Rising energy prices make us think about the possibility of providing ourselves with them ourselves. One option is a biogas plant. With its help, biogas is obtained from manure, droppings and plant residues, which, after purification, can be used for gas appliances (stoves, boilers), pumped into cylinders and used as fuel for cars or electric generators. In general, processing manure into biogas can meet all the energy needs of a home or farm.
Construction of a biogas plant is a way to independently provide energy resources
General principles
Biogas is a product that is obtained from the decomposition of organic substances. During the process of rotting/fermentation, gases are released, collecting which you can meet the needs of your own household. The equipment in which this process occurs is called a “biogas plant.”
In some cases, the gas output is excessive, then it is stored in gas tanks for use during periods of insufficient quantity. If the process is properly organized, there may be too much gas, then the excess can be sold. Fermented leftovers are another source of income. This is a highly effective and safe fertilizer - during the fermentation process, most microorganisms die, plant seeds lose their viability, and parasite eggs become unviable. Exporting such fertilizers to the fields has a positive effect on crop yields.
Conditions for gas production
The process of biogas formation occurs due to the vital activity of various kinds of bacteria that are contained in the waste itself. But in order for them to actively “work”, they need to create certain conditions: humidity and temperature. To create them, a biogas plant is being built. This is a complex of devices, the basis of which is a bioreactor, in which waste decomposition occurs, which is accompanied by gas formation.
Organization of a cycle for processing manure and plant waste into biogas
There are three modes for processing manure into biogas:
- Psychophilic mode. The temperature in the biogas plant is from +5°C to +20°C. Under such conditions, the decomposition process is slow, much gas is formed, and its quality is low.
- Mesophilic. The unit enters this mode at temperatures from +30°C to +40°C. In this case, mesophilic bacteria actively reproduce. In this case, more gas is formed, the processing process takes less time - from 10 to 20 days.
- Thermophilic. These bacteria multiply at temperatures from +50°C. The process goes the fastest (3-5 days), the gas output is the largest (under ideal conditions, with 1 kg of delivery you can get up to 4.5 liters of gas). Most reference tables for gas yield from processing are given specifically for this mode, so when using other modes it is worth making a smaller adjustment.
The most difficult thing to implement in biogas plants is the thermophilic mode. This requires high-quality thermal insulation of the biogas plant, heating and a temperature control system. But at the output we get the maximum amount of biogas. Another feature of thermophilic processing is the impossibility of additional loading. The remaining two modes - psychophilic and mesophilic - allow you to add a fresh portion of prepared raw materials daily. But, in the thermophilic mode, the short processing time makes it possible to divide the bioreactor into zones in which their share of raw materials will be processed with different loading times.
Mechanism of gas formation from organic raw materials
Biogas is a volatile substance without color or any odor, which contains up to 70% methane.
In terms of its quality indicators, it approaches the traditional type of fuel - natural gas. It has a good calorific value; 1 m3 of biogas emits as much heat as is obtained from the combustion of one and a half kilograms of coal. We owe the formation of biogas to anaerobic bacteria, which actively work to decompose organic raw materials, which include farm animal manure, bird droppings, and any plant waste.
In self-production of biogas, bird droppings and waste products of small and large livestock can be used. Raw materials can be used in pure form or in the form of a mixture including grass, foliage, old paper
To activate the process, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the life of bacteria. They should be similar to those in which microorganisms develop in a natural reservoir - in the stomach of animals, where it is warm and there is no oxygen.
Actually, these are the two main conditions that contribute to the miraculous transformation of rotting manure into environmentally friendly fuel and valuable fertilizers.
To produce biogas, you need a sealed reactor without access to air, where the process of fermentation of manure and its decomposition into components will take place:
- methane (up to 70%);
- carbon dioxide (approximately 30%);
- other gaseous substances (1-2%).
The resulting gases rise to the top of the container, from where they are then pumped out, and the residual product settles down - high-quality organic fertilizer, which, as a result of processing, has retained all the valuable substances present in the manure - nitrogen and phosphorus, and has lost a significant part of pathogenic microorganisms.
