The heat exchanger can be connected using three different schemes: parallel, two-stage mixed and series. The specific connection method must be selected taking into account the maximum heat flows for DHW (Qh max) and heating (Qo max).
If - a parallel circuit is selected.
At - two-stage scheme.
At the moment, the connection diagram of a plate heat exchanger is regulated by the rules of SP 41-101-95 “Design of heating points”
Now let's look at all 3 installation methods in more detail.
Schematic diagram of independent single-stage parallel DHW
| 2 — Control valve with electric drive | 9 - Cranes |
| 3 - Immersion temperature sensor | 10 - Check valve |
| 4 - Controller | 11 — Differential pressure switch |
| 5 - Flow meter | 12 — Drain pump |
| 6 — Cold water pump (cold water supply) | 13 — Pressure gauge |
| 7 - DHW circulation pump (hot water supply) | 14 — Thermometer |
Advantages of parallel connection of the heat exchanger: it saves usable space in the room and is very simple to implement.
Disadvantages: no cold water heating.
Very easy to implement and relatively inexpensive. Allows you to save useful visiting space, but at the same time it is unprofitable in terms of coolant consumption. In addition, with such a connection, the pipeline must be of increased diameter.
Selection and calculation of the cost of a heat exchanger in a convenient way for you
To get a consultation
We'll advise you on the task We'll tell you where to get the data We'll help you with the selection We'll tell you the price according to the labeling Call you back?
Let's calculate according to parameters
We make calculations accurately and professionally, without any manipulation
Calculate
Do you have a ready-made heat exchanger calculation?
We will calculate the cost
according to the calculation number, serial number, calculation sheet, specification, according to the heat exchanger nameplate.
Get a price
. We will call you back within 1 minute.
results from 30 minutes
results in 5 minutes
Where can I get the calculation data for VET?
Calculated data (loads, pressures, temperature graphs) are issued by heat supply organizations (heating networks, boiler houses) in the form of explanatory notes, Technical Conditions (TU).
You can also take this data from a contract with a heat supply organization, or from a project for modernization or re-equipment of ITP, UUTO. If you still have questions about the calculation data, you can contact the manager for advice.
Design and principle of operation
A plate heat exchanger (PHE) ensures the transfer of heat from a heated coolant to a cold one, without mixing them, decoupling the two circuits from each other. The coolant can be steam, water or oil. In the case of hot water supply, the heat source is often the heating fluid of the heating system, and the heated medium is cold water.
Structurally, the heat exchanger is a group of corrugated plates assembled parallel to each other. Between them, channels are formed through which the coolant and the heated medium flow, and they alternate layer by layer without mixing. By alternating the layers through which fluids of both circuits flow, the heat exchange area increases.
Heat exchanger operating diagram
The corrugation of the bowl is performed in the form of waves, moreover, oriented so that the channels of one circuit are located at an angle to the channels of the second circuit.
The connections of the inputs and outputs are made so that the liquids flow towards each other.
The surface and material of the plates are selected based on the required heat transfer power and the type of coolant. In particularly efficient and sophisticated heat exchangers, the surface is shaped to generate vortices near the surface of the plate, increasing heat transfer without creating much resistance to the overall current.
The heat exchanger is connected between two circuits:
- In series with the heating system or in parallel with the presence of control valves.
- To the inlet from the cold water supply and the outlet to the DHW consumer.
Cold water flowing through the heat exchanger is heated by heat from the heating system to the required temperature and supplied to the consumer tap.
Main characteristics of plate heat exchanger:
- Power, W;
- Maximum coolant temperature, oC;
- Throughput, productivity, liters/hour;
- Hydraulic resistance coefficient.
The power depends on the total heat exchange area, the temperature difference in both circuits between the input and output, and even on the number of plates.
The maximum temperature is set by the selection of materials and the method of connecting the plates and the heat exchanger body.
The throughput increases with the number of plates, since they are connected virtually in parallel, each new pair of plates adds an additional channel for fluid flow.
The coefficient of hydraulic resistance is important when calculating the load on the heating system, where the choice of a circulation pump depends on it, and is also important for other heat sources. Depends on the type of corrugation of the plates and the cross-sectional size of the channels and their number.
It is based on these parameters that a heat exchanger is ultimately selected for a specific situation. Most often, plate heat exchangers have a collapsible design, in which you can increase or decrease the number of plates and choose their type and size. The power and performance of the heat exchanger must be sufficient to heat running cold water without creating a critical load on the heating system.
