 30 THz (10 µm). The lower part can be called microwaves. These rays are absorbed due to rotation in gas-phase molecules, molecular motions in liquids and photons in solids. Water in the earth's atmosphere is absorbed so strongly that it becomes opaque. But there are certain wavelengths (windows) used for transmission.
- Mid-IR range: 30 to 120 THz (10 to 2.5 µm). The sources are hot objects. Absorbed by molecular vibrations (various atoms vibrate in equilibrium positions). This range is sometimes called a fingerprint because it is a specific phenomenon.
- Nearest IR range: 120 to 400 THz (2500-750 nm). These physical processes resemble those that occur in visible light. The highest frequencies can be found with a certain type of photographic film and sensors for infrared, photography and video.
IR lamp for gastritis
You can use an infrared lamp for gastritis only outside the period of exacerbation. Its therapeutic effect for this disease is to strengthen local immune defense, heal the gastric mucosa, activate metabolism and accelerate blood flow.
During the procedure, it is necessary to direct the lamp for 10-15 minutes on the stomach, and then for the same time on the back in the area of the lower part of the thoracic spine. Sessions must be repeated daily for 10-12 days.