The reactor for producing biogas must have a completely sealed design in which there is no oxygen, otherwise the process of decomposition of manure will be extremely slow
The second important condition for the effective decomposition of manure and the formation of biogas is compliance with the temperature regime. Bacteria taking part in the process are activated at temperatures from +30 degrees
Moreover, manure contains two types of bacteria:
- mesophilic. Their life activity occurs at a temperature of +30 – +40 degrees;
- thermophilic. To reproduce them, it is necessary to maintain a temperature regime of +50 (+60) degrees.
The processing time of raw materials in installations of the first type depends on the composition of the mixture and ranges from 12 to 30 days. At the same time, 1 liter of useful reactor area produces 2 liters of biofuel. When using installations of the second type, the production time of the final product is reduced to three days, and the amount of biogas increases to 4.5 liters.
The efficiency of thermophilic plants is visible to the naked eye, however, the cost of their maintenance is very high, so before choosing one or another method of producing biogas, you need to calculate everything very carefully
Despite the fact that the efficiency of thermophilic plants is tens of times higher, they are used much less frequently, since maintaining high temperatures in the reactor is associated with high costs.
Maintenance and maintenance of mesophilic type plants is cheaper, so most farms use them to produce biogas.
In terms of energy potential, biogas is slightly inferior to conventional gas fuel. However, it contains sulfuric acid fumes, the presence of which should be taken into account when choosing materials for the construction of the installation
Biogas plant diagram
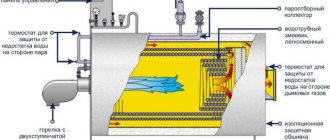
The basis of a biogas plant is a bioreactor or bunker. The fermentation process occurs in it, and the resulting gas accumulates in it. There is also a loading and unloading hopper; the generated gas is discharged through a pipe inserted into the upper part. Next comes the gas treatment system - cleaning it and increasing the pressure in the gas pipeline to working pressure.
Installation diagram for processing manure into biogas
For mesophilic and thermophilic modes, a bioreactor heating system is also required to reach the required modes. For this purpose, gas boilers running on produced fuel are usually used. From it, a pipeline system goes to the bioreactor. Usually these are polymer pipes, since they best withstand being in an aggressive environment.
A biogas plant also needs a system for mixing the substance. During fermentation, a hard crust forms at the top, and heavy particles settle down. All this together worsens the process of gas formation. Mixers are needed to maintain a homogeneous state of the processed mass. They can be mechanical or even manual. They can be started by timer or manually. It all depends on how the biogas plant is made. An automated system is more expensive to install, but requires a minimum of attention during operation.
The simplest biogas plant from a plastic barrel
According to the type of location, a biogas plant can be:
- Overground.
- Semi-recessed.
- Recessed.
Recessed ones are more expensive to install - a large amount of excavation work is required. But when used in our conditions, they are better - it is easier to organize insulation, and the heating costs are lower.
Biomass waste after gas production
After processing manure in a reactor, the by-product is biosludge. During anaerobic processing of waste, bacteria dissolve about 30% of organic matter. The rest is released unchanged.
The liquid substance is also a by-product of methane fermentation and is also used in agriculture for root feeding.
Carbon dioxide is a waste fraction that biogas producers strive to remove. But if you dissolve it in water, then this liquid can also be beneficial.
Full utilization of biogas plant products
In order to completely utilize the products obtained after processing manure, it is necessary to maintain a greenhouse. Firstly, organic fertilizer can be used for year-round cultivation of vegetables, the yield of which will be stable.
Secondly, carbon dioxide is used as fertilizing - root or foliar, and its output is about 30%. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and at the same time grow better and gain green mass. If you consult with specialists in this field, they will help you install equipment that converts carbon dioxide from liquid form into a volatile substance.
Video: Biogas in 2 days
The fact is that to maintain a livestock farm, the energy resources obtained can be a lot, especially in the summer, when heating the barn or pigsty is not needed.
Therefore, it is recommended to engage in another profitable activity - an environmentally friendly greenhouse. Remaining products can be stored in refrigerated rooms - using the same energy. Refrigeration or any other equipment can run on electricity generated by a gas battery.
