If the home is not connected to centralized heating, then it becomes necessary to provide it yourself. An effective option is to install a gas boiler that will heat the coolant for the radiators. Modern industry offers a large number of options, among which the owner must choose the appropriate one. One of the most effective is the use of a convection gas boiler.
Convection gas boiler needs fine tuning Source boilervdom.ru
Convection and condensing boilers: what is the difference?
Which boiler will you install: convection or condensation?
This question often confuses the customer, since not everyone knows the true difference between the two types of equipment. And there is a significant difference. Convection boilers are traditional gas boilers with an open (less often closed) firebox and a heat exchanger. Externally, they look almost the same as condensation ones. But for some reason the latter are more expensive. Why exactly will become clear if you look under the casing of the condensing boiler.
In traditional boilers, the temperature of the combustion products is so high that condensation of water vapor contained in the combustion products does not occur. Part of the thermal energy goes out into the pipe, but together with, albeit warm, but aggressive condensate.
If you cause condensation of the steam generated by the combustion of gas, which in traditional boilers exits through the chimney, you can thereby obtain the so-called latent heat. For condensation to occur, it is necessary to lower the temperature of the combustion products. Stainless steel welding technology helped bring this idea to life. Before its discovery, it was not possible to produce a condensing boiler, since the unprotected metal was highly vulnerable to the aggressive environment of the condensate. However, the materials used for the production of condensing boilers, as well as the welding technology itself, make them more expensive than traditional (convection) boilers.
Steam condensation. To cause condensation of water vapor in the combustion products of the gas, its temperature must drop below the dew point. For natural gas, the condensation temperature is 56°, for liquefied gas – 52°, and for liquid fuel – 47°. To cool the combustion products in condensing boilers, special heat exchangers are provided. Some models have a two-stage reduction of combustion products, and accordingly two heat exchangers.
Condensing boilers are not only gas, but also liquid fuel. However, gas appliances are more cost-effective because burning gas produces much more water vapor. In addition, when burning liquid fuel, a lot of sulfur is formed, which gives the condensate very aggressive properties, which in turn forces the use of more expensive materials in the manufacture of heat exchangers. However, such boilers exist and can be purchased.
The removal of combustion products from traditional boilers, which most often have a closed chamber, is carried out thanks to natural draft in the chimney. But for this, a compensating volume of air must enter the room where the boiler is installed.
Condensing boilers cannot provide conditions for the generation of sufficient natural draft, since the combustion products are cooled and have a low temperature. In such boilers there is a closed combustion chamber, and fresh air is forced in using a fan. Accordingly, the excess pressure it creates ensures forced removal of gases. Thanks to the closed firebox, gases cannot enter the room, which makes the operation of such boilers safer. Combustion products are discharged through a coaxial pipe, which is also an air intake pipe. The pipes of boilers with a power of up to 30 kW can be discharged through the wall, and more powerful boilers are connected to a pipe that has an outlet above the roof.
It is important to understand that the presence of a closed combustion chamber does not mean that the boiler is a condensing boiler. Traditional boilers can also have a closed combustion chamber and forced ventilation.
Condensing boilers have an efficiency above 100%. Such a statement, in fact, contradicts the law of conservation of energy, discovered by Mayer back in the 19th century. However, exceeding 100% occurs due to outdated methods for calculating efficiency for heating equipment, during the development of which latent heat was not taken into account. The first condensing boilers appeared in the 80s of the last century. Then the efficiency was calculated in such a way that the so-called calorific value of the fuel was taken as 100%, without taking into account the factor of the formation of hot water vapor. Most vapors are generated when natural gas is burned, due to which it has a latent heat of up to 11%. For propane this figure is lower - 9%, and for liquid fuel - only 6%. Thus, the efficiency of the condensation principle of heat extraction when burning natural gas will be almost twice as high as when burning diesel fuel.
The heat index is added to the calorific value of the fuel, and it turns out that condensing boilers operating on natural gas have an efficiency of 111%, on liquefied propane - 109%, and on liquid fuel - 106%. But this is in theory. In practice, these figures turn out to be 2-4% less due to various heat losses and incomplete combustion of fuel.
Combustion chamber type
The open combustion chamber uses atmospheric burners and requires air from the environment to operate. In this regard, special requirements are imposed on the premises where such models are installed. The area of the room must comply with established standards; for normal operation of this type of gas boiler, it is necessary to install a chimney with natural draft and a supply and exhaust ventilation system is required.
Gas boilers with a closed burner are equipped with a fan that forces air through a coaxial chimney. The latter consists of two pipes inserted into each other. Air from the street enters the burner through an external channel formed by the walls of the pipes. The combustion products of the gas-air mixture are removed through the central part. This design ensures complete autonomy of the camera—it is not necessary to install a ventilation system in the room.
