10/07/2019 There are many skeptics who claim that insulating a house or apartment from the inside is not the best option. But, in some cases, it is simply not possible to insulate the walls from the outside. Internal thermal insulation is becoming practically the only way that can provide a home with warmth and comfort and reduce energy consumption.
How to insulate a house from the inside, what features of the process need to be taken into account - we tried to cover the topic to the maximum. In the publication you will find the following:
- Features of internal insulation of a house: what is important to know first;
- Preparing the room for internal insulation;
- Insulation of walls from the inside with polystyrene foam; Selection of expanded polystyrene for internal insulation;
- Installation of extruded polystyrene foam for internal insulation;
- How PIR boards are installed for internal insulation;
- Selection of mineral wool for internal insulation;
Features of internal insulation of a house: what is important to know first
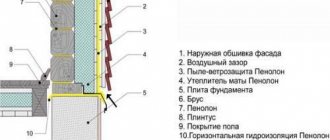
The main and hidden “enemy” of internal insulation is condensation. The air around us contains vapors in different concentrations. As a rule, in residential premises the concentration of vapors is often high. This is due to cooking in the kitchen, using bathrooms, watering flowerpots, wet cleaning and other reasons. Excess moisture is always removed through ventilation ducts and open windows. But in addition, they penetrate into the walls due to the porosity of the materials. When passing the wall, the vapor molecules necessarily collide with a conventional line, at which they turn into a liquid state - they condense. This line is called the "Dew Point".
With internal insulation, the dew point will always be located immediately behind the installed thermal insulation - that is, on the inner surface of the wall. When steam hits the wall, it forms condensation and moistens the wall material. The consequences of this are sad: immediately behind the insulation, a zone is formed with ideal conditions for the growth of bacteria, fungi, and mold. Thus, the premises may even become dangerous for living.
Based on what was described above, we conclude that the main task with internal insulation is to do everything possible to prevent contact of moist air with the dew point. That is, task No. 1 is to protect the inner surface of the wall from the slightest contact with steam . And this can be done quite simply. You need to do three things:
- follow the insulation installation technology;
- be sure to install a vapor barrier;
- choose the right material for wall insulation.
What is important to know
How to insulate a ceiling from the inside in a private house? What materials are best to use for this? These questions are relevant for owners of wooden houses and brick cottages. Currently, there are several materials suitable for insulation on the construction market:
- foil;
- ecowool;
- mineral wool;
- Styrofoam;
- penoplex.
Foil material is suitable for insulating concrete surfaces. When used for internal ceiling insulation, the home owner does not need to purchase additional thermal insulation materials. Manufacturers offer foil sheets with locking mechanisms, so the joints between individual sheets are securely closed from cold air entering the room. On the building materials market, foil insulation is presented in two versions: one-sided, two-sided.
Preparing the room for internal insulation
Like any other construction project, internal insulation begins with preparation. At this stage you need to do the following:
- Eliminate weak and defective areas;
- Perform antiseptic surface treatment.
First of all, you need to assess the general condition of the walls, the presence of cracks, chips in the plaster, and weak spots. It is recommended to eliminate all defects found. And the point here is not so much the quality of insulation, but rather the improvement of the performance characteristics of the walls. Correcting defects in a timely manner will prevent them from aggravating the situation in the future. After all, if the crack spreads further and the plaster falls off, then to fix this problem you will need to dismantle a large section of the insulation and redo everything again. This is not only unpleasant, but also expensive, time-consuming, and labor-intensive.
It is imperative to check the walls for existing mold and fungi before insulating them from the inside. Under no circumstances should you carry out further work until the problem has been completely eliminated. If fungal infections are found, we recommend removing the plaster in this area completely - to the base of the wall. Next, you need to treat the area with a special antifungal chemical 2-3 times. There should be no visible marks on the surface after treatment.
For pre-treatment of surfaces in order to destroy existing lesions, we recommend using the following compositions:
- Antiseptic Anti-mold Propitex 1l. A composition that contains active substances to destroy mold on wood, stone, cement and other substrates. Can be used to effectively remove spores, yeast and other types of fungi.