What can be recycled
A biogas plant is essentially omnivorous - any organic matter can be processed. Any manure and urine, plant residues are suitable. Detergents, antibiotics, and chemicals negatively affect the process. It is advisable to minimize their intake, as they kill the flora that processes them.
How much biogas can be obtained from various wastes?
Cattle manure is considered ideal, since it contains large quantities of microorganisms. If there are no cows on the farm, when loading the bioreactor, it is advisable to add some of the manure to populate the substrate with the required microflora. Plant residues are pre-crushed and diluted with water. Plant materials and excrement are mixed in a bioreactor. This “filling” takes longer to process, but at the end, under the correct mode, we have the highest product yield.
Reactor for a large farm
A simple bioreactor design is suitable for small farms with 1-2 animals. If you own a farm, it is best to install an industrial reactor that can handle large volumes of fuel. It is best to involve special companies involved in developing the project and installing the system.
Membrane bioreactor
Industrial complexes consist of:
- Interim storage tanks;
- Mixing installations;
- Bioreactor;
- A small thermal power plant that provides energy for heating buildings and greenhouses, as well as electricity;
- Containers for fermented manure used as fertilizer.
The most effective option is to build one complex for several neighboring farms. The more biomaterial is processed, the more energy is produced as a result.
Before receiving biogas, industrial installations must be approved by the sanitary and epidemiological station, fire and gas inspection. They are documented; there are special standards for the location of all elements.
Location determination
To minimize the costs of organizing the process, it makes sense to locate the biogas plant close to the source of waste - near buildings where poultry or animals are kept. It is advisable to develop the design so that loading occurs by gravity. From a barn or pigsty, you can lay a pipeline at a slope through which manure will flow by gravity into the bunker. This greatly simplifies the task of maintaining the reactor, and also removing manure.
It is most advisable to locate the biogas plant so that waste from the farm can flow by gravity
Typically, buildings with animals are located at some distance from a residential building. Therefore, the generated gas will need to be transferred to consumers. But laying one gas pipe is cheaper and easier than organizing a line for transporting and loading manure.
Forums
We have prepared a list of online forums where users discuss various issues related to the production of biogas from manure and the equipment necessary for this:
- Farmer RU;
- Farmer BY;
- Abok;
- IMHO House;
- Technical forum on ;
- Agroforum;
- Merry courtyard;
- Business forum Profitable Business;
- RMNT.
Bioreactor
There are quite strict requirements for manure processing tanks:
- It must be impermeable to water and gases. Water resistance should work in both directions: the liquid from the bioreactor should not pollute the soil, and groundwater should not change the state of the fermented mass.
- The bioreactor must have high strength. It must withstand the mass of the semi-liquid substrate, the gas pressure inside the container, and the soil pressure acting outside. In general, when constructing a bioreactor, special attention must be paid to its strength.
For home use and seasonal production of biofuel (during the warm season) in small volumes, a plastic tank with a lid is suitable - Ease of maintenance. Cylindrical containers are more convenient to use - horizontal or vertical. In them, mixing can be organized throughout the entire volume; stagnant zones do not form in them. Rectangular containers are easier to implement when building with your own hands, but cracks often form in their corners, and the substrate stagnates there. Stirring it in the corners is very problematic.
All these requirements for the construction of a biogas plant must be met, as they ensure safety and create normal conditions for processing manure into biogas.
What materials can it be made from?
Resistance to aggressive environments is the main requirement for materials from which containers can be made. The substrate in the bioreactor can be acidic or alkaline. Accordingly, the material from which the container is made must tolerate various environments well.
Not many materials meet these requests. The first thing that comes to mind is metal. It is durable and can be used to make containers of any shape. The good thing is that you can use a ready-made container - some old tank. In this case, the construction of a biogas plant will take very little time. The disadvantage of metal is that it reacts with chemically active substances and begins to collapse. To neutralize this disadvantage, the metal is coated with a protective coating.