Gas boilers are also equipped with manual or automatic controls and various safety devices. For example, automatic fuel shut-off. If the model does not have such equipment, it is better to refrain from purchasing it.
Source
Design and principle of operation
In convection units, the temperature of the return and supply branches differ slightly.
This prevents the appearance of drops of water with dissolved acids on the parts of the heat exchanger, chimney and firebox. With radiator heating, the supply line heats up to +80°C, and in the return line - up to +60°C, which eliminates condensation. Sometimes an automatic mixer is installed to mix the liquid from the supply circuit into the return circuit. Work begins with gas supply and activation of the piezoelectric ignition element. A spark ignites the igniter, which burns throughout the entire operation; if the device goes out, it threatens an explosion. The igniter turns on the base burner, which heats the energy carrier to the required temperature. The automation turns off the main burner when the value is reached, and a drop in the value leads to the flame turning on again.
The burner and heat exchanger determine the type of boiler. The first element is made of stainless steel, and regenerators and recuperators are made of materials:
- stainless steel;
- copper;
- carbon steel.
The disadvantage of the convection method is the irrational use of heat. If you set a low temperature mode, cooling of the final products leads to condensation in the chimney.
Differences in spending and calculations
The technical characteristics of the product are indicated by the manufacturer in the passport; for boilers they are as follows: efficiency of convection boilers - 90-93%, condensing - up to 110%, the difference is purely arithmetic no more than 20%. Comparison of figures is not in favor of the latter, since their cost is several times higher. A more detailed analysis should be carried out taking into account site-specific factors and calculation methods.
European data indicate a payback for condensing models within five years; for domestic consumers the time frame is different due to the low cost of fuel, the weak distribution of low-temperature types of heating with heated floors and multi-section radiators of increased area.
Therefore, potential savings should be calculated in advance. A house insulated according to building codes loses 1 kW hour per 10 square meters. meters. For a house of 100 sq. m. in central Russia, 240 kW will be required to replenish daily heat losses. For the convenience of calculations, the accepted fuel is natural gas, the specific heat of combustion of which is 10 kW per cubic meter, and 1 kW of the boiler will require 0.1 cubic meter. m. of its combustion in the furnace.
A convection boiler (efficiency - 90%) will require 240 kW * 0.1 cubic meters. m.*1.07(90%) = 26 cubic meters. m per day.
At a price of 5 rubles/m³, daily expenses will be 128 rubles.
For condensing, the calculations will be as follows: 240 kW * 0.1 cubic meters. m.*0.91(110%) = 22 cubic meters. m per day.
The cost of gas is 109 rubles per day. Daily estimated savings – 20 rubles per day.
But do not forget that there are also regions with much more expensive gas and there are houses with a much larger area.
Efficiency used in calculations differ from the passport ones prescribed by the manufacturers. This is explained by the specifics of calculating the calorie content of fossil fuels. There are two terms: “higher” and “lower” fuel combustion heat. Initially, it was believed that the energy consumption for moisture evaporation and condensation formation is insignificant, and they can be neglected in calculations. Therefore, the characteristics of thermal systems were calculated based on “lower” indicators. As the value of this share of costs became more precise, figures for the “higher” fuel heat of combustion began to be used, which led to values exceeding one hundred percent. From a physical point of view, this is impossible, because the amount of energy obtained during combustion cannot be greater than that stored in the composition of chemical bonds, but traditionally established methods have not been changed, which has led to an efficiency indicator of 110 percent.
Advantages
Convection boilers are less efficient than condensing models. Such units heat the coolant only due to the heat obtained from gas combustion. At the same time, approximately 20 percent of the energy is lost along with combustion products into the atmosphere.
But despite this, such boilers have a number of the following important advantages, which determine their popularity among consumers:
Is it advisable to use a condensing boiler in a radiator heating system?
Condensing boilers are usually accused of not being suitable for high temperature radiator heating systems. But is it? After all, when heating a house with radiators, even in our winter conditions, there is simply no need to make them hotter than 55°C for most of the heating period. With the exception of a maximum of two or three frosty weeks, the average daily temperature outside the window is about 0°C, and there is absolutely no point in “heating up” the batteries at this time, consuming extra fuel. Thus, when the heating needs of the house can be fully satisfied at a lower coolant temperature, the condensing boiler will also perfectly serve radiator heating systems. Well, if a real frost hits (-25...30°C) and the boiler room switches to an increased operating mode (for example, 90°C), then the condensation process will stop and the efficiency of the boiler will decrease, but still, albeit slightly, it will be higher than convection devices.