For the most popular cases, such as providing hot water to a private household, house or apartment, ready-made heat exchangers with constant characteristics are produced.
Two-stage mixed scheme
As in the case of parallel, it requires the mandatory installation of a temperature regulator, and is most often used when connecting public buildings.
| 2 — Plate heat exchanger (2nd stage) | 10 - Check valve |
| 3 — Control valve with electric drive | 11 — Differential pressure switch |
| 4 - Immersion temperature sensor | 12 — Drain pump |
| 5 - Controller | 13 — Pressure gauge |
| 6 — Cold water pump (cold water supply) | 14 — Thermometer |
| 7 - DHW circulation pump (hot water supply) | 15 — Flow meter |
| 8 - Filters |
The symbols in the drawing completely coincide with the symbols in the parallel diagram.
Advantages: the heat of the return water is spent on heating the input flow, which allows you to save up to 40% of the coolant.
Disadvantage: high cost due to the connection of two heat exchangers for preparing hot water.
In comparison with the above scheme, it helps reduce coolant consumption (by about 20-40%), but it also has a number of disadvantages:
- requires professional and very precise selection of equipment;
- for implementation, 2 heat exchangers will be required at once, which will increase the budget;
- with such a connection, the hot water supply and the heating system strongly influence each other.
How to use heat exchangers to obtain hot water from heating
There are several possibilities to heat water for domestic needs using a heat exchanger and heating:
- Heating running water. Disadvantages - limited possibilities for hot water consumption, lack of reserve, difficulty in maintaining a stable temperature (you need to organize a mixing unit or install a controller). Advantages: little space required, few components.
- Heating water in some container. The heat exchanger for hot water from heating is lowered into some container filled with water. In fact, this is already an indirect heating boiler. But a heat exchanger is installed in it and it is connected to the hot water supply. But we are not talking about them now, so not in this article.
The most basic heat exchanger is a pipe through which the coolant flows
Types of plate heat exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are divided according to the degree of accessibility of the heat exchange surface for mechanical cleaning and inspection:
- collapsible
- semi-collapsible (semi-welded)
- non-separable (soldered and welded)
The most widely used are plate heat exchangers , in which the plates are separated from one another by rubber seals. Installation and dismantling of these devices is carried out quite quickly, cleaning the heat exchange surfaces requires little labor.
What factors does effectiveness depend on?
Several factors influence performance:
- Device design.
- Operating mode, temperature of the releasing coolant.
- The amount of heat loss or, more simply, the condition of the inner surface of the tubes (the absence of scale or deposits that act as a heat insulator and reduce the ability to receive or release thermal energy).
Since the device is selected at the design and installation stage, and the operating mode is set when setting up the heating system as a whole, the most important factor is the fight against losses. To do this, the household heat exchanger is periodically washed and cleaned using various means.
, of which there are plenty on sale.
Acid compounds are used to remove scale, and fatty deposits are cleaned with caustic soda. After cleaning, the device is thoroughly washed and reconnected to the equipment. Another means of prevention and reduction of pollution are filters. With their help, foreign particles, suspension, and fatty compounds are eliminated. At the same time, filters also need to be periodically washed or replaced.
Requirements for gaskets
Devices with plates are subject to rather stringent requirements regarding the tightness of the equipment; it is for this reason that today gaskets have begun to be made from polymers. For example, ethylene propylene can easily be used at elevated temperatures - both steam and liquid. However, it begins to deteriorate quite quickly in an environment that contains large amounts of fats and acids.
Heat exchangers differ in the number of plates
The seals are attached to the plates most often using clip locks, and in rare cases - using an adhesive.
Plates for plate heat exchangers
Serially produced plate heat exchangers are equipped with plates stamped from sheet metal up to 1 mm thick. The materials used are corrosion-resistant steel, titanium, and special alloys. The plates of a plate heat exchanger have a corrugated surface to turbulize flows in the channels, which increases heat transfer efficiency and prevents the deposition of contaminants. The corrugations of the plates usually have the cross-section of an equilateral triangle. The steeper the angle at which the plate corrugations are located, the greater the resistance created in the channels; the sharper the angle, the lower the resistance and the higher the flow speed.
Plates for gasketed plate heat exchangers
In what areas is a heat exchanger used?
The scope of use of heat exchangers is very extensive:
- heating systems;
- cooling systems;
- when working with chemicals;
- with solar collectors;
- for heating swimming pools;
- ventilation systems;
- air conditioning systems;
- in the field of mechanical engineering;
- metallurgical industry;
- pharmaceutical industry;
- food industry (sugar, beer, dairy and others);
- Automotive industry;
- chemical industry.