- Dufa mold removal solution. Instant action composition. Due to the inclusion of chlorine, it is characterized by the instant destruction of fungi and mold. Penetrates well into porous wall materials, due to which it is able to remove damage in the structure. When using, it is recommended to thoroughly ventilate the room and use personal protective equipment for hands and respiratory organs.
The next stage is priming the wall with a composition with antiseptic additives. This must be done regardless of whether fungal infections were found or not. In the future, such a composition will effectively prevent the formation of mold under the insulation. You should choose a primer only with special antiseptic properties and a long-lasting effect. For example, suitable:
- Primer EK GS400 ANTISEPTIK. Composition for porous surfaces of plasters and concrete. Penetrates deeply into the structure, strengthens, removes dust from the surface and binds small particles. Reduces water absorption and improves strength. Has a long-lasting antiseptic effect with protection against fungi and mold.
- Antiseptic Anti-mold Propitex 5 l. This composition has a long-term biocidal effect, due to which it can be used for subsequent insulation.
After the primer composition has completely dried, you can begin subsequent work. The technology for installing insulation will depend directly on the material used for wall insulation. In particular, this can be thermal insulation using polystyrene foam or mineral wool.
Dew point - physics of the phenomenon
A cold wall is not the only drawback of panel or brick houses. Often dampness and accompanying fungus and mold appear on it. The best way to combat this is to insulate the wall from the outside (this is also a requirement of SNiP), but this is not always possible. Therefore, we have to deal with the cold wall by insulating it from the inside. But there are pitfalls here.
Even if the cold wall was previously dry, when insulating it from the inside, dampness may appear. And the so-called dew point will be to blame.
The dew point is a conditional boundary at which the temperature of water vapor becomes equal to the temperature of condensation formation. It naturally appears during the cold season. With proper design of the house (taking into account the characteristics of the region), it is located approximately in the middle of the thickness of the facade made of a material of uniform density.
If insulation is carried out from the outside, the dew point shifts towards decreasing density (that is, towards the outer surface of the wall). When insulating from the inside, it moves inward, and condensation may appear on the surface of the main wall or inside the insulation.
And to assess the scale of possible damage, it is enough to say that as a result of the life activity of one person, about 4 liters of water evaporate per day (cooking, wet cleaning, personal hygiene, washing, etc.).
Insulation of walls from the inside with polystyrene foam
Expanded polystyrene is objectively the most acceptable type of thermal insulation material for internal wall insulation. At the same time, only a special type of it should be used for internal thermal insulation - extruded polystyrene foam . The peculiarity of this building material is as follows:
- Increased density. Extruded polystyrene foam slabs are produced by the extrusion method - squeezing raw materials through a narrow nozzle of an extruder (special equipment) under pressure. The material forms a dense, airless structure and is characterized by increased strength, rigidity, and geometric accuracy.
- Almost zero vapor permeability. Installed as thermal insulation, XPS foam boards allow virtually no vapor to pass through them. Thus, this particular insulation is rational and suitable for internal thermal insulation. It becomes a natural barrier between the internal surfaces of the wall and the humid air in the room.
- Thermal insulation properties. Extruded polystyrene foam is characterized by an ultra-low thermal conductivity coefficient of about 0.037-0.041 W/m*K. It demonstrates excellent resistance to heat transfer, due to which the maximum insulation effect is achieved with a small thickness. At the same time, losses of useful volume from internal insulation are minimized.
- Low price. The material has an excellent cost-performance ratio.
Selection of extruded polystyrene foam for internal insulation
Extruded polystyrene foam boards differ in thickness and type of edge. For internal insulation, choose slabs with the following thickness:
- 2-3 cm for a small room area;
- 5 cm in large rooms;
- 10 cm when insulating a loggia balcony that is part of a living space.
The edge of the slabs is an important nuance that is always taken into account when choosing internal thermal insulation. Foam plastic slabs with a straight edge form a small gap when they meet, but still a gap. It is a natural bridge through which cold enters the room and vapor passes under the insulation.
For internal insulation, we recommend using only slabs with a locking joining system - L-edge . Due to this configuration, the thermal characteristics of the heat insulator are improved and vapor permeability is minimized.