Design Features
Structurally, condensing boilers are not too different from traditional gas-fuel units, but the declared high efficiency, efficiency and reliability of this equipment directly depend on what type of device they use as the most important components.
Heat exchanger,
serving to cool exhaust gases, constantly experiences the aggressive effects of condensate, which is a caustic acid-containing liquid, therefore the main requirement for this structural element is high chemical resistance. Heat exchangers are made of stainless steel or silumin (aluminum-silicon alloy), and the best option would be cast products, since a seam with the slightest flaw is a potential source of corrosion.
‘ >
Sectional view of the boiler
Condensing heat generators have a closed combustion chamber
and, as a rule, are equipped with high-performance
fan (blown) burners,
adjustable over a wide power range, which makes it possible to control the temperature of the exhaust gases as accurately as possible (not higher than 57 ° C). Automation is responsible for the operation of the burner, which monitors all settings and safety parameters of the equipment.
Some boiler models are equipped with modulating circulation pumps
with smooth adjustment of engine power and coolant pressure height. This allows them to flexibly adjust to the specified hydraulic and temperature parameters, even when the heating system is operating at partial load. Conventional pumps provide a constant flow of coolant, which means that its temperature in the return line can exceed the values necessary for condensation of water vapor from the exhaust gases. Thus, the condensing boiler, in fact, begins to function as a simple convection boiler, that is, the efficiency of the equipment decreases.
To organize a hot water system based on a condensing boiler, many manufacturers produce units with a built-in secondary heat exchanger and an expansion tank. Compact wall-mounted units are equipped with tanks of only 30–40 liters, while floor-standing models can hold 150–200 liters of water or more
Automatic control
Automatic control, especially remote control, significantly increases the level of comfort when operating boiler equipment, and also provides the ability to connect the boiler to an integrated heating and hot water system, organized on the basis of several heat sources. Thus, the Logamatic EMS plus RC300 automation, which is equipped with Buderus brand units, can control a system consisting of four heating circuits, two DHW circuits and a solar installation. Buderus implements the principle of remote control using the Logamatic TC100 electronic thermostat, and, for example, De Dietrich uses the Diematic VM ISystem wall panel for this.
The control module is connected to the boiler via a low-voltage wire connection. And user interaction with any elements of the system (adjusting parameters and operating modes, short-term or long-term programming, etc.) is carried out via Wi-Fi or through a special application on a computer or smartphone.
Condensing boilers of most brands can be combined into cascades - groups of several (usually up to four in everyday life) devices. This cascade allows you to very accurately regulate the power of devices
An example of a gas boiler condensate neutralizer filled with granules
Let's take a closer look at those points that may make you doubt certain advantages and disadvantages of air-conditioned boilers.
The first thing that needs to be said concerns the maximum efficiency of such a boiler, which is achieved during operation at low temperatures.
The second concerns a condensing boiler together with a special condensate neutralizer that forms in the heating chimney. Remember that installing a condensing boiler may not always lead to cost savings.
Third is the financial aspect. A condensing boiler is an expensive thing that requires very careful and careful operation. If you are sure that you will not be able to service it on time, then you should not choose such a heating system.
Functionality
Modern heating units have a wide range of functionality that must be taken into account when choosing a gas heating boiler.
One of the key functions is to regulate the power of the equipment. It can be of the following types:
- single-stage - only the ability to turn on and off is provided;
- two-stage - there are two operating modes with different heating power;
- smooth adjustment with flame modulation - depending on the set temperatures and coolant pressure, the system automatically adjusts the number of burner nozzles used and the flame height.
The most efficient and easy-to-use boiler option is with smooth flame modulation.
It is important to choose boilers from trusted manufacturers who equip them with a whole range of devices and systems to maintain safe operation. Such protections include:
- gas and water pressure control sensors;
- sensors that control the combustion mode;
- systems for blocking equipment operation in emergency modes;
- water purification filters;
- thermostats that prevent overheating of the coolant;
- valves for releasing excess pressure, etc.
In addition, leading manufacturers equip gas boilers with advanced automation, which makes the use of the equipment as efficient and user-friendly as possible.
Equipment selection
The boiler power is determined at the rate of 100 W per 1 m2 of room. The indicator can increase to 150 W depending on the heating of neighboring rooms, ceiling height and window opening area. The figure is multiplied by the area of the room and the calculated power is obtained.
The type of ignition of the unit matters. Piezo ignition works by pressing a key and does not depend on electricity. The disadvantage is the additional fuel consumption for the burning igniter and the dependence on the supply of gas from the main line. An electric igniter is more economical; there are models that turn on automatically after a power outage.