The design and operating principle of heat exchangers affects the operation of various areas, including industrial production and objects of public and cultural significance. At the same time, their use is also possible in heating systems of private residential buildings, where the issue of maintaining temperature is most acute. Installation and assembly of heat exchangers can be done either independently or with the help of specialists. The point of the device is to distribute heat evenly throughout the room.
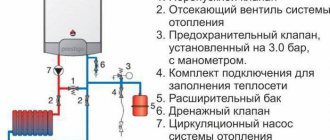
Installation of a floor-standing unit
Stationary double-circuit heat generators burning natural gas are divided into 2 types - non-volatile and requiring power supply. The latter are connected to heating and electricity in the same way as their wall-mounted “brothers”.
A non-volatile floor-standing boiler heats DHW water using a copper or stainless steel coil built into the main heat exchanger. The heater's equipment is minimal - a burner, automatic safety system and a heat exchanger, nothing else. In addition to the cranes listed in the previous section, for installation you will need to buy:
- safety group with a safety valve designed for the operating pressure of the heat generator (indicated in the passport);
- circulation pump;
- expansion tank of calculated volume (10% of the total amount of coolant).
The diagram for connecting a heating unit to a closed-type heating network is shown in the picture above.
A few words about how to connect a double-circuit floor-standing boiler to a gravity heating system. Here you will need an open expansion tank with an overflow, but a pump and safety group are not needed. Pipe diameters are at least 40 mm, laying is carried out with a slope of 5 mm per 1 linear meter. highways. The heater is the lowest point of the system, and the open tank is placed at the highest. If electricity is available, forced circulation can be organized using a pump installed on the bypass.
Integration of a dual-circuit heater into a gravity system with the possibility of forced circulation from a pump
Safety valves
open heating system to protect the boiler from damage
When the valve responds, some of the water flows out of the system, providing pressure relief and protection. You should not insert the drain tube into the sewer, since the reason for the decrease in pressure will not be clear. You can get by with a funnel. By the way, there is no need to throw the septic tank into the coolant.
Air vent
. The part must be installed immediately after installing the boiler to avoid “airing”. Often they simply forget to open it. This is also typical for wall-mounted options with a factory function. By the way, the circulation pump is also ventilated.
The air vent must stand strictly vertically upward. When it starts to leak, there is a shut-off valve in front of it, so replacing it with a new one will take a couple of minutes.
Circulation pump
. The pump will operate properly only when the axis is in a horizontal position, and this position will significantly extend the “life” of the bearings.
It is advisable to protect the mechanism from dirt and debris from the outside. Strainers sold separately
Radiators.
Disadvantages when connecting a panel radiator to the coolant.
The radiator design involves connecting the supply pipe to the internal vent, located almost in the center, and to the outermost one - in the return pipe. The reverse connection order will reduce the heat transfer of the radiator by half. By the way, decorative screens disrupt heat transfer by 10-20%. Proper installation and correct power calculations will help create maximum comfort for living in a country house at any time of the year.
What is the difference between solid fuel boilers
In addition to burning various types of solid fuel, heat generators have a number of differences from other heat sources. These features should be taken for granted and always taken into account when connecting a solid fuel boiler to a water heating system. What are they:
- High inertia. At the moment, there are no ways to quickly extinguish a solid fuel fire in a combustion chamber.
- Formation of condensation in the firebox during heating. The peculiarity is manifested due to the flow of coolant with a low temperature (below 50 ° C) into the boiler tank.
Diagram of the design of a direct combustion TT boiler with forced air injection.
Inertia creates the danger of overheating the water jacket of the heater, as a result of which the coolant in it boils. Steam is generated, which creates high pressure, rupturing the body of the unit and part of the supply pipeline. As a result, there is a lot of water in the furnace room, a lot of steam and a solid fuel boiler unsuitable for further use.
A similar situation can arise when the heat generator piping is done incorrectly. After all, in fact, the normal operating mode of wood-burning boilers is maximum; it is at this time that the unit reaches its rated efficiency. When the thermostat reacts to the coolant reaching a temperature of 85 °C and closes the air damper, combustion and smoldering in the firebox still continues. The water temperature rises another 2-4 °C, or even more, before its growth stops.