Products suitable for internal insulation of houses and apartments include:
- TECHNONICOL CARBON ECO 1180x580x30 mm. Characterized by an optimal ratio of thickness and thermal insulation. Suitable for rooms with a small area, as it practically does not “eat up” square meters. Equipped with L-edge, has high heat transfer resistance.
- TECHNONICOL Technoplex 1180x580x50 mm. Equipped with excellent strength and thermal characteristics. It has an optimal thickness for insulating medium and large rooms and balconies.
- TECHNONICOL CARBON ECO 1180x580x100 mm. The most effective thermal insulation is achieved when installing such material. Equipped with an L-edge, it can be used for insulating open balconies and loggias, large rooms.
Installation of extruded polystyrene foam for internal insulation
Installation of this type of insulation is possible in two ways - using polystyrene foam glue or using dowels.
Dowel mounting:
- Fastening with dowels is carried out after preliminary arrangement of the vapor barrier. A metallized substrate, membrane or overlapping polyethylene film is installed on the wall.
- The seams are taped with aluminum tape to prevent steam from getting under the film.
- The slabs, pre-cut to size, are installed on the wall and fixed using plastic mushroom dowels with a plastic nail.
- The joints of the plates and the dowel heads are glued with aluminum foil.
- Finishing is carried out - plastering or cladding of gypsum boards.
Glue fastening:
- In this case, installing a vapor barrier is impossible, therefore, special attention is paid to the joints.
- You can use dry glue for polystyrene foam, for example, EK THERMEX or Yunis Teplomontazh. It is also permissible to use special glue in cylinders in the form of low-expansion foam.
- For better adhesion, the internal surfaces of the slabs are processed with a float until a rough surface is obtained.
- The glue can be applied evenly to the wall or in “bloops” on the slab along the edges and in the center.
- The plate is placed against the wall and pressed down. Flatness and level are checked at the same time.
- The joints are taped with aluminum tape.
- Finishing is in progress.
There is a combined method of fastening using glue and dowels. But it is rational for external insulation of a room. The foam inside will not experience increased stress. Therefore, it is enough to choose one of the options.
Liquid thermal insulation
Polyurethane foam
PPU insulation meets all requirements for vapor barrier, water absorption and absence of seams. Therefore, even if there is a dew point inside the layer, it will remain “conditional”, since there is no condensation in vapor-tight materials. This results in a completely sealed thermal insulation layer from the room side.
The environmental friendliness of polyurethane foam after hardening meets the requirements for residential premises. Harmful fumes are present only when the components are mixed during the spraying process - after polymerization, the structure of the material remains stable.
Apply thermal insulation between the sheathing and cover it with moisture-resistant sheet materials (gypsum plasterboard, OSB or plywood). Essentially, it's like a large prefabricated sandwich panel.
The disadvantage of this method is the use of special equipment.
Liquid ceramics
This is a relatively young thermal insulation material, the action of which is based on the use of two principles - the creation of a thin layer with high resistance to heat transfer and the reflection of heat towards the radiation source.
Of course, a thin thermal insulation layer cannot provide good thermal insulation - this is an auxiliary, but mandatory factor. Although it gives a fairly high effect - the wall becomes much “warmer” to the touch.
The main task of reducing heat loss is performed by microscopic ceramic spheres that reflect infrared radiation.
According to the manufacturers, the effect of a 1.5 mm layer can be compared with thermal insulation with 5 cm thick foam plastic or 6.5 cm mineral wool.
The application method is the same as for acrylic paint (the base is the same). After polymerization, a dense and durable film is formed on the surface, and latex additives improve waterproofing properties.
PIR insulation is a modern analogue of extruded polystyrene foam
PIR insulation appeared on the market relatively recently. Therefore, they need to be considered separately. This heat insulator is a three-layer material consisting of an inner layer of polyisocyanurate foam, covered on both sides with aluminum reflective foil.
In fact, PIR (or polyisocyanurate foam) is a special type of polyurethane with a rigid structure, ultra-low thermal conductivity and increased strength parameters. Due to this, it has successfully proven itself as a heater for internal thermal insulation of any premises, from bedrooms to balconies and loggias.