Boilers from Korean manufacturers combine quality, reliability, low cost and adapt to surges in gas pressure. The downside is the problems with finding spare parts during repairs, as well as the lack of service workshops.
What is a convection boiler?
This type of device is often used for a private home with an area of more than 300 m². The principle of operation of the device is simple: gas enters the burner, the flame lights up, and it heats the heat exchanger with water. Combustion products are discharged through the connected chimney. The efficiency of the device is over 90%.
A convection gas boiler can be:
- single-circuit - designed only for heating the coolant for heating the house;
- double-circuit - provides the home with heating and hot water supply (DHW).
Installation is performed in two ways:
- Floor-standing - such units require a separate room or a large area; A solid foundation is provided for their installation.
- Wall-mounted - such models are compact and can be placed in any non-residential area of the apartment.
Operating principle and device
Heating devices come with open and closed combustion chambers. An open chamber boiler takes combustion air from the room and exhausts exhaust gas through the chimney. A device with a closed chamber provides for a coaxial chimney. This is a “pipe-in-pipe” design: air enters through one to maintain the flame, and combustion products are discharged through the other.
How does convective heating work? Inside the device there is a heat exchanger and a burner with flame modulation. With automatic or piezo ignition, gas enters the system, a spark is created and the burner ignites. The flame heats the heat exchanger through which the coolant moves. As soon as the liquid reaches the set temperature, the automation is activated and heating stops. When the coolant cools, the thermocouple turns on, the fuel valve opens and heating occurs again.
The circulation pump forcibly moves the coolant in the system, which avoids freezing when the temperature drops. The pump speed can be adjusted.
Installation methods
Floor-standing boiler
The floor-mounted or wall-mounted option is selected depending on the power and heated area. Wall-mounted units provide heating for a room of no more than 200 m2 and have a capacity of no more than 14 l/min. If the needs of the building are higher, a floor-mounted unit is installed.
Floor
The equipment is mounted on the floor or a special foundation, and the piping elements are purchased separately from the boiler.
Types of units available:
- fire tube steel boilers;
- gas cast iron equipment.
The first type has increased power and high efficiency. The heat exchanger is made in the form of a cylinder with a welded joint and contains steel collectors for moving water. The gas combustion chamber receives the prepared gas-air composition from the blow burner.
Cast iron equipment is often produced with sectional heat exchangers and has blown or tubular burners. The power of the boilers is average, the weight is much lower than fire tube boilers. A cast iron heat exchanger serves for a long time if a certain temperature regime is observed. For installation, the first and second types of boilers are supplied disassembled due to their significant weight.
Floor-standing units are chosen if it is necessary to heat several separate buildings or a large room, even if the total heating area does not exceed 200 m2.
Wall
Wall-mounted model
A suspended gas convection boiler is mounted on a vertical fence or a metal frame is welded for it. The heat exchanger is made of steel or copper, the burners are often of the tubular type. Wall-mounted equipment is compactly placed in the room; boilers go on sale with all the necessary elements and fittings. The sales kit is a kind of boiler unit controlled by a remote control.
The wall-mounted version with an open chamber is not often purchased, although it is cheaper and does not depend on electricity supplies. Closed wall-mounted boilers are purchased more often; popular models are compact and have an attractive appearance. Manufacturers use advanced technologies, the equipment is equipped with modern electronic components. This can be a disadvantage because the electronics cannot withstand voltage fluctuations and are dependent on the electrical network.
Wall-mounted boilers are sensitive to the quality of the energy carrier. The liquid is heated in a small-sized housing with thin-walled internal elements. Poor quality water in the system leads to sedimentation. Antifreeze is also not applied to all wall-mounted units, as there are instructions in the technical data sheet.
Principle of operation
Convection boilers
Increasing the temperature of the coolant for the heating system and maintaining it at the required level, preparing hot water for own needs (DHW) is provided by the burner flame. A significant drawback of this (convective) method is that part of the thermal energy is wasted irrationally - it goes into the atmosphere through the chimney. Its coaxial version mitigates the problem somewhat, but not enough to talk about significant savings.
All convection boilers have one more drawback, which the average user may not be aware of. Operating the unit at a reduced mode leads to “cooling” of the combustion products. And if their temperature drops below 55±50C (depending on the modification), then the gases begin to condense on the walls of the chimney or chamber. Aggressive chemical compounds contained in liquid droplets do not have the best effect on metals. The result is a reduction in boiler life and unscheduled repairs.