Another unpleasant feature of the unit operating on wood is the appearance of condensation on the inner walls of the firebox due to the passage of not yet heated coolant through the water jacket. This condensate is not God’s dew at all, since it is an aggressive liquid that quickly corrodes the steel walls of the combustion chamber. Then, having mixed with the ash, the condensate turns into a sticky substance that is not so easy to tear off from the surface. The problem is solved by installing a mixing unit in the piping circuit of a solid fuel boiler.
This coating serves as a heat insulator and reduces the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler.
It is too early to breathe a sigh of relief for owners of heat generators with cast iron heat exchangers that are not afraid of corrosion. Another misfortune may await them - the possibility of destruction of cast iron from temperature shock. Imagine that in a private house the electricity was turned off for 20-30 minutes and the circulation pump driving water through the solid fuel boiler stopped. During this time, the water in the radiators has time to cool down, and in the heat exchanger it has time to heat up (due to the same inertia).
Electricity appears, the pump turns on and directs the cooled coolant from the closed heating system into the heated boiler. Due to a sharp temperature change, the heat exchanger experiences a temperature shock, the cast iron section cracks, and water runs onto the floor. It is very difficult to repair; it is not always possible to replace a section. So even in this situation, the mixing unit will prevent an accident, which will be discussed below.
Emergency situations and their consequences are described not with the aim of scaring users of solid fuel boilers or encouraging them to purchase unnecessary elements of piping schemes. The description is based on practical experience, which must always be taken into account. If the heating unit is connected correctly, the likelihood of such consequences is extremely low, almost the same as with heat generators using other types of fuel.
Installation and connection of the heat exchanger and tank in the bath
- Find a suitable location to mount the remote tank. If all the structural parts are located in one room, it is most often hung on the wall closest to the heating unit, 200-300 mm above the recuperator.
- Secure the wooden dies with dowels - these are the guides on which you will hang the tank. This is necessary so that the container does not touch the interior elements with its hot surface.
- Strengthen the assembly with brackets for greater reliability.
- Equip the remote tank with 4 pipes, then, using fittings, connect the first two with the corresponding ones at the tank (for direct and reverse water supply), close the third with a valve, and connect the shower (faucet) to the fourth.
- Install (at the lowest point) a valve on the reverse line to drain the water.
- Connect all elements and check the system for leaks.
What you need to know about operation
If you have read the instructions and purchased a heat exchanger for your bath, make sure that the following conditions are met:
- Fastening connections must be movable - this will help minimize deformation of the recuperator components under the influence of high temperatures.
- Seals must be made of heat-resistant materials.
- The capacity of the remote tank is selected so that it can accommodate the volume of water heated in 2 hours.
- It is important that full compatibility with the heating unit is maintained.
- The device should consume no more than 10% of the energy generated by the oven.
Operational safety
To prevent emergency situations, observe the following precautions:
- do not attach pipes directly to walls;
- Make sure that there is always enough water in the tank, otherwise you will quickly encounter a scale problem or even a fire hazard;
- constantly check the operation of the device and sound the alarm if it suddenly breaks down;
- Use only heat-resistant gaskets and regularly pay attention to their condition.
Flushing the plate heat exchanger
The functionality and performance of the unit largely depends on high-quality and timely washing. The frequency of washing is determined by the intensity of work and the characteristics of technological processes.
Methodology for cleaning work
Scale formation in heat exchange channels is the most common type of PHE contamination, leading to a decrease in heat exchange intensity and a decrease in the overall efficiency of the installation. Descaling is carried out using chemical washing. If, in addition to scale, other types of contamination are present, it is necessary to mechanically clean the heat exchanger plates.
Chemical washing
The method is used for cleaning all types of PHE, and is effective with minor contamination of the working area of the heat exchanger. To carry out chemical cleaning, disassembling the unit is not required, which can significantly reduce the work time. In addition, no other methods are used for cleaning brazed and welded heat exchangers.
Chemical washing of heat exchange equipment is carried out in the following sequence:
- a special cleaning solution is introduced into the working area of the heat exchanger, where scale and other deposits are intensively destroyed under the influence of chemically active reagents;
- ensuring circulation of detergent through the primary and secondary maintenance circuits;
- flushing heat exchange channels with water;
- draining cleaning agents from the heat exchanger.
During the chemical cleaning process, special attention should be paid to the final rinsing of the unit, since chemically active components of detergents can destroy seals.