An excellent option is a bioreactor container made of polymer. Plastic is chemically neutral, does not rot, does not rust. You just need to choose from materials that can withstand freezing and heating to fairly high temperatures. The reactor walls should be thick, preferably glass fiber reinforced. Such containers are not cheap, but they last a long time.
It is possible to build a bioreactor for the production of biogas from brick, but it must be well plastered using additives that ensure water and gas impermeability
A cheaper option is a biogas plant with a container made of bricks, concrete blocks, or stone. In order for the masonry to withstand high loads, it is necessary to reinforce the masonry (in every 3-5 rows, depending on the thickness of the wall and the material). After completing the wall construction process, to ensure water and gas impermeability, subsequent multi-layer treatment of the walls is necessary both inside and outside. The walls are plastered with a cement-sand composition with additives (additives) that provide the required properties.
Reactor sizing
The reactor volume depends on the selected temperature for processing manure into biogas. Most often, mesophilic is chosen - it is easier to maintain and it allows for the possibility of daily reloading of the reactor. Biogas production after reaching normal mode (about 2 days) is stable, without surges or dips (when normal conditions are created). In this case, it makes sense to calculate the volume of the biogas plant depending on the amount of manure generated on the farm per day. Everything is easily calculated based on average statistical data.
| Animal breed | Volume of excrement per day | Initial humidity |
| Cattle | 55 kg | 86% |
| Pig | 4.5 kg | 86% |
| Chickens | 0.17 kg | 75% |
The decomposition of manure at mesophilic temperatures takes from 10 to 20 days. Accordingly, the volume is calculated by multiplying by 10 or 20. When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the amount of water that is necessary to bring the substrate to an ideal state - its humidity should be 85-90%. The found volume is increased by 50%, since the maximum load should not exceed 2/3 of the tank volume - gas should accumulate under the ceiling.
For example, there are 5 cows, 10 pigs and 40 chickens on a farm. The result is 5 * 55 kg + 10 * 4.5 kg + 40 * 0.17 kg = 275 kg + 45 kg + 6.8 kg = 326.8 kg. To bring chicken manure to 85% humidity, you need to add a little more than 5 liters of water (that’s another 5 kg). The total weight is 331.8 kg. For processing in 20 days you need: 331.8 kg * 20 = 6636 kg - about 7 cubic meters only for the substrate. We multiply the found figure by 1.5 (increase by 50%), we get 10.5 cubic meters. This will be the calculated value of the reactor volume of the biogas plant.
Advantages of using biotechnology
The technology for producing biofuel from various natural sources is not new. Research in this area began at the end of the 18th century and developed successfully in the 19th century. In the Soviet Union, the first bioenergy plant was created in the forties of the last century.
Biotechnologies have long been used in many countries, but today they are gaining particular importance. Due to the deteriorating environmental situation on the planet and the high cost of energy, many are turning their attention to alternative sources of energy and heat.
Of course, manure is a very valuable fertilizer, and if there are two cows on the farm, then there are no problems with its use. It’s a different matter when it comes to farms with large and medium-sized livestock, where tons of foul-smelling and rotting biological material are generated per year.
In order for manure to turn into high-quality fertilizer, areas with a certain temperature regime are needed, and this is an extra expense. Therefore, many farmers store it wherever they can and then take it to the fields.
If storage conditions are not met, up to 40% of nitrogen and the bulk of phosphorus evaporate from manure, which significantly worsens its quality indicators. In addition, methane gas is released into the atmosphere, which has a negative impact on the environmental situation of the planet.
Modern biotechnologies make it possible not only to neutralize the harmful effects of methane on the environment, but also to make it serve for the benefit of people, while reaping considerable economic benefits. As a result of manure processing, biogas is formed, from which thousands of kW of energy can then be obtained, and production waste represents a very valuable anaerobic fertilizer.
