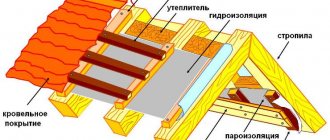
In the previous article we talked about waterproofing the basement and the importance of this event. Today we will talk about how to reduce heat loss at home through the ceiling. To do this, you need to insulate the attic hatch and ceiling. There are many thermal insulation materials suitable for work: bulk, liquid, in rolls and sheets. Each of the materials has its own characteristics, but the installation method for all of them is quite similar, not counting liquid thermal insulation, such as polyurethane foam and penoizol.
Polymer insulation for attic floors
The use of expanded polystyrene for attic insulation.
One of the most common options is insulating the attic floor with foam plastic or penoplex. The first option is much cheaper, and the characteristics of ordinary polystyrene foam are quite sufficient, since there is neither extreme dampness nor high mechanical loads in the attic. Therefore, a material with a minimum density of 15 kg/m can be used. cube It is laid between the joists, the joints are foamed with polyurethane foam. This material is very convenient if you need to insulate an attic hatch.
The polymer does not allow moisture and steam to pass through, which can become a problem. Moisture rises to the ceiling along with warm air. When insulating the attic floor with polystyrene foam, moisture has nowhere else to go but penetrate into the structure of the wood, because the polymer is vapor-proof. If there is too much water vapor, the tree cannot cope with its transit through itself and because of this, the wood is constantly wet. Where moisture stagnates, mold will not be long in coming, and the beams begin to turn black.
To avoid this, insulating the attic floor with your own hands should be accompanied by laying a vapor barrier. Installation diagram (bottom to top):
- ceiling;
- vapor barrier film;
- beams and insulation.
You can leave the insulation uncovered on top; the main goal is to prevent moisture from entering the wood structure from the room. When insulating the attic floor with your own hands, you don’t have to install a vapor barrier membrane if you plan to install a suspended ceiling. This is also a polymer film that does not allow moisture or steam to pass through. Moisture penetration around the perimeter will be minimal.
The first question from buyers about heating pipes is: which ones are better? It is impossible to answer in one phrase, because many factors need to be taken into account.
You can read everything about connecting heating pipes to a heating boiler in this article.
Health effects
If you delve a little deeper into the properties and composition of polystyrene foam, the conclusion is obvious - such material is harmful to human health. Polymer materials emit toxic substances that must be removed from residential premises.
To prevent the permissible concentration of toxins from exceeding the permissible concentration, the room must be constantly ventilated. To insulate the walls of the house from the outside, this problem is not too acute, since the penetration of toxins into the house is not great. But, the attic, due to internal insulation, requires a high degree of environmental friendliness of the material. Polystyrene foam cannot cope with this task because: Thin walls of plasterboard slabs or linings, which line the internal surfaces of the attic, allow toxins to pass through unhindered. The concentration of harmful substances can be so high that that it cannot be reduced even by intensive ventilation. Over the years of operation, decomposition processes occur in the foam that are harmful to health. For example, after 20 years, polystyrene foam will degrade by 10%.
Under this condition, the amount of styrene released will increase, which is the most dangerous of all other foam components. The harmfulness of foam components can be assessed by asking how carbon monoxide, ammonia, formaldehyde, phenol and nitric oxide affect health. The release of toxins increases with thermal exposure. Attic insulation can be constantly heated on both sides. From the outside, the foam is heated by the hot roof, and from the inside by the warm air of the living quarters.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool must be protected from moisture.
It is not entirely correct to use polystyrene foam, since you need to create all the conditions for the house to be environmentally friendly and fireproof. In this regard, it is better to use mineral wool. There are several types of mineral wool:
- glass wool;
- slag;
- basalt (stone) wool.
Most of them, except stone wool, are afraid of moisture. That is, they absorb it well, release it poorly and, when wet, lose their thermal insulation qualities. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent moisture from entering the insulation layer, and even if some of it does penetrate the thermal insulation, it must be allowed to escape. How to properly insulate an attic floor with mineral wool:
- From below, the thermal insulation is protected by a vapor barrier, which does not allow steam and water to pass through;
- the insulation layer must be at least 20 cm - in two rows of 10 cm with seams apart;
- waterproofing is laid over the wool, which does not allow water to pass through, but allows steam to escape;
- There must be ventilation gaps between the thermal insulation and the membranes.
If you choose how to insulate an attic floor among all types of mineral wool, then preference should be given to basalt wool. It practically does not absorb moisture, so it is allowed (although not advisable) to lay it without additional membranes. At the same time, rodents feel great in cotton wool, as well as in polystyrene foam, which becomes a serious problem.
To lay heating pipes in the floor, you need to protect them from mechanical damage and compensate for their thermal expansion. You can use plastic sleeves for this.
Here you can find information about noise in heating pipes: causes, elimination methods, possible consequences.
Is a vapor barrier necessary for thermal insulation?
In the process of life, a person produces a large amount of moisture. They are found in almost all residential areas in the form of vapors. In some there are more, and in others in less.
Therefore, warm air from all rooms tends to go outside. If the building is built of red brick or wood, which have good vapor permeability, everything escapes without lingering either in the walls themselves or on their surface. This means the microclimate throughout the house will be comfortable.
If the materials used for construction or finishing of housing have low vapor permeability, then unpleasant consequences arise. When moist air, passing through the thickness of the wall, collides with a colder surface, the moisture begins to condense. Depending on the location of the dew point, water droplets appear:
- On the outer surface.