A special property of this insulation is the additional reflection of heat back into the room due to the foil. Thus, the thermal conductivity coefficient decreases to an unprecedented 0.022 W/m*K, water absorption is only 1% (this is when immersed in water for a day). But the main thing is that the vapor permeability of PIR insulation is reduced to zero due to the same foil coating.
For internal insulation, an excellent solution would be to choose materials such as:
- LOGICPIR universal insulation L 1190x590x50 mm. It has the optimal thickness for medium and large rooms, equipped with an L-edge to prevent the formation of cold bridges.
- Insulation LOGICPIR Balcony L 1185x585x30 mm. It is used on the bottom of small unheated balconies. L-edge present.
- Insulation LOGICPIR Balcony L 1190x590x50 mm. Recommended for insulating a heated balcony, as well as a balcony that is part of a living space.
How PIR boards are installed for internal insulation
The aluminum surface of Pir-plates does not allow high-quality fixation of the insulation using the traditional adhesive method. In this case, the technology with plastic mushroom dowels with plastic nails is used.
The very essence of the technology does not differ from the fastening of polystyrene foam described above. After completing the installation of the last slab, the joints are glued. The gaps between the floor and the slab can be filled with polyurethane foam. Next comes finishing. Instead of dowels, you can use wood sheathing. The beam presses the insulation against the wall, after which the cladding is carried out with panels, lining, gypsum board and other materials. An example of installation can be seen in the photo instructions:
Izolon
Izolon is an elastic insulating material made from polyethylene with a cellular structure . It is available in the form of plates or rolls and may additionally have an aluminum foil coating.
Its main advantages include:
- durability;
- environmental safety;
- excellent shock and sound protection.
Izolon
Insulating a house from the inside with mineral wool
Mineral wool is not an optimal thermal insulation material for internal insulation. There is only one reason for this - cotton wool allows steam to pass through perfectly. Because of this, described at the beginning of the article, the dew point shifts from the inner surface of the wall into the insulation itself. Condensation can accumulate in it, thermal performance deteriorate, and mold and mildew can form. However, it is possible to use mineral wool for internal insulation if all technological nuances are observed.
Choosing mineral wool for internal insulation
Mineral wool should be selected based on criteria such as thickness and environmental friendliness. It is possible to use rolled wool, which is cut to the required length directly during installation. Also, such products are produced in slabs. For internal insulation, 50 mm is the optimal thickness at which good insulation is achieved without significant loss of the usable volume of the room.
Example of suitable types of mineral wool:
- Ecoroll Plate 40. It has a relatively small thickness of 50 mm and does not contain phenol resins. Recommended by the manufacturer for internal insulation, including walls.
- TeploKNAUF For COTTAGE Thermo Plate is a modern insulation material from a well-known manufacturer, the features of which are: low thermal conductivity (0.37 W/m*K) and excellent water-repellent properties due to impregnation of the fibers with a special composition. In addition, this board has a special fiber arrangement structure, due to which sound absorption significantly increases. Thus, this insulating material is recommended for insulating the inside of walls, floors, and attics in houses located in noisy areas.
Basalt wool for internal insulation
Separately, attention should be paid to a type of mineral insulation such as basalt wool. The peculiarity of this heat insulator is not only its excellent thermal insulation properties and environmental friendliness, but also its high fire safety. Basalt fiber is obtained from natural stone. Accordingly, such a material has excellent resistance to open flames.
The fire resistance of basalt wool is an important nuance that must be taken into account when insulating the walls of wooden houses, country houses, and baths. In this case, we especially recommend choosing certified products.
These could be slabs:
- Rockwool Light Butts SCANDIC. Products that are designed specifically for insulating residential buildings, apartments and cottages. It is characterized by compliance with environmental standards (has low resin emissions, safe in residential areas). Flexi technology ensures simple installation with filling of gaps in the frame due to the spring properties of the insulation. The material is biostable - bacteria and mold do not form in it, and it is not a good habitat for insects or rodents.
- Rocklight insulation. Manufacturer TechnoNIKOL recommends using this insulation for internal thermal insulation from inside walls, floors, and attics. The material has low thermal conductivity (0.39-0.41 W/m*K). It is non-flammable, bioresistant, and due to special impregnations, it repels water well without accumulating it inside the structure. At the same time, the compressibility of the slab is 30%, which makes it possible to simplify the process of laying it between the joists and efficiently seal all the cracks and gaps.