Image galleryPhoto from Organizing a system for producing biogas is economically feasible for farms. If only two cows provide raw materials, it is better to use it as fertilizer. The gas obtained by processing manure will provide heat and energy. After cleaning, it can be supplied to a stove and boiler, pumped into a cylinder and used by an electric generator. Structurally, the simplest processing plant is not difficult to build with your own hands. Its main organ is a bioreactor, which needs to be well hydro- and thermally insulated. For those who want to reduce the construction time of the system, a factory-made plastic container is suitable. When using it, similar principles of construction and insulation apply. Farms are the main suppliers of raw materials for the production of biogas. Production and use of gaseous biofuels. Construction of a processing plant with one’s own hands. Ready-made plastic container in a bioreactor device.
Loading and Unloading
Loading and unloading hatches lead directly into the bioreactor tank. In order for the substrate to be evenly distributed over the entire area, they are made at opposite ends of the container.
Diagram of a biogas reactor without half-heating
When installing a biogas plant in-depth, the loading and unloading pipes approach the body at an acute angle. Moreover, the lower end of the pipe should be below the liquid level in the reactor. This prevents air from entering the container. Also, rotary or shut-off valves are installed on the pipes, which are closed in the normal position. They open only during loading or unloading.
Since manure may contain large fragments (litter elements, grass stems, etc.), small diameter pipes will often become clogged. Therefore, for loading and unloading, they must have a diameter of 20-30 cm. They must be installed before the start of work on insulating the biogas plant, but after the container is installed in place.
Bioreactor shapes and options for loading and unloading hatches
The most convenient mode of operation of a biogas plant is with regular loading and unloading of the substrate. This operation can be performed once a day or once every two days. Manure and other components are preliminarily collected in a storage tank, where they are brought to the required state - crushed, if necessary, moistened and mixed. For convenience, this container may have a mechanical stirrer. The prepared substrate is poured into the receiving hatch. If you place the receiving container in the sun, the substrate will be preheated, which will reduce the cost of maintaining the required temperature.
It is advisable to calculate the installation depth of the receiving hopper so that waste flows into it by gravity. The same applies to unloading into the bioreactor. The best case is if the prepared substrate moves by gravity. And a shutter will fence it off during preparation.
Biogas plant with stirrer and heating
To ensure the tightness of the biogas plant, the hatches on the receiving hopper and in the unloading area must have a sealing rubber seal. The less air there is in the container, the cleaner the gas will be at the outlet.
Getting permission
Despite the fact that manure belongs to the third hazard class, that is, moderately hazardous waste, for disposal it is necessary to obtain a license .
But this applies only to those cases when biogas or the electricity obtained from it is going to be sold.
In addition, licensing is necessary if the digester will operate on purchased raw materials. If the resulting biogas will be used only for the needs of the person who produces it, then there is no need to obtain a license.
In addition, it is necessary to obtain a construction permit, and also coordinate the project with the following departments:
- Rostechnadzor;
- Fire Inspectorate;
- SES;
- Gas service.
Sometimes owners of small and not very small farms neglect approvals and permits, because they build everything on their own land and do not sell processed products to anyone.
This position is fraught with a serious fine, because biogas plants are classified as hazardous industries, so they must be included in the state register of hazardous production facilities of Rostechnadzor.
In addition, such objects must be insured in case of an accident , and before launch they must be inspected by specialists from the relevant departments.
However, owners of small home installations neglect registration because the cost of permits negates the benefits of this method of manure disposal.
However, they do this at their own peril and risk, because in the event of any emergency, they will not only have to pay fines for the lack of information in the register, but also be responsible for all the consequences.
Collection and removal of biogas
Biogas is removed from the reactor through a pipe, one end of which is under the roof, the other is usually lowered into a water seal. This is a container with water into which the resulting biogas is discharged. There is a second pipe in the water seal - it is located above the liquid level. Cleaner biogas comes out into it. A gas shut-off valve is installed at the outlet of their bioreactor. The best option is a ball one.
What materials can be used for the gas transmission system? Galvanized metal pipes and gas pipes made of HDPE or PPR. They must ensure tightness; seams and joints are checked using soap foam. The entire pipeline is assembled from pipes and fittings of the same diameter. No contractions or expansions.
Cleansing from impurities
The approximate composition of the resulting biogas is:
Approximate composition of biogas
- methane - up to 60%;
- carbon dioxide - 35%;
- other gaseous substances (including hydrogen sulfide, which gives the gas an unpleasant odor) - 5%.