- On the inner surface.
- In the thickness of the wall.
If condensation forms outside and the wall is well ventilated, then there will be no problems. But when formed inside a house or in the thickness of a structure, it will lead to the following consequences:
- the appearance of mold and mildew on the walls;
- accumulation of moisture in the insulation - which leads to a decrease in its technical characteristics;
- frozen water slowly destroys all materials.
Liquid insulation for attic floors
Liquid insulation is sprayed over the beams and ceiling.
There are two types of liquid insulation that are used to insulate attic floors:
- polyurethane foam (PPU);
- penoizol.
Despite their similarity, these heat insulators differ in the materials used for their production and characteristics. In this case, the device for insulating the attic floor with both materials is identical. The liquid composition is sprayed over wooden floors. After polymerization, the thermal insulation can be covered with a finishing finish or left open. The advantage of these materials is that they allow steam to pass through, allowing the structure to breathe.
The density of polyurethane foam is much higher than that of penoizol, it is much more durable and, accordingly, more expensive.
Penoizol appeared as a cheaper alternative to polyurethane foam. Liquid thermal insulation has proven itself well, but not everyone could afford such luxury; today this type of insulation is more affordable. In addition to high performance characteristics, the material belongs to the G1 flammability group, that is, it does not burn and mice do not breed in it. Installation requires special equipment; the quality of work largely depends on the professionalism of the performer. Therefore, the option to do it yourself is eliminated.
Bulk insulation for attic floors
Vermiculite is the best option for insulating attic floors.
We wrote a separate article about bulk insulation materials, in which we talked about their types and characteristics. Today we will only briefly consider the main points that relate to the insulation of the attic floor. For this purpose the following can be used:
- expanded clay;
- perlite;
- vermiculite;
- sawdust;
- ecowool.
Perlite and vermiculite are rocks that, after swelling, can be used as thermal insulation. The material is quite expensive, but it lasts almost forever. It does not burn, does not enter into chemical reactions, and mice do not live in it. It has the property of distributing moisture evenly over its entire area and quickly removing it outside, when wet, it does not lose its characteristics. In principle, this is an ideal option for insulating horizontal floors.
The insulation of attic floors with expanded clay was already familiar to our grandfathers. The only advantage of expanded clay is its cost. The rest of the material is frankly weak.
Its thermal conductivity is high and it absorbs moisture (weakly, but still). Compared to other modern insulation materials, the characteristics are clearly inadequate, so it is used only when it is available for free. Although there are even worse options - insulating the attic floor with sawdust.
Expanded clay is a frankly weak thermal insulator.
To achieve at least some insulation effect, you need to pour sawdust in a layer of at least 30 cm. At the same time, they tend to absorb moisture and rot. In order to allow moisture to escape, sawdust is mixed with clay or expanded clay. Sawdust is not suitable as independent thermal insulation. By the way, vermiculite can be mixed with sawdust, resulting in quite decent insulation. Mixing should be 50/50.
We wrote about ecowool insulation in one of the previous articles. This is also a loose insulation material and can be applied dry or wet. Strongly absorbs moisture, while easily parting with it. The material contains a lot of chemistry, so it is indirectly related to environmental friendliness, and only due to the fact that it was developed as part of a program for recycling recyclable materials.
For all bulk heat insulators, insulation of the attic floor is carried out according to the following scheme:
- ceiling;
- film or membrane - prevents steam from entering and prevents thermal insulation from spilling into the house;
- layer of insulation.
If you plan to make a floor in the attic, then it can be laid directly on top of the thermal insulation without additional film barriers.
Conclusions about insulating the attic floor
All methods of insulating the attic floor are aimed only at reducing heat loss in the room. As you know, the main amount of heat escapes through the ceiling, and then through windows/doors and walls. Warm air tends to rise upward, taking with it all the moisture. In fact, a lot of moisture is generated in the house, so the insulation in the attic needs to be protected with film barriers (waterproofing, vapor barrier).
To insulate the attic floor, you need to choose a material that meets the following requirements:
- low heat transfer coefficient;
- environmental friendliness;
- preferably should not be afraid of moisture;
- must allow steam to pass through;
- Mice should not live in it.
The material that will meet all these requirements will undoubtedly not be cheap. We are talking about vermiculite, but it is possible to slightly reduce the cost of insulation. It is necessary to mix vermiculite with sawdust, but this will lead to the fact that the material will be less able to protect the house from heat loss. In addition, a good budget option is penoizol (liquid thermal insulation). It is better to avoid polystyrene foam. The use of mineral wool has both pros and cons, although the material is very popular.
What is better: polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam?
Ecotermix 600 is the best material for insulating an attic from the inside!
In conclusion, it should be noted that using polyurethane foam as insulation can save more than 20% of the heat that the house previously lost. Moreover, polyurethane foam allows you to hide all defects of the surface on which it is applied. In the absence of seams, heat losses will be minimized, and the use of a centralized ventilation and air conditioning system will ensure that the attic space will always be ventilated and will not be hot there in the summer.
As a result, answering the question: is it possible to insulate an attic with polystyrene foam, it should be noted that this method undoubtedly represents the most cost-effective insulation option, i.e. is optimal when insulation work needs to be completed as quickly as possible at the lowest cost. But to achieve the best result, it is recommended to use polyurethane foam spraying technology. Thus, the overall thermal insulation of the attic will be performed at the highest level!