The most common types of contamination and cleaning methods
Depending on the working media used, temperature conditions and pressure in the system, the nature of the contaminants can be different, so for effective cleaning it is necessary to choose the right detergent:
- cleaning from scale and metal deposits uses solutions of phosphoric, nitric or citric acid;
- inhibited mineral acid is suitable for removing iron oxide;
- organic deposits are intensively destroyed by sodium hydroxide, and mineral deposits by nitric acid;
- fatty stains are removed using special organic solvents.
Since the thickness of the heat exchange plates is only 0.4 - 1 mm, special attention should be paid to the concentration of active elements in the detergent composition. Exceeding the permissible concentration of aggressive components can lead to destruction of plates and sealing gaskets.
The widespread use of plate heat exchangers in various sectors of modern industry and public utilities is due to their high performance, compact overall dimensions, ease of installation and maintenance. Another advantage of VET is the optimal price/quality ratio.
Peculiarities
If a heating apparatus can be likened to the heart of a heating system, then the boiler piping is the vessels and peripheral organs.
When using such a system, the following actions are carried out:
- ensures normal temperature in heating circuits;
- the air contained in the line is discharged;
- a normal supply of coolant is maintained;
- the uniform heating of heating devices is monitored;
- supports connecting various heating circuits and adjusting them to a particular temperature;
- increasing the efficiency of distribution of the resulting heat.
Review of furnaces with heat exchanger
There are built-in models of heat exchangers. Below we will look at the popular ones.
Sauna stove with boiler
Let's start with how justified such a decision is from an economic point of view. Installation of this device increases the efficiency of the equipment used. With it, exhaust gases not only fly away uselessly into the atmosphere, but also simultaneously heats water, which can then be used for bathing or other household needs. Therefore, it repeatedly justifies the fact of its installation in the long term.
Vesuvius Skif 16 VChT
Powerful and fast, with a right- or left-side location of the water heater, equipped with a mesh. It boasts a steel firebox with thick walls (8 mm), thanks to which it is not afraid of even constant exposure to high temperatures.
Tornado 20M2
Productive, heavy (125 kg). Equipped with a cast iron door, built-in heat exchanger and a spacious side casing designed for 240 kg of stones. Must be installed on a reinforced foundation. But the efficiency is impressive.
Harvia 20SL Boiler
A heater from a Finnish manufacturer, weighing 75 kg, with 40 kg of stones. Modern, with a recuperator in the form of a tank, with a remote structure and a built-in condenser, designed for a steam room with an area of up to 20 m3. It has stable legs and a stainless frame, has smooth shapes and an attractive design.
How and how to connect the external tank to the heat exchanger
Remember that the elements in contact with the stove become hot, their surface temperature exceeds 100 0C. Therefore, the pipes must be made of stainless steel (cast iron will not work, as it is susceptible to corrosion). But ordinary pipes are allowed to be made of metal-plastic; they can even be replaced with flexible hoses. The main thing is that the diameter is 1 inch or 3/4, otherwise the circulation will be poor.
Use tangit for seals, and paronite for fittings. Feel free to replace factory elements with non-standard ones, but made of heat-resistant material. Don't forget about the drain valve - it is simply necessary to preserve the system for the cold season or to quickly remove stagnant liquid. Otherwise, during frosts, the remaining water will freeze and burst the pipes.
Maintenance Recommendations
An inspection schedule is drawn up to monitor the condition of the plate heat exchanger. The absence of leaks and the tightness of the circuits are checked daily. Pressure and temperature readings can be taken by automatic operators (dispatching) or by a responsible person. The first increases the reliability of the entire system and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Planned maintenance of components - visual inspection, monitoring the condition of fittings, assessing functionality. Medium repairs include replacement of fittings and restoration of anti-corrosion coating. During a major overhaul, a complete disassembly of the heat exchanger is performed, identifying defective plates and seals.
Assembly and startup of a gasketed plate heat exchanger must be carried out in accordance with technical regulations. It is important to monitor the current indicators and compare them with the passport ones. Additionally, acceptable discrepancies are taken into account.
How to make a calculation
The calculation for the DHW heat exchanger is made through rather complex calculations that require special training. A detailed calculation requires drawing up a heat balance, taking into account heat transfer devices, calculating the average temperature difference, etc.
All these operations require knowledge in the field of heating engineering, which not everyone has, and the probability of error is very high even for a specialist.
A way out of this situation can be found on the Internet - online calculators, available in sufficient quantities on the websites of heating equipment manufacturers, allow you to obtain the necessary data simply and quite reliably. To check, the calculation should be duplicated several times, the results should be compared to select the most correct one.