In order for biogas to be odorless and burn well, it is necessary to remove carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and water vapor from it. Carbon dioxide is removed in a water seal if slaked lime is added to the bottom of the installation. Such a bookmark will have to be changed periodically (as soon as the gas starts to burn worse, it’s time to change it).
Gas drying can be done in two ways - by making water seals in the gas pipeline - by inserting curved sections into the pipe under the water seals, in which condensate will accumulate. The disadvantage of this method is the need to regularly empty the water seal - if there is a large amount of collected water, it can block the passage of gas.
The second way is to install a filter with silica gel. The principle is the same as in a water seal - the gas is supplied to the silica gel, and dried out from under the lid. With this method of drying biogas, the silica gel must be dried periodically. To do this, you need to warm it up in the microwave for some time. It heats up and the moisture evaporates. You can fill it up and use it again.
Filter for cleaning biogas from hydrogen sulfide
To remove hydrogen sulfide, a filter loaded with metal shavings is used. You can load old metal scourers into the container. Purification occurs in exactly the same way: gas is supplied to the lower part of the container filled with metal. As it passes, it is cleared of hydrogen sulfide, collected in the upper free part of the filter, from where it is discharged through another pipe/hose.
Gas tank and compressor
The purified biogas enters a storage tank - a gas holder. This can be a sealed plastic bag or plastic container. The main condition is gas tightness; shape and material do not matter. The gas holder stores a supply of biogas. From it, with the help of a compressor, gas under a certain pressure (set by the compressor) is supplied to the consumer - to the gas stove or boiler. This gas can also be used to generate electricity using a generator.
One of the gas tank options
To create stable pressure in the system after the compressor, it is advisable to install a receiver - a small device for leveling pressure surges.
Creating a biogas plant from manure at home
To design a plant for processing manure into biogas you will need:
- a hermetically sealed container (made of metal, concrete, plastic) with a volume of at least one cubic meter;
- cover for the reactor with a sealed passage for the stirrer handle;
- material for thermal insulation of the bottom (plays the role of a heating system);
- a hand mixer made from scrap materials (you can use a shovel or a screw auger);
- pipes for feeding/extracting substrate and for removing biogas.
During the construction process, you may need additional materials: pipes, filters, valves. All this can be found at a hardware store. The design is quite simple, and you can improve it as you build it.
DIY Tips
The most important rule is the absence of oxygen in the reactor. If present, an explosion may occur. To prevent the reactor lid from being blown off by high pressure, counterweights and protective gaskets between the tanks and lids are needed
To prevent the reactor lid from being blown off by high pressure, counterweights and protective gaskets between the tanks and lids are needed.
At the site before installation, the equipment must:
- choose the right location (preferably as far as possible from a residential building)
- calculate the daily volumes of manure produced
- select a location for pipes (shipping, loading, condensing)
- find a place for manure waste
- dig a pit
- purchase a container for the tank and secure it to the bottom of the pit
- seal all joints
- construct a hatch for inspecting the reactor (be sure to place a gasket between the hatch and the reactor)
If the installation takes place in a cold climate, then you should definitely consider ways to heat it.
The final stage of construction is checking the equipment for leaks.
We make an installation from a plastic barrel
As an experiment, you can try making an installation from an ordinary plastic barrel. They are available in volumes from 100 to 200 liters. The barrel will serve as a reactor. Make two holes in it for the inlet and outlet of the pipes. The inlet hole is made closer to the bottom, and the outlet hole is made from above. The diameter of the holes depends on the diameter of the pipes used. Plastic pipes can be purchased at a hardware store. We insert them into the holes and securely insulate them. A curved pipe (with a connector) is suitable for the inlet, and a short straight pipe for the outlet.
Don't forget about the thermal insulation of the barrel. It can be wrapped with mineral wool, polyethylene foam or any other material. It is best to place the barrel in the sun to increase the temperature inside the reactor. We pour raw materials inside in a ratio of 0.7 liters of water per 1 kg of manure. We put any suitable container for removing sludge, place a bucket on top and wait for fermentation. We are waiting about three weeks for the first batch of our home biogas. Remember that methane must be stripped of carbon dioxide before use. A special filter, which is sold in the store as a “filter for purifying compressed air, carbon dioxide and steam,” will cope with this task.