Condensing boilers
In such installations, thermal energy for heating water is used to the maximum. It is released not only as a result of fuel combustion; is also contained in steam (it has a high temperature), which escapes along with the gases through the pipe to the outside. Everything is implemented in a simple and original way: condensing boilers are equipped with water economizers. Essentially, another heat exchanger.
Its purpose is described briefly: to ensure condensation of vapors on its walls and redirect the resulting energy to specific purposes. In total terms, when burning the same “dose” of fuel, it turns out significantly more. This increases the efficiency of boiler equipment for systems (heated hot water or domestic hot water), depending on the mode.
Practice confirms theoretical calculations: gas savings on heating a building can reach 35%. Consequently, costs for heating (DHW) are reduced.
What is the difference in practical terms? For the normal functioning of a heating system with a convection boiler included in the circuit, it is necessary to ensure a minimum temperature difference at its outlet and inlet (in the return line). Failure to comply with this condition is fraught with temperature imbalance in the heat exchanger. There is no need to explain what the flow of cold coolant into the hot metal body of the device leads to. This is one of the reasons for the rapid failure of equipment, especially when independently designing the system and installing it.
With a condensing boiler everything is different. The cooled water returning through the return to the economizer is heated by thermal energy released during condensation of vapors. In the main heat exchanger, its temperature only needs to be raised to the required value. The benefits are easy to understand: a traditional (convection) gas boiler is characterized by an efficiency of about 90%. That is, 10 literally “flies away” through the chimney. In a condensing unit, these percentages are also used to heat water (OB or DHW) in the heat exchanger. Therefore, their efficiency reaches 98%.
Gas convector – DIY installation
Only specially trained people can install a gas heating convector, observing regulatory requirements and safety measures.
The basic requirements for a safe installation are clear from the diagram
Installation of gas outlet pipe
Only professionals can install a gas convector heater correctly.
You can watch video instructions on how to install a gas convector here:
73831.7586f9b8c15cfca120f27d392028
In general, gas heating convectors are an excellent alternative to both a central water heating system and an electric one.
Cost-effectiveness of a heating gas convector
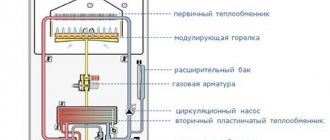
Construction of the main components of a condensing boiler
From a structural point of view, a condensing boiler is not very different, but still differs from a conventional gas boiler.
Its main elements are:
• combustion chamber equipped with a burner, fuel supply system and fan for air injection;
• chamber for additional cooling of the vapor-gas mixture to a temperature as close as possible to 56-57°C;
• heat exchanger No. 2 (condensation heat exchanger);
• tank for collecting condensate;
• chimney for removing cold flue gases;
• a pump that circulates water in the system.
In the primary heat exchanger connected to the combustion chamber, the released gases are cooled to a temperature significantly above the dew point (in fact, this is what ordinary convection gas boilers look like). Then the smoke mixture is forced to the condensation heat exchanger, where it is further cooled to a temperature below the dew point, that is, 56°C. In this case, water vapor condenses on the walls of the heat exchanger, giving up the last of its energy. The condensate is collected in a special tank, from where it flows down the drain pipe into the sewer.
Water, which acts as a coolant, moves in the direction opposite to the movement of the vapor-gas mixture. Cold water (heating system return fluid) is preheated in the condensing heat exchanger. It then enters the primary heat exchanger where it is heated to a higher temperature set by the user.
Condensate is not pure water, but a mixture of dilute inorganic acids. Their concentration is small, but taking into account the fact that the temperature in the system is always elevated, condensate can be considered an aggressive liquid. That is why in the production of such boilers (and, first of all, the corresponding heat exchangers), acid-resistant materials are used - stainless steel or silumin (aluminum-silicon alloy). The heat exchanger, as a rule, is made cast, since the welds are a vulnerable point - this is where the process of corrosive destruction of the material first begins.
The steam must condense on the condensation heat exchanger. Everything that passes further into the chimney, on the one hand, is lost for heating, and on the other, has a destructive effect on the chimney material. It is for this last reason that the chimney is made of acid-resistant stainless steel or plastic, and its horizontal sections are given a slight slope so that the water formed by the condensation of small amounts of steam that still enter the chimney is drained back into the boiler. The flue gases leaving the condenser are very cooled, and everything that did not condense in the boiler will certainly do so in the chimney.
At different times of the day, different amounts of heat are required from the heating boiler, which can be adjusted using a burner. For a condensing boiler, it can be either modulated - with the ability to smoothly change the power during operation, or unmodeled - with a fixed power. In the latter case, the boiler adapts to the requirements of its owner, who can turn on the burner at different frequencies. Most modern boilers intended for heating private homes are equipped with simulated burners.