Installation of mineral wool indoors
- A vapor barrier film must be installed around the perimeter of the wall.
- A frame made of wooden blocks is mounted on top of the vapor barrier. It is not recommended to use metal profiles. Metal perfectly transmits heat and will become an artificial bridge of cold
- !!! The metal frame should be used when arranging thermal insulation from the inside of objects with increased fire safety requirements together with basalt wool. These include wooden buildings: baths, saunas, etc. !!!
- The joints between the frame and the vapor barrier are taped with tape, since when fastened to the vapor barrier, a hole from the dowel is formed.
- Cotton wool is installed in the frame and carefully compacted to avoid the formation of any cracks.
- A second layer of vapor barrier is installed on top of the frame. This creates a double vapor barrier between the insulated wall and the room.
- The fastening points and joints of the vapor barrier are taped with aluminum tape.
- The frame is covered with preferred slabs - gypsum plasterboard, chipboard, etc.
If the technology is followed and only if a vapor barrier is installed in the insulation, a good result of internal thermal insulation can be achieved. On our own behalf, we would only like to add that insulating a house or apartment from the inside is, rather, an extreme and necessary measure. It is recommended to use it only if it is impossible to install thermal insulation from the outside. If such an opportunity exists, then we definitely recommend considering its implementation as a priority. We hope that the prepared publication will allow us to avoid mistakes and carry out internal insulation as efficiently as possible.
Primary requirements
In order to prevent precious heat from leaking through the ceiling, you can use various materials: expanded clay, sawdust, slag. Each of them has certain pros and cons. For example, sawdust rots, and slag accumulates harmful substances. To choose how to insulate the ceiling in a house from the inside, we will highlight the criteria that you need to pay attention to when selecting insulation:
- thermal conductivity;
- moisture resistance;
- minimal flammability of the material;
- long service life;
- environmental friendliness.
We analyze all the shortcomings
As for the negative points, there are plenty of them:
- Significant reduction in room area, especially if interior decoration is planned. Of course, you can make a small thickness of the thermal insulation layer, but this will negatively affect the efficiency.
Tip: Choose the right insulator size. To avoid making a mistake with your choice, look at online calculators or calculate the recommended insulator thickness with your own hands.
Condensation begins to form under the insulation at a faster rate. This is due to the incorrect dew point shift.
How to correct this consequence with your own hands will be discussed in the next paragraph. When insulating indoors, the walls will practically stop warming up. They will not participate in protecting the house from the cold, and most importantly, their service life will begin to decrease. If you create frames indoors for laying insulation, this will inevitably lead to the formation of so-called “cold bridges”. As a result, the efficiency of the insulation will decrease.
Installation stages
How to insulate a ceiling from the inside using foil material? We offer a detailed algorithm of actions:
- A cellular sheathing is made from wooden beams or metal profiles.
- Cut sheets of foil to the desired size.
- They are fastened to the sheathing with a construction stapler.
- Cover the ceiling with plasterboard or clapboard.
Advice! In order to avoid excessive heating of the foil insulation, “air cushions” are created between the sheets.
Creating a frame of strength
Now you need to build a frame from bars (their size should be no less than the expected thickness of the thermal insulation layer). In a wooden house they are fixed directly to large self-tapping screws. For brick and concrete buildings, you will have to pre-drill holes and install dowels and nails in them.
The distance between the bars is made according to the size of the selected insulation - this makes the work easier. In addition to vertical logs, several more horizontal ones are installed, in increments of 1-1.5 meters. They are needed to ensure maximum rigidity of the frame.
We are trying to find the advantages of the technique
This technique has few positive qualities:
Simplicity - all work can be done without problems with your own hands, because there is no need to create large “scaffolding”. The ability to carry out work regardless of the time of year. Proper external insulation should be carried out at positive temperatures, in the absence of precipitation and low humidity.
Work inside can be carried out under any conditions. Accessibility. You can do the work gradually. This is convenient in cases where a person does not have the opportunity to immediately begin large-scale work, and he plans to insulate the most important rooms with his own hands first, and not the entire building.