Do-it-yourself biogas from manure: building an underground installation
Another easy way to build your own manure-to-biogas plant is to build an underground system. First you need to dig a hole with a volume of at least one cubic meter. Its walls and bottom are filled with expanded clay concrete. From opposite walls there is one pipe for supplying biomass and removing sludge. The outlet pipe should be located closer to the bottom, and the input pipe should be 50 cm above the bottom. The end of the outlet pipe is connected to a waste container. The end of the inlet pipe should be located in such a way that it is convenient for you to pump new raw materials through it.
The upper part of this “bunker” is a dome- or cone-shaped gas holder. It is easiest to make from metal sheets or brickwork. A sealed hatch and a gas pipe with a water seal are mounted on the top of the gas holder.
Mixing of the substrate in such an installation occurs according to the bubbling principle. To do this, take several plastic pipes and make as many holes in them as possible. After this, secure the pipes inside the reactor in a vertical position. When the gas rises, it will emit bubbles, which will begin to bubble in the substrate, thereby mixing it.
Biomass waste after gas production
The sludge formed after heating manure is used throughout agriculture in the form of fertilizers.
The carbon dioxide produced is usually purified, but when it is dissolved in water, a useful liquid is obtained.
Mixing devices
In order for the biogas plant to operate normally, it is necessary to regularly mix the liquid in the bioreactor. This simple process solves many problems:
- mixes a fresh portion of the load with a colony of bacteria;
- promotes the release of produced gas;
- equalizes the temperature of the liquid, excluding warmer and colder areas;
- maintains the homogeneity of the substrate, preventing the settling or floating of some components.
Typically, a small homemade biogas plant has mechanical agitators that are driven by muscle power. In large-volume systems, the agitators can be driven by motors that are activated by a timer.
Types of stirrers for bioreactors
The second method is to stir the liquid by passing some of the generated gas through it. To do this, after exiting the metatank, a tee is installed and part of the gas flows into the lower part of the reactor, where it exits through a tube with holes. This part of the gas cannot be considered a consumption, since it still enters the system again and, as a result, ends up in the gas tank.
The third method of mixing is to use fecal pumps to pump the substrate from the lower part and pour it at the top. The disadvantage of this method is its dependence on the availability of electricity.
Completion of gasification (gas connection to the house) is also an important stage
At the final stage of gasification of the house, all that remains is to undergo training on the safe use of gas equipment, conduct a test run, and conclude an agreement for seasonal maintenance of the system. If a gas tank is installed, then it is necessary to conclude an agreement for systematic gas supplies.
The final “touch” is to give the design documentation (or an approved copy) for safekeeping in the archive, in case redevelopment is later required or any clarifications are required.
Heating system and thermal insulation
Without heating the processed liquid, psychophilic bacteria will multiply. The processing process in this case will take 30 days, and the gas output will be small. In the summer, if there is thermal insulation and preheating of the load, it is possible to reach temperatures of up to 40 degrees, when the development of mesophilic bacteria begins, but in winter such an installation is practically inoperative - the processes proceed very sluggishly. At temperatures below +5°C they practically freeze.
Dependence of the timing of processing manure into biogas on temperature
What to heat and where to place it
For best results, use heating. The most rational is water heating from a boiler. The boiler can run on electricity, solid or liquid fuel, and you can also run it on the produced biogas. The maximum temperature to which water needs to be heated is +60°C. Hotter pipes can cause particles to stick to the surface, reducing heating efficiency.
You can also use direct heating - insert heating elements, but firstly, it is difficult to organize mixing, secondly, the substrate will stick to the surface, reducing heat transfer, the heating elements will quickly burn out
A biogas plant can be heated using standard heating radiators, simply pipes twisted into a coil, or welded registers. It is better to use polymer pipes - metal-plastic or polypropylene. Corrugated stainless steel pipes are also suitable; they are easier to install, especially in cylindrical vertical bioreactors, but the corrugated surface provokes sediment sticking, which is not very good for heat transfer.
To reduce the possibility of particles settling on the heating elements, they are located in the stirrer area. Only in this case everything must be designed so that the mixer cannot touch the pipes. It often seems that it is better to place the heaters at the bottom, but practice has shown that due to sediment on the bottom, such heating is ineffective. So it is more rational to place heaters on the walls of the metatank of a biogas plant.
Water heating methods
Depending on the method of pipe arrangement, heating can be external or internal. When installed internally, heating is effective, but repair and maintenance of heaters is impossible without stopping and pumping out the system. Therefore, special attention is paid to the selection of materials and the quality of connections.
Heating increases the productivity of the biogas plant and reduces the processing time of raw materials
When the heaters are located externally, more heat is required (the cost of heating the contents of a biogas plant is much higher), since a lot of heat is spent heating the walls. But the system is always available for repair, and heating is more uniform, since the environment is heated from the walls. Another advantage of this solution is that stirrers cannot damage the heating system.
How to insulate
First, a leveling layer of sand is poured onto the bottom of the pit, then a heat-insulating layer. It can be clay mixed with straw and expanded clay, slag. All these components can be mixed and poured in separate layers. They are leveled to the horizon and the capacity of the biogas plant is installed.
The sides of the bioreactor can be insulated with modern materials or with classic old-fashioned methods. One of the old-fashioned methods is coating with clay and straw. Apply in several layers.
Modern materials are used to insulate bioreactors
Modern materials include high-density extruded polystyrene foam, low-density aerated concrete blocks, and expanded polyurethane foam. The most technologically advanced in this case is polyurethane foam (PPU), but the services for its application are not cheap. But the result is seamless thermal insulation, which minimizes heating costs. There is another heat-insulating material - foam glass. It is very expensive in slabs, but its chips or crumbs cost very little, and in terms of characteristics it is almost ideal: it does not absorb moisture, is not afraid of freezing, tolerates static loads well, and has low thermal conductivity.
Pros and cons compared to other fuels
In order to compare different types of fuel, and especially different types of energy, it is necessary to determine which parameters are to be compared. At the same time, it is incorrect to compare costs, because the price of biogas will become normal only after the payback period .
It is also incorrect to compare by calorific value, because fuel with a lower calorific value is not always worse than a higher calorific value.
For example, firewood has a lower calorific value than diesel fuel, but in many cases it turns out to be a more suitable type of fuel.
Therefore, you can compare different types of fuel and energy using the following parameters :
- Suitability for use in cars, electric generators and heating systems (in points, 1 point - suitable for all, 2 points - for some, 3 points - for any one).
- The need to create special conditions for storage (1 point - possible in any conditions, 2 points - special containers are needed, 3 points - in addition to special containers, additional equipment is required, 4 points - storage is impossible).
- Difficulty of converting equipment for another fuel or energy (1 point – minimal alterations that even a person without experience can do; 2 – alterations that are accessible to a more or less knowledgeable amateur and do not require any highly specialized equipment; 3 points – major alterations are required ).
- Negative impact on the environment (in points, 1 – least, 2 points – average, 3 points – maximum);
- Is the fuel or energy renewable (in points, 1 point – completely (for example, wind or sunlight); 2 points – conditionally, that is, under certain conditions, or after some action, 3 points – not).
- Does it depend on the terrain, time of year and weather (in points, 1 point - none, 2 points - partially, 3 points - depends on everything).
| Name of fuel or energy | Parameters for comparison | |||||
| Possibility of use | Storage | Equipment | Impact on the environment | Renewability | Dependence on external factors | |
| Purified biogas (methane content 95-99%) | 1 | 3 | 1–2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Propane | 1 | 2–3 | 1–2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Petrol | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Fuel oil | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Diesel fuel | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Firewood | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Coal | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Electricity | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Wind energy | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1–2 | 1 | 3 |
| Energy of sun | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Energy of water movement (river) | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1–2 | 1 | 3 |